Access Manager Schema
In general, a schema is a set of rules imposed on data that defines how it is stored. Sun Java System Directory Server uses the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) schema to define how its data is stored. Object classes define attributes in a LDAP schema. In Directory Server, each data entry must have one or more object class(es) to specify the type of object the entry describes and define the set of attributes it contains. Each entry then is basically a set of attributes and their corresponding values and the list of object classes to which these attributes correspond.
Access Manager uses Sun Java System Directory Server as its data repository, which includes the Access Manager schema that extends the Directory Server schema. When Access Manager is installed, the Access Manager schema, from the ds_remote_schema.ldif and sunone_schema2.ldif files, is integrated with the Directory Server schema. The ds_remote_schema.ldif file defines the LDAP object classes and attributes that are specifically used by Access Manager. The sunone_schema2.ldif file loads the Access Manager LDAP schema object classes and attributes.
You can view the ds_remote_schema.ldif, sunone_schema2.ldif, and other Access Manager LDIF files in the following directories:
-
Solaris systems: /etc/opt/SUNWam/config/ldif
-
Linux systems: /etc/opt/sun/identity/config/ldif
Marker Object Classes
Identity entries created using the Access Manager console and stored in Directory Server are appended with marker object classes. Marker object classes define the designated entries as those which Access Manager will manage. The object classes will not interfere with other aspects of the directory tree, such as servers or hardware. As well, existing identity entries can not be managed using Access Manager until they are modified to include these object classes. More detailed information about the marker object classes can be found in the Access Manager Developer’s Guide. For information about migrating existing Directory Server data for use with Access Manager, see the Sun Java Access Manager 6 2005Q1 Migration Guide.
Administrative Roles
Delegated administration of the LDAP entries (mapped to each identity-related object in Access Manager) are implemented through the use of pre-defined roles and access control instructions (ACIs). Default administrative roles and their defined ACIs are created during Access Manager installation and can be viewed and managed using the Access Manager Console. In Access Manager 7 2005Q4 in Realm mode, roles depend on policies rather then ACIs.
When an Access Manager identity-related object is created, the appropriate administrative roles (and thus, corresponding ACIs) are also created and assigned to the LDAP entry for that object. The role can then be assigned to an individual user who maintains control of that object’s node. For example, when Access Manager creates a new organization, several roles are automatically created for it and stored in Directory Server:
-
Organization Administrator has read and write access to all entries in the configured organization.
-
Organization Help Desk Administrator has read access to all entries in the configured organization and write access to the userPassword attribute in those entries.
-
Organization Policy Administrator has read and write access to all policies in the organization.
The assignation of any of these roles to a user gives that user all the permissions accorded that role.
The following table summarizes the Access Manager administrator roles and the permissions that apply to each one.
Table 3–1 Default and Dynamic Roles and Their Permissions|
Role |
Administrative Suffix |
Permissions |
|---|---|---|
|
Top-level Organization Admin (amadmin) |
Root level |
Read and write access to all entries (such as roles, policy, and groups) under top-level organization. |
|
Top-level Organization Help Desk Admin |
Root level |
Read and write access to all passwords under top-level organization. |
|
Top-level Organization Policy Admin |
Root level |
Read and write access to policies at all levels. Used by sub-organizations to delegate referral policy creation. |
|
Organization Admin |
Organization only |
Read and write access to all entries (such as roles, policy, and groups) under the created sub-organization only. |
|
Organization Help Desk Admin |
Organization only |
Read and write access to all passwords under the created sub-organization only. |
|
Organization Policy Admin |
Organization only |
Read and write access to all policies under the created sub-organization only. |
|
Container Admin |
Container only |
Read and write access to all entries (such as roles, policy, and groups) under the created container only. |
|
Container Help Desk Admin |
Container only |
Read and write access to all passwords under the created container only. |
|
Group Admin |
Group only |
Read and write access to all entries (such as roles, policy, and groups) under the created group only. |
|
People Container Admin |
People Container only |
Read and write access to all entries (such as roles, policy, and groups) under the created people container only. |
|
User (self-administrator) |
User only |
Read and write access to attributes in the user entry only (except for user attributes such as nsroledn and inetuserstatus). |
Using roles instead of group-based ACIs is more efficient and requires less maintenance. Filtered roles are simpler for LDAP clients, because they can just ask for the nsRole attribute of a user. Roles do suffer though from scope limitations, where a role must be a peer of a parent of a member of that role.
For more information about default ACIs, see the Access Manager Console Online Help.
Access Manager Administrative Accounts
During the installation of Access Manager, the following administrative accounts are created:
-
Administrator user ID (amadmin) is the Access Manager top-level administrator that has unlimited access to all entries managed by Access Manager. You cannot change the default name, amadmin.
During installation, you must provide a password for amadmin. To change the amadmin password after installation, use the Directory Server Console or the ldapmodify utility.
-
Bind DN user for LDAP, Membership, and Policy services (amldapuser) is the administrative user that has read and search access to all Directory Server entries. You cannot change the default name, amldapuser.
During installation, you must provide a password for amldapuser. Do not use the same password that you used for amadmin. To change the amldapuser password after installation, use the Directory Server Console or the ldapmodify utility.
If you change the amldapuser password, you must also modify the LDAP authentication service and policy configuration services to reflect the change (amldapuser is the default user used in these services). You must make changes in each organization where these services are registered.
-
Proxy user (puser) can take on any user's privileges (for example, an organization administrator or end user).
-
Admin user (dsameuser) is used for binding purposes when the Access Manager SDK performs operations on Directory Server that are not linked to a particular user (for example, retrieving service configuration information).
Both puser and dsameuser have an associated password that is stored in encrypted format in the serverconfig.xml file, in the following directories:
-
Solaris systems: /etc/opt/SUNWam/config
-
Linux systems: /etc/opt/sun/identity/config
After installation, it is recommended that you change the password for puser and dsameuser, but do not use the same password that you used for amadmin or amldapuser. To change the puser or dsameuser password, use the ampassword utility:
-
The ampassword --admin (or -a) option changes the password for dsameuser. (This option does not change the amadmin password.)
-
The ampassword --proxy (or -p) option changes the password for puser.
Changing the puser or dsameuser password depends on your deployment.
If Access Manager is deployed on a single host server:
-
Use the ampassword utility to change the respective password in Directory Server and in the local serverconfig.xml file.
-
Restart the Access Manager web container.
If Access Manager is deployed on multiple host servers:
-
On the first server, use the ampassword utility to change the respective password in Directory Server and in the local serverconfig.xml file.
-
Encrypt the new password using the ampassword --encrypt (or -e) option.
-
On each additional server where Access Manager is deployed, change the password manually in the serverconfig.xml file, using the new encrypted password from Step 2.
-
On each server where you changed the password, including the first server, restart the Access Manager web container.
For information about the ampassword utility, see the Sun Java System Access Manager 7 2005Q4 Administration Guide.
Schema Limitations
Access Manager abstractly represents the entries it manages. This means, for example, that an organization in Access Manager is not necessarily the same as an organization in Directory Server. Whether a specific Directory Information Tree (DIT) can be managed or not depends on how the you choose to represent or manage your directory entries and whether your DIT fits into the limitations of each Access Manager type.
The following sections describe these limitations of the Access Manager schema. At the end of this section, several Examples of Unsupported DITs are included.
Only One Type of Entry Can be Marked as an Organization
By adding the Access Manager sunISManagedOrganization auxiliary class to any entry, Access Manager can manage this entry as if it is an organization. However, only one type of entry may be marked as an organization in Access Manager. For example, if you have an entry o=sun and another entry dc=ibm in your DIT, you cannot mark them both as organizations.
In the following example, if you want both the dc and o entries to be organizations, the DIT structure will not be manageable using Access Manager:
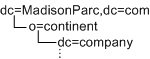
The entry at the Access Manager root suffix, however, does not count as one entry. Therefore, in the following example, the DIT structure can be managed by Access Manager:

If you were able to add dc=company1 below o=continent1, then this DIT would be manageable only if dc is marked as a container. Container is another abstract type in Access Manager that typically maps to an OrganizationalUnit. In most DITs, you would add the iplanet-am-managed-container entry to all OrganizationlUnits.

However, you could add this marker object class to any entry type. The DIT structure in the following example is allowed:
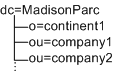
In this example, because you cannot mark both o= and ou= entries as organizations, you could mark the o= entries as organization and the ou= entries as containers. When exposed in the console, both organizations and containers have the same options. You can create subordination or subcontinents, people containers, groups, roles, and users under both of them.
People Containers Must be Parent Entries for Users
Another abstract entry type is the people container. The Access Manager type assumes that this entry is a parent entry for users. When you mark an entry as a people container with iplanet-am-managed-people-container, the UI will assume it can only contain sub-people containers or users. The attribute OrganizationUnit is typically used as a people container, but any entry can be this type in Access Manager as long as it has the iplanet-am-managed-people-container object class and it has a Access Manager manageable parent of type organization or container.
Only One Organization Description is Allowed in the Access Manager XML
The Access Manager organization is defined in amEntrySpecific.xml. Only one organization description is allowed in this file. As a result, when you customize directory entry properties, or create administration pages or search pages in the UI, your custom attributes apply globally to the entire Access Manager configuration. This Access Manager requirement may not meet the needs of some companies, especially hosting companies, that require different display attributes for each organization in the deployment.
In the following example, Edison-Watson is a hosting company that provides internet services to a number of companies. CompanyA wants to display fields for capturing a user’s name First Name, Surname, and Badge Number. CompanyB wants to display fields for capturing a user’s First Name, Last Name, and Employee Number.
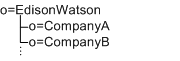
The organization description is defined at the root level (o=EdisonWatson), and not at the organization level. By default, the UI for both CompanyA and CompanyB must be identical. Also, all services globally define attributes to be of the subschema type user. So if CompanyA has attributes for its users in the auxiliary class CompanyA-user, and CompanyB has attributes in CompanyB-user then CompanyB’s attributes will be overridden and will not be displayed.
As a workaround, you can modify the ACIs to work for user display. However, this workaround will not address the attributes in Search and Create windows.
Examples of Unsupported DITs
In the following example, you would need three types of organization makers: o, ou, and l. Assuming that l=california and l=alabama are not a people containers, this DIT would not work with Access Manager:
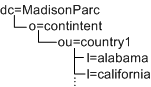
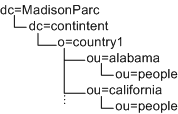
In the following example, you would need three types of Access Manager markers (dc,o,ou) plus the people container type (ou=people). Under these assumptions, the DIT would not work with Access Manager:
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
