Secure Attribute Exchange/Virtual Federation Proxy
Secure Attribute Exchange (also referred to as Virtual Federation Proxy) provides a mechanism for one application to communicate identity information to a second application in a different domain. In essence, it provides a secure gateway that enables legacy applications to communicate authentication attributes without having to deal specifically with federation protocols and processing. Virtual Federation Proxy allows:
-
Identity provider applications to push user authentication, profile and transaction information to a local instance of OpenSSO Enterprise which then passes the data to a remote instance of OpenSSO Enterprise at the service provider using federation protocols.
-
Service provider applications to consume the received information.
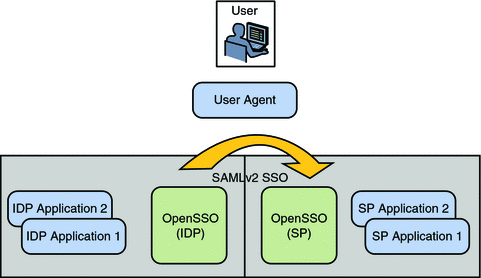
Virtual Federation Proxy uses SAML v2 to transfer identity data between the communicating entities. The Client SDK (which contains Java and .NET interfaces) runs independent of OpenSSO Enterprise and enables existing applications to handle the SAML v2 interactions. The following diagram illustrates this scenario.
Figure 10–1 Virtual Federation Architecture
The following use cases are applicable to Virtual Federation:
Authentication at Identity Provider
When a user is already authenticated within an enterprise, the legacy identity provider application sends a secure HTTP GET/POST message to OpenSSO Enterprise asserting the identity of the user. OpenSSO Enterprise verifies the authenticity of the message and establishes a session for the authenticated user. You can use Virtual Federation to transfer the user's authentication information to the local instance of OpenSSO Enterprise in order to create the session.
Virtual Federation at Identity Provider
When a user is already authenticated by, and attempts access to, a legacy identity provider application, the legacy application sends a secure HTTP POST message to the local instance of OpenSSO Enterprise asserting the user's identity, and containing a set of attribute/value pairs related to the user (for example, data from the persistent store representing certain transactional states in the application). OpenSSO Enterprise verifies the authenticity of the message, establishes a session for the authenticated user, and populates the session with the user attributes.
Virtual Federation at Service Provider
When a user is already authenticated by the instance of OpenSSO Enterprise at the identity provider and invokes an identity provider application that calls for redirection to a service provider, the identity provider invokes one of the previous use cases and encodes a SAML v2 SSO URL as a part of the request. The identity provider instance of OpenSSO Enterprise then initiates SAML v2 SSO with the instance of OpenSSO Enterprise at the service provider. The service provider's instance of OpenSSO Enterprise then verifies the SAML v2 assertion and included attributes, and redirects to the service provider application, securely transferring the user attributes via a secure HTTP POST message. The service provider application consumes the attributes, establishes a session, and offers the service to the user.
Global Single Logout
When a user is already authenticated and has established, for example, SSO with the instance of OpenSSO Enterprise at the service provider, the user might click on a Global Logout link. The identity provider will then invalidate its local session (if created) and trigger SAML v2 single log out by invoking a provided OpenSSO Enterprise URL. The OpenSSO Enterprise identity provider executes the SAML v2 single log out, terminating the session on both provider instances of OpenSSO Enterprise.
Note –
An identity provider side application can initiate single logout by sending sun.cmd=logout attributes via a Virtual Federation interaction to a local instance of OpenSSO Enterprise acting as the identity provider. In turn, this instance will execute SAML v2 single logout based on the current session.
For more information, see the Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Administration Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
