What Happens During PAP Authentication
PAP authentication occurs in the following sequence.
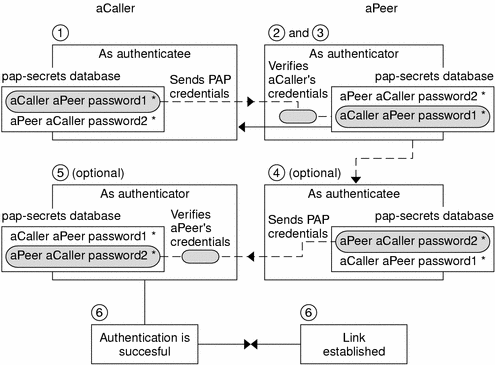
Figure 36–1 PAP Authentication Process
-
The caller (authenticatee) calls the remote peer (authenticator) and provides its PAP user name and password as part of link negotiation.
-
The peer verifies the identity of the caller in its/etc/ppp/pap-secrets file. If the peer uses the login option of PAP, it verifies the caller's user name and password in its password database.
-
If authentication is successful, the peer continues link negotiation with the caller. If authentication fails, the link is dropped.
-
(Optional) If the caller authenticates responses from remote peers, the remote peer must send its own PAP credentials to the caller. Thus, the remote peer becomes the authenticatee and the caller the authenticator.
-
The original caller reads its own /etc/ppp/pap-secrets to verify the identity of the remote peer.
Note –If the original caller does require authentication credentials from the remote peer, Step 1 and Step 4 happen in parallel.
If the peer is authenticated, negotiation continues. Otherwise, the link is dropped.
-
Negotiation between caller and peer continues until the link is successfully established.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
