Hash Table
A hash table of Elf32_Word or Elf64_Word objects supports symbol table access. The symbol table to which the hashing is associated is specified in the sh_link entry of the hash table's section header (refer to Table 7–15). Labels appear below to help explain the hash table organization, but they are not part of the specification.
Figure 7-11 Symbol Hash Table
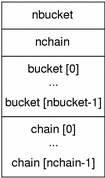
The bucket array contains nbucket entries, and the chain array contains nchain entries; indexes start at 0. Both bucket and chain hold symbol table indexes. Chain table entries parallel the symbol table. The number of symbol table entries should equal nchain, so symbol table indexes also select chain table entries.
A hashing function accepts a symbol name and returns a value that can be used to compute a bucket index. Consequently, if the hashing function returns the value x for some name, bucket [x%nbucket] gives an index y into both the symbol table and the chain table. If the symbol table entry is not the one desired, chain[y] gives the next symbol table entry with the same hash value.
You can follow the chain links until either the selected symbol table entry holds the desired name or the chain entry contains the value STN_UNDEF.
The hash function is as follows:
unsigned long
elf_Hash(const unsigned char *name)
{
unsigned long h = 0, g;
while (*name)
{
h = (h << 4) + *name++;
if (g = h & 0xf0000000)
h ^= g >> 24;
h &= ~g;
}
return h;
}
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
