Determining the Working Set Size of a Project
The following example is a continuation of the previous example, and it uses the same project.
The previous example shows that the user1 project is using more physical memory than its cap allows. This example shows how much memory the project workload requires.
user1machine% rcapstat 5 5
id project nproc vm rss cap at avgat pg avgpg
376565 user1 3 6249M 6144M 6144M 690M 0K 689M 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6144M 6144M 0K 0K 0K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6171M 6144M 27M 0K 27M 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6146M 6144M 4872K 0K 4816K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6156M 6144M 12M 0K 12M 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6150M 6144M 5848K 0K 5816K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6155M 6144M 11M 0K 11M 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6150M 10G 32K 0K 32K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6214M 10G 0K 0K 0K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6247M 10G 0K 0K 0K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6247M 10G 0K 0K 0K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6247M 10G 0K 0K 0K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6247M 10G 0K 0K 0K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6247M 10G 0K 0K 0K 0K
376565 user1 3 6249M 6247M 10G 0K 0K 0K 0K
|
Halfway through the cycle, the cap on the user1 project was increased from 6 gigabytes to 10 gigabytes. This increase stops cap enforcement and allows the resident set size to grow, limited only by other processes and the amount of memory in the machine. The rss column might stabilize to reflect the project working set size (WSS), 6247M in this example. This is the minimum cap value that allows the project's processes to operate without continually incurring page faults.
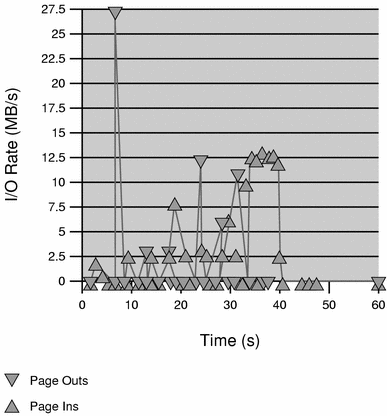
The following two figures graphically show the effect rcapd has on user1 while the cap is 6 gigabytes and 10 gigabytes. Every 5 seconds, corresponding to the sample interval, the RSS decreases and I/O increases as rcapd pages out some of the workload's memory. Shortly after the page out completes, the workload, needing those pages, pages them back in as it continues running. This cycle repeats until the cap is raised to 10 gigabytes approximately halfway through the example, and the RSS stabilizes at 6.1 gigabytes. Since the workload's RSS is now below the cap, no more paging occurs. The I/O associated with paging stops as well, as the vmstat (see vmstat(1M)) or iostat (see iostat(1M)) commands would show. Thus, you can infer that the project required 6.1 gigabytes to perform the work it was doing at the time it was being observed.
Figure 9–1 Stabilizing RSS Values After Raising the Cap of user1 Higher Than user1's WSS

Figure 9–2 Relationship Between Page Ins and Page Outs, and the Stabilization of I/O After user1's Cap Is Raised
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
