Scenario—RAID 0 (Stripe) Volume
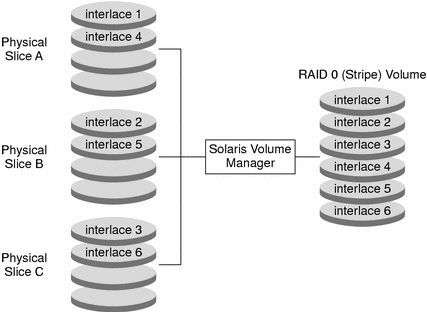
Figure 8–1 shows a stripe that is built from three components (disks).
When Solaris Volume Manager stripes data from the volume to the components, it writes data from chunk 1 to Disk A, from chunk 2 to Disk B, and from chunk 3 to Disk C. Solaris Volume Manager then writes chunk 4 to Disk A, chunk 5 to Disk B, chunk 6 to Disk C, and so forth.
The interlace value sets the size of each chunk. The total capacity of the stripe d2 equals the number of components multiplied by the size of the smallest component. (If each slice in the following example were 2 Gbytes, d2 would equal 6 Gbytes.)
Figure 8–1 RAID 0 (Stripe) Example
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
