2.4.2 Remote Notification Listeners
The connector client interface also exposes the addNotificationListener method so that notifications can be received in remote management applications. Standard proxies expose this method as well and transmit any listener registrations through the connector client.
Listeners do not need to be aware that they are remote. The connector transmits registration requests and forwards notifications back to the listeners. The whole process is transparent to the listener and to the management components.
As shown in Figure 2–3, the connector components implement a complex mechanism for registering remote listeners and forwarding notifications. Because notifications are based on the Java event model, broadcasters cannot send notifications outside their Java virtual machine. So, the connector server instantiates local listeners that receive all notifications and places them in a cache buffer, to wait to be sent to the manager application. This enables the connector to avoid saturating the communication layer in case of a burst of notifications.
Figure 2–3 Adding Remote Listeners on the Manager Side
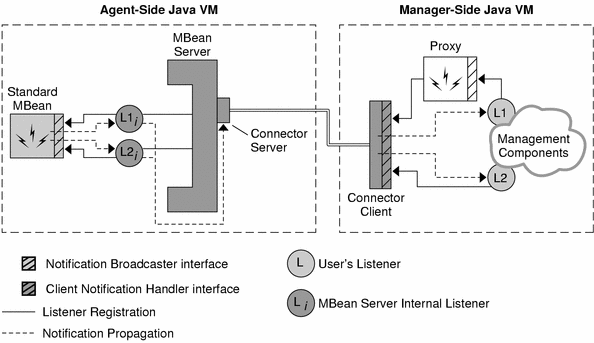
Notifications in the new RMI and JMXMP connectors are pulled periodically at the client's request. The pull mechanism is used to group notifications and reduce bandwidth usage. The connector client acts as a broadcaster and sends the notifications to their intended listeners.
Notifications in the legacy RMI and HTTP connectors are pulled in the same way as the new connectors. However, the legacy connector notifications can also can be pushed from the agent to the connector client as they are received.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
