Sun ONE Identity Server Programmer's Guide
|
Sun ONE Identity Server Programmer's Guide |
Chapter 3 Authentication Service
The Authentication Service is the point of entry for Sun™ One Identity Server. A user must pass an authentication process before being allowed access to the console or any resource that is secured using the Identity Server. As well, an application or service must pass the authentication process before it can be considered a trusted source by Identity Server. This chapter explains the process, its pluggable architecture, and the authentication APIs. It contains the following sections:
Overview
The Authentication User Interface
Default Authentication Modules
Custom Authentication Modules
Application Authentication
Authentication SPI
URL Parameters
C Programs and Authentication
Authentication Samples
Overview
Identity Server provides secure access to web-based (and non-web-based) applications and the data that they store. Gaining access to either of these resources requires that the user or application be given permission by the Authentication Service. When the requestor tries to access a protected resource, it is directed to submit credentials to one (or more) of several authentication modules; for instance, the LDAP module generally requires authentication with the user's Directory Server ID and password while the SafeWord™ module requires authentication to the ACE/Server. The Authentication Service then acts as an authority, granting or denying access upon completion of the required process. If access is granted, a session token is created and assigned to the requestor who is then, by default, directed to the Identity Server console. When the console finds and validates the token, the appropriate page is displayed based on the identity's request and their parent organization. If there is no valid session token, the console denies access.
Accessing The Authentication Service
There are a number of ways to authenticate to the Identity Server in order to allow access to protected resources. Java™ applications can use the authentication API while C applications can open a connection using a web browser. End users also access the Authentication Service using a web browser. In addition, there is a remote-auth.dtd that defines the XML structure used to format the XML request messages.
Authentication For Java Applications
External Java applications can authenticate to the Identity Server or any of its protected resources (including the Sun ONE Directory Server data store) using the Authentication API for Java. This API provides interfaces to initiate the authentication process and communicate authentication credentials to the Authentication Service. The API is defined in a Java package called com.sun.identity.authentication. Developers incorporate the classes and methods from this package into their Java applications to allow communication with the Authentication Service. The application's Java request is first converted to an XML message format and passed to the Identity Server over http or https. (XML messages are structured according to the remote-auth.dtd which is discussed further in "The remote-auth.dtd Structure".) The XML message is then converted back into Java which is able to be interpreted by the Authentication Service. These API are discussed further in "Authentication API For Java Applications".
Authentication For C Applications
Identity Server includes the resources for C applications to authenticate to the Identity Server. They must first open a connection to the Identity Server using the URL, http://<Identity Server_host.domain>/ <service_deploy_uri>/authservice. Then the application sends a request in XML message format and passes it to the Identity Server over http or https. The XML message is then processed by the Authentication Service. After passing the authentication process, a validated session token will be sent to the C application. XML messages are structured according to the remote-auth.dtd which is discussed further in "The remote-auth.dtd Structure".
Authentication For Users Using A Web Browser
A user with a web browser can authenticate to Identity Server using the authentication user interface. The URI for this web-based interface is http://<Identity Server_host.domain>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login. Once authenticated, the user gains access to the Identity Server console and based on their privileges:
Administrators can access the identity administration portion of the console in order to manage authentication data.
End users can modify authentication data in their own user profiles.
Authenticating The Request
The authentication framework has the job of validating the authentication request. The framework integrates the standard Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) API with proprietary APIs that support Identity Server-specific features. Identity Server adds features on top of the JAAS framework including account locking, web-based UI, and an XML over HTTP interface that allows authentication APIs to work on a remote machine. Because of this architecture, any custom JAAS authentication modules will also work within the Authentication Service.
|
This guide is not intended to document the JAAS framework. For more information on these APIs, see the Java Authentication And Authorization Service Developer's Guide at http://java.sun.com/security/ jaas/doc/api.html. Additional information can be found at http://java.sun.com/products/jaas/. |
Requesting Authentication
The authentication framework starts the authentication process by reading a Java request. When a request is received, the framework creates a session for the requestor and begins the authentication process by calling the Authentication Service Provider Interface (SPI) to allow interaction between the requestor and the login module for credential gathering. The SPI references the authentication module configuration file to determine the login requirements for the specific authentication module. (More information on the authentication module configuration file can be found in "The Auth_Module_Properties.dtd Structure".)
Using The Authentication SPI
Identity Server provides the Authentication SPI to invoke a specific authentication module. The SPI is defined in the com.sun.identity.authentication.spi package. All configured modules, custom and default, can extend the AMLoginModule and implement the process, init and getPrincipal methods. These methods access Identity Server objects for post-processing of user profiles, service templates, and attributes. More information on the Authentication SPI can be found in "Authentication SPI".
|
The Authentication API are also able to invoke authentication modules written using the pure JAAS API. |
Client Detection
Within the framework, the first step in authenticating a user is to identify the client type making the HTTP request. The Authentication Service uses the URL information to retrieve the browser type's characteristics. Based on these characteristics, the correct authentication pages are sent back to the client browser; for example, HTML pages. Once the user is validated, the client type is added to the session token where it can be retrieved by other services. More information on client detection can be found in Chapter 11 "Client Detection."
|
Although Identity Server has the capability to support multiple clients (including wireless), currently it only defines client data for HTML clients. |
Miscellaneous Features
The Authentication Service includes a number of new features. Account locking and Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) Mapping are explained below.
Account Locking
Account locking prohibits the user from authenticating after a fixed number of consecutive unsuccessful login attempts. Identity Server allows two additional login attempts after the user is warned about an impending lockout. The locking can be initiated by changing the status of an attribute in LDAP or by memory locking which occurs when the time-out duration is greater then 0. Email notifications are sent to administrators regarding any account lockouts. (Account locking activities are also logged.) For more information on the account locking attributes, see the Sun ONE Identity Server Administration Guide.
FQDN Mapping
FQDN Mapping enables the Authentication Service to take corrective action in the case where a user may have typed in an incorrect URL (such as specifying a partial host name or using an IP address to access protected resources). FQDN Mapping is enabled by modifying the com.sun.identity.server.fqdnMap attribute in the AMConfig.properties file. The format for specifying this property is:
com.sun.identity.server.fqdnMap[<invalid-name>]=<valid-name>
The value <invalid-name> would be a possible invalid FQDN host name that may be typed by the user, and <valid-name> would be the actual host name to which the filter will redirect the user. Any number of mappings can be specified in AMConfig.properties (as illustrated in Code Example 3-1) as long as they conform to the stated requirements.
:
Code Example 3-1 FQDN Mapping Attribute In AMConfig.properties
Possible Uses For FQDN Mapping
This property can be used for creating a mapping for more than one host name which may be the case if applications hosted on this server are accessible by more than one host name. This property can also be used to configure Identity Server to not take corrective action for certain URLs. For example, if no redirect is required for users who access applications by using an IP address, this feature can be implemented by specifying a map entry such as com.sun.identity.server.fqdnMap[<IP>]=<IP>.
|
If more than one mapping is defined, ensure that there are no overlapping values in the invalid FQDN name.Failing to do so may result in the application becoming inaccessible. |
The Authentication User Interface
The Authentication Service has a separate user interface from the Identity Server console. It provides the web-based interface for all authentication modules installed in the Identity Server deployment. The interface provides a dynamic and customizable means for gathering user credentials for authentication by presenting the web-based login requirement pages to a user requesting access. Figure 3-1 is a screenshot of the default user interface for LDAP authentication.
Figure 3-1 Default LDAP Authentication User Interface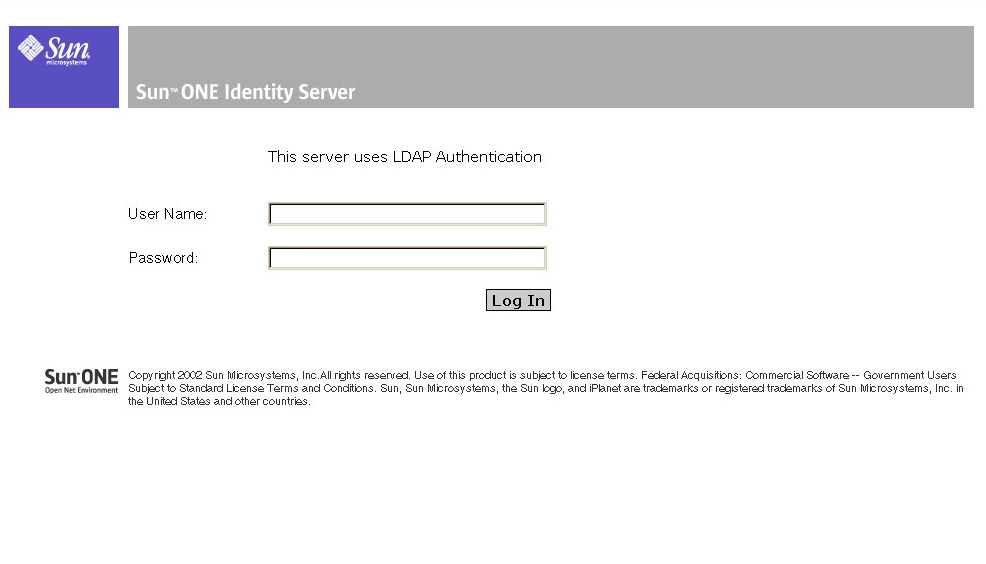
Like the Identity Server console, the Authentication Service interface is built with J2EE Assisted Take-Off (JATO), a Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) application framework used to help developers build functional web applications. It uses the Authentication API to authenticate users to their specified authentication module. (This component can be deployed on non-Identity Server machines.)
The Authentication Service interface uses Java Server Pages (JSP) and XML files to convey graphical-based user information such as login, logout and time-out information as well as error messages. The JSP templates define the layout of the pages and are located in <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/web-apps/ services/config/auth/default. The XML templates are the authentication module configuration files, discussed in "Configuring Module Credential Requirements". They are also located in <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/web-apps/services/config/auth/default. Both of these types of files can be modified to customize the user experience at the following levels:
Customizing The Authentication Interface
The JSP templates and module configuration properties files can be modified to reflect an organization's branding or to add organization-specific functionality. For example, if there are three organizations in the Identity Server deployment—org1, org2, org3—and org1 has customized templates, these templates will be located in <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/web-apps/services/config/auth/org1. Any organization that does not have its own directory of modified templates will continue to use the default set of files located in <identity_server_root>/ SUNWam/web-apps/services/config/auth/default. In the example, both directories contain a full set of templates. Org1 would use the set in the org1 directory while org2 and org3 would use the set in the default directory.
Creating A Directory
Go to the directory where the JSP templates are stored.
Create a directory using the appropriate path based on the level of customization.
Copy all the module configuration properties files and JSP templates into the new directory.
Customize the files in the new organization directory.
|
All JSP background colors, page layouts, and fonts are configurable using the style sheets located in <identity_server_root>/ web-apps/services/css. |
JSP Templates
The following JSP templates can be found in <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/ web-apps/services/config/auth/default. Strong HTML skills as well as an understanding of web servers can help in the modification of these files.
Table 3-2 List of Customizable JSP Templates
Authentication Module Configuration Files
The authentication module configuration XML files are based on the Auth_Module_Properties.dtd and the syntax of this DTD should be followed when customizing these files. Modifying elements in these XML files will automatically and dynamically customize the authentication interface. More information on modifying this type of file can be found in "Configuring Module Credential Requirements"."
Default Authentication Modules
Identity Server is installed with a set of default authentication modules that can be used to communicate with proprietary technologies. These modules are explained below.
Core Authentication Service
The Core authentication service is the configuration base for all other proprietary authentication modules. It must be registered to an organization before any user can log in using one of the default authentication modules. It allows the Identity Server administrator to define default values for the Core authentication parameters. These values can then be picked up if no overriding value is set in the specific authentication module chosen. The default values for the Core service are defined in the amAuth.xml file and stored in the Directory Server after installation.
Proprietary Authentication Modules
Identity Server provides authentication modules able to communicate with proprietary technologies. The authentication modules currently included are:
Anonymous—This module allows a user to log in without specifying a user name and/or password. Additionally, an Anonymous user can be created. Log in as Anonymous is then possible without a password. Anonymous connections are generally customized by the Identity Server administrator to have limited access to the server.
Certificate—This module allows a user to log in through a personal digital certificate (PDC) that could optionally use the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) to determine the state of a certificate. Sun ONE Certificate Server (CS) can be installed as a validation authority. For more information on CS, see the documentation set located at http://docs.sun.com/db?p=coll/S1_s1CertificateServer_47.
LDAP—This module allows for authentication using LDAP bind, an operation which associates a user ID password with a particular LDAP entry.
Membership—This module allows a new user to register themselves for authentication with a login and password as well as other fields such as first name, last name, etc.
NT—This module allows for authentication using a Windows NT server.
RADIUS—This module allows for authentication using an external Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server.
SafeWord—This module allows for authentication using Secure Computing's servers and tokens.
Unix—This Solaris only module allows for authentication using a user's UNIX identification and password.
The default authentication module used after installation is LDAP.
Assigning The Authentication Method
An authentication module can be assigned as the method to authenticate identities that belong to any of the following objects:
Once a module is defined as the authentication method for one of these objects, it can than be configured with URLs to redirect the identity on either a successful authentication or a failed authentication. When more than one URL is set, Identity Server has a defined hierarchy to pick the proper redirection URL.
|
For more information on how to define the authentication module using the Identity Server console, see the Sun ONE Identity Server Administration Guide. |
Authentication By Organization
The authentication method for an organization is set by registering the Core Authentication service to the organization and configuring the Organization Authentication Configuration attribute. The authentication service(s) defined must also be registered to the organization.
|
Authentication by organization is the default definition. It can also be accessed by providing the "org" parameter in the authentication URL. More information on this function can be found in "URL Parameters". |
Successful Organization-based Authentication Redirection URLs
Identity Server bases a successful organization-based authentication redirection determination by checking for a redirection URL in the following places:
A URL set by the module.
A URL set by a goto URL parameter.
A URL set for clientType in iplanet-am-user-success-url in user's amUser.xml service file.
A URL set for clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url in the user's role.
A URL set for clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url in the organization.
A URL set for clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url as the global default.
iplanet-am-user-success-url set at user entry
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at user's role entry
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the org entry
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url as the global default if not set in org
Failed Organization-based Authentication Redirection URLs
Identity Server bases a failed organization-based authentication redirection determination by checking for a URL in the following order:
A URL set by the module.
A URL set by a gotoOnFail parameter.
A URL set for clientType in iplanet-am-user-failure-url set at the user entry.
A URL set for clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the user's role entry.
A URL set for clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the organization entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url as the global default if it is not set in the organization.
iplanet-am-user-failure-url set at the user entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the user's role entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the organization entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url as the global default if it is not set in the organization.
Authentication By Role
The authentication method for a role is set by registering the Core Authentication service to the role and configuring the Organization Authentication Configuration attribute. The authentication service(s) defined must also be registered to the organization in which the role exists.
|
Authentication by role is accessed by providing the "role" parameter in the authentication URL. More information on this function can be found in "URL Parameters". |
Successful Role-based Authentication Redirection URLs
Identity Server bases a successful role-based authentication redirection determination by checking for a URL in the following order:
A URL set by the module.
A URL set by the goto parameter.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-user-success-url set in the user entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the role to which the user authenticates.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the user's role.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the organization.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url as the global default.
iplanet-am-user-success-url set in the user entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the role to which the user authenticates.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the user's role.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the organization.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url from the global default.
Failed Role-based Authentication Redirection URLs
Identity Server bases a failed role-based authentication redirection determination by checking for a URL in the following order:
A URL set by the module.
A URL set by the gotoOnFail parameter.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-user-failure-url set in the user entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the role to which the user authenticates.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the user's role.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the organization.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url as the global default.
iplanet-am-user-failure-url set in the user entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the role to which the user authenticates.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the user's role.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the organization.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url from the global default.
Authentication By Service
The authentication method for a service is set by registering the Core Authentication service and configuring the Organization Authentication Configuration attribute. The authentication service(s) defined must also be registered to the organization in which the role exists.
|
Authentication by service is accessed by providing the "service" parameter in the authentication URL. More information on this function can be found in "URL Parameters". |
Successful Service-based Authentication Redirection URLs
Identity Server bases a successful service-based authentication redirection determination by checking for a URL in the following order:
A URL set by the module.
A URL set by the goto parameter.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-user-success-url set in the user entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the service entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the user's role.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the organization.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the global default.
iplanet-am-user-success-url set at the user entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the service entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at user's role entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url set at the organization entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-success-url as the global default if not set in the organization.
Failed Service-based Authentication Redirection URLs
Identity Server bases a failed role-based authentication redirection
A URL set by the module.
A URL set by the gotoOnFail parameter.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-user-failure-url set at the user entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the service entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the user's role entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the organization entry.
A URL matching clientType in iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url as the global default if not set in the organization.
iplanet-am-user-failure-url set at the user entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the service entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at user's role entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url set at the organization entry.
iplanet-am-auth-login-failure-url as the global default if not set in the organization.
Authentication By User
The authentication method for a user is set by registering the Core Authentication service to the user and configuring the Organization Authentication Configuration attribute. The authentication service(s) defined must also be registered to the organization in which the role exists. More information on how this is done can be found in the Sun ONE Identity Server Administration Guide.
|
Authentication by user is accessed by providing the "user" parameter in the authentication URL. More information on this function can be found in "URL Parameters". |
Authentication By Authentication Level
The authentication method for a particular authentication level is set by the administrator. More information on how this is done can be found in the Sun ONE Identity Server Administration Guide.
|
Authentication by authentication level is accessed by providing the "authLevel" parameter in the authentication URL. More information on this function can be found in "URL Parameters". |
Authentication By Module
The authentication method for a module is set by registering the Core Authentication service to the module and configuring the Organization Authentication Configuration attribute. More information on how this is done can be found in the Sun ONE Identity Server Administration Guide.
Custom Authentication Modules
The Authentication Service framework allows an organization to plug-in custom authentication modules. The following section discusses the steps necessary to create a custom authentication module.
|
To write a custom authentication module, knowledge of the JAAS API is necessary, especially for defining the module's configuration properties. |
Creating A New Authentication Module
Create an XML service file for the new authentication module.
Create a localization properties file for the new module.
Create an authentication module configuration file.
Modify the amAuth.xml file.
Import the custom module's XML service file into the Authentication Service using the amadmin command line tool.
|
Identity Server contains a sample exercise for creating a custom authentication module. For more information, see the "Login Module". |
Configuring Localization Properties
A localization properties file specifies the localized screen text and messages that an administrator or user will see when directed to an Authentication Service's attribute configuration page. Each authentication module has a corresponding localization properties file. The name of the file follows the format amAuth<modulename>.properties; for example, amAuthLDAP.properties. The default character set is ISO-8859-1 (English). Each authentication module has its own localization properties file, located in <identity_server_root>/ SUNWam/locale/. This directory contains a sub-directory for each locale. The default English directory is en_US. For reference, Code Example 3-2 is a portion of the file amAuthLDAP.properties. (The file is in the <identity_server_root>/ SUNWam/locale/en_US directory.) Following are the concepts behind the configuration of this file.
The data following the equal (=) sign in each key/value pair (displayed in English here) would be translated to a specific language as necessary and copied into the corresponding locale directory. In Code Example 3-2, the alphanumeric keys (a1, a2, etc.) map to fields defined by the i18nKey attribute in the amAuthLDAP.xml service configuration file.
The alphanumeric keys determine the order in which the fields are displayed in the Identity Server console. The keys are taken in the order of their ASCII characters (a1 is followed by a10, followed by a2, followed by b1). For example, if an attribute needs to be displayed at the top of the service attribute page, the alphanumeric key should have a value of a1. The second attribute could then have a value of either a10, a2 or b1, and so forth.
Code Example 3-2 Portion of amAuthLDAP.properties
|
|
Configuring Module Credential Requirements
The authentication module configuration file specifies each authentication module's credential requirements by defining the screens that a user might see when directed to authenticate. Modifying elements in this XML file will automatically and dynamically customize the authentication interface. The name of this file follows the format <modulename>.xml; for example, SafeWord.xml or LDAP.xml. Each authentication module has its own configuration file, located in <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/web-apps/services/config/auth/default.
If there is more than one organization in the Identity Server deployment, each organization has its own authentication directory named <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/web-apps/services/config/auth/ org_name. If an organization has more than one locale, the files are stored separately, in directories appended with a locale, as in <identity_server_root>/ SUNWam/web-apps/services/config/auth/org_name_locale. Additionally, with service authentication, there might be an authentication directory corresponding to the service under the LDAP organization tree.
The Auth_Module_Properties.dtd Structure
The Auth_Module_Properties.dtd defines the structure for the XML-based authentication module configuration files. It provides definitions to initiate, construct and send the required authentication interface to the authentication framework. The DTD is located in <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/dtd. An explanation of the elements defined by the Auth_Module_Properties.dtd follows. Each element includes required and/or optional XML attributes.
ModuleProperties Element
ModuleProperties is the root element of the authentication module configuration file. It must contain at least one Callbacks sub-element. The required XML attributes of ModuleProperties are moduleName which takes a value equal to the name of the module and version which takes a value equal to the version number of the authentication module configuration file itself. Code Example 3-3 below is the LDAP.xml file that defines the screens for the LDAP authentication module. Note the ModuleProperties element on the first line of code.
|
|
Callbacks Element
The Callbacks element is used to request the information a module needs to gather from the client requesting authentication. Each Callbacks element signifies a separate screen that can be called during the authentication process. It can contain one or more of four sub-elements: NameCallback, PasswordCallback, ChoiceCallback or ConfirmationCallback. The required XML attributes of Callbacks are length which takes a value equal to the number of callback requests for the defined element and order which takes a value equal to the number this particular callback is in the sequence of callbacks. The order attribute value starts with the number `1'. The optional XML attributes are timeout, template, image, header and error.
timeout—takes a value equal to the amount of time in seconds before the request for information times out. It ensures that the user responds in a timely manner. If greater than the timeout value, a timeout page will be sent.
template—defines the file used as a display template for this screen.
image—defines a custom background image to be displayed on this screen.
header—defines text information that can be displayed in the browser window for this screen.
error—takes a true or false value which defines whether the error message generated by the authentication module will be used.
Code Example 3-3 defines three screen's callback elements that can be called by the LDAP Authentication module. The first asks the requestor for a name and password. The second screen allows the requestor to change their password. The final screen sends a message to reset the password.
NameCallback Element
The NameCallback element is used to request data that is entered by the user, for example, a user identification. It can contain one sub-element: Prompt. The optional XML attributes are isRequired and attribute. isRequired takes a value of true or false and defines whether the element is required information. (A value of true displays an asterisk next to the attribute's name in the GUI.) attribute takes a character value of the corresponding LDAP attribute of this value.
PasswordCallback Element
The PasswordCallback element is used to request password data that is entered by the user. It can contain one sub-element: Prompt. The XML attributes are echoPassword, isRequired and attribute. echoPassword is required and takes a value of true or false and defines whether the password should be displayed on the screen or not. isRequired is optional and takes a value of true or false and defines whether the element is required information. (A value of true displays an asterisk next to the attribute's name in the GUI.) attribute is also optional and takes a character value of the corresponding LDAP attribute of this value.
ChoiceCallback Element
The ChoiceCallback element is used when the application user must choose from multiple values. It can contain two sub-elements: Prompt or ChoiceValues. The XML attributes are multipleSelectionsAllowed, isRequired and attribute. multipleSelectionsAllowed is a required attribute and takes a value of true or false. It defines whether the user can choose a number of values or only one from the available choices. isRequired is optional and takes a value of true or false. (A value of true displays an asterisk next to the attribute's name in the GUI.) attribute is also optional and takes a character value of the corresponding LDAP attribute of this value.
ConfirmationCallback Element
The ConfirmationCallback element is used to send `button' information, such as button text which needs to be rendered on the module's screen, as well as receive the button information, such as which button is clicked by the user. It can contain one sub-element: OptionValues. There are no XML attributes.
Prompt Element
The Prompt element is used to set the prompt that will display on the browser screen to request the information. It has no sub-elements or XML attributes.
ChoiceValues and ChoiceValue Element
The ChoiceValues element provides a list of values from which the user can select. It must contain at least one sub-element of the type ChoiceValue which defines one choice. ChoiceValue must contain the sub-element Value. ChoiceValues has no XML attributes but ChoiceValue can contain the XML attribute isDefault. isDefault specifies if the defined value has to be selected by default when displayed; it takes a value of true or false.
OptionValues and OptionValue Element
The OptionValues element provides a list of text information for buttons that need to be rendered on the login screen. It must contain at least one sub-element of the type OptionValue which defines one button text value. OptionValue must contain the sub-element Value. OptionValues has no XML attributes but OptionValue can contain the XML attribute isDefault. isDefault specifies if the defined value has to be selected by default when displayed; it takes a value of true or false.
Value Element
The Value element is used by the client to return a value provided by the requestor back to the Identity Server. It has no sub-elements or XML attributes.
Modifying amAuth.xml
The amAuth.xml defines the "parent" authentication service named Core. Following are the attributes in this file that need to be extended in order for the Authentication Service to recognize a new authentication module. amAuth.xml is located in <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/config/xml.
iplanet-am-auth-authenticators—specifies the Java classes of the authentication services available to an organization within the Identity Server deployment. By default, this includes the Anonymous, Certification, LDAP, Membership, RADIUS, SafeWord, and Unix modules. To define a new authentication module, this field takes a value equal to a text string that specifies the full class name (including package) of the new module.
iplanet-am-auth-allowed-modules—lists the authentication modules available to the specific organization. An administrator can choose the authentication method for their organization. The default authentication method is LDAP.
After modifying amAuth.xml, the command line tool amadmin is used to remove the old Core service file and load the modified one.
amadmin --runasdn <admin_dn> --password <password> --deleteService iPlanetAMAuthService
amadmin --runasdn <admin_dn> --password <password> --schema amAuth.xml
Application Authentication
Java™ applications use the authentication API to access, and authenticate to, the Authentication Service while C applications use a web browser. Both types of applications use the remote-auth.dtd to format the structure of the XML request messages used to transfer the authentication information.
Authentication API For Java Applications
External Java applications use the Authentication Java API to initiate the authentication process and communicate with the required authentication module. These Authentication Java API are organized in a package called com.sun.identity.authentication and can be executed locally or remotely to communicate locally with the Authentication Service. Communication between the API and the framework occurs by sending XML messages over HTTP(s).
The AuthContext class is defined for each request desiring to authenticate to the Identity Server. Since Identity Server can handle multiple organizations, the AuthContext class must be initialized, at least, with the name of the organization to which the requestor is authenticating. Typical code would instantiate this class to begin the login process. The caller would then use the getRequirements method to ask for the requestor's credentials. The credentials are then submitted to the class using submitRequirements. If more information is required, the above process continues until all the required information has been supplied. The getStatus method is then called to check if the user has been successfully authenticated. If successful, the caller can then get the Subject and SSOToken for the user; if not, the caller obtains a LoginException. Identity Server is shipped with a sample that uses this class; for more information, see the section "Remote Client API".
|
The Authentication API are also able to invoke authentication modules written using the pure JAAS API. |
Authenticating Non-Java Applications
Non-Java applications can also authenticate to the Identity Server. Using the URL http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/authservice, the application opens a connection and then exchanges XML messages with the Identity Server. The XML messages are structured according to the remote-auth.dtd. Information on this document can be found in "The remote-auth.dtd Structure". An example of the messages used by C applications can be found in "C Programs and Authentication".
The remote-auth.dtd Structure
Authentication requests and responses are sent to and received by the Authentication Java API or non-Java applications using an XML structure. The structure of these messages is defined in the remote-auth.dtd. The remote-auth.dtd defines the structure for the XML-based messages sent to, and received by, the Identity Server console. It provides definitions to initiate the collection of credentials and perform authentication. It is located in the <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/dtd directory. An explanation of the elements defined by the remote-auth.dtd follows. Each element has required and/or optional XML attributes.
AuthContext Element
AuthContext is the root element of the XML-based message. It must contain a Request or Response sub-element. The required XML attributes of AuthContext are version which takes a value equal to the version number.
Request Element
The Request element is used by the client to initialize and pass user credentials to the Authentication Service. It may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: NewAuthContext, QueryInformation, Login, SubmitRequirements, Logout or Abort. The required XML attribute of Request is authIdentifier which takes a value equal to a unique random number set by the Authentication Service and used to keep track of the authentication session.
NewAuthContext Element
The NewAuthContext element is initiates the authentication process by initializing the Authentication Service and creating a session token for each request. It contains no sub-elements. The required XML attribute of NewAuthContext is orgName which takes a value equal to the name of the organization or sub-organization for which the process is defined.
QueryInformation Element
The QueryInformation element is used by the remote client to get information about the authentication modules supported by the Identity Server or the organization. It contains no sub-elements. The required XML attribute of QueryInformation is requestedInformation which takes a value equal to the authentication module plug-ins configured for an organization or sub-organization.
Login Element
The Login element is used to initialize the authentication session. It will have an Empty sub-element, or can have an IndexTypeNamePair. The IndexTypeNamePair element can be used to specify the defined authentication type and value. It has no required XML attributes.
SubmitRequirements Element
The SubmitRequirements element is used by the remote client to submit the identity's authentication credentials to the Identity Server. It has a Callbacks sub-element and no required XML attributes.
Logout Element
The Logout element is used by the remote client to indicate that user wants to logout. It has an Empty sub-element and no required XML attributes.
Abort Element
The Abort element is used by the remote client to indicate that the user wants to end the login process. It has an Empty sub-element and no XML attributes.
Response Element
The Response element is used by the Authentication Service to ask the remote client to gather user credentials or to inform the remote client on the success or failure of the login as well as any errors that might have occurred. It may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: QueryResult, GetRequirements, LoginStatus or Exception. Table 3-3 shows the Request sub-elements and the possible Responses for each.
Table 3-3 Request Sub-Elements And Possible Responses
The required XML attribute of Response is authIdentifier which takes a value equal to a unique random number set by the Authentication Service and used to keep track of the authentication session.
QueryResult Element
The QueryResult element is used by Identity Server to send query information requested by the remote client. It must contain a Value sub-element. The required XML attribute of QueryResult is requestedInformation which takes a value equal to the authentication module plug-ins configured for an organization or sub-organization.
GetRequirements Element
The GetRequirements element is used by the Identity Server to request authentication credentials from the client. It has a Callbacks sub-element and no required XML attributes.
LoginStatus Element
The LoginStatus element is used by the Identity Server to indicate the status of the authentication process. It will have an Empty sub-element if a Subject or Exception sub-element is not defined. The XML attributes are status, ssoToken, successURL or failureURL; the latter three are optional. If the LoginStatus is successful, the sub-element Subject will be returned with the authenticated user names. The attribute ssoToken will have the session token status set to inprogress when a new AuthContext is created, to success when a login has been successful, to failed when a login has not been successful and completed when the user logs out. The successURL attribute represents the URL that the identity will be redirected to upon successful authentication and failureURL represents the URL that the identity will be redirected to upon failed authentication.
Exception Element
The Exception element is used by the Identity Server to inform the client about an exception that occurred during the login process. It has an Empty sub-element and four optional XML attributes: message which takes a value equal to that of the exception message, tokenId which takes a value equal to that of the user ID of the failed authentication, errorCode which takes a value equal to that of the error message code and templateName which takes a value equal to the name of the JSP template which will be used for this particular exception.
IndexTypeNamePair Element
The IndexTypeNamePair element identifies the defined authentication method that will be used to validate the client. It has the IndexName sub-element. The required XML attribute is IndexType which takes a value equal to that of the generic level at which the authentication method has been defined: authLevel, role, user, moduleInstance and service.
IndexName Element
The IndexName element identifies the specific name of the value specified by the IndexType attribute in the IndexTypeNamePair element. The authentication method can be defined at the organization level, the role level, the user level, the authentication level or the service/application level. The IndexType attribute defines this level; the IndexName element takes a value equal to that of the specific name of the level at which the authentication method has been defined. It has no sub-elements and no XML attributes.
Subject Element
The Subject element identifies a collection of one or more identities. It has no sub-elements and no XML attributes.
Callbacks Element
The Callbacks element is used to request and transfer user credentials between the remote client and Identity Server. Identity Server constructs callback objects for information gathering. The client program collects the credentials by prompting the user and returns the callback objects with the required data. The Callbacks element may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: NameCallback, PasswordCallback, ChoiceCallback, ConfirmationCallback, TextInputCallback, TextOutputCallback, LanguageCallback, PagePropertiesCallback and CustomCallback. The required XML attribute is length which takes a value equal to that of a token.
NameCallback Element
The NameCallback element is used to obtain the name of the user (or service) that is requesting authentication. It may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: Prompt or Value. It has no required XML attributes.
PasswordCallback Element
The PasswordCallback element is used to obtain the password of the user (or service) that is requesting authentication. It may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: Prompt or Value. The required XML attribute is echoPassword which takes a value of true or false. The default value of false indicates that there will be no password confirmation.
ChoiceCallback Element
The ChoiceCallback element is used when the user must choose from a selection of values. It may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: Prompt, ChoiceValue or SelectedValues. The required XML attribute is multipleSelectionsAllowed which takes a value of true or false. The default value of false indicates that the user can not choose more than one from the selection.
ConfirmationCallback Element
The ConfirmationCallback element is used by the Identity Server to request a confirmation from the user. It may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: Prompt, OptionValues, SelectedValue, and DefaultOptionValue. The required XML attributes are messageType (which defines the type of message, either information, warning or the default, error), and optionType which specifies the type of confirmation (ok_cancel, yes_no_cancel, unspecified or the default, yes_no).
TextInputCallback Element
The TextInputCallback element is used to get text information from the user. It may contain one or more of the following sub-elements: Prompt or Value. There are no required XML attributes.
TextOutputCallback Element
The TextOutputCallback element is used when the user must choose from a selection of values. It may contain the sub-element Value. The required XML attribute is messageType which defines the type of message, either information, warning or the default, error.
LanguageCallback Element
The LanguageCallback element is used by the Identity Server to obtain the user's locale information. It must contain the Locale sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
PagePropertiesCallback Element
The PagePropertiesCallback element contains all GUI-related information. It may contain any of the following sub-elements: ModuleName, HeaderValue, ImageName, PageTimeOutValue, or TemplateName. The required XML attribute is isErrorState which takes a value of true or false. The default value is false which indicates that this page is not an error page.
ModuleName Element
The ModuleName element is takes a value equal to the name of the authentication module. It contains no sub-elements and no XML attributes.
HeaderValue Element
The HeaderValue element is takes a value equal to the header that will be displayed. It contains no sub-elements and no XML attributes.
ImageName Element
The ImageName element is takes a value equal to the name of the image to be displayed. It contains no sub-elements and no XML attributes.
PageTimeOutValue Element
The PageTimeOutValue element is the page time-out value in seconds. It contains no sub-elements and no XML attributes.
TemplateName Element
The TemplateName element is takes a value equal to the name of the template to be rendered. It contains no sub-elements and no XML attributes.
CustomCallback Element
The CustomCallback element is used to define user-defined Callbacks. It may contain the AttributeValuePair sub-element. The required XML attribute is the className which takes a value equal to that of the Callback name.
AttributeValuePair Element
The AttributeValuePair element contains the attribute and values for a Callback. It must contain the Attribute sub-element and it can contain the Value sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
Attribute Element
The Attribute element defines the Callback parameter. It contains no sub-elements. The required XML attribute is name which takes a value equal to the name of the Callback parameter.
Prompt Element
The Prompt element is used by Identity Server to request the remote client to display the prompt. It contains no sub-elements and there are no required XML attributes.
Locale Element
The Locale element contains the value of the locale that will be used for authentication. It contains no sub-elements. The optional XML attributes are language (which represents the language code), country (which represents the country code) and variant (which represents the variant code).
ChoiceValues Element
The ChoiceValues element provides a list of choices. It must contain at least one the ChoiceValue sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
ChoiceValue Element
The ChoiceValues element provides a single choice. It must contain at least one Value sub-element. The required XML attribute is isDefault which takes a value of yes or no. The default value of no specifies if the value has to be selected by default when displayed.
SelectedValues Element
The SelectedValues element provides a list of values selected by the user. It must contain at least one Value sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
SelectedValue Element
The SelectedValue element provides a value selected by the user. It must contain at least one Value sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
OptionValue Element
The SelectedValues element provides a single user-defined option value. It must contain at least one Value sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
DefaultOptionValue Element
The DefaultOptionValue element is the default option value. The default value depends on whether user-defined values or predefined values are used in the callback. If user-defined values are used, the default value will be an index in the OptionValues element; if predefined, it will be one of the predefined option values.It must contain at least one Value sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
Value Element
The Value element is used by the remote client to return a value, provided by the user (or service), back to the Identity Server. It must contain at least one Value sub-element. There are no required XML attributes.
Authentication SPI
The Authentication SPI implements the JAAS LoginModule API, and provides methods to access the Authentication Service and module configuration properties files. The SPI are organized in the com.iplanet.authentication.spi package and contain the abstract class, AMLoginModule, which must be sub-classed with the name of an authentication module. The class must also implement the init(), process() and getPrincipal() methods in order to communicate with the module configuration properties files. The callbacks are then dynamically generated based on this file. Other methods that can be defined include the setLoginFailureURL and setLoginSuccessURL which set the URLs to send the user to based on a failed or successful authentication, respectively. More information on the SPI can be found in the Javadocs located at <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/docs.
URL Parameters
A URL parameter is a name/value pair appended to the end of a URL. The parameter starts with a question mark (?) and takes the form name=value. If more than one URL parameter exists, each parameter is separated by an ampersand (&). URL parameters pass information from the browser to the Identity Server. The following parameters, when appended to an authentication URL and typed in a web browser's Location bar, will redirect the user to the appropriate resource after authentication.
goto—Adding a goto=<auth_success_URL> query parameter tells the Authentication Service to send the user to the noted URL when successful authentication has been completed. An example goto URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?goto=http://www.sun.com. A goto=<logout_URL> query parameter can also be used to tell the Authentication Service to send the user to the noted URL when they have logged out. An example goto URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?goto=http://www.sun.com/logout.html.
gotoOnFail—Adding a gotoOnFail=<auth_fail_URL> query parameter tells the Authentication Service to send the user to the URL noted if user authentication has failed. An example gotoOnFail URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?gotoOnFail=http://www.sun.com/auth_fail.html.
org—The Authentication Service needs to know the requesting user's organization when the user first accesses the Identity Server. From this information the correct login page, based on the organization and the locale setting in the particular organization will be displayed. Adding an org=<org_name> query parameter tells the Authentication Service the user's organization. An example org URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/ <service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?org=iplanet.
user—Authentication can be defined at the user level. For example, one user's profile can be configured to authenticate using the Certification module while another might be configured to authenticate using the LDAP module. Adding a user=<user_name> query parameter tells the Authentication Service to send the user to their configured authentication process. An example user might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?user=test.
role—Authentication can be configured on a per-role basis. Adding a role=<role_name> query parameter tells the Authentication Service to send the user to the authentication process configured for that role. An example role URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/ UI/Login?role=manager.
module—A specific authentication module can be requested by adding a module=<auth_module_name> query parameter. An example module URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/ Login?module=unix.
service—Different authentication schemes can be configured for different services using the Authentication Configuration Service. For example, an online paycheck application might require authentication using a more secure Certification module while an organization's employee directory application might require LDAP authentication only. An authentication scheme can be configured, and named, for each of these services. The service=<auth_scheme_name> query parameter tells the Authentication Service that this user desires to use the <auth_scheme_name> authentication configuration. An example service URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/ Login?service=sv1.
|
The Authentication Configuration Service is used to define a scheme for service-based authentication. More information on this service can be found in the Identity Server Administration Guide. |
arg=newsession—The Authentication Service will destroy an existing session token and perform a new login in one request with the use of the arg=newsession query parameter. This option is typically used in the Anonymous Authentication module. The user first authenticates with an anonymous session, and then hits the register or login link. An example arg=newsession URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/ <service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?arg=newsession.
authlevel—Each authentication module is defined with a fixed integer authentication level. Adding an authlevel=<value> query parameter tells the Authentication Service to call a module with, at the least, the configured authentication level. An example authlevel URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/<service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?authlevel=1.
domain—This parameter allows a user to login to the specified domain. An example domain URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/ <service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?domain=sun.com.
iPSPCookie—This parameter allows a user to login with a persistent cookie. A persistent cookie is one that continues to exist after the browser window is closed. In order to use this parameter, the organization to which the user is logging in must have Persistent Cookies enabled in their Core service. An example iPSPCookie URL might be http://<host.domain:port>/ <service_deploy_uri>/UI/Login?org=example&iPSPCookie=yes. Once the user authenticates and the browser is closed, the user can login with a new browser session and will be directed to console without having to reauthenticate. This will work until the Persistent Cookie Max Time specified in the Core Service elapses.
Login.Token1 (<username>) , Login.Token2 (<password>)—This parameter allows a user to login without having to access the authentication interface.
Login.Token0—This parameter allows a user to login anonymously.
C Programs and Authentication
Following is an example of how customers create XML messages to call the Authentication Service from a C program.
Authentication Request / Response Flow
Create an AuthContext for the organization name to login to. The successful response for this is the authIdentifier which is the sessionID for this request. Code Example 3-4 illustrates what the Request XML message would look like.
Code Example 3-4 Request XML Message For C Applications
|
|
Code Example 3-5 illustrates what the Response XML message (which returns the unique session ID for the request) would look like.
Code Example 3-5 Response XML Message From C Applications
Start the authentication process using the Login Element. Code Example 3-6 illustrates this message.
Code Example 3-6 XML Message To Start Authentication Process
|
<AuthContext version="1.0"><Request authIdentifier="<sessionid>"><Login/></Request> |
|
|
Code Example 3-7 XML Response To Authentication Process Request
|
<Response><![CDATA[<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> |
|
|
Send the required credentials back to the Identity Server. Code Example 3-8 illustrates this XML message. Code Example 3-8 illustrates the XML message that contains the authentication credentials.
Code Example 3-8 XML Request With Authentication Credentials
|
<Request><![CDATA[<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> |
|
|
Code Example 3-9 XML Response To Authentication Credentials
|
<Response><![CDATA[<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> |
|
<LoginStatus status="success" ssotoken="sessionid" successurl="http://www.yahoo.com"> |
|
|
Authentication Samples
Authentication Service samples have been provided and can be found in the directory <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/samples/authentication. They include:
Remote Client API
This sample program demonstrates how to integrate the Remote Client API for authenticating users with the Identity Server. It uses LDAP authentication although it can be modified to use other existing or customized authentication modules. The instruction file is the readme.html file found in the <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/samples/authentication/LDAP directory.
Login Module
This sample demonstrates the steps needed to integrate a custom login module into the Identity Server. All the files needed to compile, deploy and run the sample authentication module that is shipped with Identity Server can be found in the <identity_server_root>/SUNWam/samples/authentication/providers directory. The instruction file is the Readme.html file in the same directory.
Previous Contents Index Next
Copyright 2002 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Last Updated December 02, 2002