Binary Backup
Binary backup produces a copy of the database files, and is performed at the file-system level. The output of a binary backup is a set of binary files containing all entries, indexes, the change log, and the transaction log. A binary backup does not contain configuration data.
Binary backup is performed using one of the following commands:
-
dsadm backup must be run offline, that is, when the Directory Server instance is stopped. The command must be run on the local server containing the Directory Server instance.
-
dsconf backup can be run online and remote to the Directory Server instance.
Binary backup has the following advantages:
-
All suffixes can be backed up at the same time.
-
Binary backup is significantly faster than a backup to LDIF.
-
The replication change log is backed up.
Binary backup has one limitation. Restoration from a binary backup can be performed only on a server with an identical configuration.
This limitation implies the following:
-
Both machines must use the same hardware and the same operating system, including any service packs or patches.
-
Both machines must have the same version of Directory Server installed, including binary format (32 bits or 64 bits), service packs and patch levels.
-
Both servers must have the same directory tree that is divided into the same suffixes. The database files for all suffixes must be copied together Individual suffixes cannot be copied.
-
Each suffix must have the same indexes configured on both servers, including virtual list view (VLV) indexes. The database files for the suffixes must have the same name.
-
Each server must have the same suffixes configured as replicas. If fractional replication is configured, fractional replication must be configured identically on all master servers.
-
Attribute encryption must not be used on either server.
At a minimum, you need to perform a regular binary backup on each set of coherent machines. Coherent machines are machines that have an identical configuration, as defined previously.
Note –
Because restoration from a local backup is easier, perform a binary backup on each server.
These abbreviations are used in the remaining diagrams in this chapter:
|
M = master replica |
|
RA = replication agreement |
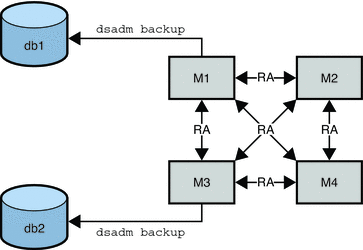
The following figure assumes that M1 and M2 have an identical configuration and that M3 and M4 have an identical configuration. In this scenario, a binary backup would be performed on M1 and on M3. In the case of failure, M1 or M2 could be restored from the binary backup of M1 (db1). M3 or M4 could be restored from the binary backup of M3 (db2). M1 and M2 could not be restored from the binary backup of M3. M3 and M4 could not be restored from the binary backup of M1.
Figure 8–2 Offline Binary Backup
For details on how to use the binary backup commands, see Binary Backup in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
