Creating Directory Sources
 To Create Directory Sources
To Create Directory Sources
You must create directory sources in the following order (based on which sources you will be synchronizing).
-
Creating a Windows NT SAM Directory Source
Note –At minimum, you must configure at least one Sun Java System Directory source and at least one Windows directory source (Active Directory and/or NT SAM).
Select the Directory Sources node in the navigation tree and the Directory Sources panel is displayed.
Figure 8–7 Accessing the Directory Sources Panel
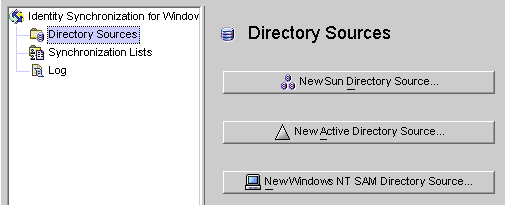
Creating a Sun Java System Directory Source
Each Sun Java System directory source is associated with a Connector and set of Plug-ins that can be deployed in a replication scenario involving multiple servers. The Directory Server Connector is capable of synchronizing changes from Windows directory source to the preferred server (master). In case, the preferred server is down, the changes will failover to the secondary server in the configured secondary servers list in a sequential manner till the preferred server comes up. Directory Server replication will replicate changes made from the preferred server (master) to other preferred secondary servers configured in the topology. Any Directory Server Plug-in can handle password validity checks from Windows directory sources and users can change passwords at any server.
 To Create a New Sun Java System Directory Source
To Create a New Sun Java System Directory Source
-
Click the New Sun Directory Source button to invoke the Define Sun Java System Directory Source wizard.
Figure 8–8 Selecting a Root Suffix
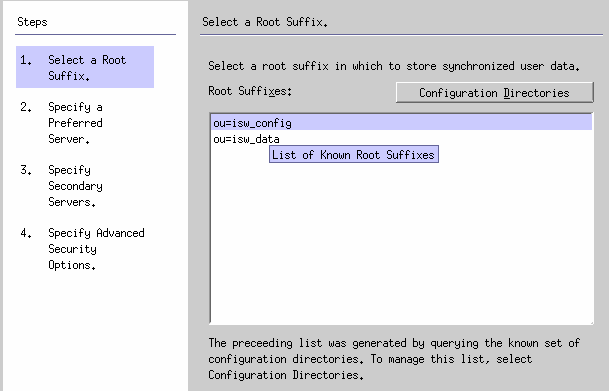
The program queries a known set of configuration directory sources and displays existing root suffix (also referred to as naming contexts ) in the list pane.
By default, the program knows about the configuration directory where you installed the product, and the root suffixes known by the configuration directory will be listed in the list pane.
-
Select the root suffix where your users are located from the list pane. (If several root suffixes are listed, select the one where your users are located.) Click Next.
If the root suffix you want to synchronize with is not affiliated with a configuration directory registered with Identity Synchronization for Windows, then you must specify a new configuration directory, as follows:
-
Click the Configuration Directories button to specify a new configuration directory.
-
When the Configuration Directories dialog box is displayed ( Step 3), click the New button to open the New Configuration Directories dialog box.
Figure 8–9 Selecting a New Configuration Directory
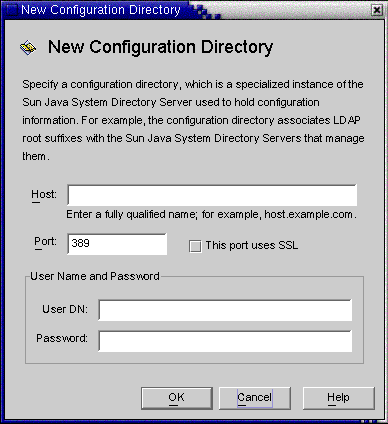
-
Enter the following information, and then click OK to save your changes and close the dialog box.
-
Host: Enter the fully qualified host name.
For example: machine1.example.com
-
Port: Enter a valid, unused LDAP port number. (Default is 389)
Enable the This port uses SSL box if Identity Synchronization for Windows is using an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) port to communicate with the configuration directory.
-
User DN: Enter your Administrator’s (bind) distinguished name. For example, uid=admin,ou=Administrators,ou=TopologyManagement,o=NetscapeRoot
-
Password: Enter your Administrator’s password.
The wizard will query the specified configuration directory to determine all of the directory servers managed by that directory.
Note –Identity Synchronization for Windows only supports one root suffix per Sun Java System Directory Server source.
Editing and Removing Configuration Directories
You can also use the Configuration Directories dialog box to manage your list of configuration directories, as follows:
-
Select a configuration directory from the list pane, and then click the Edit button. When the Edit Configuration Directories dialog is displayed, you can change the Host, Port, Secure Port, User Name, and Password parameters.
-
Select a configuration directory from the list pane, and then click Remove to delete the directory from the list.
-
-
Click OK to close the Configuration Directories dialog box and the newly selected configuration directory’s root suffixes are displayed in the list pane.
By default, Directory Server creates a root suffix whose prefix corresponds to the components of the machine’s DNS domain entry. It uses the following suffix:
dc=your_machine’s_DNS_domain_name
That is, if your machine domain is example.com, then you should configure the suffix dc=example, dc=com for your server. The entry named by the chosen suffix must already exist in the directory.
-
Select the root suffix, and click Next.
The Specify Preferred Servers panel is displayed (see Creating a Sun Java System Directory Source).
Figure 8–10 Specifying a Preferred Server
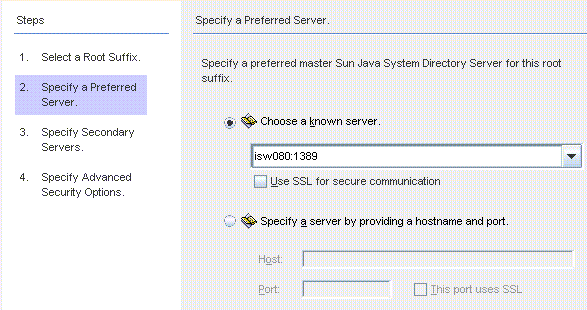
Identity Synchronization for Windows uses the preferred Directory Server to detect changes made at any Directory Server master. The preferred server also acts as the primary location where changes made on Windows systems are applied to the Sun Java System Directory Server system.
If the preferred master server fails, the secondary server can store these changes until the preferred server (master) comes back online.
-
-
Use one of the following methods to select a preferred server:
-
Select the Choose a Known Server option, and then select a server name from the drop-down list.
Note –The Directory Server must be running to appear in the list. If the server is down temporarily, select the Specify a Server by Providing a Hostname and Port option, and then enter the server information manually.
Enable the Use SSL for secure communication box if you want the Directory Server to communicate using SSL. However, if you enable this feature there are some additional setup steps you must perform after installation. For more information, see Enabling SSL in Directory Server
-
Select the Specify a Server By Providing a Hostname and Port option, and then type the server’s Host name and Port into the text fields.
Select the This Port Uses SSL checkbox if the port you specified uses SSL.
-
-
Click Next and the Specify a Secondary Server panel is displayed.
Figure 8–11 Specifying the Secondary Servers for Failover Support
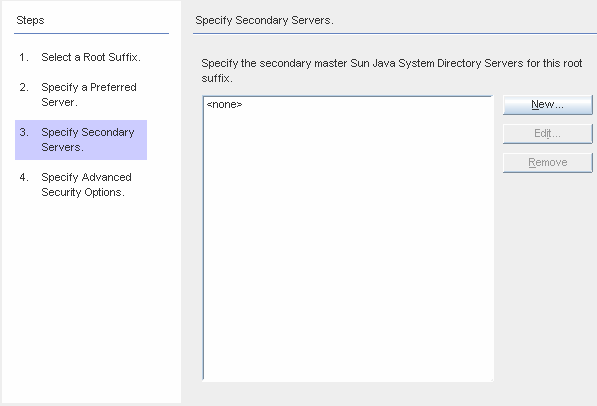
You can add, edit, or delete the Secondary Servers:
-
Click the New button to display the Add Sun Directory Source dialog box. Enter the host name, port, user DN, password, and then click OK. For more information on these fields, see Step c.
-
Click the Edit button to display the Edit Sun Directory Source dialog box. Enter the host name, port, user DN, password, and then click OK. For more information on these fields, see Step c.
-
From the Secondary Servers list, select the server you want to delete and click the Remove button.
-
-
To specify the secondary Directory Servers, select a server name from list, and then click Next.
Note –-
The Directory Server must be running or the server name will not appear in list.
-
Do not use the same host name and port for both the preferred and the secondary servers in a Sun directory source.
-
If you enable the Secure Port feature, there are additional setup steps you must perform after installation. For more information, see Enabling SSL in Directory Server
If you do not want to specify a secondary server, click Next.
-
-
If you want to use secure SSL communication, read the notes below, and then enable one or both of the following options:
Figure 8–12 Specifying Advanced Security Options
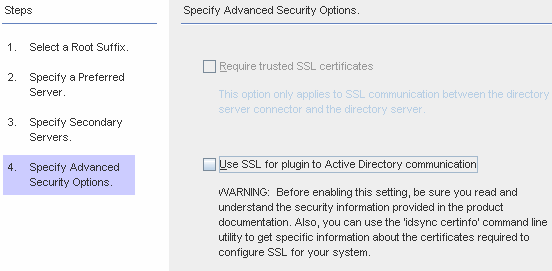
Note –You must install the Directory Server Plug-in on each Directory Server (any master, replica, or hub) where users will bind or where passwords will be changed.
When the Directory Server Plug-in synchronizes passwords and attributes to Active Directory, it must bind to Active Directory to search for users and their passwords. In addition, the Plug-in writes log messages to the central log and into the Directory Server’s log. By default these communications are not accomplished over SSL.
-
To encrypt channel communication only or to encrypt channel communication and use certificates to ensure participants’ identity verification between Directory Server and the Directory Server Connector, enable the Require Certificates for SSL box.
Clear the checkbox if you do not want to trust certificates.
-
To use secure SSL communication between the Directory Server Plug-in and Active Directory, enable the Use SSL for Plug-in to Active Directory communication box.
If you enable these features, then additional setup is required after installation. See Enabling SSL in Directory Server
-
You can use the use the idsync certinfo command line utility to determine which certificates you must add for each Directory Server Plug-in and/or Connector certificate database. See Using certinfo
-
If your primary and secondary Directory Servers are part of a multimaster replication (MMR) deployment, refer to Appendix E, Identity Synchronization for Windows Installation Notes for Replicated Environments
-
-
When you are finished with the Specify Advanced Security Options panel, click Finish.
The program adds the selected directory sources to the navigation tree under Directory Sources, and the Prepare Directory Server Now? dialog is displayed.
You must prepare the Directory Server to be used by Identity Synchronization for Windows. You can choose to perform this task now, or you can do it later — but you must prepare the Directory Server before you install the Connectors. (Instructions for installing Connectors are provided in Chapter 9, Installing Connectors).
-
If you want to prepare the Directory Server now, click Yes to open the wizard, and then proceed to the next section, Preparing Sun Directory Source
-
If you prefer to perform this process later, click No and proceed to Creating an Active Directory Source.
-
Preparing Sun Directory Source
This section explains how to prepare Sun Directory source for use by Identity Synchronization for Windows.
Preparing the Directory Server:
-
Creates the Retro-Changelog database and access control instance available on the preferred host
-
Creates the Connector user and user access control instance available on the preferred host
-
Creates an equality index on the preferred and secondary hosts
Note –
-
As an alternative to using the Console, you can use the idsync prepds command line utility to prepare the Directory Server. For more information, see Using prepds.
-
To prepare the Directory Server using the idsync prepds command line utility, you must know which hosts and suffixes you will be using and you must have Directory Manager’s credentials.
You can use the Prepare Directory Server wizard to prepare the Directory Server.
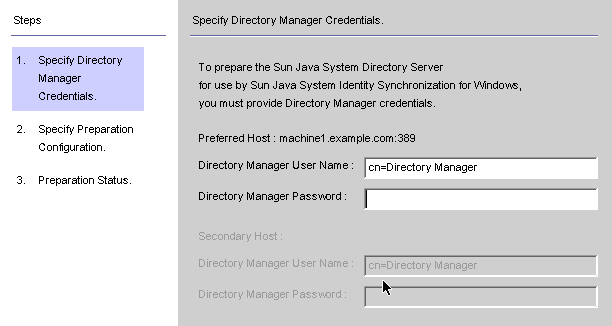
Figure 8–13 Entering Your Directory Manager Credentials
Note –
To access this wizard, use one of the following methods:
-
When the Prepare Directory Server Now? dialog box is displayed, click the Yes button.
-
When the Sun Directory Sources panel is displayed (on the Configuration tab), click the Prepare Directory Server button.
 To Prepare your Directory Server Source
To Prepare your Directory Server Source
-
Enter the following credentials for the Directory Manager account.
-
Directory Manager User Name
-
Directory Manager Password
If you are using a secondary host (MMR configurations), then the Secondary Host options will be active and you must specify credentials for these hosts too.
-
-
When you are done, click Next and the Specify Preparation Configuration panel is displayed.
Figure 8–14 Specifying the Preparation Configuration
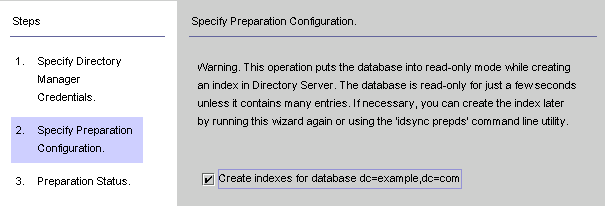
Read the warning, and then decide whether to create the Directory Server indexes now or later.
Note –-
This operation can take some time, depending on the size of your database.
-
While your database is in read-only mode, any attempts to update information in the database will fail.
-
Taking your database off-line enables you to create the indexes much faster.
-
To create the indexes now, enable the Create indexes for database box, and then click Next.
-
To create the indexes later (either manually or by running this wizard again) clear the Create indexes for database box, and then click Next.
-
-
The Preparation Status panel is displayed to provide information about the Directory Server preparation progress.
-
When a SUCCESS message is displayed at the bottom of the message pane, click Finish.
-
If error messages display, you must correct the problem(s) reported before you can continue. Check the error logs (see the Status tab) for more information.
-
-
Return to the Configuration tab in the Console. Select the Sun Directory source node in the navigation tree to view the Sun Directory Source panel.
Figure 8–15 Sun Directory Source Panel
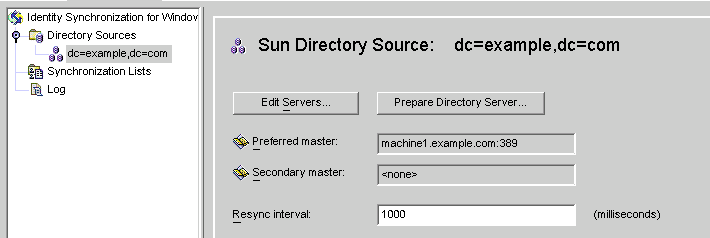
From this panel, you can perform the following tasks:
-
Edit servers: Click this button to reopen the Define Sun Java System Directory Source panel where you can change any of the server configuration parameters. If necessary, review the instructions provided for Creating a Sun Java System Directory Source.
Note –If you recreate the Retro-Changelog database for the preferred Sun directory source, the default access control settings will not allow the Directory Server Connector to read the database contents.
To restore the access control settings for new the Retro-Changelog database, run idsync prepds or click the Prepare Directory Server button after selecting the appropriate Sun directory source in the Console.
-
Prepare Directory Server: Click this button and follow the instructions for Preparing Sun Directory Source to prepare a Directory Server.
If anything changes on the Directory Server after you initially prepare the server (for example, if an index is deleted or you lose the Retro-Changelog database), you can re-prepare the server.
-
Resync interval: Specify how often you want the Directory Server Connector to check for changes. (Default is 1000 milliseconds)
-
-
Add a Directory Server directory source for each user population in your Sun Java System Directory Server enterprise that you want to synchronize.
When you are finished, you must create at least one Windows directory source:
-
To create an Active Directory source, continue to the next section, Creating an Active Directory Source.
-
To create a Windows NT directory source, continue to Creating a Windows NT SAM Directory Source
-
Creating an Active Directory Source
You should add an Active Directory directory source for each Windows domain in your network that you want to synchronize.
Each Active Directory deployment has at least one global catalog that knows about all the global information across all Active Directory domains. To access the global catalog, the rights assigned to a normal user are sufficient unless you change the default permissions.
Note –
It is possible for each Active Directory server to be a global catalog and a deployment can have multiple global catalogs, but you only need to specify one global catalog.
 To Configure and Create Windows Active Directory Servers in a
Network
To Configure and Create Windows Active Directory Servers in a
Network
Perform these steps if there are Windows Active Directory servers in your network:
-
Select the Directory Sources node in the navigation tree, and then click the New Active Directory Source button on the Directory Sources panel.
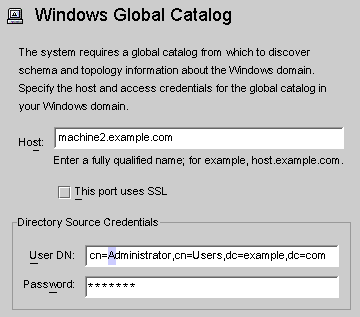
The Windows Global Catalog dialog box is displayed.
Figure 8–16 Windows Global Catalog
-
Enter the following information and then click OK:
-
Host: Enter the fully qualified host name of the machine that holds the global catalog for the Active Directory forest.
For example: machine2.example.com
-
This port uses SSL: Enable this option if Identity Synchronization for Windows is using an SSL port to communicate with the global catalog.
-
User DN: Enter your fully qualified Administrator’s (bind) distinguished name. (Any credentials that enable you to browse the schemas and determine which Active Directory domains are available on your system will suffice.)
-
Password: Enter a password for the specified user.
-
-
The Define Active Directory Source wizard is displayed, as follows.
Figure 8–17 Define an Active Directory Source Wizard
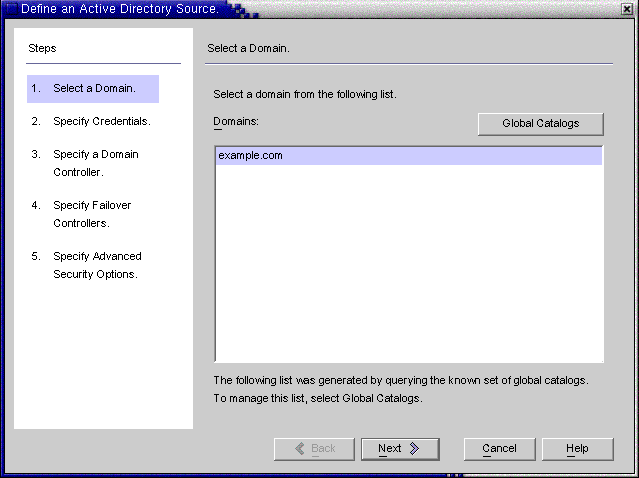
This wizard queries the Active Directory global catalog to determine what other domains exist, and displays those domains in the Domains list pane.
-
Select a name from the list pane to specify an Active Directory domain and click OK.
If the domain you want to use is not displayed in the list, you must add the global catalog that knows about that domain using the following steps:
-
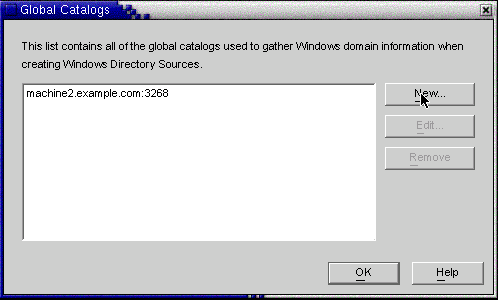
Click the Global Catalogs button and the Global Catalogs wizard is displayed.
Figure 8–18 Specifying a New Global Catalog
-
Click the New button.
-
When the Windows Global Catalog dialog box is displayed, provide the global catalog’s Host name and your Directory Source credentials (as described in Step 2), and then click OK
-
The new global catalog and port, are displayed in the Global Catalogs list panel. Select the catalog name, and then click OK.
-
Repeat these steps if you want to add more global catalogs (domains) to the system.
-
When you are done, click the Next button in the Select a Domain pane.
-
-
When the Specify Credentials panel is displayed, review the value in the User DN field.
Figure 8–19 Specifying Credentials for This Active Directory Source
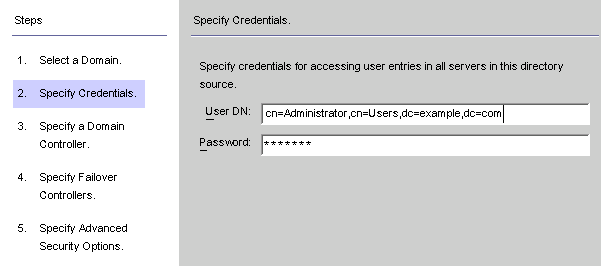
If the program did not automatically enter the Administrator’s distinguished name in the User DN field (or you do not want to use the Administrator’s credentials) enter a User DN and password manually.
When configuring an Active Directory source, you must provide a user name and password that the Active Directory Connector can use to connect to Active Directory.
Note –The Connector requires specific access rights. Minimum rights will depend on the direction of synchronization, as follows:
-
If you are configuring synchronization flow from Active Directory to Directory Server only, then the user provided for the Active Directory Connector does not require many special privileges. A normal user with the extra privilege to “Read All Properties” in the domain being synchronized will suffice.
-
If you are configuring synchronization flow from Directory Server to Active Directory, then the Connector user must have more privileges because, synchronization changes the user entries in Active Directory. In this setup, the Connector user must have either the “Full Control” privilege or be a member of the Administrators group.
-
-
Click Next to open the Specify a Domain Controller panel.
Figure 8–20 Specifying a Domain Controller
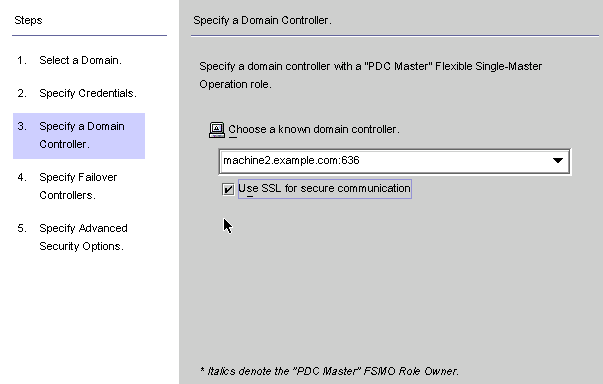
Use this panel to select a controller to synchronize within the specified domain. (The domain controller is similar in concept to a Directory Server’s preferred server.)
If the selected Active Directory domain has multiple domain controllers, select the domain controller with the Primary Domain Controller flexible single master operation (FSMO) role for synchronization.
By default, password changes made at all domain controllers will be replicated immediately to the Primary Domain Controller FSMO role owner, and if you select this domain controller, Identity Synchronization for Windows will synchronize these password changes immediately to the Directory Server.
In some deployments, the AvoidPdcOnWan attribute may be set in the Windows registry because there is a significant network “distance” to the PDC, which will delay synchronization significantly. (See Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 232690 for more information.)
-
Select a domain controller from the drop-down list.
-
If you want the Identity Synchronization for Windows Connector to communicate with the domain controller over a secure port, enable the Use a Secure Port box.
Note –The program automatically installs the CA certificate in the Active Directory Connector if you are using Microsoft certificate server. If you are not, then you must manually add the CA certificate in the Active Directory Connector (see Enabling SSL in the Active Directory Connector change your flow settings after initial configuration these procedures apply as well.
-
When you are done, click Next.
The Specify Failover Controllers panel is displayed (see Creating an Active Directory Source ). You can use this panel to specify any number of failover domain controllers.
Figure 8–21 Specifying Failover Controllers
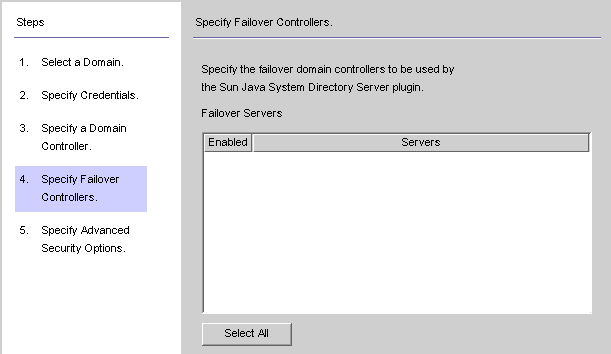
The Active Directory Connector communicates with only one Active Directory domain controller, and Identity Synchronization for Windows does not support failover changes applied by that Connector. However, the Directory Server Plug-in will communicate with any number of domain controllers when validating password changes to Directory Server.
If Directory Server tries connecting to an Active Directory domain controller and that domain controller is not available, Directory Server will iteratively try connecting to the failover domain controller(s) specified.
-
Select one or more of the server names listed in the Failover Servers list pane (or click the Select All button to specify all of the servers in the list), and then click Next.
-
The Specify Advanced Security Options panel is displayed.
The Require trusted SSL certificates option is active (available for selection) only if you enabled the Use SSL for Secure Communication box on the Specify a Domain Controller panel.
Figure 8–22 Specifying Advanced Security Options
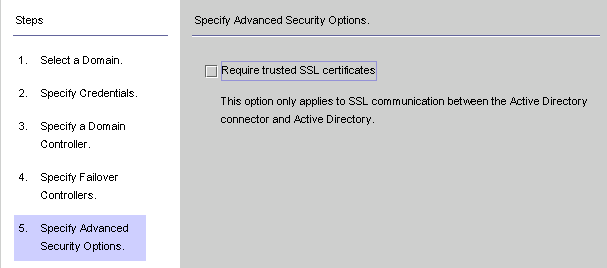
-
If the Require trusted SSL certificate box is disabled (Default setting ), the Active Directory Connector will connect to Active Directory over SSL and does not verify that it trusts the certificates passed by Active Directory.
Disabling this option simplifies the set-up process because you do not have to put an Active Directory Certificate in the Active Directory certificate database.
-
If you enable the Require trusted SSL certificate box, the Active Directory Connector will connect to Active Directory over SSL and it must verify that it trusts the certificates passed by Active Directory.
Note –You must add Active Directory Certificates to the Active Directory Connector’s certificate database. For instructions, see Adding Active Directory Certificates to the Connector’s Certificate Database.
-
-
When you are finished with the Advanced Security Options panel, click the Finish button.
The program adds the newly specified Active Directory source to the navigation tree under Directory Sources.
-
Select the Active Directory source node to view the Active Directory Source panel.
Figure 8–23 Active Directory Source Panel
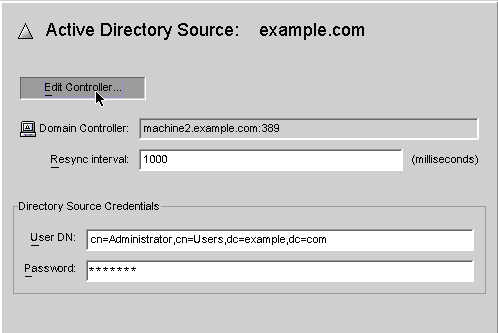
From this panel, you can perform the following tasks:
-
Edit Controllers: Click this button to reopen the Specify a Domain Controller panel where you can change any of the domain controller configuration parameters. If necessary, review the instructions provided for Creating an Active Directory Source.
-
Resync Interval: Specify how often you want the Active Directory Connector to check for changes. (Default is 1000 milliseconds)
-
Directory Source Credentials: Change the specified User DN and/or password.
-
Creating a Windows NT SAM Directory Source
This section explains how to create a Windows NT SAM Directory Source where you can deploy Identity Synchronization for Windows.
 To Deploy Identity Synchronization for Windows on Windows NT
To Deploy Identity Synchronization for Windows on Windows NT
-
Select the Directory Sources node in the navigation tree, and then click the New Windows NT SAM Directory Source button.
Figure 8–24 Directory Sources Panel

-
When the Define a Windows NT SAM Directory Source panel is displayed, follow the instructions for locating the Windows NT domain name, and enter the unique NT directory source domain name in the Domain field. When you are done, click Next.
Figure 8–25 Specifying a Windows NT SAM Domain Name
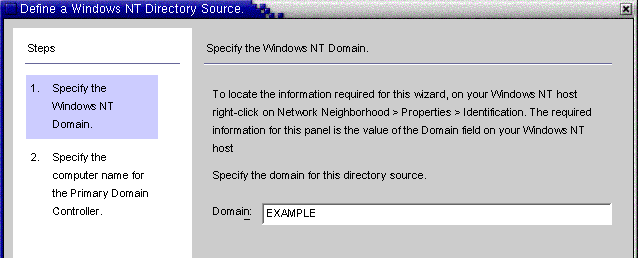
-
When the Specify the Computer Name for the Primary Domain Controller panel is displayed, follow the instructions for locating the Primary Domain Controller computer name, and enter the information in the Computer Name field.
Figure 8–26 Specifying a Name for the Primary Domain Controller

-
Click Finish.
The program adds the newly specified Windows NT SAM directory source to the navigation tree under Directory Sources. Select the new directory source node to view the Windows NT SAM Source panel.
Figure 8–27 Windows NT SAM Directory Source Panel
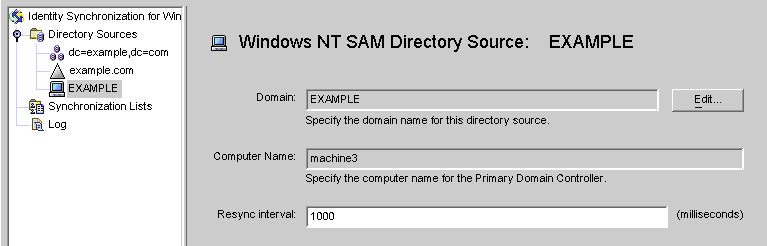
From this panel, you can perform the following tasks:
-
Edit: Click this button to reopen the Specify a Domain Controller panel where you can change any of the domain controller configuration parameters. If necessary, review the instructions provided for Creating an Active Directory Source.
-
Resync interval: Specify how often you want Identity Synchronization for Windows to check for changes made on Windows NT. (Default is 1000 milliseconds)
-
-
Add a Windows NT directory source for each Windows NT machine in your network.
When you are finished creating Windows NT SAM directory sources, you are ready to create and map attributes to be synchronized, continue to Selecting and Mapping User Attributes
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
