Chapter 3 Installing Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.0
This chapter guides you in installing Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.0 software.
-
Software Installation provides step by step instructions on how to install Directory Server Enterprise Edition software.
-
Server Instance Creation provides step by step instructions on how to create server instances after you install the software.
-
Working With Sun Cryptographic Framework on Solaris 10 Systems provides instructions for deployments that use SSL hardware acceleration.
At the end of this chapter, you will have verified that the software that you installed works as expected. You can then continue to configure the software as described in the Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide.
Software Installation
This section covers basic installation. After you install server software, see Server Instance Creation for instructions on creating server instances.
 To Install Directory Service Control Center From Native Packages
To Install Directory Service Control Center From Native Packages
This procedure covers installation of Directory Service Control Center, also known as DSCC, and remote administration command-line tools.
You must be root to perform this procedure.
When you install DSCC, you automatically also install Directory Server from native packages. DSCC uses its own local instance of Directory Server to store information about your directory service configuration. The instance is referred to as the DSCC Registry.
You can use the Directory Server software that is installed alongside DSCC to create your own additional Directory Server instances on the system.
Before You Begin
Obtain the Java Enterprise System distribution for this installation, as shown in the following figure.
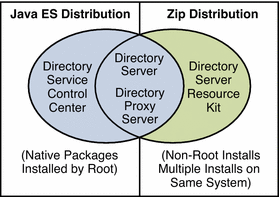
Complete the worksheet that follows for your installation.
|
Requisite Information |
Hints |
Your Answers |
|---|---|---|
|
Hostname of the system where you install DSCC |
| |
|
root password for the system |
| |
|
Java Web Console URL |
Default: https://localhost:6789 | |
|
Directory Service Manager password |
|
-
Install prerequisite patches or service packs for your platform.
-
With the Java Enterprise System distribution, run the Java ES installer as root.
# ./installer
-
Select the Directory Service Control Center component for installation.
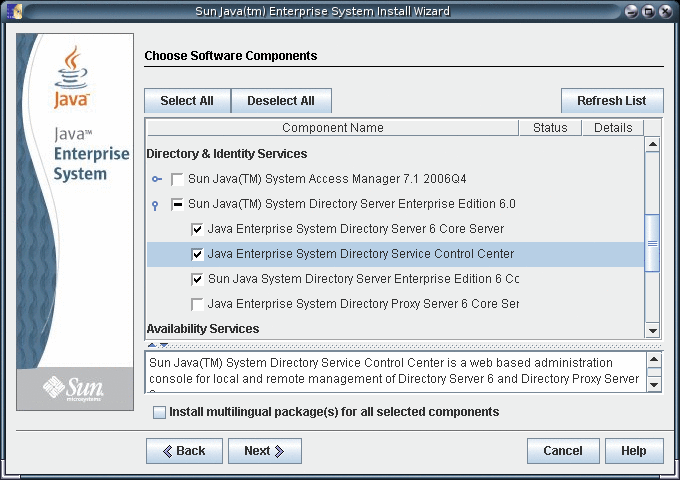
-
Choose to configure the software later, as you will register the software and create server instances after installation.
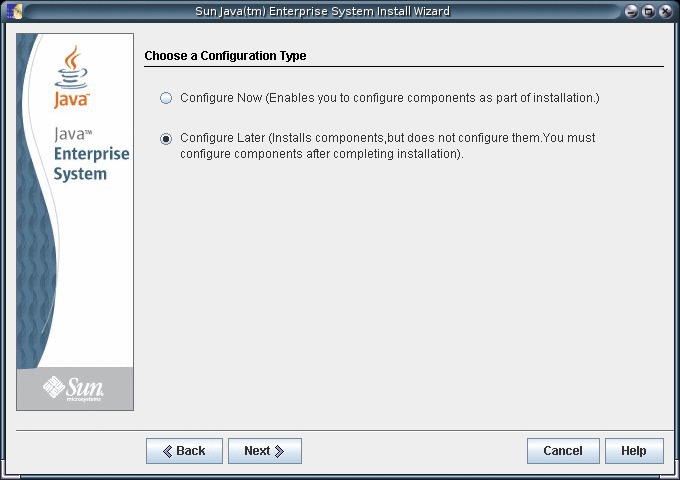
-
Complete installation with the Java ES installer.
After you complete installation, the native packages are installed on the system.
-
Initialize DSCC with the dsccsetup initialize command.
For example, on a Solaris system the following command performs initialization.
root# /opt/SUNWdsee/dscc6/bin/dsccsetup initialize *** Registering DSCC Application in Sun Java(TM) Web Console This operation is going to stop Sun Java(TM) Web Console. Do you want to continue ? [y,n] y Stopping Sun Java(TM) Web Console... Registration is on-going. Please wait... DSCC is registered in Sun Java(TM) Web Console Restarting Sun Java(TM) Web Console Please wait : this may take several seconds... Sun Java(TM) Web Console restarted successfully *** Registering DSCC Agent in Cacao... Checking Cacao status... Starting Cacao... DSCC agent has been successfully registered in Cacao. *** Choose password for Directory Service Manager: Confirm password for Directory Service Manager: Creating DSCC registry... DSCC Registry has been created successfully ***
The dsccsetup command is located in install-path/dscc6/bin/dsccsetup. See Default Paths to determine the default install-path for your system.
-
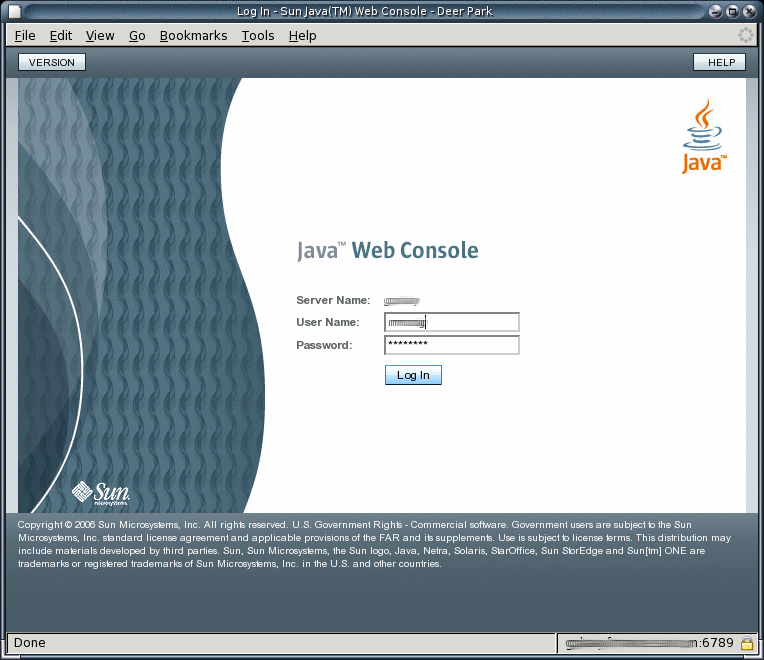
Access DSCC through Java Web Console in your browser.
-
Login to Java Web Console using your operating system login information or server's root login information.
If you do not login to Java Web Console using server's root login information, the system might required you to have the root privileges while performing certain tasks such as starting the server instances.
By default, the URL to access Java Web Console is of the following form.
https://hostname:6789
-
Click the Directory Service Control Center link.
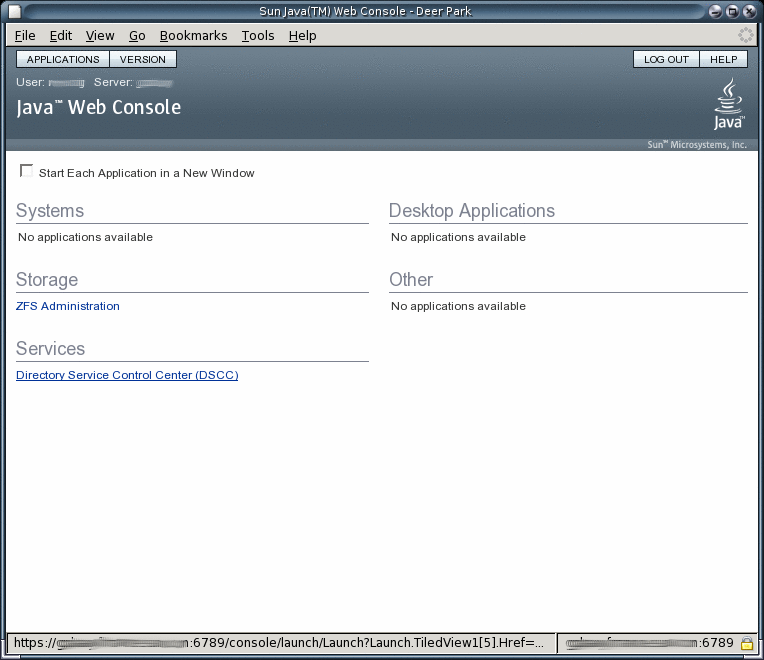
-
Login as Directory Service Manager.
Directory Service Manager's entry is stored in the Directory Service Control Center registry. Directory Service Manager has administrator access to Directory Service Control Center. Directory Service Manager also has administrator access to the server instances registered with Directory Service Control Center.
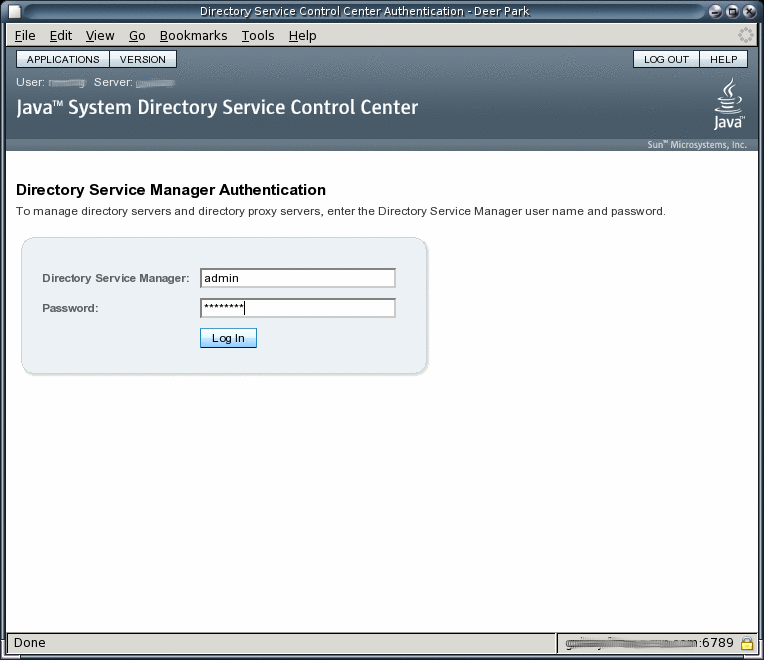
-
Begin managing your servers through Directory Service Control Center.
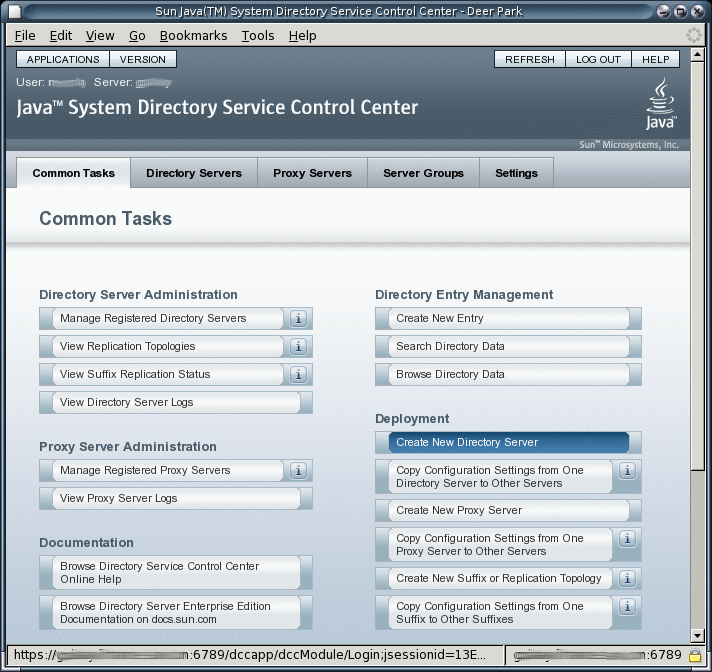
-
-
After Directory Service Control Center is working, enable Java Web Console to restart when the system reboots.
On a Solaris system, the following command enables restart upon reboot.
root# /usr/sbin/smcwebserver enable
For the exact location of this command on your system, see Command Locations.
-
(Optional) Enable the Common Agent Container, cacao, to restart when the operating system reboots.
root# cacaoadm enable
If you decide not to enable the common agent container, you would not be able to use DSCC to communicate with the servers handled by that instance of cacao.
Next Steps
After installing the software, see Environment Variables.
 To Troubleshoot Directory Service Control Center Access
To Troubleshoot Directory Service Control Center Access
Use this procedure on the host where you installed Directory Service Control Center.
You must be root to perform this procedure.
-
Verify that Directory Service Control Center has been initialized properly.
root# /opt/SUNWdsee/dscc6/bin/dsccsetup status *** DSCC Application is registered in Sun Java (TM) Web Console *** DSCC Agent is registered in Cacao *** DSCC Registry has been created Path of DSCC registry is /var/opt/SUNWdsee/dscc6/dcc/ads Port of DSCC registry is 3998 ***
The default installation path for native packages on Solaris operating systems is /opt/SUNWdsee. For the default installation path on your operating system, see Default Paths.
Fix Directory Service Control Center initialization problems with the dsccsetup(1M) command.
-
Start Java Web Console if necessary with the smcwebserver command.
root# /usr/sbin/smcwebserver status Sun Java(TM) Web Console is stopped root# /usr/sbin/smcwebserver start Starting Sun Java(TM) Web Console Version 3.0.2 ... The console is running.
-
Check the Common Agent Container if you see errors that pertain to the DSCC Agent.
The cacaoadm(1M) man page describes the error codes that the command returns. For the exact location of this command on your system, see Command Locations.
If you installed Directory Server from the zip distribution, you must run the cacaoadm command as the user who performed the installation. Otherwise, run the command as root.
After installing Directory Server, the Common Agent Container is started automatically. However, when you reboot, you might have to start the Common Agent Container manually.
root# /usr/sbin/cacaoadm status default instance is DISABLED at system startup. Smf monitoring process: 26129 Uptime: 0 day(s), 3:16
For more information about the Common Agent Container, see Sun Java Enterprise System 5 Monitoring Guide.
Note –In Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1, you can also install Directory Service Control Center with the Zip distribution by deploying the WAR file provided with the software packages. For more information, see Installing Directory Service Control Center Using the Zip Distribution.
 To Install Only Directory Server From
Native Packages
To Install Only Directory Server From
Native Packages
This procedure covers installation of Directory Server from native packages. You must be root to perform this procedure.
Note –
If you installed Directory Service Control Center, you automatically also installed Directory Server from native packages. You can use the Directory Server software that is installed alongside DSCC to create your own additional Directory Server instances on the system.
Before You Begin
Obtain the Java Enterprise System distribution for this installation, as shown in the following figure.

Complete the worksheet that follows for your installation.
|
Requisite Information |
Hints |
Your Answers |
|---|---|---|
|
Fully qualified hostname of the system where you install Directory Server |
Example: ds.example.com | |
|
(Optional) Cacao common agent container port number to access from Directory Service Control Center |
Default: 11162 | |
|
File system paths where you create Directory Server instances |
Example: /local/ds/ Create instances only on local file systems, never on network–mounted file systems such as NFS. Each path is henceforth referred to as an instance-path. | |
|
LDAP port number |
Default: 389 when installing as root; 1389 for non-root | |
|
LDAP/SSL port number |
Default: 636 when installing as root; 1636 for non-root | |
|
Directory Manager DN |
Default: cn=Directory Manager | |
|
Directory Manager password |
Must be at least 8 characters long | |
|
Base suffix DN |
Example: dc=example,dc=com | |
|
(UNIX systems) Server user (uid) |
Example: noaccess | |
|
(UNIX systems) Server group (gid) |
Example: noaccess |
-
Install prerequisite patches or service packs for your platform.
-
Using the Java Enterprise System distribution, run the Java ES installer as root.
root# ./installer
-
Select the Directory Server component for installation.
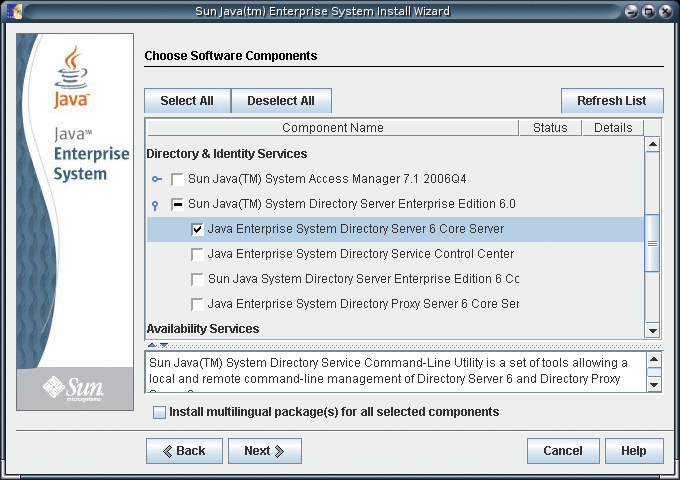
-
Choose to configure the software later, as you will register the software and create server instances after installation.

-
Complete installation with the Java ES installer.
At this point, you can now create server instances on the system. See Server Instance Creation for details.
-
(Optional) Enable the Common Agent Container, cacao, to restart when the operating system reboots.
root# cacaoadm enable
If you decide not to enable the common agent container, you would not be able to use DSCC to communicate with the servers handled by that instance of cacao.
Next Steps
After installing the software, see Environment Variables.
 To Install Only Directory Proxy Server From
Native Packages
To Install Only Directory Proxy Server From
Native Packages
This procedure covers installation of Directory Proxy Server from native packages. You must be root to perform this procedure.
Before You Begin
Obtain the Java Enterprise System distribution for this installation, as shown in the following figure.

Complete the worksheet that follows for your installation.
|
Requisite Information |
Hints |
Your Answers |
|---|---|---|
|
Fully qualified hostname of the system where you install Directory Proxy Server |
Example: dps.example.com | |
|
(Optional) Cacao common agent container port number to access from Directory Service Control Center |
Default: 11162 | |
|
File system paths where you create Directory Proxy Server instances |
Example: /local/dps/ Create instances only on local file systems, never on network–mounted file systems such as NFS. Each path is henceforth referred to as an instance-path. | |
|
LDAP port number |
Default: 389 when installing as root; 1389 for non-root | |
|
LDAP/SSL port number |
Default: 636 when installing as root; 1636 for root | |
|
Directory Proxy Manager DN |
Default: cn=Proxy Manager | |
|
Directory Proxy Manager password |
Must be at least 8 characters long | |
|
(UNIX platforms) Server user (uid) |
Example: noaccess | |
|
(UNIX platforms) Server group (gid) |
Example: noaccess | |
|
(Optional) Connection information for each server to access through the proxy |
Example: ds1.example.com:1389, ds2.example.com:1636 |
-
Install prerequisite patches or service packs for your platform.
-
Using the Java Enterprise System distribution, run the Java ES installer as root.
root# ./installer
-
Select the Directory Proxy Server component for installation.
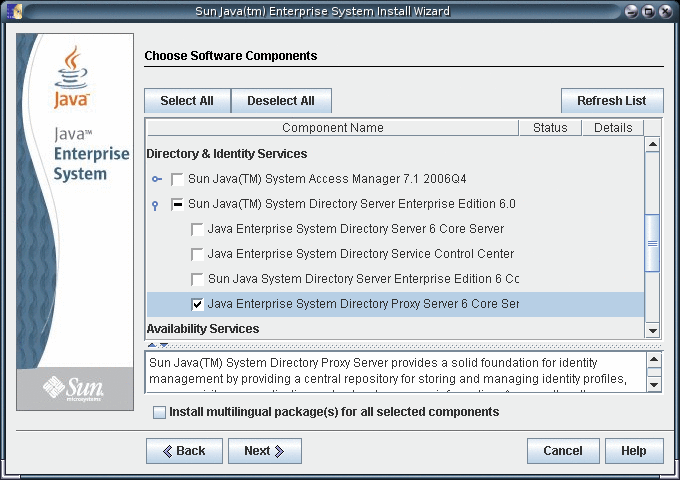
-
Choose to configure the software later, as you will register the software and create server instances after installation.

-
Complete installation with the Java ES installer.
At this point, you can now create server instances on the system. See Server Instance Creation for details.
-
(Optional) Enable the Common Agent Container, cacao, to restart when the operating system reboots.
root# cacaoadm enable
If you decide not to enable the common agent container, you would not be able to use DSCC to communicate with the servers handled by that instance of cacao.
Next Steps
After installing the software, see Environment Variables.
Environment Variables
This section lists environment variables that you can set to facilitate creating server instances and using Directory Server Resource Kit and software development kits.
|
Environment Variable |
Set to include… |
Applies to… |
|---|---|---|
|
Hostname of Directory Proxy Server for administration tools |
dpconf(1M) command |
|
|
Port number of Directory Proxy Server for administration tools |
dpconf(1M) command |
|
|
Hostname of Directory Server for administration tools |
dsconf(1M) command |
|
|
Port number of Directory Server or for administration tools |
dsconf(1M) command |
|
|
Path to the file that contains the directory administrator password To administer all servers registered with Directory Service Control Center, set this environment variable to a file containing Directory Service Manager password. |
dpconf(1M), dsconf(1M) commands |
|
|
Directory administrator DN To administer all servers registered with Directory Service Control Center, set this environment variable to cn=admin,cn=Administrators,cn=dscc. If you have not installed DSCC, use cn=admin,cn=Administrators,cn=config for Directory Server, cn=Proxy Manager for Directory Proxy Server. |
dpconf(1M), dsconf(1M) commands |
|
|
install-path/dsee6/man |
Online manual pages to browse with the man command |
|
|
Add any of the following sections not in your MANSECT environment variable. 1:1m:4:5dsconf:5dpconf:5dssd:5dsat:5dsoc Alternatively, specify the sections to search explicitly when using the man command. |
The man command can use the MANSECT environment variable to identify the sections to search by default. |
|
|
install-path/dps6/bin |
Directory Proxy Server commands |
|
|
install-path/ds6/bin |
Directory Server commands |
|
|
install-path/dscc6/bin |
Directory Service Control Center commands |
|
|
install-path/dsrk6/bin |
Directory Server Resource Kit and LDAP client commands |
Server Instance Creation
After installing server software as described in Software Installation, create server instances according to the procedures in this section.
 To Create a Directory Server Instance
With DSCC
To Create a Directory Server Instance
With DSCC
Non-root users can create server instances.
Before You Begin
Install the component software as described in Software Installation.
-
Access Directory Service Control Center through Java Web Console.
The default URL for Java Web Console on the local system is https://localhost:6789.
-
Follow the instructions in the Directory Service Control Center New Server wizard to create the server instance.
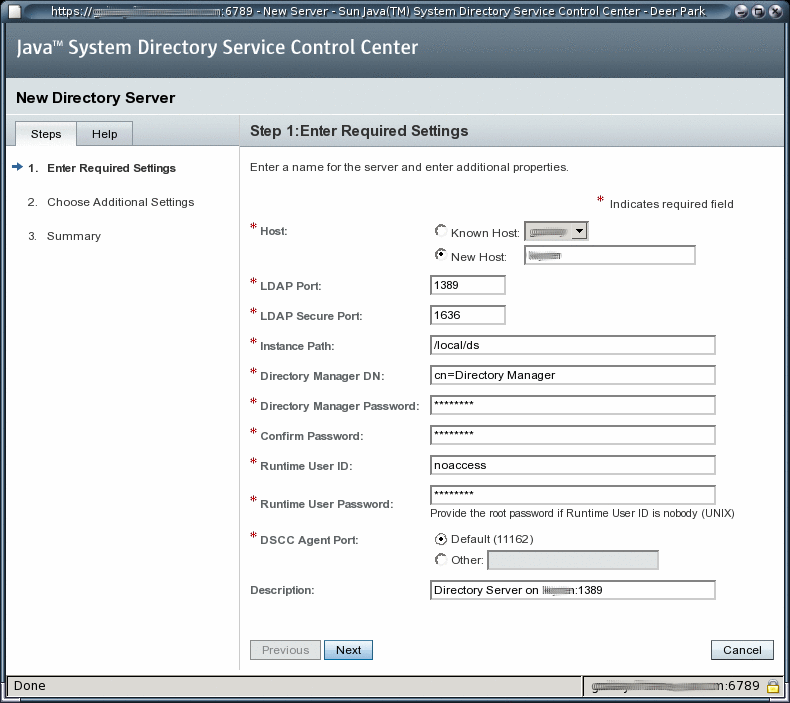
 To Create a Directory Server Instance
From the Command Line
To Create a Directory Server Instance
From the Command Line
In this procedure, you create a server instance on the local host using the dsadm command. You then create a suffix that you populate with data using the dsconf command.
Non-root users can create server instances.
A Directory Server instance contains the configuration and data necessary to respond to directory client applications. When you start or stop an instance, you start or stop the server process. The server process is what serves directory client requests corresponding to the data managed by that instance.
The dsadm command enables you to manage a Directory Server instance and the files belonging to that instance on the local host. The command does not let you administer servers over the network, but only directly on the local host. The dsadm command has subcommands for each key management task. For a complete description, see dsadm(1M).
The dsconf command is an LDAP client. The command enables you to configure nearly all server settings on a running Directory Server instance from the command line. You can configure settings whether the server is on the local host or another host that is accessible across the network. The dsconf command has subcommands for each key configuration task. For a complete description, see dsconf(1M).
Before You Begin
Install the component software, then set your PATH as described in Software Installation.
-
Create a new Directory Server instance.
$ dsadm create -p port -P SSL-port instance-path
For example, the following command creates an instance under the existing directory, /local/, in a new directory, /local/ds/. The new instance has default ports 389 for LDAP, 636 for LDAPS for root, and 1389 for LDAP, 1636 for LDAPS for non-root users.
$ dsadm create /local/ds Choose the Directory Manager password: Confirm the Directory Manager password: Use 'dsadm start /local/ds' to start the instance
Notice that the instance is created in a directory on the local file system, not a network file system.
-
Start the instance.
$ dsadm start instance-path
For example, the following command starts the instance located under /local/ds/.
$ dsadm start /local/ds Server started: pid=2845
-
Verify that you can read the root DSE of the new instance.
$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1389 -b "" -s base "(objectclass=*)" version: 1 dn: objectClass: top … supportedLDAPVersion: 3 vendorName: Sun Microsystems, Inc. vendorVersion: Sun-Java(tm)-System-Directory/6.0 …
Note –At this point in the procedure, you have a working server instance. You must further configure the server instance, however. Furthermore, the instance is not yet registered with Directory Service Control Center.
-
(Optional) Use the new password policy mode, unless the instance belongs to a topology with version 5 instances.
Your server instance might be standalone. Alternatively, your instance might belong to a replication topology that has already been migrated to the new password policy mode. In either case, perform this step.
$ dsconf pwd-compat -h localhost -p 1389 to-DS6-migration-mode Certificate "CN=hostname, CN=1636, CN=Directory Server, O=Sun Microsystems" presented by the server is not trusted. Type "Y" to accept, "y" to accept just once, "n" to refuse, "d" for more details: Y Enter "cn=Directory Manager" password: ## Beginning password policy compatibility changes. ## Password policy compatibility changes finished. Task completed (slapd exit code: 0). $ dsconf pwd-compat -p 1389 to-DS6-mode Enter "cn=Directory Manager" password: ## Beginning password policy compatibility changes. ## Password policy compatibility changes finished. Task completed (slapd exit code: 0).
-
(Optional) Prepare an example suffix.
-
Create an empty suffix.
For example, the following command creates a suffix with root dc=example,dc=com.
$ dsconf create-suffix -h localhost -p 1389 dc=example,dc=com Enter "cn=Directory Manager" password: $
-
Populate the suffix with LDIF data.
If you plan to populate the suffix with data that is replicated from another Directory Server instance, skip this step.
For example, the following command fills the suffix that you created with sample data from Example.ldif.
$ dsconf import -h localhost -p 1389 install-path/ds6/ldif/Example.ldif dc=example,dc=com Enter "cn=Directory Manager" password: New data will override existing data of the suffix "dc=example,dc=com". Initialization will have to be performed on replicated suffixes. Do you want to continue [y/n] ? y ## Index buffering enabled with bucket size 40 ## Beginning import job... ## Processing file "install-path/ds6/ldif/Example.ldif" ## Finished scanning file "install-path/ds6/ldif/Example.ldif" (160 entries) ## Workers finished; cleaning up... ## Workers cleaned up. ## Cleaning up producer thread... ## Indexing complete. ## Starting numsubordinates attribute generation. This may take a while, please wait for further activity reports. ## Numsubordinates attribute generation complete. Flushing caches... ## Closing files... ## Import complete. Processed 160 entries in 4 seconds. (40.00 entries/sec) Task completed (slapd exit code: 0).
-
Verify that you can find an entry in the new instance.
$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1389 -b dc=example,dc=com "(uid=bjensen)" version: 1 dn: uid=bjensen, ou=People, dc=example,dc=com cn: Barbara Jensen cn: Babs Jensen sn: Jensen givenName: Barbara objectClass: top objectClass: person objectClass: organizationalPerson objectClass: inetOrgPerson ou: Product Development ou: People l: Cupertino uid: bjensen mail: bjensen@example.com telephoneNumber: +1 408 555 1862 facsimileTelephoneNumber: +1 408 555 1992 roomNumber: 0209
-
-
(Optional) Register the server instance with Directory Service Control Center by using either of the following methods.
-
Login to DSCC, and then use the Register Existing Server action on the Servers tab of the Directory Servers tab.
Access DSCC through the URL https://localhost:6789.
-
Use the command dsccreg add-server.
$ dsccreg add-server -h dscchost --description "My DS" /local/ds Enter DSCC administrator's password: /local/ds is an instance of DS Enter password of "cn=Directory Manager" for /local/ds: This operation will restart /local/ds. Do you want to continue ? (y/n) y Connecting to /local/ds Enabling DSCC access to /local/ds Restarting /local/ds Registering /local/ds in DSCC on dscchost.
See dsccreg(1M) for more information about the command.
-
-
(Optional) If you installed from native packages with the Java Enterprise System distribution, enable the server to restart when the operating system reboots.
On Solaris 10 and Windows systems, use the dsadm enable-service command.
root# dsadm enable-service /local/ds
On Solaris 9, HP-UX, and Red Hat systems, use the dsadm autostart command.
root# dsadm autostart /local/ds
If you installed with the zip distribution, this step must be done manually, with a script run at system startup time, for example.
Next Steps
At this point, you can add more suffixes, configure replication with other server instances, tune the instance, and generally proceed with other configuration operations.
See the online help inside Directory Service Control Center for hints on configuring Directory Server through the graphical user interface.
See Part I, Directory Server Administration, in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide for instructions on configuring Directory Server with command-line administration tools.
 To Create a Directory Proxy Server Instance
With DSCC
To Create a Directory Proxy Server Instance
With DSCC
Non-root users can create server instances.
Before You Begin
Install the component software as described in Software Installation.
-
Access Directory Service Control Center through Java Web Console.
The default URL for Java Web Console on the local system is https://localhost:6789.
-
Follow the instructions in the Directory Service Control Center New Server wizard to create the server instance.
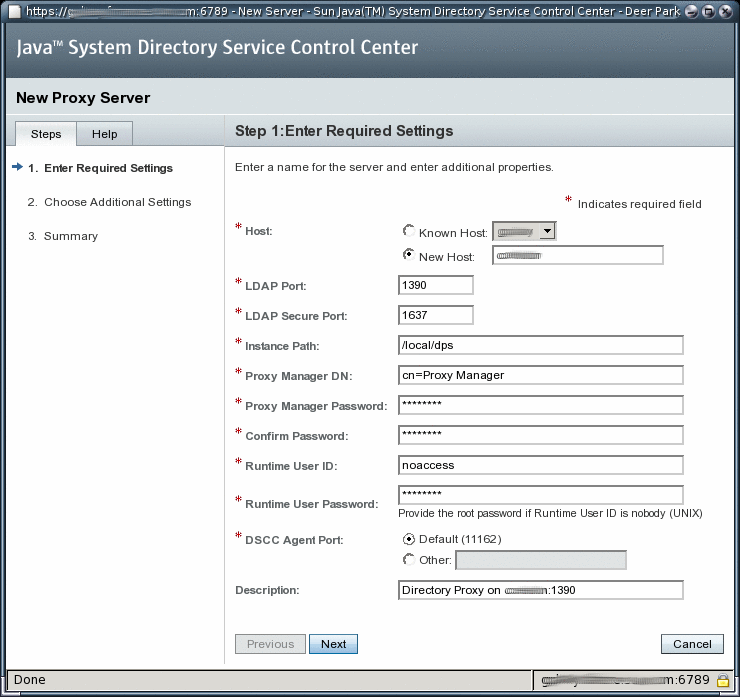
 To Create a Directory Proxy Server Instance
From the Command Line
To Create a Directory Proxy Server Instance
From the Command Line
In this procedure, you create a server instance on the local host using the dpadm command. You then configure the instance using the dpconf command.
Non-root users can create server instances.
A Directory Proxy Server instance must be configured to proxy directory client application requests to data sources through data views. When you start or stop an instance, you start or stop the server process that proxies directory client application requests.
The dpadm command enables you to manage a Directory Proxy Server instance and the files belonging to that instance on the local host. The command does not allow you to administer servers over the network, but only directly on the local host. The dpadm command has subcommands for each key management task. For a complete description, see dpadm(1M).
The dpconf command is an LDAP client. The command enables you to configure nearly all server settings on a running Directory Proxy Server instance from the command line. You can configure settings whether the server is on the local host or another host that is accessible across the network. The dpconf command has subcommands for each key configuration task. For a complete description, see dpconf(1M).
Before You Begin
Install the component software, then set your PATH as described in Software Installation.
-
Create a new Directory Proxy Server instance.
$ dpadm create -p port -P SSL-port instance-path
For example, the following command creates an instance under the existing directory, /local/, in a new directory, /local/dps/. The default ports are 389 for LDAP, 636 for LDAPS for root, and 1389 for LDAP, 1636 for LDAPS for non-root users.
$ dpadm create -p 1390 -P 1637 /local/dps Choose the Proxy Manager password: Confirm the Proxy Manager password: Use 'dpadm start /local/dps' to start the instance
Notice that the instance must be created in a directory on the local file system, not a network file system.
-
Start the instance.
$ dpadm start instance-path
For example, the following command starts the instance located under /local/dps/.
$ dpadm start /local/dps … Directory Proxy Server instance '/local/dps' started: pid=28732
-
Verify that you can read the root DSE of the new instance.
$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1390 -b "" -s base "(objectclass=*)" version: 1 dn: objectClass: top objectClass: extensibleObject supportedLDAPVersion: 2 supportedLDAPVersion: 3 … vendorName: Sun Microsystems, Inc vendorVersion: Directory Proxy Server 6.0 …
Note –At this point in the procedure, you have a working server instance. You must further configure the server instance, however. Furthermore, the instance is not yet registered with Directory Service Control Center.
-
(Optional) Enable the Directory Proxy Server instance to function as an LDAP proxy.
-
Create an LDAP data source.
For example, the following command creates a data source, My DS, pointing to the directory instance created on the local host in To Create a Directory Server Instance From the Command Line.
$ dpconf create-ldap-data-source -h localhost -p 1390 "My DS" localhost:1389 Certificate "CN=hostname:1390" presented by the server is not trusted. Type "Y" to accept, "y" to accept just once, "n" to refuse, "d" for more details: Y Enter "cn=Proxy Manager" password:
-
Create an LDAP data source pool.
$ dpconf create-ldap-data-source-pool -h localhost -p 1390 "My Pool" Enter "cn=Proxy Manager" password:
-
Attach the LDAP data source to the LDAP data source pool.
$ dpconf attach-ldap-data-source -h localhost -p 1390 "My Pool" "My DS" Enter "cn=Proxy Manager" password:
-
Create an LDAP data view into the LDAP data source pool.
For example, the following command creates a data view, My View, which allows client applications to view the suffix dc=example,dc=com:
$ dpconf create-ldap-data-view -h localhost -p 1390 "My View" \ "My Pool" dc=example,dc=com Enter "cn=Proxy Manager" password:
-
Enable the LDAP data source, then restart the server for the change to take effect.
$ dpconf set-ldap-data-source-prop -h localhost -p 1390 "My DS" is-enabled:true Enter "cn=Proxy Manager" password: $ dpadm restart /local/dps Directory Proxy Server instance '/local/dps' stopped [31/Aug/2006:11:32:26 +0200] - STARTUP - INFO - Sun Java(TM) System Directory Proxy Server/6.0 (Build 0824060144) starting up Directory Proxy Server instance '/local/dps' started: pid=28901
-
Enable searches on the LDAP data source.
$ dpconf set-attached-ldap-data-source-prop -h localhost -p 1390 \ "My Pool" "My DS" search-weight:100 Enter "cn=Proxy Manager" password:
-
Verify that you can read directory data through the new instance.
$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1390 -b dc=example,dc=com "(uid=bjensen)" version: 1 dn: uid=bjensen, ou=People, dc=example,dc=com cn: Barbara Jensen cn: Babs Jensen sn: Jensen givenName: Barbara objectClass: top objectClass: person objectClass: organizationalPerson objectClass: inetOrgPerson ou: Product Development ou: People l: Cupertino uid: bjensen mail: bjensen@example.com telephoneNumber: +1 408 555 1862 facsimileTelephoneNumber: +1 408 555 1992 roomNumber: 0209
Note –Notice that LDAP search operations work for the suffix handled by your data view, but do not work for other suffixes. If you search a suffix for which no data view is configured, the server returns an error.
$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1390 -b o=example.com "(uid=bjensen)" ldap_search: Operations error ldap_search: additional info: Unable to retrieve a backend SEARCH connection to process the search request
For instructions detailed instructions on configuring Directory Proxy Server, see Part II, Directory Proxy Server Administration, in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide.
-
-
(Optional) Register the server instance with Directory Service Control Center by using either of the following methods.
-
Login to DSCC, and then use the Register Existing Server action on the Proxy Servers tab.
Access DSCC through the URL https://localhost:6789.
-
Use the command dsccreg add-server.
$ dsccreg add-server -h dscchost --description "My Proxy" /local/dps Enter DSCC administrator's password: /local/dps is an instance of DPS Enter password of "cn=Proxy Manager" for /local/dps: Connecting to /local/dps Enabling DSCC access to /local/dps Registering /local/dps in DSCC on dscchost.
See dsccreg(1M) for more information about the command.
-
-
(Optional) If you installed from native packages with the Java Enterprise System distribution, enable the server to restart when the operating system reboots.
On Solaris 10 and Windows systems, use the dpadm enable-service command.
root# dpadm enable-service /local/dps
On Solaris 9, HP-UX, and Red Hat systems, use the dpadm autostart command.
root# dpadm autostart /local/dps
If you installed with the zip distribution, this step must be done manually, with a script run at system startup time, for example.
Next Steps
At this point, you can continue to configure further data sources and data views. You can also configure load balancing, data distribution, and other server capabilities.
See the online help inside Directory Service Control Center for hints on configuring Directory Proxy Server through the graphical user interface.
See Part II, Directory Proxy Server Administration, in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide for instructions on configuring Directory Proxy Server with command-line administration tools.
Working With Sun Cryptographic Framework on Solaris 10 Systems
This section explains briefly how to use Sun Crypto Accelerator cards through the Sun cryptographic framework on Solaris 10 systems with Directory Server, and Directory Proxy Server. See Chapter 13, Solaris Cryptographic Framework (Overview), in System Administration Guide: Security Services for more information about the framework.
 To Use Directory Server With Cryptographic Hardware on a Solaris
10 System
To Use Directory Server With Cryptographic Hardware on a Solaris
10 System
Before You Begin
This procedure is designed for use with Sun Crypto Accelerator hardware. Perform the following procedure as the same user who runs the Directory Server instance.
-
Set the PIN used to access the cryptographic framework with the pktool setpin command.
-
Export the current Directory Server certificate to a PKCS#12 file.
The following command shows how to perform this step if the Directory Server instance is located under /local/ds/.
$ dsadm export-cert -o cert-file /local/ds defaultCert
-
Configure Directory Server to use the appropriate token when accessing the key material.
Typically, the token is Sun Metaslot.
$ dsconf set-server-prop 'ssl-rsa-security-device:Sun Metaslot'
-
Stop Directory Server.
$ dsadm stop /local/ds
-
(Optional) If you have no other certificates in the existing certificate database for the Directory Server instance, remove the certificate database.
$ rm -f /local/ds/alias/*.db
This optional step ensures that no certificates are stored in the software database.
-
Create a new certificate database backed by the Solaris cryptographic framework.
If you did not remove the certificate database, you do not need to run the modutil -create line in this example.
$ /usr/sfw/bin/64/modutil -create -dbdir /local/ds/alias -dbprefix slapd- $ /usr/sfw/bin/64/modutil -add "Solaris Kernel Crypto Driver" -libfile \ /usr/lib/64/libpkcs11.so -dbdir /local/ds/alias -dbprefix slapd- $ /usr/sfw/bin/64/modutil -enable "Solaris Kernel Crypto Driver" \ -dbdir /local/ds/alias -dbprefix slapd-
-
Import the PKCS#12 certificate that you exported.
$ /usr/sfw/bin/64/pk12util -i cert-file \ -d /local/ds/alias -P slapd- -h "Sun Metaslot" $ /usr/sfw/bin/64/certutil -M -n "Sun Metaslot:defaultCert" -t CTu \ -d /local/ds/alias -P slapd-
If your accelerator board has a FIPS 140-2 keystore, make sure the private key is generated on the device. Sun Crypto Accelerator 4000 and 6000 boards have FIPS 140-2 keystores, for example. The exact process depends on the board.
-
Create a password file that contains the PIN needed to access the cryptographic framework.
$ echo "Sun Metaslot:password" > /local/ds/alias/slapd-pin.txt
-
Start Directory Server.
$ dsadm start /local/ds
 To Use Directory Proxy Server With Cryptographic Hardware on a Solaris
10 System
To Use Directory Proxy Server With Cryptographic Hardware on a Solaris
10 System
Before You Begin
This procedure is designed for use with Sun Crypto Accelerator hardware. Perform the following procedure as the same user who runs the Directory Proxy Server instance.
-
Stop Directory Proxy Server.
$ dpadm stop /local/dps
-
Turn off certificate database password storage.
$ dpadm set-flags /local/dps cert-pwd-prompt=on Choose the certificate database password: Confirm the certificate database password:
-
Set the PIN used to access the cryptographic framework with the pktool setpin command.
Use the same password that you entered when turning off certificate database password storage.
-
Generate a key pair, using the cryptographic framework as the key store.
$ keytool -genkeypair -alias defaultDPScert -dname "ou=dps server,dc=example,dc=com" -keyalg RSA -sigalg MD5withRSA -validity 3652 -storetype PKCS11 -keystore NONE -storepass pin-password
Here, pin-password is the password you set as the PIN with the pktool setpin command.
-
Edit the Directory Proxy Server configuration file, adding the following attributes to the base entry, cn=config.
serverCertificateNickName: defaultDPScert certificateKeyStore: NONE certificateKeyStoreType: PKCS11
-
Start Directory Proxy Server.
$ dpadm start /local/dps
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
