Log Management Improvements
This version of Directory Server brings improvements to time-based log rotation, rotate on-demand functionality for access, error, and audit logs, and configurable permissions for log files. It also provides more flexible logging of users involved in proxy authorization.
The following sections describe changes that have been made in the logging functionality of Directory Server.
Time-Based Log Rotation and Deletion
Directory Server supports rotating and deleting logs not only after a specified interval, but also at a specified time. This feature lets you more easily perform operations such as log analysis and trending, as each rotated log file covers the same length of time. This feature can also be used to meet auditing and security requirements because it makes it easier to determine the specific period of time covered by a given log file.
You can specify whether to rotate the log according to a time interval or according to the size of the log file. The following figure illustrates using the DSCC to configure log rotation to occur once a week at midnight, as well as to rotate the log files when the size limit exceeds 100 Mbytes:
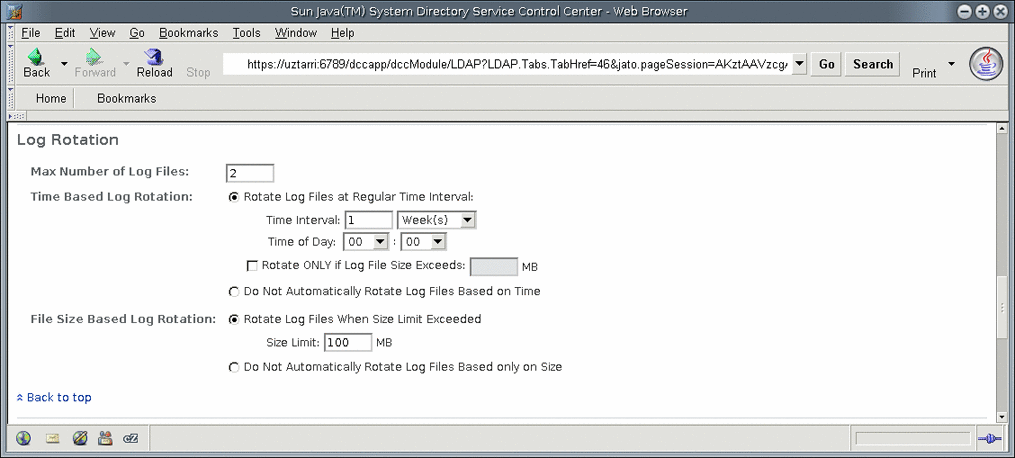
See the log(5dsconf) man page for details on the rotation-time log property.
For example, from the command line, you can display the current configuration for the access log as follows:
$ dsconf get-log-prop -p 20390 enabled : on level : default max-age : 1M max-disk-space-size : 500M max-file-count : 10 max-size : 100M min-free-disk-space-size : 5M path : /install-path/sA1/logs/access perm : 600 rotation-interval : 1d rotation-min-file-size : unlimited rotation-time : undefined verbose-enabled : N/A
You can change the rotation interval for the access log through the command line as follows:
$ dsconf set-log-prop -p 20390 rotation-interval:2d
On-Demand Log Rotation
You can manually rotate Directory Server access, error, and audit logs. This feature is useful when you want the server to stop writing to the current log file while you examine the file. You might also choose to use this feature with system scheduler utilities in addition to time-based log rotation.
You can rotate the access log by using the DSCC. The following figure illustrates the logging configuration screen and the Rotate Log File Now button. Clicking this button allows you to close the current log file and start a new one.
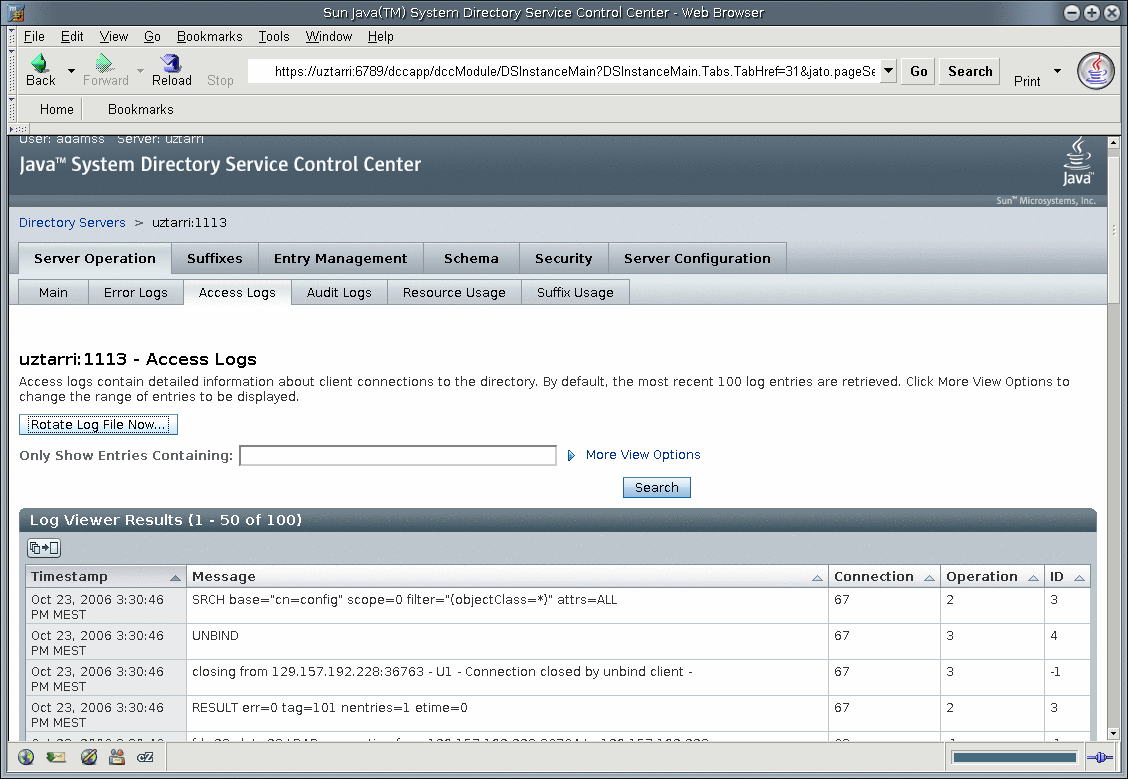
To rotate the access log from the command line, type the following:
$ dsconf rotate-log-now -p 20390
See the dsconf(1M) man page for details on the rotate-log-now subcommand.
Configurable Log File Permissions Settings
Directory Server provides the ability to configure the permissions with which the log file is created, allowing you to change permissions to logs from the default value. This feature lets you tightly control what the user who starts the server can do. At the same time, you can permit specific applications and other users to access key, time-dependent information contained in the logs.
Directory Server enables you to specify the permissions with which a log file will be created.
Log file creation permissions can be set using the dsconf command or using the DSCC as illustrated in the following figure.
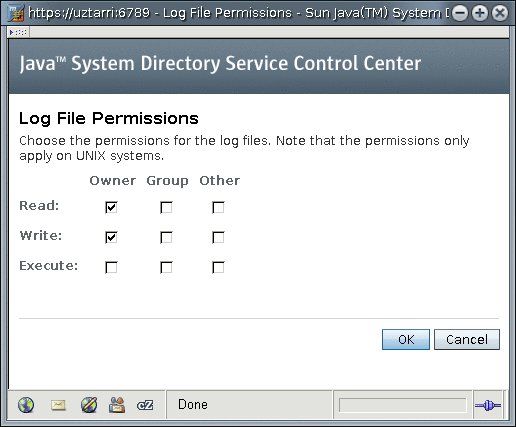
See the log(5dsconf) man page for details on the perm log property.
Monitoring and Managing Persistent Searches
You can now monitor the number of persistent searches that are running on the server, and set a maximum number of persistent searches. To monitor the number of persistent searches, view the value for the currentpsearches attribute, which is stored under cn=monitor. To set a maximum number of persistent searches, use the command dsconf set-server-prop max-psearch-count:number. This feature is useful for troubleshooting and preventing performance issues related to persistent searches.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
