Chapter 6 Deploying Web Applications
This chapter describes how web applications are assembled and deployed in Sun Java System Web Server.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Web Application Structure
Web applications have a directory structure, which is accessible from a mapping to the application's document root (for example, /hello). The document root contains JSP files, HTML files, and static files such as image files.
A WAR file (Web ARchive file) contains a web application in compressed form.
A special directory under the document root, WEB-INF, contains information related to the application that is not in the public document tree. No file contained in WEB-INF can be served directly to the client. The contents of WEB-INF include:
-
/WEB-INF/classes/*: The directory for servlet and other classes.
-
/WEB-INF/web.xml and /WEB-INF/sun-web.xml: XML-based deployment descriptors that specify the web application configuration, including mappings, initialization parameters, and security constraints.
The web application directory structure follows the structure outlined in the J2SE specification. The following is an example directory structure of a simple web application:
+ hello/
|--- index.jsp
|--+ META-INF/
| |--- MANIFEST.MF
'--+ WEB-INF/
|--- web.xml
'--- sun-web.xml
|
Creating Web Deployment Descriptors
Sun Java System Web Server web applications include two deployment descriptor files:
-
A J2SE standard file (web.xml), described in the Java Servlet 2.3 specification (chapter SRV .13, “Deployment Descriptor”). You can find the specification here:
-
An optional Sun Java System Web Server-specific file (sun-web.xml), described later in this chapter.
The easiest way to create the web.xml and sun-web.xml files is to deploy a web application using the Sun Java Studio. For example, web.xml and sun-web.xml files, see Sample Web Application XML Files.
Deploying Web Applications
When you deploy, undeploy, or redeploy a web application, you do not need to restart the server. Deployment is dynamic.
You can deploy a web application in the following ways, which are described briefly in these sections:
Using the Administration Interface
 To deploy web applications using the administration
interface
To deploy web applications using the administration
interface
-
In the Server Manager interface, click the Virtual Server Class tab.
The Manage a Class of Virtual Servers page displays.
-
Select a class of virtual servers, and then click Manage.
The Class Manager interface displays.
-
Select a virtual server, and then click Manage.
The Virtual Server Manager interface displays.
-
Click the Web Applications tab, and then click the Deploy Web Application link.
The Deploy Web Application page displays.
-
Enter the following information:
-
WAR File On. Select a Local Machine when uploading a WAR file to your server, or Server Machine when the WAR file already resides there.
-
WAR File Path. Enter the path on the local or server machine to the WAR file containing the web application. On server machines, enter the absolute path to the WAR file. On local machines, you can browse the available paths.
-
Application URI. Enter the URI on the virtual server for the web application.
-
Installation Directory. Enter the absolute path to the directory on the server machine from which the contents of the WAR file will be extracted. If the directory does not exist, a directory will be created.
-
-
-
Click OK.
For more information about using the Administration interface to manage Sun Java System Web Server, see the Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 SP6 Administrator’s Guide.
Deploying a Web Application using wdeploy
Before you can deploy a web application manually, you must make sure that the server_root/bin/https/bin directory is in your path.
You can use the wdeploy utility at the command line to deploy a WAR file into a virtual server web application environment as follows:
wdeploy deploy -u uri_path -i instance -v vs_id [-d directory] war_file
You can also delete a virtual server web application:
wdeploy delete -u uri_path -i instance -v vs_id hard|soft
You can also list the web application URIs and directories for a virtual server:
wdeploy list -i instance -v vs_id
The following table describes the command parameters. The left column lists the parameter, and the right column describes the parameter.
Table 6–1 command Parameters|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
uri_path |
The URI prefix for the web application (requires a leading “/”). |
|
instance |
The server instance name. |
|
vs_id |
The virtual server ID. |
|
directory |
(optional) The directory to which the application is deployed, or from which the application is deleted. If not specified for deployment, the application is deployed to instance_directory/webapps/vs_id/webappname. For example: /opt/SUNWwbsvr/https-test/webapps/https-test/testapp |
|
hard|soft |
Specifies whether the directory and the server.xml entry are deleted (hard), or just the server.xml entry (soft). |
|
war_file |
The WAR file name. |
When you execute the wdeploy deploy command, two things happen:
-
A web application with the given uri_path and directory gets added to the server.xml file.
-
The WAR file gets extracted at the target directory.
Example usage of the command is as follows:
wdeploy deploy -u /hello -i server.sun.com -v acme.com <server_root>/plugins/java/sample/webapps/simple/webapps-simple.war
After you have deployed an application, you can access it from a browser as follows:
http://vs_urlhost[:vs_port]/uri_path/[index_page]
The following table describes the parts of the URL. The left column lists the part, and the right column describes what the part means.
Table 6–2 Parts of the URL|
Part |
Description |
|---|---|
|
vs_urlhost |
One of the urlhosts values for the virtual server. |
|
vs_port |
(optional) Only needed if the virtual server uses a nondefault port. |
|
uri_path |
The same one you used to deploy the application. This is also the context path. |
|
index_page |
(optional) The page in the application that end users are meant to access first. |
http://acme.com:80/hello/index.jsp
- or -
http://acme.com/hello/
Using Sun Java Studio
Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 supports Sun Java Studio 5, Standard Edition. You can use Sun Java Studio to assemble and deploy web applications.
Sun Java Studio technology is Sun's powerful, extensible, integrated development environment (IDE) for Java technology developers. Sun Java Studio 8 is based on NetBeans™ software, and integrated with the Sun Java System platform. (Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 also supports NetBeans 3.5 and 3.5.1.)
Sun Java Studio support is available on all platforms supported by Sun Java System Web Server 6.1. You can obtain the plugin for the Web Server in the following ways:
-
From the Companion CD in the Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 Media Kit
-
By using the AutoUpdate feature of Sun Java Studio
-
From the download center for Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 at
Note –
The Sun Java Studio 5 plugin for Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 works only with a local Web Server (that is, with the IDE and the Web Server on the same machine).
For information about using the web application features in Sun Java Studio 8, explore the resources at
http://developers.sun.com/prodtech/javatools/jsstandard/reference/docs/index.html
The behavior of the Sun Java Studio 8 plugin for Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 is the same as that for Sun™ Java System Application Server 7. If you are using the "Web Application Tutorial" at the web site listed above, for instance, you would set the Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 instance as the default, and then take the same actions described in the tutorial.
For more information about Sun Java Studio 8, visit
http://www.sun.com/software/sundev/jde/
Note –
For information about using Sun Java Studio to debug web applications, see Using Sun Java Studio for Debugging in this guide.
Enabling and Disabling Web Applications
Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 allows you to enable or disable a web application. You can do so in either of the following ways, as discussed in this section:
Using the Administration Interface
 To enable or disable a deployed web application using
the administrator interface
To enable or disable a deployed web application using
the administrator interface
-
Access the Administration Server, select the server instance, and click Manage.
-
Click the Virtual Server Class tab.
-
Select the virtual server class that contains the virtual server instance in which the web application is deployed, and click Manage.
-
Select the virtual server in which the web application is deployed, and click Manage.
-
Click the Web Applications tab, and then click the Edit Web Applications link.
-
From the Action drop-down list, select Enable or Disable to enable or disable a specific web application.
-
Click OK.
Editing the server.xml File
By default, an application is automatically enabled with the value set to true in the server-id/config/server.xml file. You can disable the application by setting the value to false.
Example:
<WEBAPP uri="/catalog" path="/export/apps/catalog" enabled="false">
For more information, see the Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 SP6 Administrator’s Configuration File Reference.
Dynamic Reloading of Web Applications
If you make code changes to a web application and dynamic reloading is enabled, you do not need to redeploy the web application or restart the server.
To enable dynamic reloading, you must edit the following attribute of the server.xml file's JAVA element, then restart the server:
where integer specifies the interval (in seconds) after which a deployed application will be checked for modifications and reloaded if necessary. To enable dynamic reloading, you must specify a value greater than 0.
The server.xml setting is the default value for all applications. An individual application can override the value for dynamicreloadinterval by specifying a value to the class-loader element in the sun-web.xml file.
For information about sun-web.xml, see the section, The sun-web-app_2_3-1.dtd File Server 6.1 Administrator's Configuration File Reference.
 To load new servlet files or reload deployment descriptor
changes
To load new servlet files or reload deployment descriptor
changes
-
Create an empty file named .reload at the root of the deployed module. For example:
instance_dir/webapps/vs_id/uri/.reload
where vs_id is the virtual server ID in which the web application is deployed, and uri is the value of the uri attribute of the <WEBAPP> element.
-
Explicitly update the .reload file's timestamp (touch .reload in UNIX) each time you make the above changes.
For JSPs, changes are reloaded automatically at a frequency set in the reload-interval property of the jsp-config element in the sun-web.xml file. To disable dynamic reloading of JSPs, set the reload-interval property to -1.
Classloaders
In a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), the classloaders dynamically load a specific Java class file needed for resolving a dependency. For example, when an instance of java.util.Enumeration needs to be created, one of the classloaders loads the relevant class into the environment.
Classloaders in the Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 runtime follow the hierarchy shown in the following figure.
Figure 6–1 Classloader Runtime Hierarchy
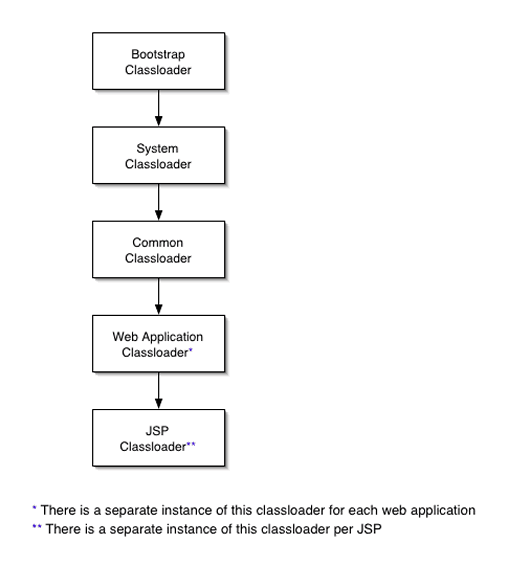
Note that this is not a Java inheritance hierarchy, but a delegation hierarchy. In the delegation design, a classloader delegates classloading to its parent before attempting to load a class itself. If the parent classloader can't load a class, the findClass()method is called on the classloader subclass. In effect, a classloader is responsible for loading only the classes not available to the parent.
The exception is the Web Application Classloader, which follows the delegation model in the Servlet specification. The Web Application Classloader searches in the local classloader before delegating to its parent. You can make the Web Application Classloader delegate to its parent first by setting delegate="true" in the class-loader element of the sun-web.xml file. For more information, see Classloader Elements
The following table describes Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 classloaders. The left column lists the classloaders, and the right column lists descriptions of those classloaders and the files they examine.
Table 6–3 Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 Classloaders|
Classloader |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The Bootstrap Classloader loads the JDK classes. Only one instance of this classloader exists in the entire server. |
|
|
The System Classloader loads the core Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 classes. It is created based on the classpathprefix, serverclasspath, and classpathsuffix attributes of the <JAVA> element in the server.xml file. The environment classpath is included if envclasspathignored="false" is set in the <JAVA> element. Only one instance of this classloader exists in the entire server. If any changes are made to these attributes/classes, the server must be restarted for the changes to take effect. For more information about the <JAVA> element in server.xml, see the Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 SP6 Administrator’s Configuration File Reference. |
|
|
The Common Classloader loads classes in the instance_dir/lib/classes directory, followed by JAR and ZIP files in the instance_dir/lib directory. The existence of these directories is optional; if they don't exist, the Common Classloader is not created. If any changes are made to these classes, the server must be restarted for the changes to take effect. |
|
|
The Web Application Classloader loads the servlets and other classes in a specific web application. That is, from WEB-INF/lib and WEB-INF/classes and from any additional classpaths specified in the extra-class-path attribute of the class-loader element in sun-web.xml. For more information, see Classloader Elements An instance of this classloader is created for each web application. If dynamic reloading is enabled, any changes made to these attributes/classes are reloaded by the server without the need for a restart. For more information, see Dynamic Reloading of Web Applications |
|
|
The JSP Classloader loads the compiled JSP classes of JSPs. An instance of this classloader is created for each JSP file. Any changes made to a JSP are automatically detected and reloaded by the server, unless dynamic reloading of JSPs has been disabled by setting the reload-interval property to -1 in the jsp-config element of the sun-web.xml file. For more information, seejsp-config |
The sun-web-app_2_3-1.dtd File
The sun-web-app_2_3-1.dtd file defines the structure of the sun-web.xml file, including the elements it can contain and the subelements and attributes these elements can include. The sun-web-app_2_3-1.dtd file is located in the install_dir/bin/https/dtds directory.
Note –
Do not edit the sun-web-app_2_3-1.dtd file. The file contents change only with new versions of Sun Java System Web Server.
For more information about DTD files and XML, see the XML specification at:
http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xml-20040204/
Each element defined in a DTD file (which may be present in the corresponding XML file) can contain the following:
Subelements
Elements can contain subelements. For example, the following file fragment defines the cache element.
<!ELEMENT cache (cache-helper*, default-helper?, property*, cache-mapping*)>
The ELEMENT tag specifies that a cache element can contain cache-helper, default-helper, property, and cache-mapping subelements.
The following table shows how optional suffix characters of subelements determine the requirement rules, or number of allowed occurrences, for the subelements. The left column lists the subelement ending character, and the right column lists the corresponding requirement rule.
Table 6–4 Requirement Rules and Subelement Suffixes|
Subelement Suffix |
Requirement Rule |
|---|---|
|
element* |
Can contain zero or more of this subelement. |
|
element? |
Can contain zero or one of this subelement. |
|
element+ |
Must contain one or more of this subelement. |
|
element (no suffix) |
Must contain only one of this subelement. |
If an element cannot contain other elements, you see EMPTY or (#PCDATA) instead of a list of element names in parentheses.
Data
Some elements contain character data instead of subelements. These elements have definitions of the following format:
<!ELEMENT element-name (#PCDATA)>
For example:
<!ELEMENT description (#PCDATA)>
In the sun-web.xml file, white space is treated as part of the data in a data element. Therefore, there should be no extra white space before or after the data delimited by a data element. For example:
<description>class name of session manager</description>
Attributes
Elements that have ATTLIST tags contain attributes (name-value pairs). For example:
<!ATTLIST cachemax-capacity CDATA "4096"
timeout CDATA "30"
enabled %boolean; "false">
A cache element can contain max-capacity, timeout, and enabled attributes.
The #REQUIRED label means that a value must be supplied. The #IMPLIED label means that the attribute is optional, and that Sun Java System Web Server generates a default value. Wherever possible, explicit defaults for optional attributes (such as "true") are listed.
Attribute declarations specify the type of the attribute. For example, CDATA means character data, and %boolean is a predefined enumeration.
Elements in the sun-web.xml File
This section describes the XML elements in the sun-web.xml file. Elements are grouped as follows:
This section also includes an alphabetical list of the elements for quick reference. See Alphabetical List of sun-web.xml Elements.
Note –
Subelements must be defined in the order in which they are listed under each Subelements heading, unless otherwise noted.
Note –
Each sun-web.xml file must begin with the following DOCTYPE header:
<!DOCTYPE sun-web-app PUBLIC '-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 Servlet 2.3//EN''http://www.sun.com/software/sunone/webserver/dtds/sun-web-app_2_3-1.dtd'>
For an alphabetical list of elements in sun-web.xml, see Alphabetical List of sun-web.xml Elements
General Elements
General elements are as follows:
sun-web-app
Defines Sun Java System Web Server-specific configuration for a web application. This is the root element; there can only be one sun-web-app element in a sun-web.xml file.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the sun-web-app element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–5 sun-web-app Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
sun-web-appsun-web-app |
zero or more |
Maps roles to users or groups in the currently active realm. |
|
servletservlet |
zero or more |
Specifies a principal name for a servlet, which is used for the run-as role defined in web.xml. |
|
zero or one |
Specifies session manager, session cookie, and other session-related information. |
|
|
zero or more |
Maps the absolute JNDI name to the resource-env-ref in the corresponding J2SE XML file. |
|
|
zero or more |
Maps the absolute JNDI name to the resource-ref in the corresponding J2SE XML file. |
|
|
zero or one |
Configures caching for web application components. |
|
|
zero or one |
Specifies classloader configuration information. |
|
|
zero or one |
Specifies JSP configuration information. |
|
|
zero or one |
Specifies internationalization settings. |
|
|
propertyproperty |
zero or more |
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. |
Attributes
none
Properties
The following table describes properties for the sun-web-app element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–6 sun-web-app Properties|
Property Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
crossContextAllowed |
true |
If true, allows this web application to access the contexts of other web applications using the ServletContext.getContext() method. |
|
true |
If true, Sun Java System Web Server URL encodes cookies before sending them to the client. If you do not want cookies to be encoded, add the following to sun-web.xml: <property name="encodeCookies" value="false"> For the above example, enter the line directly under the <sun-web-app> tag; do not embed this in any other tag. |
|
|
tempdir |
instance_dir/ClassCache/vs_id/uri |
Specifies a temporary directory for use by this web application. This value is used to construct the value of the javax.servlet.context.tempdir context attribute. Compiled JSPs are also placed in this directory. |
|
singleThreadedServletPoolSize |
5 |
Specifies the maximum number of servlet instances allocated for each SingleThreadModel servlet in the web application. |
|
reuseSessionID |
false |
If true, this property causes the web application to reuse the JSESSIONID value (if present) in the request header as the session ID when creating sessions. The default behavior of web applications is to not reuse session IDs and instead generate cryptographically random session IDs for new sessions. |
|
relativeRedirectAllowed |
false |
If true, allows the web application to send a relative URL to the client using the HttpServletResponse.sendRedirect() API (that is, it suppresses the container from translating a relative URL to a fully qualified URL). |
property
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. A property adds configuration information to its parent element that is one or both of the following:
-
Optional with respect to Sun Java System Web Server.
-
Needed by a system or object that Sun Java System Web Server does not have knowledge of, such as an LDAP server or a Java class.
For example, a manager-properties element can include property subelements:
<manager-properties>
<property name="reapIntervalSeconds" value="20" >
</manager-properties>
Which properties a manager-properties element uses depends on the value of the parent session-manager element's persistence-type attribute. For details, see the description of the session-manager element.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the property element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–7 property Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or one |
Contains a text description of this element. |
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the property element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–8 property Attributes|
Attribute |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
name |
none |
Specifies the name of the property or variable. |
|
value |
none |
Specifies the value of the property or variable. |
description
Contains a text description of the parent element.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
Security Elements
Security elements are as follows:
security-role-mapping
Maps roles to users or groups in the currently active realm.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the security-role-mapping element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–9 security-role-mapping Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
only one |
Contains the role name. |
|
|
requires at least one principal-name or group-name |
Contains a principal (user) name in the current realm. |
|
|
requires at least one principal-name or group-name |
Contains a group name in the current realm. |
Attributes
none
servlet
Specifies a principal name for a servlet, which is used for the run-as role defined in web-xml.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the servlet element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–10 servlet Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
only one |
Contains the name of a servlet, which is matched to a servlet-name in web.xml. |
|
|
only one |
Contains a principal (user) name in the current realm. |
Attributes
none
servlet-name
Contains data that specifies the name of a servlet, which is matched to a servlet-name in the web.xml file. This name must be present in the web.xml file.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
role-name
Contains data that specifies the role-name in the security-role element of the web.xml file.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
principal-name
Contains data that specifies a principal (user) name in the current realm.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
group-name
Contains data that specifies a group name in the current realm.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
Session Elements
Session elements are as follows:
Note –
The session manager interface is unstable. An unstable interface may be experimental or transitional, and thus may change incompatibly, be removed, or be replaced by a more stable interface in the next release.
session-config
Specifies session configuration information.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the session-config element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–11 session-config Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or one |
Specifies session manager configuration information. |
|
|
zero or one |
Specifies session properties. |
|
|
zero or one |
Specifies session cookie properties. |
Attributes
none
session-manager
Specifies session manager information.
Note –
In Sun Java System Web Server 6.1, you cannot define a session manager either for a single sign-on session or for a virtual server. You must define session managers at the level of web applications.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the session-manager element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–12 session-manager Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or one |
Specifies session manager properties. |
|
|
zero or one |
Specifies session persistence (storage) properties. |
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the session-manager element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–13 session-manager Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
persistence-type |
memory |
(optional) Specifies the session persistence mechanism. Allowed values are memory, file, s1ws60, and mmap. Setting the value of persistence type to memory is equivalent to using Sun Java System Web Server’s IWSSessionManager without any store. Setting the value of persistence type to file is equivalent to using Sun Java System Web Server’s IWSSessionManager with FileStore. |
manager-properties
Specifies session manager properties.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the manager-properties element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–14 manager-properties Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. |
Attributes
none
Properties
The following table describes properties for the manager-properties element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–15 manager-properties Properties|
Property Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
reapIntervalSeconds |
60 |
Specifies the number of seconds between checks for expired sessions. Setting this value lower than the frequency at which session data changes is recommended. For example, this value should be as low as possible (1 second) for a hit counter servlet on a frequently accessed web site, or you could lose the last few hits each time you restart the server. |
|
maxSessions |
-1 |
Specifies the maximum number of active sessions, or -1 (the default) for no limit. |
|
sessionFilename |
none; state is not preserved across restarts |
Specifies the absolute or relative path name of the file in which the session state is preserved between application restarts, if preserving the state is possible. A relative path name is relative to the temporary directory for this web application. Applicable only if the persistence-type attribute of the session-manager element is memory. |
store-properties
Specifies session persistence (storage) properties.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the store-properties element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–16 store-properties Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. |
Attributes
none
Properties
The following table describes properties for the store-properties element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–17 store-properties Properties|
Property Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
reapIntervalSeconds |
60 |
Specifies the number of seconds between checks for expired sessions for those sessions that are currently swapped out. Setting this value lower than the frequency at which session data changes is recommended. For example, this value should be as low as possible (1 second) for a hit counter servlet on a frequently accessed web site, or you could lose the last few hits each time you restart the server. |
|
directory |
directory specified by javax.servlet.context.tempdir context attribute |
Specifies the absolute or relative path name of the directory into which individual session files are written. A relative path is relative to the temporary work directory for this web application. |
session-properties
Specifies session properties.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the session-properties element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–18 session-properties Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. |
Attributes
none
Properties
The following table describes properties for the session-properties element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–19 session-properties Properties
cookie-properties
Specifies session cookie properties.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the cookie-properties element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–20 cookie-properties Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. |
Attributes
none
Properties
The following table describes properties for the cookie-properties element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–21 cookie-properties Properties|
Property Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
cookiePath
|
context path at which the web application is installed. |
Specifies the path name that is set when the session tracking cookie is created. The browser sends the cookie if the path name for the request contains this path name. If set to / (slash), the browser sends cookies to all URLs served by the Sun Java System Web Server. You can set the path to a narrower mapping to limit the request URLs to which the browser sends cookies. |
|
cookieMaxAgeSeconds |
-1 |
Specifies the expiration time (in seconds) after which the browser expires the cookie. The default value of -1 indicates that the cookie never expires. |
|
cookieDomain |
(unset) |
Specifies the domain for which the cookie is valid. |
|
cookieComment |
Sun Java System Web Server session tracking cookie |
Specifies the comment that identifies the session tracking cookie in the cookie file. Applications can provide a specific comment for the cookie. |
Reference Elements
Reference elements are as follows:
resource-env-ref
Maps the res-ref-name in the corresponding J2SE web.xml file resource-env-refentry to the absolute jndi-name of a resource.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the resource-env-ref element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–22 resource-env-ref Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
only one |
Specifies the res-ref-name in the corresponding J2SE web.xml file resource-env-ref entry. |
|
|
only one |
Specifies the absolute jndi-name of a resource. |
Attributes
none
resource-env-ref-name
Contains data that specifies the res-ref-name in the corresponding J2SE web.xml file resource-env-ref entry.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
resource-ref
Maps the res-ref-namee in the corresponding J2SE web.xml file resource-ref entry to the absolute jndi-name of a resource.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the resource-ref element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–23 resource-ref Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
only one |
Specifies the res-ref-name in the corresponding J2SE web.xml file resource-ref entry. |
|
|
only one |
Specifies the absolute jndi-name of a resource. |
|
|
zero or one |
Specifies the default principal (user) for the resource. |
Attributes
none
res-ref-name
Contains data that specifies the res-ref-name in the corresponding J2SE web.xml file resource-ref entry.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
default-resource-principal
Specifies the default principal (user) for the resource.
If this element is used in conjunction with a JMS Connection Factory resource, the name and password subelements must be valid entries in Sun™ Java System Message Queue's broker user repository.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the default-resource-principal element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–24 default-resource-principal Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
only one |
Contains the name of the principal. |
|
|
only one |
Contains the password for the principal. |
Attributes
none
name
Contains data that specifies the name of the principal.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
password
Contains data that specifies the password for the principal.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
jndi-name
Contains data that specifies the absolute jndi-name of a URL resource or a resource in the server.xml file.
Note –
To avoid collisions with names of other enterprise resources in JNDI, and to avoid portability problems, all names in a Sun Java System Web Server application should begin with the string java:comp/env.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
Caching Elements
For details about response caching as it pertains to servlets, see Caching Servlet Results JSP Cache Tags
Caching elements are as follows:
cache
Configures caching for web application components.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the cache element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–25 cache Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a custom class that implements the CacheHelper interface. |
|
|
zero or one |
Allows you to change the properties of the default, built-in cache-helper class. |
|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a cache property, which contains a name and a value. |
|
|
zero or more |
Maps a URL pattern or a servlet name to its cacheability constraints. |
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the cache element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–26 cache Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
max-entries |
4096 |
(optional) Specifies the maximum number of entries the cache can contain. Must be a positive integer. |
|
timeout-in-seconds |
30 |
(optional) Specifies the maximum amount of time in seconds that an entry can remain in the cache after it is created or refreshed. Can be overridden by a timeout element. |
|
enabled |
false |
(optional) Determines whether servlet and JSP caching is enabled. Legal values are on, off, yes, no, 1, 0, true, false. |
Properties
The following table describes properties for the cache element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–27 cache Properties|
Property Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
cacheClassName |
com.sun.appserv.web.cache.LruCache |
Specifies the fully qualified name of the class that implements the cache functionality. See The Table 6–28 |
|
MultiLRUSegmentSize |
4096 |
Specifies the number of entries in a segment of the cache table that should have its own LRU (least recently used) list. Applicable only if cacheClassName is set to com.sun.appserv.web.cache.MultiLruCache. |
|
MaxSize |
unlimited; Long.MAX_VALUE |
Specifies an upper bound on the cache memory size in bytes (KB or MB units). Example values are 32 KB or 2 MB. Applicable only if cacheClassName is set to com.sun.appserv.web.cache.BoundedMultiLruCache. |
Cache Class Names
The following table lists possible values of the cacheClassName property. The left column lists the value, and the right column describes the kind of cache the value specifies.
Table 6–28 cacheClassName Values|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
com.sun.appserv.web.cache.LruCache |
A bounded cache with an LRU cache replacement policy. |
|
com.sun.appserv.web.cache.BaseCache |
An unbounded cache suitable if the maximum number of entries is known. |
|
com.sun.appserv.web.cache.MultiLruCache |
A cache suitable for a large number of entries (>4096). Uses the MultiLRUSegmentSize property. |
|
com.sun.appserv.web.cache.BoundedMultiLruCache |
A cache suitable for limiting the cache size by memory rather than number of entries. Uses the MaxSize property. |
cache-helper
Specifies a class that implements the CacheHelper interface. For details, see CacheHelper Interface
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the cache-helper element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–29 cache-helper Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. |
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the cache-helper element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–30 cache-helper Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
name |
default |
Specifies a unique name for the helper class, which is referenced in the cache-mapping element. |
|
class-name |
none |
Specifies the fully qualified class name of the cache helper, which must implement the com.sun.appserv.web.CacheHelper interface. |
default-helper
Allows you to change the properties of the built-in default cache-helper class.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the default-helper element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–31 default-helper Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a property, which contains a name and a value. |
Attributes
none
Properties
The following table describes properties for the default-helper element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–32 default-helper Properties|
Property Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
cacheKeyGeneratorAttrName |
uses the built-in default cache-helper key generation, which concatenates the servlet path with key-field values, if any. |
The caching engine searches in the ServletContext for an attribute with a name equal to the value specified for this property to determine whether a customized CacheKeyGenerator implementation is used. An application may provide a customized key generator rather than using the default helper. For more information, see CacheKeyGenerator Interface |
cache-mapping
Maps a URL pattern or a servlet name to its cacheability constraints.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the cache-mapping element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–33 cache-mapping Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
requires one servlet-name or url-pattern |
Contains the name of a servlet. |
|
|
requires one servlet-name or url-pattern |
Contains a servlet URL pattern for which caching is enabled. |
|
|
required if timeout, refresh-field,http-method, key-field, and constraint-field are not used |
Contains the name of the cache-helper used by the parent cache-mapping element. |
|
|
zero or one if cache-helper-ref is not used |
Contains the cache-mapping specific maximum amount of time in seconds that an entry can remain in the cache after it is created or refreshed |
|
|
zero or one if cache-helper-ref is not used |
Specifies a field that gives the application component, programmatic way to refresh a cached entry. |
|
|
zero or more if cache-helper-ref is not used |
Contains an HTTP method that is eligible for caching. |
|
|
zero or more if cache-helper-ref is not used |
Specifies a component of the key used to look up and extract cache entries. |
|
|
zero or more if cache-helper-ref is not used |
Specifies a cacheability constraint for the given url-pattern or servlet-name. |
Attributes
none
url-pattern
Contains data that specifies a servlet URL pattern for which caching is enabled. See the Java Servlet 2.3 specification, section SRV 11.2 for applicable patterns.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
cache-helper-ref
Contains data that specifies the name of the cache-helper used by the parent cache-mapping element.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
timeout
Contains data that specifies the cache-mapping specific maximum amount of time in seconds that an entry can remain in the cache after it is created or refreshed. If not specified, the default is the value of the timeout attribute of the cache element.
Subelements
none
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the timeout element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–34 timeout Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
name |
none |
Specifies the timeout input parameter, whose value is interpreted in seconds. The field's type must be java.lang.Long or java.lang.Integer. |
|
scope |
context.attribute |
(optional) Specifies the scope in which the input parameter can be present. Allowed values are context.attribute, request.header, request.parameter, request.cookie, session.id, and session.attribute. |
refresh-field
Specifies a field that gives the application component a programmatic way to refresh a cached entry.
Subelements
none
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the refresh-field element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–35 refresh-field Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
name |
none |
Specifies the input parameter name. If the parameter is present in the specified scope and it’s value is true, the cache will be refreshed. |
|
scope |
request.parameter |
(optional) Specifies the scope in which the input parameter can be present. Allowed values are context.attribute, request.header, request.parameter, request.cookie, session.id, and session.attribute. |
http-method
Contains data that specifies an HTTP method that is eligible for caching. The default is GET.
Subelements
none
Attributes
none
key-field
Specifies a component of the key used to look up and extract cache entries. The web container searches for the named parameter, or field, in the specified scope.
If this element is not present, the web container uses the Servlet Path (the path section that corresponds to the servlet mapping that activated the current request). See the Servlet 2.3 specification, section SRV 4.4, for details on the Servlet Path.
Subelements
none
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the key-field element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–36 key-field Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
name |
none |
Specifies the input parameter name. |
|
scope |
request.parameter |
(optional) Specifies the scope in which the input parameter can be present. Allowed values are context.attribute, request.header, request.parameter, request.cookie, session.id, and session.attribute. |
constraint-field
Specifies a cacheability constraint for the given url-pattern or servlet-name.
All constraint-field constraints must pass for a response to be cached. If there are value constraints, at least one of them must pass.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the constraint-field element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–37 constraint-field Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Contains a value to be matched to the input parameter value. |
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the constraint-field element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–38 constraint-field Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
name |
none |
Specifies the input parameter name. |
|
scope |
request.parameter |
(optional) Specifies the scope in which the input parameter can be present. Allowed values are context.attribute, request.header, request.parameter, request.cookie, session.id, and session.attribute. |
|
cache-on-match |
true |
(optional) If true, caches the response if matching succeeds. Overrides the same attribute in a value subelement. |
|
cache-on-match-failure |
false |
(optional) If true, caches the response if matching fails. Overrides the same attribute in a value subelement. |
value
Contains data that specifies a value to be matched to the input parameter value. The matching is case sensitive. For example:
<value match-expr="in-range">1-60</value>
Subelements
none
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the value element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–39 value Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
match-expr |
equals |
(optional) Specifies the type of comparison performed with the value. Allowed values are equals, not-equals, greater, lesser, and in-range. If match-expr is greater or lesser, the value must be a number. If match-expr is in-range, the value must be of the form n1-n2, where n1 and n2 are numbers. |
|
cache-on-match |
true |
(optional) If true, caches the response if matching succeeds. |
|
cache-on-match-failure |
false |
(optional) If true, caches the response if matching fails. |
Classloader Elements
Classloader elements are as follows:
class-loader
Configures the classloader for the web application.
Subelements
none
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the class-loader element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–40 class-loader Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
extra-class-path |
null |
(optional) Specifies additional classpath settings for this web application. |
|
delegate |
false |
(optional) If true, the web application follows the standard classloader delegation model and delegates to its parent classloader first before looking in the local classloader. If false, the web application follows the delegation model specified in the Servlet specification and searches in its classloader before looking in the parent classloader. For a web component of a web service, you must set this value to true. Legal values are on, off, yes, no, 1, 0, true, false. |
|
value of the dynamicreloadinterval attribute of the <JAVA> element in server.xml |
(optional) Allows an application to override the dynamicreloadinterval setting in server.xml. Specifies the frequency (in seconds) at which a web application is checked for modifications, and then reloaded if modifications have been made. Setting this value to less than or equal to 0 disables dynamic reloading of the application. If not specified, the value from server.xml is used. For more information about server.xml, see the Sun Java System Web Server 6.1 SP6 Administrator’s Configuration File Reference. |
JSP Elements
JSP elements are as follows:
jsp-config
Specifies JSP configuration information.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the jsp-config element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–41 jsp-config Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
zero or more |
Specifies a property. |
Attributes
none
Properties
The following table describes properties for the jsp-config element. The left column lists the property name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the property does.
Table 6–42 jsp-config Properties|
Property Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ieClassId |
clsid:8AD9C840-044E-11D1-B3E9-00805F499D93 |
The Java plugin COM class ID for Internet Explorer. Used by the <jsp:plugin> tags. |
|
javaCompilerPlugin |
internal JDK compiler (javac) |
The fully qualified class name of the Java compiler plugin to be used. Not needed for the default compiler. For example, to use the jikes compiler for JSP pages, set the javaCompilerPlugin property to org.apache.jasper.compiler.JikesJavaCompiler, then set the javaCompilerPath property to point to the jikes executable. To use sun.tools.javac.Main to compile JSP-generated servlets, set the javaCompilerPlugin property to org.apache.jasper.compiler.SunJavaCompiler (see also the -deprecatedjavac switch of jspc, described in |
|
javaCompilerPath |
none |
Specifies the path to the executable of an out-of-process Java compiler such as jikes. Ignored for the default compiler. It is required only if the javaCompilerPlugin property is specified. |
|
javaEncoding |
UTF8 |
Specifies the encoding for the generated Java servlet. This encoding is passed to the Java compiler used to compile the servlet as well. By default, the web container tries to use UTF8. If that fails, it uses the javaEncoding value. For encodings, see: http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4.2/docs/guide/intl/encoding.doc.html |
|
classdebuginfo |
false |
Specifies whether the generated Java servlets should be compiled with the debug option set (-g for javac). |
|
keepgenerated |
true |
If set to true, keeps the generated Java files. If false, deletes the Java files. |
|
largefile |
false |
If set to true, static HTML is stored in a separate data file when a JSP is compiled. This is useful when a JSP is very large, because it minimizes the size of the generated servlet. |
|
mappedfile |
false |
If set to true, generates separate write calls for each HTML line and comments that describe the location of each line in the JSP file. By default, all adjacent write calls are combined and no location comments are generated. |
|
scratchdir |
default work directory for the web application |
The working directory created for storing all of the generated code. |
|
reload-interval |
0 |
Specifies the frequency (in seconds) at which JSP files are checked for modifications. Setting this value to 0 checks JSPs for modifications on every request. Setting this value to -1 disables checks for JSP modifications and JSP recompilation. |
|
initial-capacity |
32 |
Specifies the initial size of the hash table of compiled JSP classes. |
The following example illustrates the use of the initial-capacity property described in the table above. The example shows how you can configure a value of 1024:
<jsp-config> <property name=”initial-capacity” value=”1024” > </jsp-config>
Internationalization Elements
Internationalization elements are as follows:
parameter-encoding
Specifies a hidden field or default charset that determines the character encoding the web container. This web container is used to decode parameters for request.getParameter calls when the charset is not set in the request's Content-Type.
For encodings you can use, see:
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4.2/docs/guide/intl/encoding.doc.html
Subelements
none
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the parameter-encoding element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–43 parameter-encoding Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
form-hint-field |
j_encoding |
The value of the hidden field in the form that specifies the parameter encoding. |
|
default-charset |
none |
This value is used for parameter encoding if neither request.setCharacterEncoding() is called nor form-hint-field is found in the request. |
locale-charset-info
Specifies the mapping between the locale and the character encoding that should be set in the Content-type header of the response if a servlet or JSP sets the response locale using the ServletResponse.setLocale method. This overrides the web container's default locale-to-charset mapping.
Subelements
The following table describes subelements for the locale-charset-info element. The left column lists the subelement name, the middle column indicates the requirement rule, and the right column describes what the element does.
Table 6–44 locale-charset-info Subelements|
Element |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
one or more |
Maps a locale to a character set. |
|
|
zero or one |
Deprecated. Use the parameter-encoding element under sun-web-app instead. This is supported only for backward compatibility with applications developed under Sun Java System Application Server 7. |
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the locale-charset-info element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–45 locale-charset-info Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
default-locale |
none |
Ignored in Sun Java System Web Server 6.1. |
locale-charset-map
Maps a locale to a specific character encoding.
For encodings you can use, see:
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4.2/docs/guide/intl/encoding.doc.html
Attributes
The following table describes attributes for the locale-charset-map element. The left column lists the attribute name, the middle column indicates the default value, and the right column describes what the attribute does.
Table 6–46 locale-charset-map Attributes|
Attribute |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
locale |
none |
Specifies the locale name. |
|
agent |
none |
Ignored in Sun Java System Web Server 6.1. |
|
charset |
none |
Specifies the character set for that locale. |
The following table provides a locale-charset-map example, listing the locale and the corresponding charset:
Table 6–47 locale-charset-map Example|
Locale |
Charset |
|---|---|
|
ja |
EUC-JP |
|
zh |
UTF-8 |
Alphabetical List of sun-web.xml Elements
This section provides an alphabetical list for the easy lookup of sun-web.xml elements.
Note –
For a list of sun-web.xml elements by category, see Elements in the sun-web.xml File.
Sample Web Application XML Files
This section includes the following:
Sample web.xml File
The following is a sample web.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
Copyright 2002 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
-->
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC '-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web
Application 2.3//EN' 'http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd'>
<web-app>
<display-name>i18n-simple</display-name>
<distributable></distributable>
<filter>
<filter-name>Simple Filter</filter-name>
<filter-class>samples.i18n.simple.servlet.SimpleFilter
</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>usefilter</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>Simple Filter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/SimpleFilterServlet</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SimpleI18nServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>samples.i18n.simple.servlet.SimpleI18nServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>IncludedServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>samples.i18n.simple.servlet.IncludedServlet
</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ForwardedServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>samples.i18n.simple.servlet.ForwardedServlet
</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SimpleFilterServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>samples.i18n.simple.servlet.SimpleFilterServlet
</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>LocaleCharsetServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>samples.i18n.simple.servlet.LocaleCharsetServlet
</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SimpleI18nServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/SimpleI18nServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>IncludedServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/IncludedServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ForwardedServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ForwardedServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SimpleFilterServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/SimpleFilterServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LocaleCharsetServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/LocaleCharsetServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/i18ntaglib</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/tlds/i18ntaglib.tld
</taglib-location>
</taglib>
</web-app>
Sample sun-web.xml File
The following is a sample sun-web.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
Copyright 2002 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
-->
<!DOCTYPE sun-web-app PUBLIC '-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Sun ONE
Web Server 6.1 Servlet 2.3//EN' 'http://www.sun.com/software/sunone
/webserver/dtds/sun-web-app_2_3-1.dtd'>
<sun-web-app>
<session-config>
<session-manager/>
</session-config>
<cache enabled="true" timeout-in-seconds="300" >
<cache-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServCache</servlet-name>
<key-field name="inputtext"
scope="request.parameter"/>
<constraint-field name="inputtext"
scope="request.parameter">
<value>one</value>
<value>two</value>
</constraint-field>
</cache-mapping>
</cache>
</sun-web-app>
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
