About Servlets
Servlets, like applets, are reusable Java applications. Servlets, however, run on a Web Server rather than in a Web Browser.
Servlets provide a component-based, platform-independent method for building web-based applications, without the performance overheads, process limitations, and platform-specific liabilities of CGI programs.
Servlets supported by the Sun Java System Web Server are based on the Java Servlet 2.3 specification.
The following list describes the fundamental characteristics of servlets.
Servlets:
-
Are created and managed at runtime by the Sun Java System Web Server servlet engine.
-
Operate on input data that is encapsulated in a request object.
-
Respond to a query with data encapsulated in a response object.
-
Are extensible.
-
Provide user session information persistence between interactions.
-
Can be dynamically reloaded while the server is running.
-
Are addressable with URLs. Buttons on an application's pages often point to servlets.
-
Can call other servlets and/or JSPs.
This section includes the following topics:
Servlet Data Flow
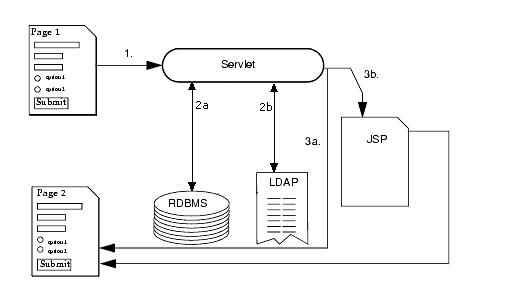
When a user clicks a Submit button, information entered in a display page is sent to a servlet. The servlet processes the incoming data and orchestrates a response by generating content. Once the content is generated, the servlet creates a response page, usually by forwarding the content to a JSP. The response is sent back to the client, which sets up the next user interaction.
The following illustration shows the information flow to and from the servlet.
 To show the servlet data flow
To show the servlet data flow
-
The servlet processes the client request.
-
The servlet generates content.
-
The servlet creates a response and either:
Servlet Types
There are two main servlet types, generic and HTTP:
-
Generic servlets
-
Extend javax.servlet.GenericServlet.
-
Are protocol independent. They contain no inherent HTTP support or any other transport protocol.
-
-
HTTP servlets
-
Extend javax.servlet.HttpServlet.
-
Have built-in HTTP protocol support and are more useful in a Sun Java System Web Server environment.
For both servlet types, you implement the constructor method init() and the destructor method destroy() to initialize or deallocate resources.
All servlets must implement a service() method, which is responsible for handling servlet requests. For generic servlets, simply override the service method to provide routines for handling requests. HTTP servlets provide a service method that automatically routes the request to another method in the servlet based on which HTTP transfer method is used. So, for HTTP servlets, override doPost() to process POST requests, doGet() to process GET requests, and so on.
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates