SNMP Basics
SNMP is a protocol used to exchange data about network activity. With SNMP, data travels between a managed device and a Network Management Station (NMS). A managed device is anything that runs SNMP: hosts, routers, your web server, and other servers on your network. The NMS is a machine used to remotely manage that network. Usually, the NMS software provides a graph to display collected data or use that data to make sure the server is operating within a particular tolerance.
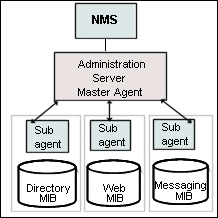
The NMS is usually a powerful workstation with one or more network management applications installed. A network management application such as HP OpenView, graphically shows information about managed devices, such as your web servers. For example, it might show the servers in your enterprise that are up or down, or the number and type of error messages received. When you use SNMP with a Sun Java System Web Server, this information is transferred between the NMS and the server through the use of two types of agents, the subagent and the master agent.
The subagent gathers information about the server and passes the information to the server’s master agent. Every Sun Java System server, except for the Administration Server, has a subagent.
Note –
After making any SNMP configuration changes, you must click the Apply button, and restart SNMP subagent.
The master agent communicates with the NMS. The master agent is installed with the Administration Server.
You can have multiple subagents installed on a host computer, but only one master agent. For example, if you had Directory Server, Sun Java System Web Server, and the Messaging Server installed on the same host, the subagents for each of the servers would communicate with the same master agent, as shown below
Figure 11–1 The Network Management Station and SNMP Agents
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
