Multi-Master Replication
In multi-master replication, replicas of the same data exist on more than one server. For information about multi-master replication, see the following sections:
Concepts of Multi-Master Replication
In a multi-master configuration, data is updated on multiple masters. Each master maintains a change log, and the changes made on each master are replicated to the other servers. Each master plays the role of supplier and consumer.
Multi-master replication can cause synchronization conflicts. Conflicts are usually resolved automatically by using the timestamp associated with each change, where the most recent change takes precedence. Some rare conflicts must be resolved manually. For more information, see Solving Common Replication Conflicts in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.2 Administration Guide.
Each supplier in a multi-master environment must have a replication agreement. The following figure shows two master servers and their replication agreements.
Figure 4–1 Multi-Master Replication Configuration (Two Masters)

In the preceding figure, Master A and Master B have a master replica of the same data. Each master has a replication agreement that specifies the replication flow. Master A acts as a master in the scope of Replication Agreement 1, and as a consumer in the scope of Replication Agreement 2.
Multi-master replication can be used for the following tasks:
-
To replicate updates by using the replica ID.
Updates by using the replica ID make it possible for a consumer to be updated by multiple suppliers at the same time, provided that the updates originate from different replica IDs.
-
To enable or disable a replication agreement.
Replication agreements can be configured but left disabled, then enabled rapidly when required. This feature provides flexibility in replication configuration. This can be done whether you use multiple masters or not.
Multi-Master Replication Over Wide Area Networks
Directory Server supports multi-master replication over WANs, enabling multi-master replication configurations across geographical boundaries in international, multiple data center deployments.
The replication protocol provides full asynchronous support, window and grouping mechanisms, and support for compression. These features render multi-master replication over WAN a viable deployment possibility.
In a multi-master replication over WAN configuration, all instances of Directory Server separated by a WAN must support multi-master replication over WANs.
Group Mechanism and Window Mechanism
The group mechanism and window mechanism can be used to group changes rather than send them individually. The group mechanism and window mechanism can also be used to specify a number of requests that can be sent to the consumer without the supplier waiting for an acknowledgement from the consumer.
For information about how to adjust the group size and window size, see Configuring Network Parameters in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.2 Administration Guide.
Replication Compression Mechanisms
Replication compression helps to streamline replication flow and avoid bottlenecks caused by limited bandwidth.
Fully Meshed Multi-Master Topology
In a fully meshed multi-master topology, each master is connected to each of the other masters. A fully meshed topology provides high availability and guaranteed data integrity. The following figure shows a fully meshed, four-way, multi-master replication topology with some consumers.
Figure 4–2 Fully Meshed, Four-Way, Multi-Master Replication Configuration
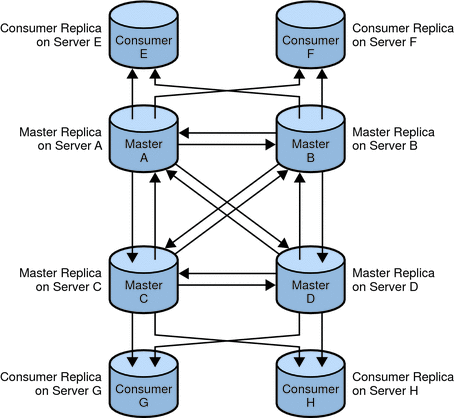
In Figure 4–2, the suffix is held on four masters to ensure that it is always available for modification requests. Each master maintains its own change log. When one of the masters processes a modification request from a client, it records the operation in its change log. The master then sends the replication update to the other masters, and in turn to the other consumers. Each master also stores a Replication Manager entry used to authenticate the other masters when they bind to send replication updates.
Each consumer stores one or more entries that correspond to the Replication Manager entries. The consumers use the entries to authenticate the masters when they bind to send replication updates. It is possible for each consumer to have just one Replication Manager entry that enables all masters to use the same Replication Manager entry for authentication. By default, the consumers have referrals set up for all masters in the topology. When consumers receive modification requests from the clients, they send the referrals to back to the client. For more information about referrals, see Referrals and Replication.
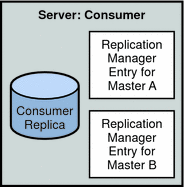
Figure 4–3 presents a detailed view of the replication agreements, change logs, and Replication Manager entries that must be set up on Master A.Figure 4–4 provides the same detailed view for Consumer E.
Figure 4–3 Replication Configuration for Master A (Fully Meshed Topology)
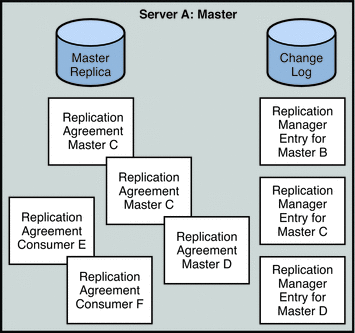
Figure 4–4 Replication Configuration for Consumer Server E (Fully Meshed Topology)
Master A requires the following:
-
A master replica
-
A change log
-
Replication Manager entries for Masters B, C, and D, unless you use the same Replication Manager entry on each replica
-
Replication agreements for Masters B, C, and D, and for Consumers E, and F
Consumer E requires the following:
-
A consumer replica
-
Replication Manager entries to authenticate Masters A, and B when they bind to send replication updates
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
