About the Sun Java System Application Server
What is the Application Server?
The Application Server provides a robust J2EE platform for the development, deployment, and management of enterprise applications. Key features include transaction management, performance, scalability, security, and integration. The Application Server supports services from Web publishing to enterprise-scale transaction processing, while enabling developers to build applications based on JavaServer Pages (JSP), Java servlets, and Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) technology.
The Application Server Platform Edition is free for development, production deployment, and redistribution. For more information on redistribution, please visit http://www.sun.com/software/products/appsrvr/appsrvr_oem.xml.
Application Server Architecture
This section describes Figure 1–1, which shows the high-level architecture of the Application Server.
Figure 1–1 Application Server Architecture
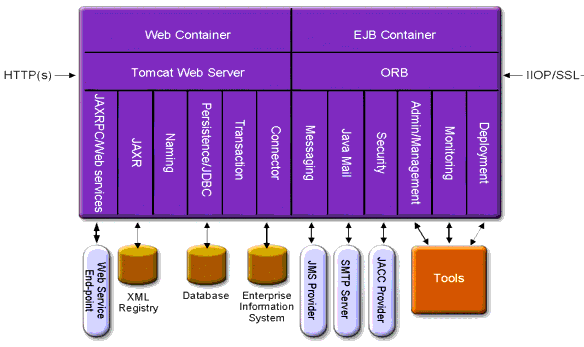
-
Containers - A container is a runtime environment that provides services such as security and transaction management to J2EE components. Figure 1–1 shows the two types of J2EE containers: Web and EJB. Web components, such as JSP pages and servlets, run within the Web container. Enterprise beans, the components of EJB technology, run within the EJB container.
-
Client Access - At runtime, browser clients access Web applications by communicating with the Web server via HTTP, the protocol used throughout the internet. The HTTPS protocol is for applications that require secure communication. Enterprise bean clients communicate with the Object Request Broker (ORB) through the IIOP or IIOP/SSL (secure) protocols. The Application Server has separate listeners for the HTTP, HTTPS, IIOP, and IIOP/SSL protocols. Each listener has exclusive use of a specific port number.
-
Web Services - On the J2EE platform, it is possible to deploy a Web application that provides a Web service implemented by Java API for XML-Based RPC (JAX-RPC). A J2EE application or component can also be a client to other Web services. Applications access XML registries through the Java API for XML Registries (JAXR).
-
Services for Applications - The J2EE platform was designed so that the containers provide services for applications. Figure 1–1 shows the following services:
-
Naming - A naming and directory service binds objects to names. A J2EE application locates an object by looking up its JNDI name. JNDI stands for the Java Naming and Directory Interface API.
-
Security - The Java Authorization Contract for Containers (JACC) is a set of security contracts defined for the J2EE containers. Based on the client’s identity, the containers restrict access to the container’s resources and services.
-
-
Transaction management - A transaction is an indivisible unit of work. For example, transferring funds between bank accounts is a transaction. A transaction management service ensures that a transaction either completes fully or is rolled back.
Access to External Systems
The J2EE platform enables applications to access systems that are outside of the application server. Applications connect to these systems through objects called resources. One of the responsibilities of an administrator is resource configuration. The J2EE platform enables access to external systems through the following APIs and components:
-
JDBC - A database management system (DBMS) provides facilities for storing, organizing, and retrieving data. Most business applications store data in relational databases, which applications access via the JDBC API. The information in databases is often described as persistent because it is saved on disk and exists after the application ends. The Application Server bundle includes the PointBase DBMS.
-
Messaging - Messaging is a method of communication between software components or applications. A messaging client sends messages to, and receives messages from, any other client. Applications access the messaging provider through the Java Messaging Service (JMS) API. The Application Server includes a JMS provider.
-
Connector - The J2EE Connector architecture enables integration between J2EE applications and existing Enterprise Information Systems (EIS). An application accesses an EIS through a portable J2EE component called a connector or resource adapter.
-
JavaMail - Through the JavaMail API, applications connect to an SMTP server in order to send and receive email.
-
Server Administration -The lower right-hand corner of Figure 1-1 shows some of the tasks performed by the administrator of the Application Server. For example, an administrator deploys (installs) applications and monitors the server’s performance. These tasks are performed with the administration tools provided by the Application Server.
See Also:
Tools for Administration
Admin Console
The Admin Console is a browser-based tool that features an easy-to-navigate interface and online help. This manual provides step-by-step instructions for using the Admin Console. The administration server must be running to use the Admin Console.
When the Application Server was installed, you chose a port number for the server, or used the default port of 4848. You also specified a user name and master password.
To start the Admin Console, in a web browser type:
http://hostname:port |
For example:
http://kindness.sun.com:4848 |
If the Admin Console is running on the machine on which the Application Server was installed, specify localhost for the host name.
On Windows, start the Application Server Admin Console from the Start menu.
The installation program creates the default administrative domain (named domain1) with the default port number 4848, as well as an instance separate from the domain administration server (DAS). After installation, additional administration domains can be created. Each domain has its own domain administration server, which has a unique port number. When specifying the URL for the Admin Console, be sure to use the port number for the domain to be administered.
asadmin Utility
The asadmin utility is a command-line tool. Use the asadmin utility and the commands associated with it to perform the same set of tasks that can be performed in the Admin Console. For example, start and stop domains, configure the server, and deploy applications.
Use these commands either from a command prompt in the shell, or call them from other scripts and programs. Use these commands to automate repetitive administration tasks.
To start the asadmin utility:
$ asadmin |
To list the commands available within asadmin:
asadmin> help |
It is also possible to issue an asadmin command at the shell’s command prompt:
$ asadmin help |
To view a command’s syntax and examples, type help followed by the command name. For example:
asadmin> help create-jdbc-resource |
The asadmin help information for a given command displays the UNIX man page of the command. These man pages are also available in HTML format.
Application Server Management Extension (AMX)
The Application Server Management eXtension is an API that exposes all of the Application Server configuration and monitoring JMX managed beans as easy-to-use client-side dynamic proxies implementing the AMX interfaces.
For more information on using the Application Server Management Extension, see the JMX chapter in the Application Server Developer's Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
