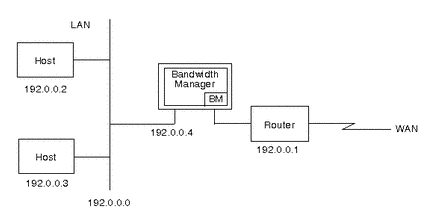
IP-Transparent Mode
On a host that is between a LAN and a router, run Solaris Bandwidth Manager in IP-transparent mode.
This mode is called IP-transparent because the host running Solaris Bandwidth Manager is completely transparent to the IP network and is perceived as just another machine connected to the LAN. The LAN and the WAN behave as though they are directly connected through the router only. It is not necessary to modify the routing tables.
Figure 2-4 Network Configuration Without Solaris Bandwidth Manager
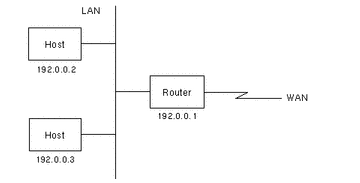
Figure 2-5 Network Configuration--IP-Transparent Mode
Kernel Architecture
The Kernel contains three modules which receive, filter, classify, schedule and forward the packets between the LAN and the router. The logical flow of data in IP-transparent mode is shown by the dashed lines in Figure 2-6.
|
ipqos1 |
implemented into the IP stack by autopush.ba and autopush_usr.ba during system startup. This module monitors the packets arriving at the host from the LAN but only processes packets addressed to the host machine. |
|
ipqos2 |
implemented when the policy agent is started. This module monitors the packets arriving at the host from the LAN, and is used to filter and distribute them within the kernel. |
|
ipqos3 |
implemented when the policy agent is started. This module interface monitors the packets arriving at the host from the LAN or WAN and classifies and schedules them. The classes for the configuration file are stored in this module. |
Traffic Flow From the LAN
Traffic from the LAN to the host running Solaris Bandwidth Manager is received by the LAN interface.
If the destination IP address of the packet is the host running Solaris Bandwidth Manager it is dropped by ipqos2 as it will have already been sent up the IP stack by ipqos1.
If the destination IP address of the packet is not the host running Solaris Bandwidth Manager then the packet is forwarded directly to the router in the following cases:
-
the IP packet is addressed to the router
-
the packet is not an IP packet and non-IP mode is set to direct in the configuration file
-
it is a multicast packet and multicast mode is set to direct
Otherwise, the packet will be classifed and scheduled by ipqos3.
Traffic Flow From the WAN
Traffic from the WAN is forwarded to the LAN via ipqos3 and ipqos2.
-
ipqos3. Packets are not classified and scheduled in the following circumstances:
-
if ipqos3 is not configured for regulating incoming traffic
-
the multicast parameter is set to direct
-
the packet is not an IP packet and non-IP mode is set to direct
-
-
ipqos2. This module checks the destination IP address. If the packet is addressed to the host running Solaris Bandwidth Manager, it is sent up the IP stack, via ipqos1. Otherwise it is forwarded to its destination.
Figure 2-6 Traffic Flow in IP-Transparent Mode
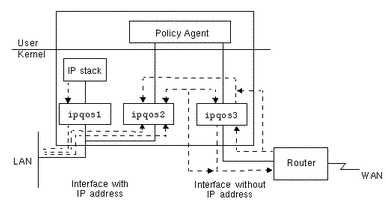
Only ipqos3 can be configured via the configuration file so any reference to the interface in this file must be the WAN interface. Configure the network device option in the configuration file to reference the LAN interface in one of the following ways:
-
by editing the network keyword in the interface section of the configuration file
-
using the Configuration Interface window of batool.
Non-IP Packets
Non-IP traffic bypasses ipqos if the nonip_mode parameter is set to direct. These packets are not logged in the flow statistics. If set to ipqos, the traffic is sent to the default class, or the root class if no default class is configured.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
