Chapter 9 Name Service Administration
Note -
This chapter discusses the alternatives available for the resolution of the name of the Netra Proxy Cache Server or Array. This name service resolution is independent of the activity of the Domain Name Service (DNS) within a Netra Proxy Cache Array.
The Netra Proxy Cache Server uses a name service whenever a URL is processed: the host name part of a URL is mapped to its address.
Every machine on a network, including the Internet, must have a unique identifier to distinguish itself from other machines on the network. Thus, every machine is given a host address. A host address has the form 129.144.79.5, where each of the four numbers separated by periods can be in the range of 0 to 255. Each machine is also given a host name that is associated with its host address. Users generally use a host name, such as stimpy.comedy.tv.net, to access a specific machine on a given network.
The process by which a host name is translated to its host address is called name resolution. It is usually performed by a name service.
Name Services Used by the Netra Proxy Cache Server
The Netra Proxy Cache Server can use three types of name services:
-
DNS: Translation is provided by a DNS server
-
Local name service: Translation is done locally (by looking up the name in a file)
-
Network Information Service (NIS): Translation is done by an NIS server (running on another host)
The Netra Proxy Cache Server can use any or all of the name services at the same time. If more than one name service is used, they are interrogated in the following order: local name service, NIS, DNS. For example, suppose the Netra server is configured to use the local name service and DNS. When a name service query is made, the server attempts name resolution by looking up the host name in the local database first. If the host name is found, the server returns the host address. If not, the query is passed to the DNS server. If the DNS server resolves the query, it returns the information, otherwise it returns "not found."
Domain Name Service Background
DNS gives different groups responsibility for subsets of names. Each subset or level is called a domain. At the top level of the DNS hierarchy are a small number of large domains, such as com (for commercial organizations). Individual organizations set up their own domains within these domains (sun.com, oracle.com, stanford.edu). Domains, in turn, can have subdomains. Contact your ISP for a domain name, which they can register for a fee.
The host name of a system, together with its full domain specification, makes up a complete DNS name. For example, Figure 9-1 shows such a DNS name: ren.comedy.tv.net. The machine ren is a node residing in the subdomain comedy within the domain tv, which is in the domain net.
Figure 9-1 Example of DNS Domains
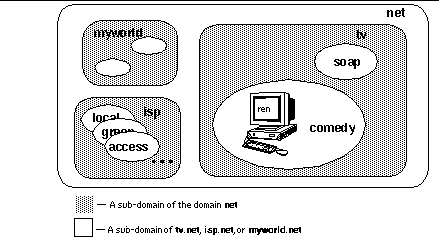
Every domain has two or more systems that keep a database of DNS names for that domain. These systems also contain the DNS names of the subdomains, unless this responsibility is delegated to systems in the subdomain. Thus, there are several systems that contain the database for the domain net. In that database, there is a delegation entry pointing to a system that keeps the database for tv. The DNS database for tv contains entries for delegating the domains soap and comedy. The database for comedy contains the host address for ren.
The DNS system of resolving names is strictly hierarchical. Using the previous example, the system that acts as the DNS server for the domain tv translates a host name to a host address only if that host name exists directly within the domain. All other host names are forwarded to the appropriate sub-domain for resolution. (Thus, the name ren.comedy.tv.net is forwarded from tv's DNS server to the DNS server for the subdomain tv for resolution.
Options for Resolving Names
Using DNS to Resolve Names
To enable the use of DNS to resolve host names, the IP addresses of on or more DNS servers must be provided to the Netra Proxy Cache Server.
Local Name Service
The Netra Proxy Cache Server can use a local name service to resolve host names. In this case, the Netra server contains a list of host-name-to-host-address mappings for its own use. Unlike hostname/address pairs in a DNS database, the mappings specified by the local name service are only available to applications running on the Netra server. Information entered in the local database is automatically available to programs running locally.
Network Information Service
NIS provides name services and other information, such as users on the network, for a local network. If there is a NIS server on the network, use the Netra Name Service module to configure the Netra server to use NIS. This means that it uses NIS to resolve host names, host addresses and host aliases.
Name Service Procedures
DNS Administration
To Configure the Netra Server to Use DNS
-
Choose Network Services Administration: Name Service DNS (Domain Name System) Configure DNS Resolver.
The DNS Administration page is displayed.
-
Type the information in the form using Table 9-1.
Table 9-1 DNS Client InformationDNS Domain Name
The DNS domain that is used to resolve partially qualified host names. Usually, this is the local domain name. Example: comedy.tv.net
Name Server 1
The host address of the DNS server that is tried first for all DNS queries. Example: 129.144.79.5
Name Server 2 (optional)
The host address of the DNS server to use, if the first name server is unreachable. Example: 129.144.79.6
Name Server 3 (optional)
The host address of the DNS server to use, if the first two name servers are unreachable. Example: 129.144.102.6
To Modify DNS Resolver Configuration
-
Choose Network Services Administration: Name Service DNS (Domain Name System) Modify DNS resolver.
The DNS Administration page is displayed.
-
Make the changes in the form using Table 9-1.
To Delete A DNS Configuration
-
Choose Network Services Administration: Name Service DNS (Domain Name System) Delete DNS resolver.
The Delete DNS Administration page is displayed.
-
Click OK to confirm the operation.
Local Name Server Administration
To Configure the Netra Server to Use a Local Name Server
-
Choose Network Services Administration: Name Service Local Name Service.
The Local Name Service Administration page is displayed.
-
Type the information in the form using Table 9-2.
Table 9-2 Host Name and AddressHost Addresses/ Host Names/ Aliases
The host addresses and corresponding host names and aliases. The host names may be partially or fully qualified to be compatible with other name services. However, this database only resolves host names that have an exact match in the database. Example: stimpy only matches stimpy, not
stimpy.comedy.tv.net. Maximum 2000 records.
NIS Administration
To Configure the Netra Server to Use NIS to Resolve Names
-
Choose Network Services Administration: Name Service NIS (Network Information Name Service).
The NIS Administration page is displayed.
-
Type the information in the form using Table 9-3.
Table 9-3 NIS Domain NameNIS Domain Name
The NIS domain in which the Netra server resides.
To Modify or Unconfigure an NIS Domain Name
Note -
The Modify and Unconfigure options are only displayed when the Netra server is configured as an NIS client.
-
Choose Network Service Administration: Name Service NIS (Network Information Name Service).
-
Choose one of the following:
-
To modify an NIS domain name, choose Modify, type a new NIS domain name, and confirm the operation.
-
To unconfigure an NIS domain name, choose Unconfigure NIS, and confirm the operation. The Netra server no longer uses NIS to resolve host names, and the NIS domain name is ignored.
Note -You must reboot the server if you make changes to your NIS configuration.
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
