Task Page
A task page is also called a form. There are two types of forms: regular and special.
Regular forms provide the only way to change the system state. When a form is displayed, the values in the fields are either the current operating or default conditions. Information is entered into a regular form by typing it into the text boxes or by selecting the radio button options.
Regular forms have an OK button. If information is entered or changed in the form, then the OK button must be clicked to save or activate the changes, and hence change the system state.
Some forms also have a Reset button. To discard the changes, use the Reset button to return fields to their previous conditions.
The user-input elements in a form are described in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 User-Input Elements|
Element |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Text Box |
Accepts one line of text input. |
|
Text Area |
Accepts multiple lines of text input. |
|
Radio Buttons |
A group of one or more buttons, only one of which can be chosen. Click on a radio button to choose it. This de-selects any other chosen radio button in its group. The only way to de-select a radio button is to choose another one. |
|
Check Box |
Selects an option. Click on the button to change its state. |
|
Pop-up Menu |
A list of options displayed in a menu. Only one option can be chosen. The chosen item is shown. Click and hold on the menu to display the list of options. Release over a new option to choose it. |
|
Scrolling List |
A list of options displayed in a window. Click on an option to choose it. Scrolling lists permit multiple selections. |
Figure 2-2 shows a form for the Host Access module.
Figure 2-2 Task Page/Form
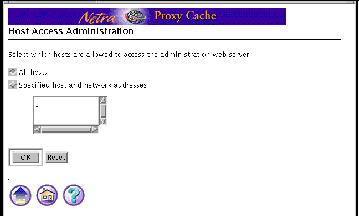
Special forms are based on regular forms. There are two types of special forms: an error form and a verify form.
-
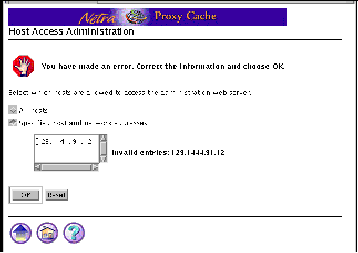
An error form, or error page, does not change the system state. It displays an Error icon, and enables the user to correct the error and re-type information in the form. Errors are marked on the form, alongside the relevant field.
Figure 2-3 shows an error form for the Host Access module.
Figure 2-3 Error Form
Note -
If the information typed into a form produces an error, the system state is not changed. The form is redisplayed with the erroneous data. The data must be corrected.
-
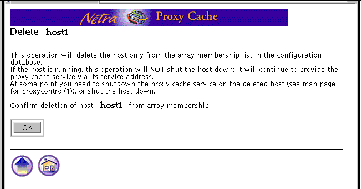
A verify form is used only to confirm a previous choice.
Figure 2-4 shows a verify form for the deleting an array member from a Netra Proxy Cache Array.
Figure 2-4 Verify Form
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
