Organization of the Compiler
The C compilation system consists of a compiler, an assembler, and a link editor. The cc command invokes each of these components automatically unless you use command-line options to specify otherwise.
Chapter 2, cc Compiler Options," discusses all the options available with cc.
The following figure shows the organization of the C compilation system.
Figure 1-1 Organization of the C Compilation System
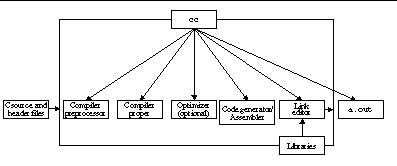
The following table summarizes the components of the compilation system.
Table 1-1 Components of the C Compilation System|
Component |
Description |
Notes on Use |
|---|---|---|
| cpp |
Preprocessor | -Xs |
| acomp |
Compiler (preprocessor built in for non-Xs modes) |
|
| iropt |
Code optimizer |
(SPARC) -O, -xO [2-5], -fast |
| cg386 |
Intermediate language translator |
(Intel) Always invoked |
| inline |
Inline expansion of assembly language templates |
.il file specified |
| mwinline |
Automatic inline expansion of functions |
(Intel) -xO4, -xinline |
| fbe |
Assembler |
|
| cg |
Code generator, inliner, assembler |
(SPARC) |
| codegen |
Code generator |
(Intel) |
| ld |
Linker |
|
| ild |
Incremental linker |
(SPARC) -g, -xildon |
The C compiler optimizer removes redundancies, optimally allocates registers, schedules instructions, and reorganizes code. Select from multiple levels of optimization to obtain the best balance between application speed and use of memory.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
