Chapter 5 Browsing the Directory Through the Web Gateway
The Web Gateway provides an interface to a Sun Directory Services directory from any web browser. You can view the directory, search for and read entries, and modify some directory information. This is useful for checking information in the directory, but it is a general-purpose tool and should not be used in place of Deja.
The Web Gateway requires that the gateway daemon, dswebd, and the directory services daemon, dsservd, are running on the server that holds the directory. If they are not, start them as described in "Starting the dsservd and dswebd Daemons".
The Web Gateway is configured by modifying the configuration files on the directory server. See the Sun Directory Services 3.1 Administration Guide for information.
Displaying the Web Gateway
From any machine, open the following URL is a web browser:
http://server:webgwport/ |
Where server is the name of a directory server running the dsservd and dswebd daemons and webgwport is the port used by dswebd. The default port is 1760.
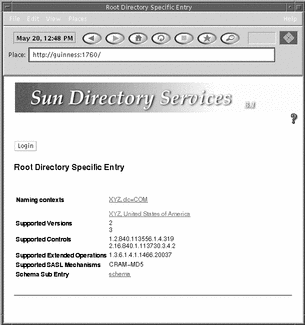
The Root Directory Specific Entry page is displayed. See Figure 5-1.
It shows the root directory specific entry in the data store to which you are connected. If the data store holds several naming contexts, several entries are listed, sorted by object class. By default there are two naming contexts defined, o=xyz,c=us and dc=xyz,dc=us. Each entry is a hot link to a search facility that enables you to browse the naming context.
Figure 5-1 Web Gateway Root Directory Specific Entry
Browsing the Directory
-
Click a hotlink for a naming context.
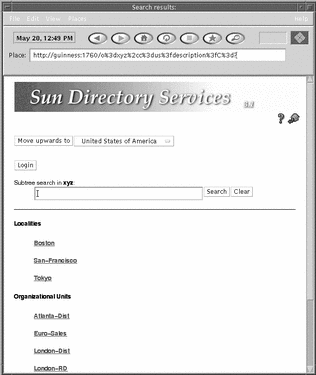
Your browser displays a search page, as shown in Figure 5-2.
The search page shows the root entry for the naming context; in Figure 5-2 this entry is o=XYZ, c=US.
Figure 5-2 Browsing the Directory
-
Specify the top of the subtree you want to browse.
Use the Move upwards control to move up the directory tree hierarchy. At each position, the naming context list shows you the parent naming context and any child naming contexts. Choose the naming context you want to browse. The top entry in that naming context becomes the currently-selected entry.
-
Click on the Browse the Directory button.
The child entries of the currently-selected entry are listed. To see the contents of any entry, click on the link for that entry.
Searching the Directory
-
Specify the top of the subtree you want to browse.
Use the Move upwards control to move up the directory tree hierarchy. At each position, the naming context list shows you the parent naming context and any child naming contexts. Choose the naming context you want to browse. The top entry in that naming context becomes the currently-selected entry.
-
Enter the search string in the Subtree search field and click on the Search button.
The search string can be an attribute value, or a valid LDAP filter. See Table 2-1.
After a short delay, a list of entries that match the search string is displayed, up to the limit configured for the gateway. See the Sun Directory Services 3.1 Administration Guide for information. Click on an entry to see the attributes it contains.
Figure 5-3 Search Results Page
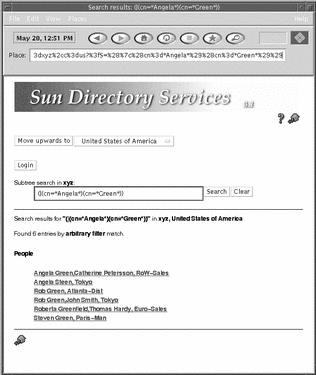
By default, a search at the upper levels of the directory tree (root or country level) is a one-level search, that is, only child entries of the currently selected entry is searched and the target of the search is assumed to be a country, organization or locality entry. In the rest of the directory tree, a search is a subtree search and the target is assumed to be a entry relating to a person. This search strategy is configured in the file dswebfilter.conf. See the dswebfilter.conf(4) manpage for information.
Reading a Directory Entry
For any entry, you have the option of viewing all the attributes and their values. Use the View All Attributes button to show all the attributes and values assigned to the entry.
Some attributes are handled in a special way:
-
An attribute's value that is a distinguished name (DN) is a hotlink to the entry identified by the DN.
-
An attribute containing an email address is a hotlink to a mailer to send mail to that address.
-
An attribute containing an URL is a hotlink to the target of the URL.
-
A photograph or other image is either displayed as an inline image or can be downloaded by clicking on a hotlink. The display format depends on your browser.
-
Audio data is retrieved by clicking on a hotlink.
Modifying a Directory Entry
To modify an entry you must bind to the directory, supplying your distinguished name and password. Not all attributes can be modified using the Web Gateway. To modify an attribute of an entry:
-
Display the entry that you want to modify.
At the end of the attribute list there is a Modify Attributes button. Depending on the configuration of your Web Gateway, there may also be buttons for modifying specific attributes.
-
Click on the button for modifying the attribute you want to change, or click on the Modify Attributes button.
If you are not logged in, an authentication request window is displayed. See "Authentication" for information. Enter your distinguished name and password.
The access controls defined for the entry will determine whether you are permitted to modify any attributes in the entry.
-
Supply a new value for the attribute you want to modify.
-
When you have finished modifying the entry, click the Apply button.
Authentication
Login Button
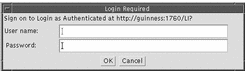
The Login Button provides a means of logging in for the duration of your connection to the directory. The login button grants the access rights specified in the access control rules on the directory server. Click the Login button to display a login request window. See Figure 5-4.
Type your user name and password and click OK.
If there are more than one entry in the directory with the attribute uid matching the user name, the login fails.
Figure 5-4 Login Request Window
To logout, click the logout button.
The access priviledges are cleared.
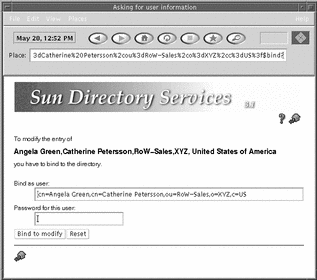
Authentication Request Window
If you are not logged in, and you try to modify the directory contents, you will get an authentication request. This authentication is for the current modify operation only. You will have to authenticate for each subsequent modification. The bind DN is supplied pre-filled.
Type your password and click the Bind to Modify button.
The password is checked against the password stored in the directory. If the access control rules deny you modification rights to the entry you are modifying, the authentication fails. See Figure 5-5.
Figure 5-5 Authentication Request Page
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
