Two-Tier Service Architecture
For some applications, especially existing services, a two-tier architecture for access via Sun Internet Administrator is more practical. These services can be managed from Sun Internet Administrator, but do not receive the security benefits of single sign-on and central logging (though they can do their own logging in syslog).
Figure 1-6 Two-Tier ISP Service Architecture
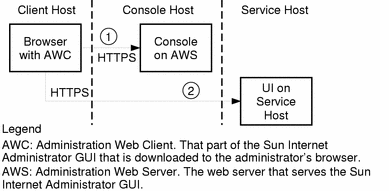
As shown in Figure 1-6, an administrator uses the following steps to access a service's administration functions:
-
From a browser, the administrator accesses either http://<hostname>:50080/ispmc or https://<hostname>:50087/ispmc (the location of the main Sun Internet Administrator GUI page).
This step is the same as for the three-tier architecture. The AWC is downloaded to the client browser, where the administrator can choose a service to manage.
The selected service resolves to a URL, designating the component's user interface.
-
Subsequent access is directly between the client browser and the service's remote agent. Appropriate IP-level security measures should be taken to protect this connection and its traffic.
In a two-tier architecture, services are not able to take advantage of the single sign-on feature. If a two-tier web-based application uses Sun WebServer to support its user interface, it can configure the web server to provide the same service-level access protection as a three-tier application enjoys. See Chapter 7, Integrating Existing Service Applications for information on this configuration.
To secure the communications for a two-tier application, we recommend using SSL or SunScreen SKIP.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
