2.2.2 Establishing Names and Naming Conventions
Before configuring the cluster, you must decide on names for the following:
-
The cluster itself
-
Physical hosts
-
Logical hosts
-
Disk groups
-
Network interfaces
The network interface names (and associated IP addresses) are necessary for each logical host on each public network. Although you are not required to use a particular naming convention, the following naming conventions are used throughout the documentation and are recommended. Use the configuration worksheets included in Appendix A, Configuration Worksheets and Examples.
Cluster - As part of the configuration process, you will be prompted for the name of the cluster. You can choose any name; there are no restrictions imposed by Sun Cluster.
Physical Hosts - Physical host names are created by adding the prefix phys- to the logical host names (for physical hosts that master only one logical host each). For example, the physical host that masters a logical host named hahost1 would be named phys-hahost1 by default. There is no Sun Cluster naming convention or default for physical hosts that master more than one logical host.
If you are using DNS as your name service, do not use an underscore in your physical or logical host names. DNS will not recognize a host name containing an underscore.
Logical Hosts and Disk Groups - Logical host names can be different from disk group names in Sun Cluster. However, using the same names is the Sun Cluster convention and eases administration. Refer to "2.2.9 Planning Your Logical Host Configuration", for more information.
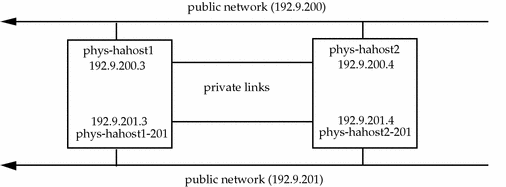
Public Network - The names by which physical hosts are known on the public network are their primary physical host names. The names by which physical hosts are known on a secondary public network are their secondary physical host names. Assign these names using the following conventions, as illustrated in Figure 2-1:
-
For the primary physical host names, simply use the physical host names as described previously; for example, phys-hahost1 would be used for a physical host associated with logical host hahost1.
-
For the secondary physical host names, start with the physical host name and add a suffix indicating the secondary network address. For example, the connection to a secondary network with a network address 192.9.201 from physical host phys-hahost1 would be named phys-hahost1-201.
Note -
The primary physical host name should be the node name returned by uname -n.
Private Interconnect - There is no default naming convention for the private interconnect.
Naming convention examples are illustrated in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1 Public and Private Network Naming Conventions
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
