Sequence of Events in a WAN Boot Installation
Figure 9–1 shows the basic sequence of events in a WAN boot installation. In this figure, a SPARC based client retrieves configuration data and installation files from a web server and an install server over a WAN.
Figure 9–1 Sequence of Events in a WAN Boot Installation
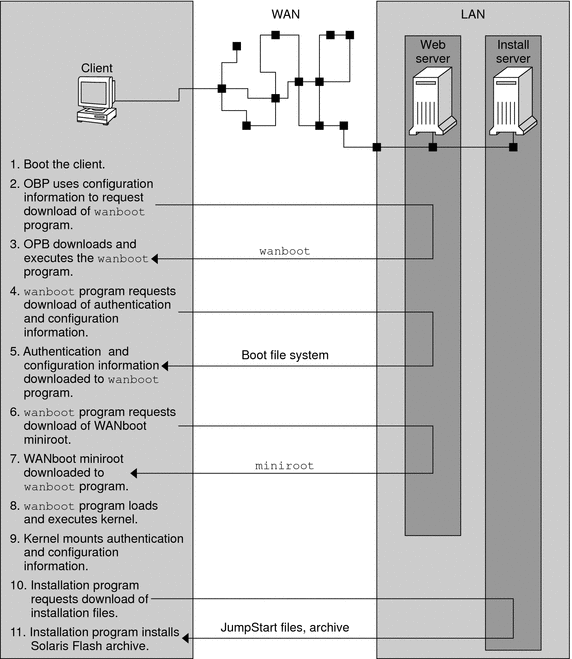
-
You boot the client in one of the following ways.
-
Boot from the network by setting network interface variables in the Open Boot PROM (OBP).
-
Boot from the network with the DHCP option.
-
Boot from a local CD-ROM.
-
-
The client OBP obtains configuration information from one of the following sources.
-
From boot argument values that are typed at the command line by the user
-
From the DHCP server, if the network uses DHCP
-
-
The client OBP requests the WAN boot second level boot program (wanboot).
The client OBP downloads the wanboot program from the following sources.
-
From a special web server, called the WAN boot server, by using the Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
-
From a local CD-ROM (not shown in the figure)
-
-
The wanboot program requests the client configuration information from the WAN boot server.
-
The wanboot program downloads configuration files that are transmitted by the wanboot-cgi program from the WAN boot server. The configuration files are transmitted to the client as the WAN boot file system.
-
The wanboot program requests the download of the WAN boot miniroot from the WAN boot server.
-
The wanboot program downloads the WAN boot miniroot from the WAN boot server by using HTTP or secure HTTP.
-
The wanboot program loads and executes the UNIX kernel from the WAN boot miniroot.
-
The UNIX kernel locates and mounts the WAN boot file system for use by the Solaris installation program.
-
The installation program requests the download of a Solaris Flash archive and custom JumpStart files from an install server.
The installation program downloads the archive and custom JumpStart files over an HTTP or HTTPS connection.
-
The installation program performs a custom JumpStart installation to install the Solaris Flash archive on the client.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
