Chapter 4 Discovering Manageable Servers
This chapter describes the ways to discover a manageable server using the N1 System Manager, how to choose which method of discovery use, and what level of service to expect from the N1 System Manager for a managed server, based on how the server was discovered.
To manage servers with the N1 System Manager, you must first allow the N1 System Manager to discover the manageable servers. Before the N1 System Manager discovers a server, the server is referred to as a manageable server. After it has been discovered, the server becomes a managed server.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Choosing a Method of Discovery
This section describes how to choose which method of discovery is best for your installation. The method you choose is related to how you have cabled and configured the N1 System Manager environment. For details on the configuration of the management network, see Sun N1 System Manager Connection Information in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Note –
If your installation provides only a management network, or only a provisioning network, the N1 System Manager must operate in restricted mode. See Restricted Mode Capabilities for details.
The types of discovery available in this version of the N1 System Manager are as follows:
- SP-Based Discovery
-
Discovery of a manageable server through its Service Processor (SP). Choose this method of discovery if you want the N1 System Manager to be able to completely manage and monitor servers. Also, choose this method of discovery if your data center configuration allows the N1 System Manager to connect to both the provisioning and management networks.
See SP-Based Discovery for details about this method of discovery.
- OS-Based Discovery
-
Discovery of a manageable server using its operating system (OS). Choose this method of discovery for servers that are already running a supported OS.
If you require full manageability of servers, do not choose this method of discovery, because the N1 System Manager must run in restricted mode as described in Restricted Mode Capabilities. Consider configuring your data center's N1 System Manager installation so that the management server is connected to both the provisioning and management networks, which allows SP-based discovery to be used.
See OS-Based Discovery for details about this method of discovery.
- Manual Discovery
-
Discovery of a manageable server manually, using its MAC address and model name. Choose this method if you want to discover servers that satisfy the following conditions:
-
The server does not have an installed OS.
-
You cannot access the server's service processor and are therefore unable to use SP-based discovery.
-
The server hardware appears in the supported hardware list. See Manageable Server Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
This method of discovery is useful if your data center configuration does not allow the N1 System Manager to connect to the management network. If you require full manageability of servers, do not choose this method of discovery, because the N1 System Manager must run in restricted mode as described in Restricted Mode Capabilities.
See Manual Discovery for details about this method of discovery.
-
Note –
Once you have used the N1 System Manager to discover manageable servers, rehosting of the management server is not supported.
For details on rehosting, see Management Server Rehosting in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
The procedures in this chapter focus on discovery of manageable servers using the command line. You can also use browser interface, or a special Discovery wizard. For information about how to use the browser interface, see the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help. The wizard help is separate from the main online help, as shown in the following figure.

Capability of Managed Servers Based on Discovery
Depending on how a server was discovered, some features are not be available. The following table shows the features of the N1 System Manager that are available for a managed server once it is discovered.
Table 4–1 Capabilities of a Managed Server Based on Discovery Method
The features that are available for a managed server are displayed in the managed server's Capabilities table. The Capabilities table is available in the Server Details page in the browser interface or by using the show server command.
Restricted Mode Capabilities
If your data center configuration does not allow the N1 System Manager to connect to both the management network and the provisioning network, the N1 System Manager operates in restricted mode.
The restricted mode is related to the privileges associated with the role of N1 System Manager users. Depending on how the N1 System Manager is configured, the administrator should assign the appropriate restricted mode role to users.
-
If the N1 System Manager is configured so that it only has access to the provisioning network, the administrator should assign only the ProvAdmin restricted mode role to non-root users.
-
If the N1 System Manager is configured so that it only has access to the management network, the administrator should assign only the MgmtAdmin restricted mode role to non-root users.
When the N1 System Manager is operating in restricted mode, users should be assigned only those privileges associated with the ProvAdmin or MgmtAdmin restricted mode roles, depending on the configuration. The ProvAdmin and MgmtAdmin restricted mode roles have been created specifically for the N1 System Manager's restricted mode of operation. It is possible to delete or modify the ProvAdmin and MgmtAdmin roles. Any custom roles you create should conform to the privilege set included in the ProvAdmin and MgmtAdmin roles, for stable performance of the product in restricted mode.
For information about roles, see Introduction to User Security.
Some N1 System Manager functions are not available based on whether your restricted mode installation has access to a management network only, or a provisioning network only. The following table lists all the commands that are valid for each restricted installation mode. If your installation provides only a management network, then only those items marked X in the management network column are available in the restricted mode. If you have only a provisioning network, then only those items marked X in the provisioning network column are available in the restricted installation mode.
Table 4–2 Restricted Mode Command Map|
Command |
Management Network |
Provisioning Network |
|---|---|---|
|
add group |
X |
X |
|
add osprofile |
- |
X |
|
add server feature |
- |
X |
|
add role |
X |
X |
|
add user |
X |
X |
|
connect |
X |
- |
|
create firmware |
X |
- |
|
create group |
X |
X |
|
create notification |
X |
X |
|
create os |
- |
X |
|
create osprofile |
- |
X |
|
create update |
- |
X |
|
create role |
X |
X |
|
delete firmware |
X |
- |
|
delete group |
X |
X |
|
delete job |
X |
X |
|
delete notification |
X |
X |
|
delete os |
- |
X |
|
delete osprofile |
- |
X |
|
delete server |
X |
X |
|
delete update |
- |
X |
|
discover |
X |
X |
|
exit |
X |
X |
|
help |
X |
X |
|
load server firmware |
X |
- |
|
load group firmware |
X |
- |
|
load server osprofile |
- |
X |
|
load group osprofile |
- |
X |
|
load server update |
- |
X |
|
load group update |
- |
X |
|
remove group |
X |
X |
|
remove osprofile |
- |
X |
|
remove server |
X |
X |
|
reset |
X |
X |
|
set firmware |
X |
- |
|
set group |
X |
X |
|
set notification |
X |
X |
|
set os |
- |
X |
|
set osprofile |
- |
X |
|
set role |
X |
X |
|
set server agent SSH |
- |
X |
|
set server SSH |
X |
- |
|
set server filesystem threshold |
- |
X |
|
set server IP |
X |
- |
|
set server IPMI |
X |
- |
|
set server locator |
X |
- |
|
set server monitored |
X |
X |
|
set server |
X |
X |
|
set server name |
X |
X |
|
set server note |
X |
X |
|
set server refresh |
X |
X |
|
set session |
X |
X |
|
set user |
X |
X |
|
show firmware |
X |
X |
|
show os |
- |
X |
|
show osprofile |
- |
X |
|
show update |
- |
X |
|
show group |
X |
X |
|
show job |
X |
X |
|
show log |
X |
X |
|
show privilege |
X |
X |
|
show notification |
X |
X |
|
show role |
X |
X |
|
show server |
X |
X |
|
show session |
X |
X |
|
show user |
X |
X |
|
start group command |
- |
X |
|
start server command |
- |
X |
|
start group |
X |
- |
|
start server |
X |
- |
|
stop job |
X |
X |
|
stop notification |
X |
X |
|
unload server |
- |
X |
|
unload group |
- |
X |
SP-Based Discovery
This section describes how to use the N1 System Manager to discover a server through the service processor (SP).
The SP-based discovery of manageable servers is possible if your data center configuration allows the N1 System Manager to connect to both the provisioning and management networks. For details on the configuration of provisioning and management networks, see Sun N1 System Manager Connection Information in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide. In addition, servers discovered by their service processors must be fully supported by the N1 System Manager. For a list of supported hardware and software, see Sun N1 System Manager Hardware and OS Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Using SP-based discovery, you can discover a manageable server through its management network interface (management IP address). After the server is discovered, you can change the management IP address using the set server command with the ip configuration attribute.
The IP address of the server's system controller or service processor must be assigned as a prerequisite for SP-based discovery. Initiate SP-based discovery of multiple servers by specifying a range of IP addresses to search for servers.
Hardware Requirements for SP-Based Discovery
For SP-based discovery to work, manageable servers must comply with the revisions of firmware listed in Manageable Server Firmware Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide. See Managing Firmware Updates (Tasks) in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide for instructions, or refer to Sun System Handbook documentation for your server.
SP-based discovery uses a Service Access Point (SAP) to access server capabilities. A SAP is generically defined as an IP address, protocol, and security credentials. Each hardware platform requires a minimum set of credentials to be discovered. If you do not specify the correct credentials such as Secure Shell (SSH) and Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) accounts and passwords, the discovery process assumes that the default credentials are configured on the manageable servers. For details about default credentials for each hardware type, see Setting Up Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Note –
Automatic configuration of credentials is supported for Sun Fire V20z and V40z servers and X4000 series servers, if they are in the factory default state. See Setting Up Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
If you do specify the login accounts and passwords, the SP-based discovery process configures the credentials you specify. If only one credential is specified, the missing credentials are configured with one of the defaults specified in Setting Up Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
If you want to disable autoconfiguration, add the following line to the /etc/opt/sun/n1gc/hal.properties file before you run SP-based discovery:
initialize=false
The N1 System Manager must be restarted for the disabling of autoconfiguration to take effect. Note that after autoconfiguration is disabled, any servers in the factory default state cannot be discovered using SP-based discovery until their SSH and IPMI accounts are configured. For further information, see Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
How to Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based Discovery
The To Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based Discovery Using the Command Line procedure shows how to use the command line to execute this task. You can also use the browser interface to execute this task. Use the discover button in the Servers table to call the Discover Servers wizard. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
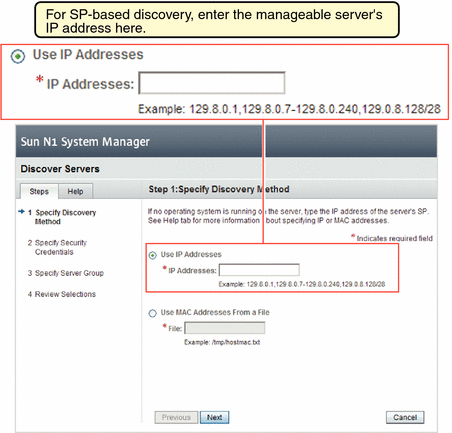
As shown by Table 2–6, you cannot execute the discover command without having the JobRead privilege.
 To Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based
Discovery Using the Command Line
To Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based
Discovery Using the Command Line
Note –
Servers discovered through their SP are automatically monitored for hardware health.
Before You Begin
Before you discover a new hardware component, read Chapter 2, Sun N1 System Manager System and Network Preparation, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide for details on setting up a server for discovery.
Do not use the N1 System Manager to discover servers that have system management software installed on them such as Sun Management Center, Sun Control Station, or any other system management applications including the N1 System Manager.
Step
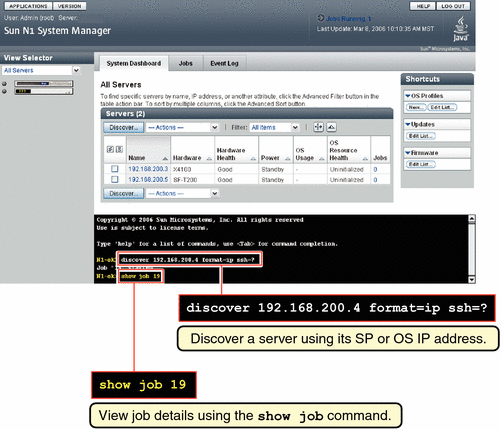
Use the discover command to discover a server through its SP.
N1-ok> discover IP,IP-IP,subnet/mask format ip [group group] [ipmi username/password] [snmp credential/credential] [ssh username/password] [telnet username/password] |
IP addresses, IP address ranges, and IP subnets can be input as a comma-separated list. Overlapping IP address ranges are allowed.
Note –
When you specify the range of IP addresses for discovery, ensure that the IP address range does not include the IP addresses of the N1 System Manager management server.
Security credentials for IPMI, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), SSH and Telnet are optional. If credentials are not specified, the manufacturer defaults are used. See Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide for information about the default accounts.
See discover in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for more details about the syntax used in the discover command.
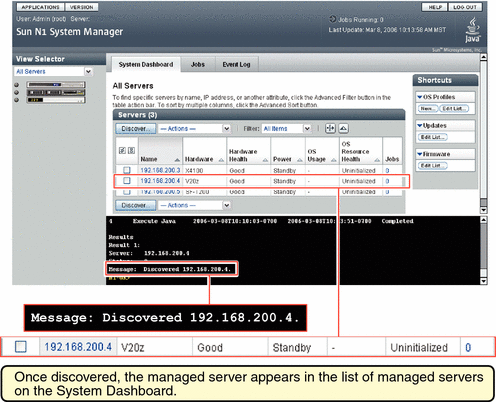
After successful completion of the Discovery job, a managed server is identified by its management name. If the server was discovered using SP-based discovery, its management name is initially set to the server's management IP address. You can rename discovered servers at any time.
Example 4–1 Using SP-based Discovery With Management Network IP Addresses
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover servers through their service processor. The servers have the following management network IP addresses: 192.168.1.1–192.168.1.3, 192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95, and 192.168.1.107.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.3,192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95,192.168.1.107 format ip group dev ssh root/admin Job 3 started. |
The group subcommand adds the successfully discovered servers into a server group called dev. The ssh option specifies the user name and password configured for access on the management port. In this example, the SSH user name root and password admin are used to authenticate the hardware discovery.
The following example command shows how to view the Discovery job and the job status.
N1-ok> show job all Job ID Date Type Status Owner 3 2005-06-28T06:53:53-0700 Discovery Completed root 2 2005-06-28T06:01:20-0700 Create OS Distribution Completed root 1 2005-06-28T05:57:14-0700 Create OS Distribution Completed root |
The following example command shows how to verify that the discovered servers were added to the server group.
N1-ok> show group all Name us Jobs Servers Spare dev 7 |
The following example command shows how to view the list of managed servers in the group and the power and hardware health status.
N1-ok> show group dev Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
Example 4–2 Using SP-Based Discovery With Netmask
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover any servers through their SP, using the netmask. The servers have management network IP addresses assigned in the 192.168.1.0/8 netmask.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.0/8 ssh root/admin Job 18 started. |
The following example shows how to view the discovered servers.
N1-ok> show server all Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.200 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.245 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.255 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
Troubleshooting
The discover command credential attributes are used for security. If used, SSH, IPMI, and Telnet require a username and a password. SNMP requires that you input a valid value for the read security community string. If credentials are not specified, the discovery process uses the default credentials that were defined during installation.
Sun Fire X4000 series servers only initialize custom accounts once. For Sun Fire X4000 series servers discovered using a username and password combination:
-
If user is root and the password supplied is not the default, and the SP root password is the default: the SP root password is changed by the N1 System Manager to the password.
-
If user is not root and if user does not exist, and the SP root password is the default: the N1 System Manager creates the new user with a password of password. The N1 System Manager also changes the root password to the password.
For information about default credentials, see Setting Up Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Discovery might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the discover command fails with an error message indicating that there are invalid credentials or SSH key changed: Cannot connect to host and no true security breach has occurred, remove the known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the managed server. Then, retry the discover command. See To Update the ssh_known_hosts File in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
The problem of stale SSH entries on the management server can be avoided if, during the n1smconfig configuration process, you modify SSH policies by accepting changed or unknown host keys. Accepting changed or unknown host keys carries a security risk but avoids the problem of stale SSH entries on the management server. For more information, see To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Discovery might fail due to a firmware version problem with drivers. See Cannot Discover a Manageable Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
The OS does not belong to the server in question if the add command fails with the following error:
Internal error: No mac address match found
Discovery can fail with the following error message:
Check the Standard Output field for possible reasons for this failure
To see the Standard Output field, check the job details in the browser interface or by using the show job command with the job number of the discovery job that failed.
See Also
Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide and Troubleshooting Discovery.
Next Steps
Open the server's serial console. To view information about accessing a server's serial console, in the Sun N1 System Manager online help, find the topic `To Open the Serial Console for a Server'.
OS-Based Discovery
This section describes how to use the N1 System Manager to discover servers through their OS. The N1 System Manager provides a limited level of support for managed servers that are discovered using OS-based discovery. For more information, see Capability of Managed Servers Based on Discovery.
Use OS-based discovery to allow the N1 System Manager to find and manage servers that have an operating system already installed, even if the manageable servers are running on a configuration where access to their service processors is not possible. For details on the configuration of provisioning and management networks, see Sun N1 System Manager Connection Information in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
To enable OS-based discovery, use the n1smconfig script. See Configuring the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide for details about running the n1smconfig script.
Note –
By default, the OS-based discovery feature is turned off.
To avoid discovering the same server more than once, do not issue the discover commands within the OS IP address space once OS-based discovery has been enabled. Only issue these commands, for example, if you have a platform itself whose service processor is not supported by the N1 System Manager, or have networking constraints that prohibit the use of a management network. For details about discovering duplicate servers, see Discovering and Identifying Duplicate Servers.
Using OS-based discovery, you can discover a manageable server through its provisioning network interface (its provisioning IP address, referred to as its OS IP address). After the server is discovered, you can change the OS IP address using the set server command with the ip configuration attribute.
Software Requirements for OS-Based Discovery
For OS-based discovery of a server, the server's OS must be supported by the N1 System Manager. All of the operating systems listed in Manageable Server Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide are supported for OS-based discovery by the N1 System Manager, with the exception of Microsoft Windows.
Note –
OS-based discovery of managed servers that run the Microsoft Windows operating system is not possible in this release.
Hardware Requirements for OS-Based Discovery
OS-based discovery for each supported operating system has been officially qualified on supported hardware models for that operating system. The hardware supported by the N1 System Manager for each OS is described in Sun N1 System Manager Hardware and OS Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
The N1 System Manager can provision an OS on a managed server that was discovered by OS-based discovery, only if that managed server and target OS combination is supported by the N1 System Manager.
How to Discover Manageable Servers Using OS-Based Discovery
The To Discover Manageable Servers Using OS-Based Discovery Using the Command Line procedure shows how to use the command line to execute the task. You can also use the browser interface to execute this procedure. Use the discover button in the Servers table to call the Discover Servers wizard. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
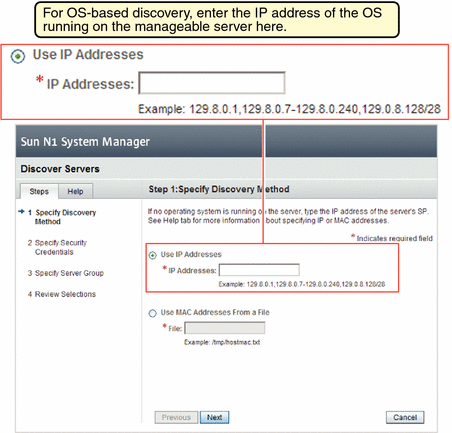
As shown by Table 2–6, you cannot execute the discover command without having the JobRead privilege.
 To Discover Manageable Servers Using OS-Based
Discovery Using the Command Line
To Discover Manageable Servers Using OS-Based
Discovery Using the Command Line
Note –
Servers discovered through their OS are not monitored for hardware health, as indicated in Table 4–1.
Before You Begin
Before you discover a new hardware component, read Chapter 2, Sun N1 System Manager System and Network Preparation, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide for details on setting up a server for discovery.
This procedure focuses on using the command line of the N1 System Manager.
The manageable server must be powered on and have a running OS before being discovered. The OS must be supported by the N1 System Manager. See Software Requirements for OS-Based Discovery for details.
Before attempting to discover a manageable server using OS-based discovery, the OS-based discovery feature must be enabled. To enable OS discovery, use the n1smconfig script. See Configuring the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide for details about running the n1smconfig script.
Do not use the N1 System Manager to discover servers that have system management software installed on them such as Sun Management Center, Sun Control Station, and any other system management applications including the N1 System Manager.
Step
Use the discover command to discover a server through its OS.
N1-ok> discover IP,IP-IP,subnet/mask [group group] ssh username/password |
IP addresses, IP address ranges, and IP subnets can be input as a comma-separated list. Overlapping IP address ranges are allowed. See Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide for information about the default accounts.
For OS-based discovery, SSH credentials should be provided. If not specified, default SSH credentials of root/admin are read.
Note –
When you specify the range of IP addresses for discovery, ensure that the IP address range does not include the IP addresses of the N1 System Manager management server.
See discover in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for more details about the syntax used in the discover command.
After successful completion of the Discovery job, a managed server is identified by its management name. If the server was discovered using OS-based discovery, its management name is initially set to the server's provisioning (or OS) IP address. You can rename discovered servers at any time.

Example 4–3 OS-based Discovery Using OS IP Addresses
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover manageable servers through their OS. The servers have the following OS (or provisioning network) IP addresses: 192.168.1.1–192.168.1.3, 192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95, and 192.168.1.107.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.3,192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95,192.168.1.107 group dev ssh root/admin Job 3 started. |
The group subcommand adds the successfully discovered servers into a server group called dev. The ssh option specifies the user name and password configured for access on the management port. In this example, the SSH user name root and password admin are used to authenticate OS-based discovery.
The following example command shows how to view the Discovery job and the job status.
N1-ok> show job all Job ID Date Type Status Owner 3 2005-06-28T06:53:53-0700 Discovery Completed root |
The following example command shows how to verify that the discovered servers were added to the server group.
N1-ok> show group all Name us Jobs Servers Spare dev 7 |
The following example command shows how to view the list of managed servers in the group and the power and hardware health status.
N1-ok> show group dev Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
The following example shows how to view the discovered servers.
N1-ok> show server all Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.200 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.245 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.255 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
Example 4–4 OS-based Discovery Using Netmask
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover any manageable servers through their OS, using the netmask. The servers have OS IP addresses assigned in the 192.168.1.0/8 netmask.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.0/8 ssh root/admin Job 18 started. |
Troubleshooting
The discover command credential attributes are used for security. SSH credentials are required for OS-based discovery. If not specified, SSH credentials or root/admin are used by the N1 System Manager.
For information about default credentials, see Setting Up Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Discovery might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the discover command fails with an error message indicating that there are invalid credentials or SSH key changed: Cannot connect to host and no true security breach has occurred, remove the known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the managed server. Then, retry the discover command. See To Update the ssh_known_hosts File in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
The problem of stale SSH entries on the management server can be avoided if, during the n1smconfig configuration process, you modify SSH policies by accepting changed or unknown host keys. Accepting changed or unknown host keys carries a security risk but avoids the problem of stale SSH entries on the management server. For more information, see To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Some commands are not supported for managed servers that were discovered through OS-based discovery. See Capability of Managed Servers Based on Discovery for details about which features are not available for managed servers that were discovered through OS-based discovery. Unsupported commands generate the following error:
Unsupported operation
This error is displayed either in the job status or immediately in the command line interface.
The OS does not belong to the server in question if the add command fails with the following error:
Internal error: No mac address match found
Discovery can fail with the following error message:
Check the Standard Output field for possible reasons for this failure
To see the Standard Output field, check the job details in the browser interface or by using the show job command with the job number of the discovery job that failed.
Discovery might fail due to a firmware version problem with drivers. See Cannot Discover a Manageable Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
See Also
Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide and Troubleshooting Discovery.
Next Steps
Open the server's serial console. To view information about accessing a server's serial console, in the Sun N1 System Manager Online Help, find the topic `To Open the Serial Console for a Server'.
Manual Discovery
Read Choosing a Method of Discovery to see if you should use this method of discovering servers.
You can manually discover servers that have no operating system installed, even if you have no access to the service processor. Servers with no OS installed are called bare metal servers.
Note –
When using the N1 System Manager to load an OS on managed servers that were discovered using manual discovery, the manualnetboot feature must be turned on. For more information, see Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
To avoid discovering the same server more than once, do not use manual discovery unless absolutely necessary. For example, unless you have a platform whose service processor is not supported by the N1 System Manager, or have networking constraints that prohibit the use of a provisioning network. For details about discovering duplicate servers, see Discovering and Identifying Duplicate Servers.
The N1 System Manager provides only a restricted level of support for managed servers that were discovered manually. For more information, see Capability of Managed Servers Based on Discovery. Consider configuring your data center's N1 System Manager installation so that the management server is connected to both the provisioning and management networks, which allows SP-based discovery to be used. For details on the configuration of provisioning and management networks, see Sun N1 System Manager Connection Information in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide. For details on the restricted mode of operation of the N1 System Manager, see Restricted Mode Capabilities.
For manual discovery, use an XML file containing MAC addresses of the server that you want to discover. The file format should be similar to the following example:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <servers> <server name="stinger1" model="V20z" guid="01234567-89ab-cdef-0123-456789abcdef"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="00:11:22:33:44:55"/> <ethernetPort name="GB_1" mac="00:11:22:33:44:56"/> </server> </servers> |
The guid attribute is optional.
In the example, the model number used is V20z, which represents a Sun Fire V20z server. See Table 4–3 for a list of recognized model numbers to be used in the file for manual discovery.
Discovering and Identifying Servers by Their Model Numbers
In the manual discovery XML file, use the appropriate model number for manageable servers that you want to discover manually. For details about this file, see Manual Discovery.
The following table shows the model numbers recognized by the N1 System Manager for manual discovery.
Table 4–3 Model Numbers for Discovering Managed Servers|
Server Type |
Model Type for Manual Discovery |
|---|---|
|
Sun Netra 240 |
NETRA-240 |
|
Sun Netra 440 |
NETRA-250 |
|
Sun Fire V210 |
SF-V210 |
|
Sun Fire V240 |
SF-V240 |
|
Sun Fire V250 |
SF-V250 |
|
Sun Fire V440 |
SF-V440 |
|
Sun Fire V490 |
SF-490 |
|
Sun Fire V890 |
SF-890 |
|
Sun Fire V20z |
V20z |
|
Sun Fire V40z |
V40z |
|
Sun Fire X2100 |
X2100 |
|
Sun Fire X4100 |
X4100 |
|
Sun Fire X4200 |
X4200 |
|
Sun Fire T1000 |
SF-T1000 |
|
Sun Fire T2000 |
SF-T2000 |
How to Discover a Manageable Server Using Manual Discovery
The To Discover a Manageable Server Using Manual Discovery Using the Command Line procedure shows how to use the command line to execute the task. You can also use the browser interface to execute this procedure. Use the discover button in the Servers table to call the Discover Servers wizard. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.

As shown by Table 2–6, you cannot execute the discover command without having the JobRead privilege.
 To Discover a Manageable Server Using Manual Discovery
Using the Command Line
To Discover a Manageable Server Using Manual Discovery
Using the Command Line
Note –
Servers discovered manually are not automatically monitored for hardware health, as indicated in Table 4–1.
Before You Begin
Before you discover a new hardware component, read Chapter 2, Sun N1 System Manager System and Network Preparation, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide for details on setting up a managed server for discovery.
The N1 System Manager can provision an OS on a managed server that was discovered by OS-based discovery, only if that managed server and target OS combination is supported by the N1 System Manager.
Note –
Manual discovery of diskless clients is not supported.
The manageable server must be powered on before being discovered.
Note –
When using the N1 System Manager to load an OS on managed servers that were discovered manually, the manualnetboot feature must be turned on. For more information, see Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
Step
Use the discover command to discover a server manually.
N1-ok> discover file format file [group group] |
The file must be a fully qualified path to an XML file, containing the manageable server's MAC address. To manually discover a group of manageable servers with one command, their MAC addresses must be specified in the same XML file.
This command makes the servers part of the same group.
See discover in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for more details about the syntax used in the discover command.
After successful completion of the Discovery job, a managed server is identified by its management name. This name is the name you provided in the XML file. You can rename discovered servers at any time.
Example 4–5 Discovering Manageable Servers Manually
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover manageable servers manually. The servers have the following MAC addresses: 00:11:22:33:44:55 and 00:11:22:33:44:77.
N1-ok> discover /net/machine1.brasil/XMLfiles/manual_disco.xml format file group group1 Job 1 started. |
The XML file contains the machine names and MAC addresses for manual discovery.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <servers> <server name="galaxy1" model="X4100" guid="01234567-89ab-cdef-0123-456789abcdff"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="00:11:22:33:44:55"/> <ethernetPort name="GB_1" mac="00:11:22:33:44:56"/> </server> <server name="galaxy2" model="X4100" guid="01234567-89ab-cdef-0123-456789abcdee"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="00:11:22:33:44:77"/> <ethernetPort name="GB_1" mac="00:11:22:33:44:76"/> </server> </servers> |
The guid attribute is optional.
The group subcommand adds the successfully discovered servers into a server group called group1.
The following example command shows how to view the Discovery job and the job status.
N1-ok> show job all Job ID Date Type Status Owner 3 2005-06-28T06:53:53-0700 Discovery Completed root |
The following example command shows how to verify that the discovered servers were added to the server group.
N1-ok> show group all Name us Jobs Servers Spare group1 2 |
Troubleshooting
Some commands are not supported for managed servers that were discovered manually. See Capability of Managed Servers Based on Discovery for details about which features are not available for managed servers that were discovered manually. Unsupported commands generate the following error:
Unsupported operation
This error is displayed either in the job status or immediately in the command line interface.
Discovery can fail with the following error message:
Check the Standard Output field for possible reasons for this failure
To see the Standard Output field, check the job details in the browser interface or by using the show job command with the job number of the discovery job that failed.
Discovery might fail due to a firmware version problem with drivers. See Cannot Discover a Manageable Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
See Also
Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide and Troubleshooting Discovery
Next Steps
Open the server's serial console. To view information about accessing a server's serial console, in the Sun N1 System Manager Online Help, find the topic `To Open the Serial Console for a Server'.
Software Requirements for Manual Discovery
To manually discover a manageable server, the server does not need to have an OS installed before being discovered.
Hardware Requirements for Manual Discovery
All of the hardware listed at Sun N1 System Manager Hardware and OS Requirements in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide is supported for manual discovery.
Troubleshooting Discovery
This section describes potential problems with server discovery and explains how to deal with these problems.
Discovery and Routers
Discovery of manageable servers using N1 System Manager works across routers if the network services used by the discovery process are not blocked by a firewall. Network services used by the discovery process can include SSH and SNMP.
RSC Server Discovery Problems
Manageable servers based on the Remote System Control (RSC) technology, such as Sun Fire V800 series servers, must be powered off before they can be discovered by the N1 System Manager. See Discovery of RSC Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
Discovering and Identifying Duplicate Servers
For managed servers that were discovered manually or by OS-based discovery, the N1 System Manager could discover the same server more than once. This duplication can happen in the following conditions:
-
You discover a server manually. You then use SP-based discovery to discover another server but one of the platform MAC addresses of the second server matches a MAC address in the manual discovery file. A duplicate server has been discovered.
-
You discover a server using OS-based discovery but its service processor is on a different subnet from its OS. You then use SP-based discovery to discover another server, but due to the conflict with subnets, the SP-based discovery command discovers the same server. A duplicate server has been discovered.
-
Both of the above cases happen. Two duplicate servers have been discovered, and the same server appears three times.
Discovery of duplicate servers can lead to confusion and is not recommended. In addition, there is a risk that multiple attempts to provision an OS on the same managed server might occur simultaneously, or simultaneous attempts might be made to provision an OS on a server and power off the server.
If you use OS-based discovery or manual discovery to discover servers, use the detectduplicates utility to identify duplicate servers:
N1-ok> /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/detectduplicates Name Hardware Discovered At Network manual1 V20z - File manual2 V20z - File 192.168.79.2 V20z 192.168.79.2 Management 192.168.79.67 SF-T2000 192.168.79.67 Management manual3 T2000 - File |
In the output of the detectduplicates utility, duplicates are organized into groups, separated by a blank line. In this example, the detectduplicates utility has detected two groups of duplicates.
The output of the detectduplicates utility displays the following information:
-
Name – The name of the server, as reported by the show server command.
-
Hardware – The model of the server as reported by the show server command.
-
Discovered At – The IP address that was used to discover the server. The IP address is reported as '-' for manually discovered servers.
-
Network – The network that was used to discover the server. Possible values are:
-
Management – The management (service processor) network
-
Data – The provisioning network
-
File – Manually asserted
-
Server Details Information Is Missing
The N1 System Manager provides a limited set of features for managed server that were discovered manually or using OS-based discovery. Some server details might not be displayed in the Server details page for the server, or using the show server command. See Capability of Managed Servers Based on Discovery for more information about what capabilities are provided for servers depending on how they were discovered.
Identifying How a Managed Server Was Discovered
You can identify whether a managed server was discovered by OS-based discovery if in the server details section of the N1 System Manager browser interface or by using the show server command, the following states should be true:
-
The connection section does not show a mgmtEth interface
-
The management IP address is identical to the IP address used in the discover command when the server was discovered
-
Power control capability is listed as unavailable
Some functionality might be absent, based on how the server was discovered. Table 4–1 lists supported and unsupported operations for managed servers based on how they were discovered. For managed servers discovered manually or by OS-based discovery, attempts to execute operations that are unsupported because of how the server was discovered are flagged by unsupported operation error messages.
Some servers support Remote System Control (RSC). For some models of RSC servers, the model number displayed by the N1 System Manager can depend on how the server was discovered.
-
For Sun Fire V490 servers discovered manually or through OS-based discovery, the model name returned is SF-V490. If the Sun Fire V490 server was discovered through its service processor, the model name is returned as SF-RSC.
-
For Sun Fire V890 servers discovered manually or through OS-based discovery, the model name returned is SF-V890. If the server was discovered automatically through its service processor, the model name is returned as SF-RSC.
See Discovering and Identifying Servers by Their Model Numbers for details.
Reprovisioning Servers That Were Discovered Manually or Using OS-based Discovery
There are several issues to be aware of when attempting to reprovision managed servers that were discovered manually or using OS-based discovery. Using the load server command, reset the SSH and management IP address if they have changed. For more information, see Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
Note –
When using the N1 System Manager to load an OS on managed servers that were discovered manually or using OS-based discovery, the manualnetboot feature must be turned on. For more information, see Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
