Chapter 6 Working With N1 Grid Engine Queues
This chapter describes how to access information about a grid's queues. You can see a general picture of the performance health of all the queues and view details about a particular queue.
Monitoring Queues
Queue information is available from the Queue Summary tab. You use this page to see whether a queue is functioning and how efficiently it is performing. From this page you can also view extensive details on any queue.
A queue in the N1GE environment is a means of defining a job's execution environment. This context includes features like:
-
job runtime limits (memory, stack, and CPU time)
-
control action methods (how to suspend and resume the job)
-
virtual job container (Solaris, Linux, or MS–Windows resource pools)
A queue instance is the portion of the queue that exists on a single host.
The information in this tab is presented in a table of queue instances, that is, the portion of the queue that runs on a particular host. Every queue instance that exists in the grid is listed.
Figure 6–1 Queue Summary Page
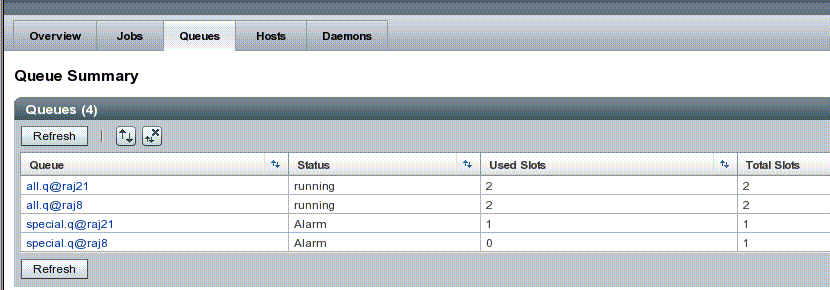
The Queue Summary page show the following information:
-
Queue – The queue name. To see more detailed information on any queue, click the queue instance name.
-
Status – Describes whether this queue instance is running, suspended (manually or automatically in the case of an error), or waiting for a required resource to become available or a condition be met. If a queue instance is suspended or waiting, you may want to see more queue details.
-
Used Slots – The number of total slots this queue instance is consuming
-
Total Slots – The number of slots defined for this queue instance. Slots are the maximum number of jobs that a queue can run simultaneously.
Note –
You do not prioritize jobs using an N1GE queue. You define priorities using the extended policy system of the Sun N1 Grid Engine software. For information on job priorities, see the sge_priority(5) man page and Scheduler Policies for Job Prioritization in the Sun N1 Grid Engine 6 System (www.sun.com/blueprints/1005/819-4325.html).
For information on cluster queues, see the Monitoring and Controlling Queues section in the N1GE 6 User's Guide and the qmon man page. For more information on queue states, see the Queue Alerts page.
Viewing Complete Queue Information
The Queue Details page contains complete information for the queue instance that you selected on the Queue Summary page.
Figure 6–2 Queue Details Page
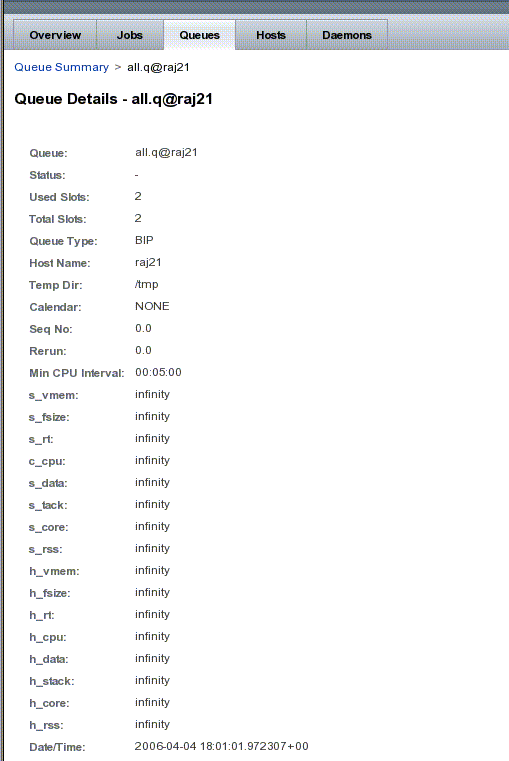
The Queue Details page shows the following information:
-
Queue – The queue instance name.
-
Status – Describes whether this queue instance is running, suspended (manually or automatically in the case of an error), or waiting for a required resource to become available or condition be met. See the Queue Alerts page for more information.
-
Used Slots – The number concurrently executing in the queue instance. The type is number
-
Total Slots – The maximum number of concurrently executing jobs allowed in the queue instance. The type is number.
-
Queue Type – The type of queue. Currently one of batch, interactive, parallel, or checkpointing or any combination in a comma separated list. The type is string; the default is batch interactive parallel.
-
Hostname – The fully qualified host name of the node (type string; template default: host.dom.dom.dom).
-
Calendar – Specifies the valid calendar for this queue instance or contains NONE (the default). A calendar defines the availability of a queue instance depending on time of day, week, and year. Refer to the calendar_conf man page for details on the N1 Grid Engine calendar facility.
-
Seq No – The sequence number. This parameter combined with the host's load situation specifies this queue's position within the suitable queue scheduling order. A job is dispatched under consideration of the queue_sort_method (see the sched_conf man page). Regardless of the queue_sort_method setting, qstat reports queue information in the order defined by the value of the seq_no. Set this parameter to a monotonically increasing sequence. The type is number and the default is 0.
-
Rerun – Defines a default behavior for jobs which are aborted by system crashes or manual violent shutdown (using kill) of the complete Sun N1 Grid Engine system on the queue host (including the sge_shepherd of the jobs and their process hierarchy). As soon as the sge_execd daemon restarts and detects that a job has been aborted for such reasons, it can be restarted if the jobs are restartable. A job may not be restartable, for example, if it updates databases (first reads then writes to the same record of a database/file) because the cancellation of the job may have left the database in an inconsistent state. The type of this parameter is Boolean, so you can specify either TRUE or FALSE. The default is FALSE, that is, do not restart jobs automatically. To overrule the default behavior for the jobs in the queue, the owner of the job can use the- r option of the qsub command.
-
Min Cpu Interval – The time between two automatic checkpoints in case of transparently checkpointing jobs. The maximum of the time requested by the user (using qsub) and the time defined by the queue configuration is used as checkpoint interval. The checkpoint files may be quite large and writing them to the file system may become expensive. So, users and administrators are advised to choose sufficiently large time intervals. The type of min_cpu_interval is time and the default is 5 minutes which usually is suitable for test purposes only.
-
s_rt (soft real time) and h_rt (hard real time) resource limit parameters define the real time (also called elapsed or wall clock time) passed since the start of the job. If h_rt is exceeded by a job running in the queue, it is stopped using the SIGKILL signal (see the kill command. If the s_rt is exceeded, the job is first warned by the SIGUSR1 signal which can be caught by the job and finally stopped after the notification time defined in the queue configuration notify parameter has passed.
-
s_cpu (soft cpu) and h_cpu (hard cpu — the per-job CPU time limit in seconds) resource limit parameters impose a limit on the amount of combined CPU time consumed by all the processes in the job. If h_cpu is exceeded by a job running in the queue, it is stopped by a SIGKILL signal (see the kill command). If s_cpu is exceeded, the job is sent a SIGXCPU signal which can be caught by the job. To warn a job so it can exit gracefully before it is killed, set the s_cpu limit to a lower value than h_cpu. For parallel processes, the limit is applied per slot. The limit is multiplied by the number of slots being used by the job before being applied.
-
s_vmem (soft virtual memory) – The same as s_data. If both are set the minimum is used and h_vmem (hard virtual memory — This is the same as h_data. If both are set the minimum is used and resource limit parameters impose a limit on the amount of combined virtual memory consumed by all the processes in the job. If h_vmem is exceeded by a job running in the queue, it is topped by a SIGKILL signal. If s_vmem is exceeded, the job is sent a SIGXCPU signal which can be caught by the job. To warn a job so it can exit gracefully before it is killed, Set the s_vmem limit to a lower value than h_vmem. For parallel processes, the limit is applied per slot. The limit is multiplied by the number of slots being used by the job before being applied.
-
s_core (soft core) - The per-process maximum core file size in bytes
-
s_data (soft data) – The per-process maximum memory limit in bytes.
-
h_data (hard data) – The per-job maximum memory limit in bytes.
-
h_fsize (hard file size) – The total number of disk blocks that this job can create.
These parameters specify per job soft and hard resource limits as implemented by the setrlimit(2) system call. By default, each limit field is set to infinity which means RLIM_INFINITY as described in the setrlimit man page. The value type for the CPU-time limits s_cpu and h_cpu is time. The value type for the other limits is memory.
Note –
Not all systems support the setrlimit command. Also, s_vmem and h_vmem are only available on systems supporting RLIMIT_VMEM (see the setrlimit(2) man page on system hosting the queue).
For more information, see the complex man page.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
