Basic Secure Remote Access Configuration
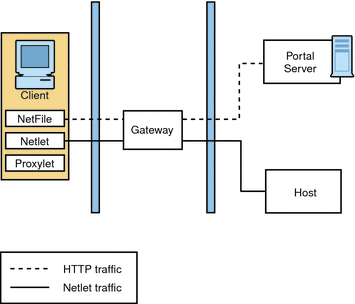
Figure 4–12 shows the most simple configuration possible for Secure Remote Access. The figure shows a client browser running NetFile and Netlet. The Gateway is installed on a separate machine in the DMZ between two firewalls. The Portal Server is located on a machine beyond the second firewall in the intranet. The other application hosts that the client accesses are also located beyond the second firewall in the intranet.
The Gateway is in the DMZ with the external port open in the firewall through which the client browser communicates with the Gateway. In the second firewall, for HTTP or HTTPS traffic, the Gateway can communicate directly with internal hosts. If security policies do not permit it, use Secure Remote Access proxies between the Gateway and the internal hosts. For Netlet traffic, the connection is direct from the Gateway to the destination host.
Without a Secure Remote Access proxy, the SSL traffic is limited to the Gateway and the traffic is not encrypted from the Gateway to the internal host unless the internal host is running in HTTPS mode. Any internal host to which the Gateway has to initiate a Netlet connection should be directly accessible from DMZ. This can be a potential security problem and hence this configuration is recommended only for the simplest of installations.
Figure 4–12 Basic Secure Remote Access Configuration
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
