创建和存储管理对象
本节介绍了用于创建和存储以下管理对象的指令,这些指令是示例方案正常工作所必需的:
-
连接工厂对象
-
目的地对象
您可以将管理对象存储到 LDAP 目录或文件中。如果使用的是文件,该文件的所有实例必须相同。
有关说明,请参见
注 –
-
本节的说明假定您已安装 Sun Java System Message Queue。(所需工具位于安装 Message Queue 的 bin/ 目录中。)
-
您可以使用该 Message Queue 管理 GUI (imqadmin) 或命令行工具 (imqobjmgr) 以创建这些管理对象。以下指令使用命令行工具。
将管理对象存储到 LDAP 目录
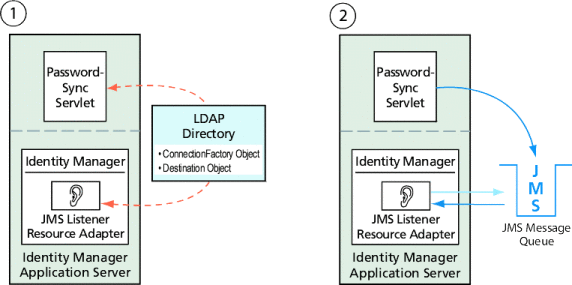
可以将 PasswordSync 和 JMS 侦听器配置为使用 LDAP 目录中存储的管理对象。图 11–14 展示了该过程。PasswordSync Servlet 和 JMS 侦听器适配器必须从 LDAP 目录中检索连接工厂和目的地设置才能发送和接收消息。
图 11–14 从 LDAP 目录中检索连接工厂和目的地对象
使用 Message Queue 命令行工具
本节介绍了如何使用 Message Queue 命令行工具 (imqobjmgr) 将受管理对象存储到 LDAP 目录中。
存储连接工厂对象
打开 Message Queue 命令行工具 (imqobjmgr),然后键入存储连接工厂对象中的命令以存储连接工厂对象。
示例 11–1 存储连接工厂对象
#> ./imqobjmgr add -l "cn=mytestFactory" -j "java.naming.factory.initial=com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory" -j "java.naming.provider.url=ldap://gwenig.coopsrc.com:389/ou=sunmq,dc=coopsrc,dc=com" -j "java.naming.security.principal=cn=directory manager" -j "java.naming.security.credentials=password" -j "java.naming.security.authentication=simple" -t qf -o "imqAddressList=mq://gwenig.coopsrc.com:7676/jms" Adding a Queue Connection Factory object with the following attributes: imqAckOnAcknowledge [Message Service Acknowledgement of Client Acknowledgements] ... imqSetJMSXUserID [Enable JMSXUserID Message Property] false Using the following lookup name: cn=mytestFactory The object’s read-only state: false To the object store specified by: java.naming.factory.initial com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory java.naming.provider.url ldap://gwenig.coopsrc.com:389/ou=sunmq,dc=coopsrc,dc=com java.naming.security.authentication simple java.naming.security.credentials netscape java.naming.security.principal cn=directory manager Object successfully added. |
在存储连接工厂对象中,imqAddressList 定义了 JMS 服务器/代理主机名 (gwenig.coopsrc.com)、端口 (7676) 以及访问方法 (jms)。
存储目的地对象
在 Message Queue 命令行工具 (imqobjmgr) 中,键入存储目的地对象中的命令以存储目的地对象。
示例 11–2 存储目的地对象
#> ./imqobjmgr add -l "cn=mytestDestination" -j "java.naming.factory.initial=com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory" -j "java.naming.provider.url=ldap://gwenig.coopsrc.com:389/ou=sunmq,dc=coopsrc,dc=com" -j "java.naming.security.principal=cn=directory manager" -j "java.naming.security.credentials=password" -j "java.naming.security.authentication=simple" -t q -o "imqDestinationName=mytestDestination" Adding a Queue object with the following attributes: imqDestinationDescription [Destination Description] A Description for the Destination Object imqDestinationName [Destination Name] mytestDestination Using the following lookup name: cn=mytestDestination The object’s read-only state: false To the object store specified by: java.naming.factory.initial com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory java.naming.provider.url ldap://gwenig.coopsrc.com:389/ ou=sunmq,dc=coopsrc,dc=com java.naming.security.authentication simple java.naming.security.credentials netscape java.naming.security.principal cn=directory manager Object successfully added. |
您可以使用 ldapsearch 或 LDAP 浏览器来查看新创建的对象。
有关在 LDAP 服务器上存储受管理对象的一节到此结束。请跳过下一节(介绍如何在文件中存储管理对象),并转到为该方案配置 JMS 侦听器适配器上的一节。
将管理对象存储到文件
可以将 PasswordSync 和 JMS 侦听器配置为使用文件中存储的受管理对象。如果未在 LDAP 服务器上存储管理对象(将管理对象存储到 LDAP 目录),请按照本节中的说明进行操作。
存储连接工厂对象
打开 Message Queue 命令行工具 (imqobjmgr),然后键入存储连接工厂对象中的命令以存储连接工厂对象并指定查找名。
示例 11–3 存储连接工厂对象并指定查找名称
#> ./imqobjmgr add -l "mytestFactory" -j "java.naming.factory.initial= com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory" -j "java.naming.provider.url=file:///home/gael/tmp" -t qf -o "imqAddressList=mq://gwenig.coopsrc.com:7676/jms" Adding a Queue Connection Factory object with the following attributes: imqAckOnAcknowledge [Message Service Acknowledgement of Client Acknowledgements] ... imqSetJMSXUserID [Enable JMSXUserID Message Property] false Using the following lookup name: mytestFactory The object’s read-only state: false To the object store specified by: java.naming.factory.initial com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory java.naming.provider.url file:///home/gael/tmp Object successfully added. To specify a destination: #> ./imqobjmgr add -l "mytestQueue" -j "java.naming.factory.initial=com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory" -j "java.naming.provider.url=file:///home/gael/tmp" -t q -o "imqDestinationName=myTestQueue" Adding a Queue object with the following attributes: imqDestinationDescription [Destination Description] A Description for the Destination Object imqDestinationName [Destination Name] myTestQueue Using the following lookup name: mytestQueue The object’s read-only state: false To the object store specified by: java.naming.factory.initial com.sun.jndi.fscontext.RefFSContextFactory java.naming.provider.url file:///home/gael/tmp Object successfully added. |
在代理上创建目的地
默认情况下,Sun Message Queue 代理允许自动创建队列目的地(请参见 config.properties,其中 imq.autocreate.queue 的默认值为 true)。
如果没有自动创建队列目的地,则必须使用在代理上创建目的地(其中 myTestQueue 为目的地)中所示的命令在代理上创建目的地对象。
示例 11–4 在代理上创建目的地对象
name (Queue name): #> cd /opt/sun/mq/bin #>./imqcmd create dst -t q -n mytestQueue Username: <admin> Password: <admin> Creating a destination with the following attributes: Destination Name mytestQueue Destination Type Queue On the broker specified by: ------------------------- Host Primary Port ------------------------- localhost 7676 Successfully created the destination. |
您可以将管理对象存储到目录或文件:
-
在目录中:使用目录是一种集中存储连接工厂和目的地对象的方法。
使用目录时,这些管理对象将存储为目录条目。
注 –如果 Identity Manager PasswordSync Servlet 和 Identity Manager 服务器不在同一台计算机上,则它们都必须能够访问 .bindings 文件。您可以在每台计算机上将受管理对象的创建过程重复两次,或者将.bindings 文件复制到每台计算机上的正确位置。
-
在文件中:如果 Identity Manager PasswordSync Servlet 和 Identity Manager 服务器在同一台服务器上运行(或者没有可用目录),则可以将管理对象存储到文件中。
使用文件时,这两个管理对象将存储在单个文件(在 Windows 和 UNIX 上,文件名均为 .bindings)中,该文件位于为 java.naming.provider.url 指定的目录(例如,在 Windows 上为 file:///c:/temp,在 Unix 上为 file:///tmp )下。
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
