| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
System Administration Guide: Oracle Solaris Zones, Oracle Solaris 10 Containers, and Resource Management Oracle Solaris 11 Express 11/10 |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
System Administration Guide: Oracle Solaris Zones, Oracle Solaris 10 Containers, and Resource Management Oracle Solaris 11 Express 11/10 |
Part I Oracle Solaris Resource Management
1. Introduction to Resource Management
2. Projects and Tasks (Overview)
3. Administering Projects and Tasks
4. Extended Accounting (Overview)
5. Administering Extended Accounting (Tasks)
6. Resource Controls (Overview)
7. Administering Resource Controls (Tasks)
8. Fair Share Scheduler (Overview)
9. Administering the Fair Share Scheduler (Tasks)
10. Physical Memory Control Using the Resource Capping Daemon (Overview)
11. Administering the Resource Capping Daemon (Tasks)
13. Creating and Administering Resource Pools (Tasks)
14. Resource Management Configuration Example
15. Introduction to Oracle Solaris Zones
About Oracle Solaris Zones in This Release
Processes Running in a Branded Zone
Branded Zones Available in this Release
Summary of Oracle Solaris Zone Features
How Non-Global Zones Are Administered
How Non-Global Zones Are Created
Non-Global Zone Characteristics
Using Resource Management Features With Non-Global Zones
Features Provided by Non-Global Zones
Setting Up Zones on Your System (Task Map)
16. Non-Global Zone Configuration (Overview)
17. Planning and Configuring Non-Global Zones (Tasks)
18. About Installing, Halting, Uninstalling, and Cloning Non-Global Zones (Overview)
19. Installing, Booting, Halting, Uninstalling, and Cloning Non-Global Zones (Tasks)
20. Non-Global Zone Login (Overview)
21. Logging In to Non-Global Zones (Tasks)
22. Moving and Migrating Non-Global Zones (Tasks)
23. About Packages on an Oracle Solaris 11 Express System With Zones Installed
24. Oracle Solaris Zones Administration (Overview)
25. Administering Oracle Solaris Zones (Tasks)
26. Troubleshooting Miscellaneous Oracle Solaris Zones Problems
Part III Oracle Solaris 10 Zones
27. Introduction to Oracle Solaris 10 Zones
28. Assessing an Oracle Solaris 10 System and Creating an Archive
30. Configuring the solaris10 Branded Zone
31. Installing the solaris10 Branded Zone
32. Booting a Zone and Zone Migration
33. solaris10 Branded Zone Login and Post-Installation Configuration
Zones are ideal for environments that consolidate a number of applications on a single server. The cost and complexity of managing numerous machines make it advantageous to consolidate several applications on larger, more scalable servers.
The following figure shows a system with four zones. Each of the zones apps, users, and work is running a workload unrelated to the workloads of the other zones, in a sample consolidated environment. This example illustrates that different versions of the same application can be run without negative consequences in different zones, to match the consolidation requirements. Each zone can provide a customized set of services.
Figure 15-1 Zones Server Consolidation Example
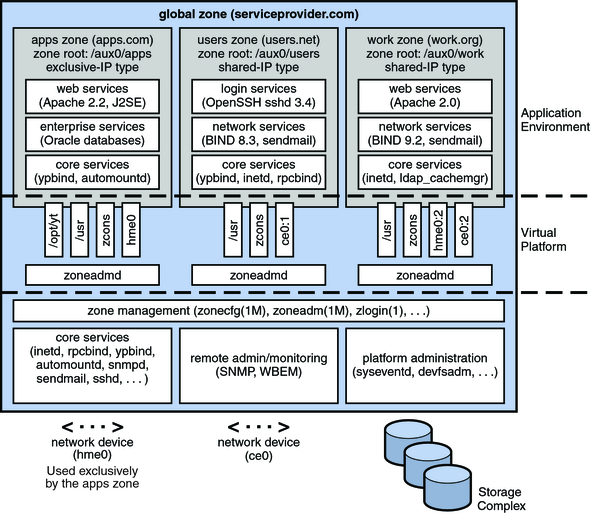
Zones enable more efficient resource utilization on your system. Dynamic resource reallocation permits unused resources to be shifted to other zones as needed. Fault and security isolation mean that poorly behaved applications do not require a dedicated and under-utilized system. With the use of zones, these applications can be consolidated with other applications.
Zones allow you to delegate some administrative functions while maintaining overall system security.