| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Configuring Secure Network Communications for SAP Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Configuring Secure Network Communications for SAP Java CAPS Documentation |
Configuring Secure Network Communications for SAP
Overview of Secure Network Communications for SAP
Communication using Secure Network Communications
Configuring the SAP Server and Java CAPS
Setting up Secure Network Communications on the SAP Server
To Install the SAP Cryptographic Library
To Create the PSE for the Server
Profile Parameter Settings on the Gateway
Using Secure Network Communications in Java CAPS
To Create a SAP BAPI OTD Using Secure Network Communications
To Create a SAP IDOC OTD Using Secure Network Communications
Perform the following steps to configure Secure Network Communications:
The following sections cover the installation and configuration of SNC.
In the following example, this directory is represented with the notation $(DIR_EXECUTABLE).
Windows NT:
DIR_EXECUTABLE:<DRIVE>:\usr\sap\<SID>\SYS\exe\run\
Location of SAP Cryptographic Library: <DRIVE>:\usr\sap\<SID>\SYS\exe\run\sapcrypto.dll
DIR_INSTANCE: <DRIVE>:\usr\sap\<SID>\<instance>
Location of the ticket: <DRIVE>:\usr\sap\<SID>\<instance>\sec\ticket
The application server uses this variable to locate the ticket and its credentials at runtime. If you set the environment variable using the command line, the value may not be applied to the server's processes. Therefore, setting SECUDIR in the startup profile for the server's user or in the registry is recommended.
Note - These instructions are available at http://help.sap.com/saphelp_erp2004/helpdata/en/96/709b3ad94e8a3de10000000a11402f/frameset.htm
For example: snc/identity/as p:CN=IDS, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE (Do not forget to add "p:" in front of the name, as shown below).
Note - While specifying the distinguished name for your Client/Server PSE CN=xx, OU=xx, O=xx, C=xx, the cryptographic tool validates the country code for the "C=xx" attribute.
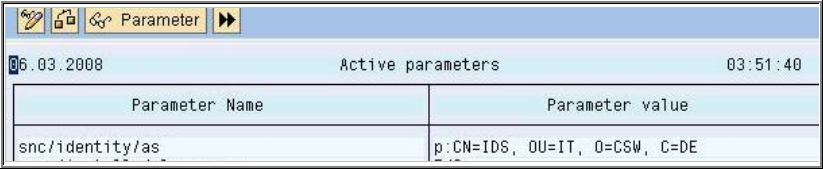
This example shows an X.500 Name. It is formed from different elements that represent a hierarchical name space. Where CN = Common Name, OU = Organizational Unit, O = Organization and C = Country.
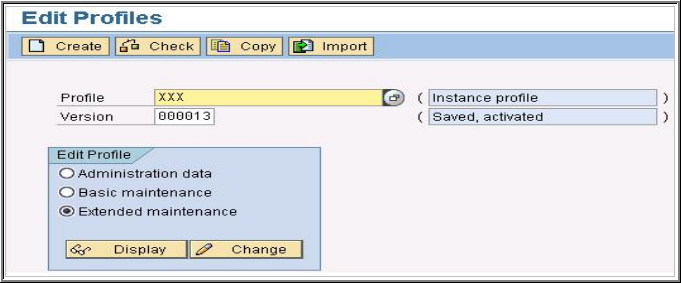
After restarting your server you can now create the SNC PSE.
The Password can contain both letters and numbers. Without the password the server would not start when you set the instance parameter snc/enable to 1.
|
Setting the profile parameter snc/enable to 1 activates SNC on the application server. If this parameter is set but the SNC PSE and credentials do not exist, then the application server will not start. Therefore, setting the SNC parameters should be the last step in the configuration procedure.
These values will enable you to connect to the system without encryption.
To use SNC for securing connections that connect via the SAP gateway, you also need to set the appropriate parameters in the gateway profile. The gateway itself does not directly use the routines from the security product; however, it does supply the SNC configuration parameters to the programs that it starts. Release 3.1 does not offer SNC protection for the RFC and CPIC communication protocols. In Release 3.1, you need to set the profile parameter snc/permit_insecure_comm to the value "1".
Note - The rest of the description in this section applies only as of Release 4.0.
The following profile parameters are relevant for the gateway settings:
snc/enable — For a gateway to accept SNC-protected connections, you need to set the profile parameter snc/enable to the value 1. The gateway then knows that an SNC environment is in operation and takes the following precautions: - In addition to the standard port (sapgw<nn>), it opens a "secured" port (sapgw<nn>s), where it accepts only connections that use SNC protection. - It starts programs only when SNC protection for the communication is used. You may explicitly allow the starting of programs without using SNC protection by setting the parameter snc/permit_insecure_start (see the description below)
snc/gssapi_lib — As with the application server, if snc/enable = 1, then the parameter snc/gssapi_lib must contain the path and file name of the external library. The gateway passes this information to the external programs that it starts.
snc/permit_insecure_start (snc/permit_insecure_comm in Release 3.1) — If snc/enable = 1, then the gateway does not start or register any external programs without using SNC-protected communications (as default). You can explicitly override this configuration by setting the parameter snc/permit_insecure_start to the value "1". The gateway will then start or register programs even if SNC protection is not used for the communication. The parameter is only necessary if programs without SNC protection are to be directly started by or registered on the gateway. If the gateway is started directly on an application server, it uses the application server's profile settings. In this case, the parameters snc/enable and snc/gssapi_lib are set in the application server's profile. For the gateway, you then only need to consider the parameter snc/permit_insecure_start (or snc/permit_insecure_comm). If a gateway is to be started independent of the SAP System application server ("Stand Alone Gateway"), then you need to consider all of the above mentioned parameters.
Make sure you set the SECUDIR environment variable to this directory, copy the library to a different directory, and add this path to your "PATH" environment variable.
The client PSE is named as RFC.pse. From the command line, you can specify the distinguished name. For example: "CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE"
> sapgenpse gen_pse -v -p RFC.pse
Got absolute PSE path "<your path>/RFC.pse".
Please enter PIN: ********
Please reenter PIN: ********
get_pse: Distinguished name of PSE owner: CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
Supplied distinguished name: "CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE"
Generating key (RSA, 1024-bits) ... succeeded.
certificate creation... ok
PSE update... ok
PKRoot... ok
Generating certificate request... ok.
PKCS#10 certificate request for "<your path>/RFC.pse"
The exported certificate is named as RFC.crt.
> sapgenpse export_own_cert -v -p RFC.pse -o RFC.crt
Opening PSE your path>/RFC.pse"...
No SSO credentials found for this PSE.
Please enter PIN: ********
PSE open ok.
Retrieving my certificate... ok.
writing to file ...... ok
You can import the client Certificate via Transaction STRUST.
Export the Server Certificate via the Transaction STRUST.
On the command line run:
> sapgenpse maintain_pk -v -a SNC.crt -p RFC.pse
Opening PSE your path>/RFC.pse"...
No SSO credentials found for this PSE.
Please enter PIN: ********
PSE open ok.
Adding new certificate from file "SNC.crt"
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Subject : CN=IDS, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
Issuer : CN=IDS, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
Serialno: 00
KeyInfo : RSA, 2048-bit
Validity - NotBefore: Wed Mar 6 21:37:32 2008 (060927193732Z)
NotAfter: Fri Jan 1 01:00:01 2038 (380101000001Z)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
PKList updated (1 entries total, 1 newly added)
After setting up the client PSE you must create a file called cred_v2 which is used to securely give the RFC Program access to the PSE without providing the password for the PSE.
On the command line run:
> sapgenpse seclogin -p RFC.pse -O root running seclogin with USER="root"
creatingcredentials for yourself (USER="root")...
Please enter PIN: ********
Added SSO-credentials for PSE "<your path>/RFC.pse"
"CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE"
Note - When you generate the cred_v2 file, the seclogin must be carried out under the account of the <sid>adm.
Now you need to map the x.509 certificates that were created for the user accounts on the SAP Server.
This view is used to restrict the SNC RFC Connections by an Access Control List (ACL). You will see an alert window pop-up, just click on the "right" symbol.
Note - Do not forget the "p:" in front of the DN.
Note - When trying to edit the entry, you might see an alert window pop-up. Just click on the "right" symbol and make your changes.
The X.509 Certificate must be accepted for a successful Login.
Using the view VUSREXTID, you can setup a mapping between the Distinguished Name provided by a X.509 Certificate and an ABAP User.
Secure Network Communication connections are provided to the SAP Server during design-time and runtime in the SAP BAPI Adapter. Perform the following tasks to use SNC in Java CAPS:
To Create a SAP BAPI OTD Using Secure Network Communications
To Create a SAP IDOC OTD Using Secure Network Communications
SNC Library Path: The path to the Security Library you are using, for example: <your drive>:/Secude/secude.dll
SNC Partner Name: The SNC Name you specified for the SAP Server (Server PSE), for example: p:CN=IDS, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
X.509 Certificate: The certificate information of your Client PSE
SNC My Name: The name you specified for the Client PSE, for example: p:CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
The SNC Quality of Protection is defaulted to 1, since only authentication during the OTD creation is provided.
Note - You can connect to SAP Server without using SNC. Simply leave the Enable SNC checkbox disabled and only specify the enabled parameters.
Secure Network Communication connections are provided to the SAP Server for SAP IDOC OTD creation, when you select the metadata source from the SAP directly option.
SNC Library Path: The path to the Security Library you are using, for example: <your drive>:/Secude/secude.dll
SNC Partner Name: The SNC Name you specified for the SAP Server (Server PSE), for example: p:CN=IDS, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
X.509 Certificate: The certificate information of your Client PSE
SNC My Name: The name you specified for the Client PSE, for example: p:CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
The SNC Quality of Protection is defaulted to 1, since only authentication during the OTD creation is provided.
During runtime, you can enable SNC for both outbound and inbound. You can specify the SNC parameters in the SAP BAPI External System.
Note - You can connect to SAP Server without using SNC. Simply leave the Enable SNC checkbox disabled and only specify the enabled parameters.
In the Outbound SAP BAPI Adapter node, of the SAP BAPI External System properties window, a new Client Security Settings section has been created. You can specify the SNC properties in this section.
If you select Yes for the value of Enable SNC then you must specify the following parameters:
SNC Library Path : The path to the Security Library you are using. For example: <your drive>:/Secude/secude.dll
SNC Partner Name : The SNC Name you specified for the SAP Server (Server PSE). For example: p:CN=IDS, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
X.509 Certificate: The certificate information of your Client PSE
SNC My Name: The name you specified for the Client PSE. For example: p:CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
SNC Level of Protection: Level of data protection for connections initiated by the SAP System. You can specify the following Level of Protection values:
1: Apply authentication only
2: Apply integrity protection (authentication)
3: Apply privacy protection (integrity and authentication)
8: Apply the default protection
9: Apply the maximum protection
Note - To use the values "8" or "9", you need to make sure you have set the instance parameters snc/data_protection/max and snc/data_protection/use during the SNC configuration on the SAP Server.
In the Inbound SAP BAPI Adapter node, of the SAP BAPI External System properties window, a new Server Security Settings section has been created. You can specify the SNC properties in this section.
If you select Yes for the value of Enable SNC, you must specify the following parameters:
SNC Library Path : The path to the Security Library you are using. For example: <your drive>:/Secude/secude.dll
X.509 Certificate: The certificate information of your Client PSE
SNC My Name: The name you specified for the Client PSE. For example: p:CN=RFC, OU=IT, O=CSW, C=DE
SNC Level of Protection: Level of data protection for connections initiated by the SAP System. You can specify the following Level of Protection values:
1: Apply authentication only
2: Apply integrity protection (authentication)
3: Apply privacy protection (integrity and authentication)
8: Apply the default protection
9: Apply the maximum protection
Note - To use the values "8" or "9", you need to make sure you have set the instance parameters snc/data_protection/max and snc/data_protection/use during the SNC configuration on the SAP Server.