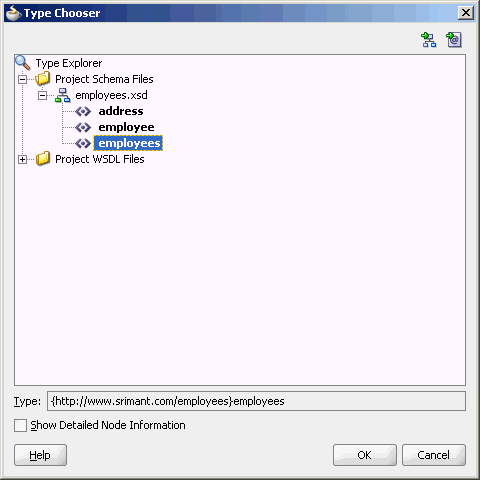
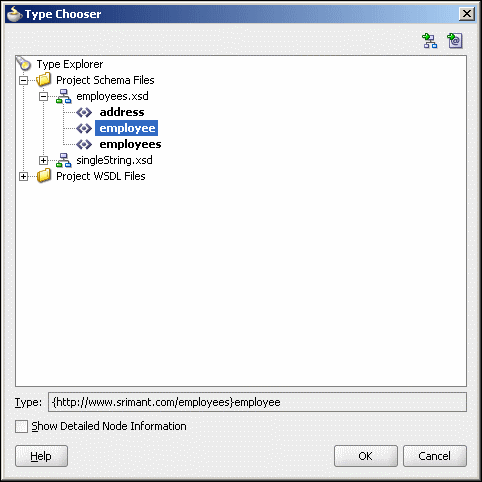
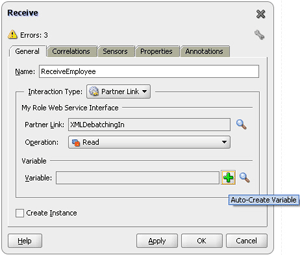
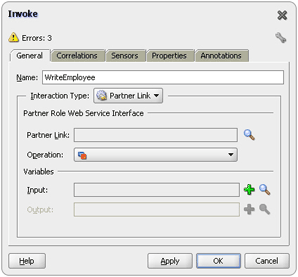
4 Oracle JCA Adapter for Files/FTP
This chapter describes how to use the Oracle File and FTP Adapters, which work with Oracle BPEL Process Manager and Oracle Mediator. References to use cases for the Oracle File and FTP Adapters are also provided.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Note:
The term Oracle JCA Adapter for Files/FTP is used for the Oracle File and FTP Adapters, which are separate adapters with very similar functionality.4.1 Introduction to Oracle File and FTP Adapters
Oracle BPEL PM and Mediator include the Oracle File and FTP Adapters. The Oracle File and FTP Adapters enable a BPEL process or a Mediator to exchange (read and write) files on local file systems and remote file systems (through use of the file transfer protocol (FTP)). The file contents can be both XML and non-XML data formats.
This section includes the following topics:
-
Section 4.1.2, "Oracle File and FTP Adapters Integration with Oracle BPEL PM"
-
Section 4.1.3, "Oracle File and FTP Adapters Integration with Mediator"
4.1.1 Oracle File and FTP Adapters Architecture
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters are based on JCA 1.5 architecture. JCA provides a standard architecture for integrating heterogeneous enterprise information systems (EIS). The JCA Binding Component of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters expose the underlying JCA interactions as services (WSDL with JCA binding) for Oracle BPEL PM integration. For details about Oracle JCA Adapter architecture, see Chapter 1, "Introduction to Oracle JCA Adapters."
4.1.2 Oracle File and FTP Adapters Integration with Oracle BPEL PM
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters are automatically integrated with Oracle BPEL PM. When you drag and drop File Adapter for FTP Adapter from the Component Palette of JDeveloper BPEL Designer, the Adapter Configuration Wizard starts with a Welcome page, as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Welcome Page
Description of "Figure 4-1 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Welcome Page"
This wizard enables you to select and configure the Oracle File and FTP Adapters. The Adapter Configuration Wizard then prompts you to enter a service name, as shown in Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Service Name Page
Description of "Figure 4-2 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Service Name Page"
When configuration is complete, a WSDL and JCA file pair is created in the Application Navigator section of Oracle JDeveloper. (JDeveloper) This JCA file contains the configuration information you specify in the Adapter Configuration Wizard.
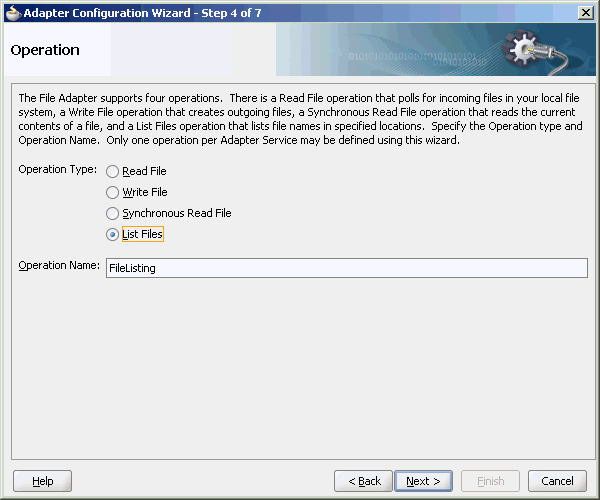
The Operation Type page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard prompts you to select an operation to perform. Based on your selection, different Adapter Configuration Wizard pages appear and prompt you for configuration information. Table 4-1 lists the available operations and provides references to sections that describe the configuration information you must provide.
Table 4-1 Supported Operations for Oracle BPEL Process Manager
| Operation | Section |
|---|---|
|
Oracle File Adapter |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Section 4.3.3, "Oracle File Adapter Synchronous Read Concepts" |
|
|
|
Oracle FTP Adapter |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Section 4.3.7, "Oracle FTP Adapter Synchronous Get File Concepts" |
|
For more information about Oracle JCA Adapter integration with Oracle BPEL PM, see Chapter 1, "Introduction to Oracle JCA Adapters."
4.1.3 Oracle File and FTP Adapters Integration with Mediator
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters are automatically integrated with Mediator. When you create an Oracle File or FTP Adapter service in JDeveloper Designer, the Adapter Configuration Wizard is started.
This wizard enables you to select and configure the Oracle File and FTP Adapters. When configuration is complete, a WSDL, JCA file pair is created in the Application Navigator section of JDeveloper. This JCA file contains the configuration information you specify in the Adapter Configuration Wizard.
The Operation Type page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard prompts you to select an operation to perform. Based on your selection, different Adapter Configuration Wizard pages appear and prompt you for configuration information. Table 4-2 lists the available operations and provides references to sections that describe the configuration information you must provide.
Table 4-2 Supported Operations for Oracle Mediator
| Operation | Section |
|---|---|
|
Oracle File Adapter |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Section 4.3.3, "Oracle File Adapter Synchronous Read Concepts" |
|
|
|
Oracle FTP Adapter |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Section 4.3.7, "Oracle FTP Adapter Synchronous Get File Concepts" |
|
For more information about Oracle JCA Adapter integration with Mediator, see Chapter 1, "Introduction to Oracle JCA Adapters."
4.1.4 Oracle File and FTP Adapters Integration with SOA Composite
A composite is an assembly of services, service components (Oracle BPEL PM and Mediator), wires, and references designed and deployed together in a single application. The composite processes the information described in the messages. The details of the composite are stored in the composite.xml file. For more information about integration of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters with SOA composite, see Section 3.2.4, "Oracle SOA Composite Integration with Adapters."
4.2 Oracle File and FTP Adapters Features
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters enable you to configure a BPEL process or a Mediator to interact with local and remote file system directories. This section explains the following features of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters:
Note:
For composites with Oracle File and FTP Adapters, which are designed to consume very large number of concurrent messages, you must set the number of open files parameter for your operating system to a larger value. For example, to set the number of open files parameter to8192 for Linux, use the ulimit -n 8192 command.4.2.1 File Formats
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters can read and write the following file formats and use the adapter translator component at both design time and run time:
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters can also treat file contents as an opaque object and pass the contents in their original format (without performing translation). The opaque option handles binary data such as JPGs and GIFs, whose structure cannot be captured in an XSD or data you do not want to have translated.
The translator enables the Oracle File and FTP Adapters to convert native data in various formats to XML. The native data can be simple (just a flat structure) or complex (with parent-child relationships). The translator can handle both XML and non-XML (native) formats of data.
4.2.2 FTP Servers
Oracle FTP Adapter supports most RFC 959 compliant FTP servers on all platforms. It also provides a pluggable mechanism that enables Oracle FTP Adapter to support additional FTP servers. In addition, Oracle FTP Adapter supports FTP over SSL (FTPS) on Solaris and Linux. Oracle FTP Adapter also supports SFTP (Secure FTP) using SSH transport.
Note:
Oracle FTP Adapter supports SFTP server version 4 or later.4.2.3 Inbound and Outbound Interactions
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters exchange files in the inbound and outbound directions. Based on the direction, the Oracle File and FTP Adapters perform different sets of tasks.
For inbound files sent to Oracle BPEL PM or Mediator, the Oracle File and FTP Adapters perform the following operations:
-
Poll the file system looking for matches.
-
Read and translate the file content based on the native schema (NXSD) defined at design time.
-
Publish the translated content as an XML message.
This functionality of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters is referred to as the file read operation, and the component that provides this function is the file reader. This operation is known as a Java Connector Architecture (JCA) inbound activation.
For outbound files sent from Oracle BPEL PM or Mediator, the Oracle File and FTP Adapters perform the following operations:
-
Receive messages from BPEL or Mediator.
-
Format the XML contents as specified at design time.
-
Produce output files. The output files can be created based on the following criteria: time elapsed, file size, and number of messages. You can also specify a combination of these criteria for output files.
This functionality of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters is referred to as the file write operation. This operation is known as a JCA outbound interaction.
For the inbound and outbound directions, the Oracle File and FTP Adapters use a set of configuration parameters. For example:
-
The inbound Oracle File and FTP Adapters have parameters for the inbound directory where the input file appears and the frequency with which to poll the directory.
-
The outbound Oracle File and FTP Adapters have parameters for the outbound directory in which to write the file and the file naming convention to use.
Note:
You must use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to modify the configuration parameters, such as publish size, number of messages, and polling frequency.You must not manually change the value of these parameters in JCA files.
The file reader supports polling conventions and offers several postprocessing options. You can specify to delete, move, or leave the file as it is after processing the file. The file reader can split the contents of a file and publish it in batches, instead of as a single message. This feature can be used for performance tuning of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters. The file reader guarantees once and once-only delivery.
following sections for details about the read and write functionality of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters:
4.2.4 File Debatching
When a file contains multiple messages, you can choose to publish messages in a specific number of batches. This is referred to as debatching. During debatching, the file reader, on restart, proceeds from where it left off in the previous run, thereby avoiding duplicate messages. File debatching is supported for files in XML and native formats.
Note:
You must not manually change the value of the publish size parameter inJCA files. You must use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to modify this parameter.4.2.4.1 Indicating if the Current Batch is the Last Batch
You can register a batch notification callback (Java class) which will be invoked when the last batch is reached in a debatching scenario.
<service ...
<binding.jca ...
<property name="batchNotificationHandler">com.acme.batchHandler</property>
where com.acme.batchHandler must implement
package oracle.tip.adapter.api.callout.batch;
public interface BatchNotificationCallout extends Callout
{
public void onInitiateBatch(String rootId,
String metaData)
throws ResourceException;
public void onFailedBatch(String rootId,
String metaData,
long currentBatchSize,
Throwable reason)
throws ResourceException;
public void onCompletedBatch(String rootId,
String metaData,
long finalBatchSize)
throws ResourceException;
4.2.5 File ChunkedRead
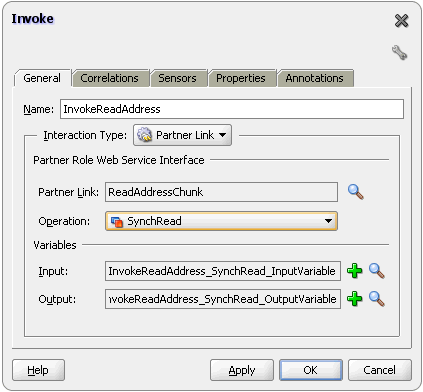
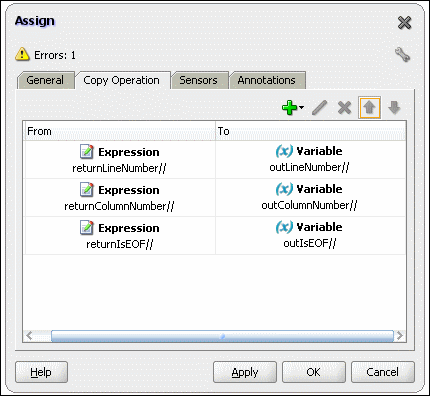
This is a feature of Oracle File and FTP Adapters that uses an invoke activity within a while loop to process the target file. This feature enables you to process arbitrarily large files.
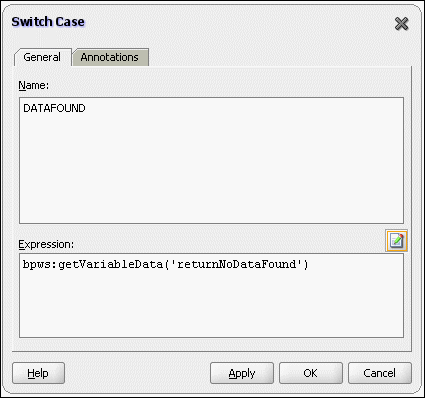
If an invalid payload is provided, then ChunkedRead scenarios do not throw an exception. When a translation exception (bad record violating the NXSD specification) is encountered, the return header is populated with the translation exception message that includes details such as line and column where the error occurred. All translation errors do not result in a fault. These errors are manifested as a value in the return header. You must check the jca.file.IsMessageRejected and jca.file.RejectionReason header values to ascertain whether an exception has occurred. Additionally, you can also check the jca.file.NoDataFound header value.
4.2.6 File Sorting
When files must be processed by Oracle File and FTP Adapters in a particular order, you must configure the sorting parameters. For example, you can configure the sorting parameters for Oracle File and FTP Adapters to process files in ascending or descending order by time stamps.
You must meet the following prerequisites for sorting scenarios of Oracle File and FTP Adapters:
-
Use a synchronous operation
-
Add the following property to the inbound JCA file:
<property name="ListSorter" value="oracle.tip.adapter.file.inbound.listing.TimestampSorterAscending"/> <property name="SingleThreadModel" value="true"/>
4.2.7 Dynamic Outbound Directory and File Name Specification
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters enable you to dynamically specify the logical or physical name of the outbound file or outbound directory. For information about how to specify dynamic outbound directory, see Section 4.3.2.2, "Outbound File Directory Creation."
4.2.8 Security
The Oracle FTP Adapter supports FTP over SSL (FTPS) and Secure FTP (SFTP) to enable secure file transfer over a network.
For more information, see Section 4.4.3, "Using Secure FTP with the Oracle FTP Adapter" and Section 4.4.4, "Using SFTP with Oracle FTP Adapter."
4.2.9 Nontransactional
The Oracle File Adapter picks up a file from an inbound directory, processes the file, and sends the processed file to an output directory. However, during this process if a failover occurs in the Oracle RAC backend or in an SOA managed server, then the file is processed twice because of the nontransactional nature of Oracle File Adapter. As a result, there can be duplicate files in the output directory.
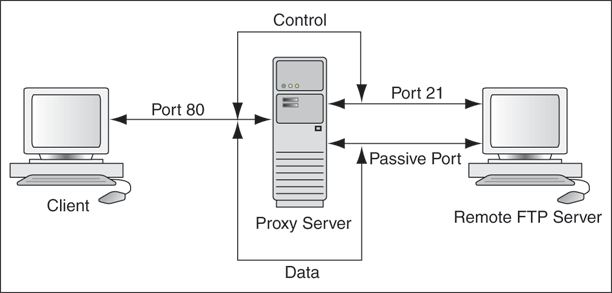
4.2.10 Proxy Support
The proxy support feature of the Oracle FTP Adapter can be used to transfer and retrieve data to and from the FTP servers that are located outside a firewall or can only be accessed through a proxy server. A proxy server enables the hosts in an intranet to indirectly connect to hosts on the Internet. Figure 4-3 shows how a proxy server creates connections to simulate a direct connection between the client and the remote FTP server.
Figure 4-3 Remote FTP Server Communication Through a Proxy Server
Description of "Figure 4-3 Remote FTP Server Communication Through a Proxy Server"
To use the HTTP proxy feature, your proxy server must support FTP traffic through HTTP Connection. In addition, only passive data connections are supported with this feature. For information about how to configure the Oracle FTP Adapter, see Section 4.4.5, "Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter for HTTP Proxy."
4.2.11 No Payload Support
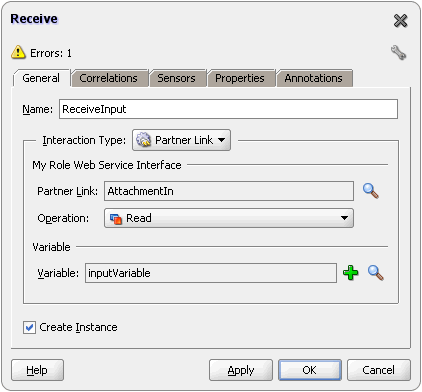
For Oracle BPEL PM and Mediator, the Oracle File and FTP Adapters provide support for publishing only file metadata such as file name, directory, file size, and last modified time to a BPEL process or Mediator and excludes the payload. The process can use this metadata for subsequent processing. For example, the process can call another reference and pass the file and directory name for further processing. So, the Oracle File and FTP Adapters can be used as a notification service to notify a process whenever a new file appears in the inbound directory. To use this feature, select the Do not read file content check box in the JDeveloper wizard while configuring the "Read operation."
4.2.12 Large Payload Support
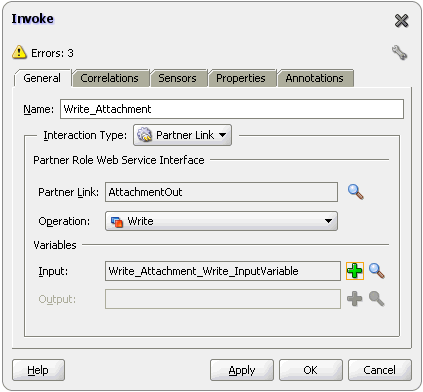
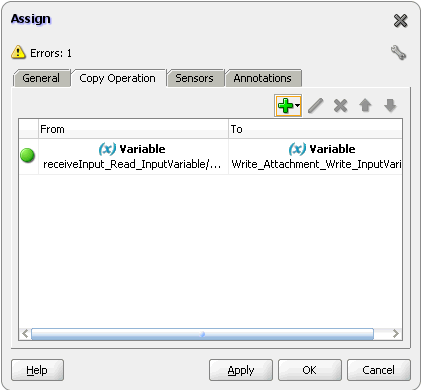
For Oracle BPEL PM and Mediator, the Oracle File Adapter provides support for transferring large files as attachments. To use this feature, select the Read File As Attachment check box in the JDeveloper wizard while configuring the "Read operation." This option opaquely transfers a large amount of data from one place to another as attachments. For example, you can transfer large MS Word documents, images, and PDFs without processing their content within the composite application. For information about how to pass large payloads as attachments, see Section 4.5.6, "Oracle File Adapter Read File As Attachments."
Note:
You must not pass large payloads as opaque schemas.4.2.13 File-Based Triggers
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters provide support for file-based triggers, which can be used to control inbound adapter endpoint activation. For information about how to use file-based triggers, see Section 4.3.1.4, "File Polling."
4.2.14 Pre-Processing and Post-Processing of Files
The process modeler may encounter situations where files must be pre-processed before they are picked up for processing or post-processed before the files are written out to the destination folder. For example, the files that the Oracle File and FTP adapters receive may be compressed or encrypted and the adapter must decompress or decrypt the files before processing. In this case you must use a custom code to decompress or decrypt the files before processing. The Oracle File and FTP Adapters supports the use of custom code that can be plugged in for pre-processing or post-processing of files.
The implementation of the pre-processing and post-processing of files is restricted to the following communication modes of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters:
-
Read File or Get File
-
Write File or Put File
-
Synchronous Read File
-
Chunked Read
This section contains the following topics:
-
Section 4.2.14.1, "Mechanism For Pre-Processing and Post-Processing of Files"
-
Section 4.2.14.3, "Using a Re-Entrant Valve For Processing Zip Files"
4.2.14.1 Mechanism For Pre-Processing and Post-Processing of Files
The mechanism for pre-processing and post-processing of files is configured as pipelines and valves. This section describes the concept of pipelines and valves.
A pipeline consists of a series of custom-defined valves. A pipeline loads a stream from the file system, subjects the stream to processing by an ordered sequence of valves, and at the end of the processing returns the modified stream to the adapter.
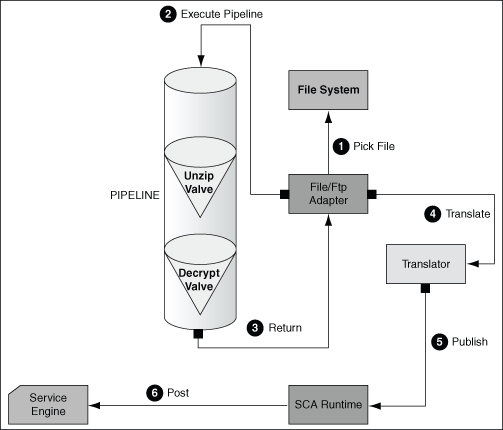
A valve is the primary component of execution in a processing pipeline. A valve processes the content it receives and forwards the processed content to the next valve. For example, in a scenario where the Oracle File and FTP Adapters receive files that are encrypted and zipped, you can configure a pipeline with an unzip valve followed by a decryption valve. The unzip valve extracts the file content before forwarding it to the decryption valve, which decrypts the content and the final content is made available to the Oracle File or FTP Adapter as shown in Figure 4-4.
Figure 4-4 A Sample Pre-Processing Pipeline
Description of "Figure 4-4 A Sample Pre-Processing Pipeline"
4.2.14.2 Configuring a Pipeline
Configuring the mechanism for pre-processing and post-processing of files requires defining a pipeline and configuring it in the corresponding JCA file.
To configure a pipeline, you must perform the following steps:
- Step 1 Implementing and Extending Valves
-
All valves must implement
ValveorStagedValveinterface.Tip:
You can extend either theAbstractValveor theAbstractStagedValveclass based on business requirement rather than implementing a valve from scratch.Example 4-1 is a sample valve interface.
Example 4-1 The Valve Interface
package oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline; import java.io.IOException; /** <p> * Valve component is resposible for processing the input stream * and returning a modified input stream. * The <code>execute()</code> method of the valve gets invoked * by the caller (on behalf) of the pipeline. This method must * return the input stream wrapped within an InputStreamContext. * The Valve is also responsible for error handling specifically * * The Valve can be marked as reentrant in which case the caller * must call the <code>execute()</code> multiple times and each * invocation must return a new input stream. This is useful, if * you are writing an UnzipValve since each iteration of the valve * must return the input stream for a different zipped entry. * <b> You must note that only the first Valve in the pipeline can * be reentrant </b> * * The Valve has another flavor <code>StagedValve</code> and if * the valve implements StagedValve, then the valve must store * intermediate content in a staging file and return it whenever * required. * </p> */ public interface Valve { /** * Set the Pipeline instance. This parameter can be * used to get a reference to the PipelineContext instance. * @param pipeline */ public void setPipeline(Pipeline pipeline); /** Returns the Pipeline instance. * @return */ public Pipeline getPipeline(); /** Returns true if the valve has more input streams to return * For example, if the input stream is from a zipped file, then * each invocation of <code>execute()</code> returns a different * input stream once for each zipped entry. The caller calls * <code>hasNext()</code> to check if more entries are available * @return true/false */ public boolean hasNext(); /** Set to true if the caller can call the valve multiple times * e.g. in case of ZippedInputStreams * @param reentrant */ public void setReentrant(boolean reentrant); /** Returns true if the valve is reentrant. * @return */ public boolean isReentrant(); /** The method is called by pipeline to return the modified input stream * @param in * @return InputStreamContext that wraps the input stream along with required metadata * @throws PipelineException */ public InputStreamContext execute(InputStreamContext in) throws PipelineException, IOException; /** * This method is called by the pipeline after the caller publishes the * message to the SCA container. * In the case of a zipped file, this method gets called repeatedly, once * for each entry in the zip file. * This should be used by the Valve to do additional tasks such as * delete the staging file that has been processed in a reentrant scenario. * @param in The original InputStreamContext returned from <code>execute()</code> */ public void finalize(InputStreamContext in); /**Cleans up intermediate staging files, input streams * @throws PipelineException, IOException */ public void cleanup() throws PipelineException, IOException; }
The
StagedValvestores intermediate content in staging files. Example 4-2 shows theStagedValveinterface extending theValveinterface.Example 4-2 The StagedValve Interface Extending the Valve Interface
package oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline; import java.io.File; /** * A special valve that stages the modified * input stream in a staging file. * If such a <code>Valve</code> exists, then * it must return the staging file containing * the intermediate data. */ public interface StagedValve extends Valve { /** * @return staging file where the valve stores its intermediate results */ public File getStagingFile(); }
Example 4-3 is a sample of an
AbstractValveclass implementing theValveinterface.Example 4-3 The AbstractValve Class Implementing the Valve Interface
package oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline; import java.io.IOException; /** * A bare bone implementation of Valve. The user should extend from * AbstractValve rather than implementing a Valve from scratch * */ public abstract class AbstractValve implements Valve { /** * The pipeline instance is stored as a member */ private Pipeline pipeline = null; /** * If reentrant is set to true, then the Valve must adhere to the following: * i) It must the first valve in the pipeline ii) Must implement hasNext * method and return true if more input streams are available A reentrant * valve will be called by the pipeline more than once and each time the * valve must return a different input stream e.g. Zipped entries within a * zip file */ private boolean reentrant = false; /* * Save the pipeline instance. * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#setPipeline(oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Pipeline) */ public void setPipeline(Pipeline pipeline) { this.pipeline = pipeline; } /* * Return the pipeline instance (non-Javadoc) * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#getPipeline() */ public Pipeline getPipeline() { return this.pipeline; } /* * Return true if the valve is reentrant (non-Javadoc) * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#isReentrant() */ public boolean isReentrant() { return this.reentrant; } /* * If set to true, the valve is reentrant (non-Javadoc) * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#setReentrant(boolean) */ public void setReentrant(boolean reentrant) { this.reentrant = reentrant; } /* * By default, set to false For valves that can return more than one * inputstreams to callers, this parameter must return true/false depending * on the availability of input streams (non-Javadoc) * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#hasNext() */ public boolean hasNext() { return false; } /* * Implemented by concrete valve (non-Javadoc) * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#execute(InputStreamContext) */ public abstract InputStreamContext execute(InputStreamContext in) throws PipelineException, IOException; /* * Implemented by concrete valve (non-Javadoc) * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#finalize(oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.InputStreamContext) */ public abstract void finalize(InputStreamContext in); /* * Implemented by concrete valve (non-Javadoc) * * @see oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.Valve#cleanup() */ public abstract void cleanup() throws PipelineException, IOException; }
Example 4-4 shows the
AbstractStagedValveclass extending theAbstractValveclass.Example 4-4 The AbstractStagedValve Class Extending the AbstractValve Class
package oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public abstract class AbstractStagedValve extends AbstractValve implements StagedValve { public abstract File getStagingFile(); public abstract void cleanup() throws IOException, PipelineException; public abstract InputStreamContext execute(InputStreamContext in) throws IOException, PipelineException; }
For more information on valves, see Appendix B, "Oracle JCA Adapter Valves."
- Step 2 Compiling the Valves
-
You must use the
bpm-infra.jarfile to compile the valves. Thebpm-infra.jarfile is located at$MW_HOME/AS11gR1SOA/soa/modules/oracle.soa.fabric_11.1.1/bpm-infra.jar.-
Reference the SOA project to the
bpm-infra.jarfile, by using the following procedure:-
In the Application Navigator, right-click the SOA project.
-
Select Project Properties. The Project Properties dialog is displayed.
-
Click Libraries and Classpath. The Libraries and Classpath pane is displayed as shown in Figure 4-5.
-
Click Add Jar/Directory. The Add Archive or Directory dialog is displayed.
-
Browse to select the
bpm-infra.jarfile. TheBpm-infra.jarfile is located at$MW_HOME/AS11gR1SOA/soa/modules/oracle.soa.fabric_11.1.1/bpm-infra.jar. -
Click OK. The
bpm-infra.jarfile is listed under Classpath Entries.
-
-
Compile the valves using the
bpm-infra.jarfile. -
Make the
JARfile containing the compiled valves available to the Oracle WebLogic Server classpath by adding the jar file to thesoainfradomain classpath. For example,$MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/soainfra/lib.
Note:
Ensure that you compilebpm-infra.jarwith JDK 6.0 to avoid compilation error such as"class file has wrong version 50.0, should be 49.0". -
- Step 3 Creating a Pipeline
-
To configure a pipeline, you must create an XML file that conforms to the following schema:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.oracle.com/adapter/pipeline/"> <xs:element name="pipeline"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element ref="valves"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element ref="valve" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xs:complexType mixed="true"> <xs:attribute name="reentrant" type="xs:NMTOKEN" use="optional" /> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> <xs:attribute name="useStaging" type="xs:NMTOKEN" use="optional" /> <xs:attribute name="batchNotificationHandler" type="xs:NMTOKEN" use=" optional" /> </xs:element> </xs:schemaThe following is a sample XML file configured for a pipeline with two valves,
SimpleUnzipValveandSimpleDecryptValve:<?xml version="1.0"?> <pipeline xmlns="http://www.oracle.com/adapter/pipeline/"> <valves> <valve>valves.SimpleUnzipValve</valve> <valve> valves.SimpleDecryptValve </valve> </valves> </pipeline> - Step 4 Adding the Pipeline to the SOA Project Directory
-
You must add the
pipeline.xmlfile to the SOA project directory. This step is required to integrate the pipeline with the Oracle File or FTP Adapter. Figure 4-6 shows a samplepipeline.xmlfile (unzippipeline.xml) added to theInboundUnzipAndOutboundZipproject.Figure 4-6 Project with unzippipeline.xml File
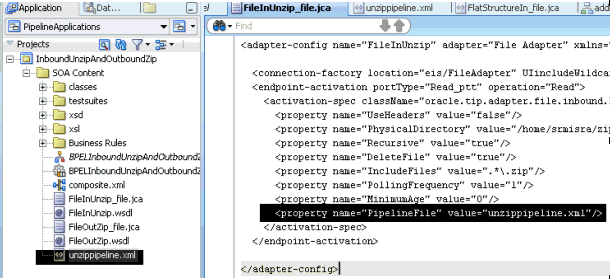
Description of "Figure 4-6 Project with unzippipeline.xml File"
- Step 5 Registering the Pipeline
-
The pipeline that is a part of the SOA project must be registered by modifying the inbound JCA file, by adding the following property:
<property name="PipelineFile" value="pipeline.xml"/>
For example, in the JCA file shown in Figure 4-6,
FileInUnzip_file.jca, the following property has been added to register anUnzippipeline with an Oracle File Adapter:<property name="PipelineFile" value="unzippipeline.xml"/>
There may be scenarios involving simple valves. A simple valve is one that does not require additional metadata such as reentrancy, and
batchNotificationHandlers. If the scenario involves simple valves, then the pipeline can be configured as anActivationSpecor anInteractionSpecproperty as shown in the following sample:<adapter-config name="FileInUnzip" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" UIincludeWildcard="*.zip" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-activation portType="Read_ptt" operation="Read"> <activation-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.inbound.FileActivationSpec"> <property../> <property name="PipelineValves" value="valves.SimpleUnzipValve,valves.SimpleDecryptValve"/> </activation-spec> </endpoint-activation> </adapter-config>Note:
There is no space after the comma (,) in thePipelineValvespropertyvalue.Note:
If you configure a pipeline using the"PipelineValves"property, then you cannot configure additional metadata such as Re-entrant Valve and Batch Notification Handler. Additional metadata can be configured only with"PipelineFile"that is used for the XML-based approach.
4.2.14.3 Using a Re-Entrant Valve For Processing Zip Files
The re-entrant valve allows a user to process individual entries within a zip file. In a scenario that involves processing all entries within a zip file, wherein each entry is encrypted using the Data Encryption Standard (DES), you can configure the valve by adding the reentrant="true" attribute to the unzip valve as follows:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<pipeline xmlns="http://www.oracle.com/adapter/pipeline/">
<valves>
<valve reentrant="true">valves.ReentrantUnzipValve</valve>
<valve> valves.SimpleDecryptValve </valve>
</valves>
</pipeline>
In this example, the pipeline invokes the ReentrantUnzipValve and then the SimpleDecryptValve repeatedly in the same order until the entire zip file has been processed. In other words, the ReentrantUnzipValve is invoked first to return the data from the first zipped entry, which is then fed to the SimpleDecryptValve for decryption, and the final content is returned to the adapter. The process repeats until all the entries within the zip file are processed.
Additionally, the valve must set the message key using the setMessageKey() API. For more information refer to Appendix B, "An Unzip Valve for processing Multiple Files."
If there are translation errors for individual entries within the zip file, then entries with the translation errors are rejected and the other entries are processed.
If there are errors during the publish operation, then the publish operation is retried and the retry semantic holds. If the retry semantic does not hold, then the original file is rejected and the pipeline ends.
4.2.14.4 Configuring Batch Notification Handler
The BatchNotificationHandler API is used in conjunction with the Oracle File and FTP Adapter inbound de-batchability. In a de-batching scenario, each file contains multiple messages, and some sort of bookkeeping is required for crash-recovery. This is facilitated by the BatchNotificationHandler API, which lets you receive notification from the pipeline whenever a batch begins, occurs, or ends. The following is the BatchNotificationHandler interface:
package oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline; /* * Whenever the caller processes de-batchable files, each file can * have multiple messages and this handler allows the user to plug in * a notification mechanism into the pipeline. * * This is particularly useful in crash recovery situations */ public interface BatchNotificationHandler { /* * The Pipeline instance is set by the PipelineFactory when the * BatchNotificationHandler instance is created */ public void setPipeline(Pipeline pipeline); public Pipeline getPipeline(); /* * Called when the BatchNotificationHandler is instantiated */ public void initialize(); /* * Called by the adapter when a batch begins, the implementation must return * a BatchContext instance with the following information: * i) batchId: a unique id that will be returned every time onBatch is invoked by called * ii)line/col/record/offset: for error recovery cases */ public BatchContext onBatchBegin(); /* * Called by the adapter when a batch is submitted. The parameter holds the * line/column/record/offset for the successful batch that is published. * Here the implementation must save these in order to recover from crashes */ public void onBatch(BatchContext ctx); /* * Called by the adapter when a batch completes. This must be used to clean * up */ public void onBatchCompletion(boolean success); }
To use a pipeline with de-batching, you must configure the pipeline with a BatchNotificationHandler instance as follows:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <pipeline xmlns="http://www.oracle.com/adapter/pipeline/" batchNotificationHandler="oracle.tip.pc.services.pipeline.ConsoleBatchNotificationHandler"> <valves> <valve reentrant="true">valves.SimpleUnzipValve</valve> <valve>valves.SimpleDecryptValve</valve> </valves> </pipeline>
4.2.15 Error Handling
The Oracle File Adapter and Oracle FTP Adapter provide inbound error handling capabilities, such as the uniqueMessageSeparator property.
In the case of debatching (multiple messages in a single file), messages from the first bad message to the end of the file are rejected.
If each message has a unique separator and that separator is not part of any data, then rejection can be more fine grained. In these cases, you can define a uniqueMessageSeparator property in the schema element of the native schema to have the value of this unique message separator. This property controls how the adapter translator works when parsing through multiple records in one file (debatching).
This property enables recovery even when detecting bad messages inside a large batch file. When a bad record is detected, the adapter translator skips to the next unique message separator boundary and continues from there. If you do not set this property, then all records that follow the record with errors are also rejected.
The unique-message-separator (ums) is used in debatching mode in exception conditions where the translator skips to the next ums character whenever it gets an exception. This behavior is only applicable to de-batching since the translator is needed to reject bad records and to continue processing the good ones.
If the ums character is part of the data, the translator does not behave properly because the ums character would be read as a part of the data.
The following schema file provides an example of using the uniqueMessageSeparator property:
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:nxsd="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/nxsd"
targetNamespace="http://TargetNamespace.com/Reader"
xmlns:tns="http://TargetNamespace.com/Reader"
elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified"
nxsd:encoding="US-ASCII" nxsd:stream="chars"
nxsd:version="NXSD" nxsd:uniqueMessageSeparator="${eol}">
<xsd:element name="emp-listing">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="emp" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="GUID" type="xsd:string" nxsd:style="terminated"
nxsd:terminatedBy="," nxsd:quotedBy=""">
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="Designation" type="xsd:string"
nxsd:style="terminated" nxsd:terminatedBy=","
nxsd:quotedBy=""">
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="Car" type="xsd:string" nxsd:style="terminated"
nxsd:terminatedBy="," nxsd:quotedBy=""">
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="Labtop" type="xsd:string"
nxsd:style="terminated" nxsd:terminatedBy=","
nxsd:quotedBy=""">
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="Location" type="xsd:string"
nxsd:style="terminated" nxsd:terminatedBy=","
nxsd:quotedBy=""">
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:schema>
<!--NXSDWIZ:D:\work\jDevProjects\Temp_BPEL_process\Sample2\note.txt:-->
<!--USE-HEADER:false:-->
For information about handling rejected messages, connection errors, and message errors, see Section 2.22, "Error Handling."
4.2.15.1 Sending a Malformed XML File to a Local Filesystem Folder
During an Inbound Read operation, if a malformed XML file is read, the malformed file results in an error. The errored file is by default sent to the remote file system for archival.
The errored file can be archived at a local filesystem by specifying the useRemoteErrorArchive property in the jca file and setting that property to false.
The default value for this property is true.
4.2.16 Threading Model
This section describes the threading models that Oracle File and FTP Adapters support. An understanding of the threading models is required to throttle or de-throttle the Oracle File and FTP Adapters. The Oracle File and FTP Adapters use the following threading models:
4.2.16.1 Default Threading Model
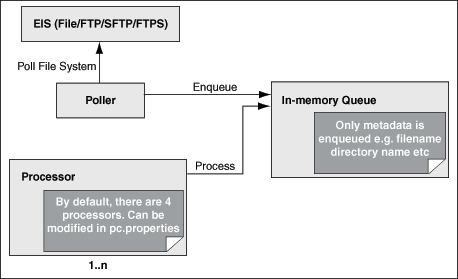
In the default threading model, a poller is created for each inbound Oracle File or FTP Adapter endpoint. The poller enqueues file metadata into an in-memory queue, which is processed by a global pool of processor threads. Figure 4-7 shows a default threading model.
The following steps highlight the functioning of the default threading model:
-
The poller periodically looks for files in the input directory. The interval at which the poller looks for files is specified using the
PollingFrequencyparameter in the inboundJCAfile. -
For each new file that the poller detects in the configured inbound directory, the poller enqueues information such as file name, file directory, modified time, and file size into an internal in-memory queue.
Note:
New files are files that are not already being processed. -
A global pool of processor worker threads wait to process from the in-memory queue.
-
Processor worker threads pick up files from the internal queue, and perform the following actions:
-
Stream the file content to an appropriate translator (for example, a translator for reading text, binary, XML, or opaque data.)
-
Publishes the XML result from the translator to the SCA infrastructure.
-
Performs the required postprocessing, such as deletion or archival after the file is processed.
-
4.2.16.2 Modified Threading Model
You can modify the default threading behavior of Oracle File and FTP Adapters. Modifying the threading model results in a modified throttling behavior of Oracle File and FTP Adapters. The following sections describe the modified threading behavior of the Oracle File and FTP Adapters:
The single threaded model is a modified threaded model that enables the poller to assume the role of a processor. The poller thread processes the files in the same thread. The global pool of processor threads is not used in this model. You can define the property for a single threaded model in the inbound JCA file as follows:
<activation-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.inbound.FileActivationSpec"> <property../> <property name="SingleThreadModel" value="true"/> <property../> </activation-spec>
The partitioned threaded model is a modified threaded model in which the in-memory queue is partitioned and each composite application receives its own in-memory queue. The Oracle File and FTP Adapters are enabled to create their own processor threads rather than depend on the global pool of processor worker threads for processing the enqueued files. You can define the property for a partitioned model in the inbound JCA file as follows:
<activation-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.inbound.FileActivationSpec"> <property../> <property name="ThreadCount" value="4"/> <property../> </activation-spec>
In the preceding example for defining the property for a partitioned model:
-
If the
ThreadCountproperty is set to0, then the threading behavior is like that of the single threaded model. -
If the
ThreadCountproperty is set to-1, then the global thread pool is used, as in the default threading model. -
The maximum value for the
ThreadCountproperty is40.
4.2.17 Performance Tuning
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters support the performance tuning feature by providing knobs to throttle the inbound and outbound operations. The Oracle File and FTP Adapters also provide knobs that can be used to tune the performance of outbound operations.
For more information about performance tuning, see "Oracle JCA Adapters for Files/FTP" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Performance and Tuning Guide.
4.2.18 High Availability
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters support the high availability feature for the active-active topology with Oracle BPEL Process Manager and Mediator service engines. It supports this feature for both inbound and outbound operations.
4.2.19 Multiple Directories
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters support polling multiple directories within a single activation. You can specify multiple directories in JDeveloper as opposed to a single directory. This is applicable to both physical and logical directories.
Note:
If the inbound Oracle File Adapter is configured for polling multiple directories for incoming files, then all the top-level directories (inbound directories where the input files appear) must exist before the file reader starts polling these directories.After selecting the inbound directory or directories, you can also specify whether the subdirectories must be processed recursively. If you check the Process Files Recursively option, then the directories would be processed recursively. By default, this option is selected, in the File Directories page, as shown in Figure 4-8.
When you choose multiple directories, the generated JCA files use semicolon(;) as the separator for these directories. However, if you want, you can change the separator to something else. If you do so, manually add DirectorySeparator="chosen separator" in the generated JCA file. For example, if you want to use comma (,) as the separator, you must first change the separator to "," in the Physical directory and then add <property name="DirectorySeparator" value=","/>, in the JCA file.
Additionally, if you choose to process directories recursively and one or more subdirectories do not have the appropriate permissions, then the inbound adapter throws an exception during processing. If you want to ignore this exception, then you must define a binding property with the name ignoreListingErrors in your composite.xml as shown in the following example:
<service name="FlatStructureIn">
<interface.wsdl interface="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/FlatStructureIn/#wsdl.interface(Read_ptt)"/>
<binding.jca config="FlatStructureIn_file.jca">
<property name="ignoreListingErrors" type="xs:string" many="false">true</property>
</binding.jca>
</service>
Figure 4-8 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Directories Page
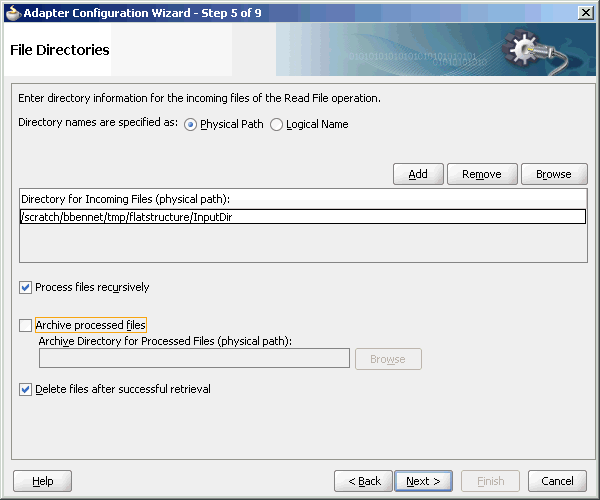
Description of "Figure 4-8 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Directories Page"
4.2.20 Append Mode
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters enable you to configure outbound interactions that append to an existing file. The Append to Existing File option allows the outbound invoke to write to the same file. There are two ways in which you can append to a file name:
-
Statically - in the JCA file for the outbound Oracle File Adapter
-
Dynamically - using the header mechanism
Note:
The append mode is not supported for SFTP scenarios, where instead of appending to the existing file, the file is overwritten.When you select the Append to existing file option in the File Configuration page, the batching options such as Number of Messages Equals, Elapsed Time Exceeds, File Size Exceeds options are disabled. Figure 4-9 displays the Append to Existing File option.
Figure 4-9 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Configuration Page
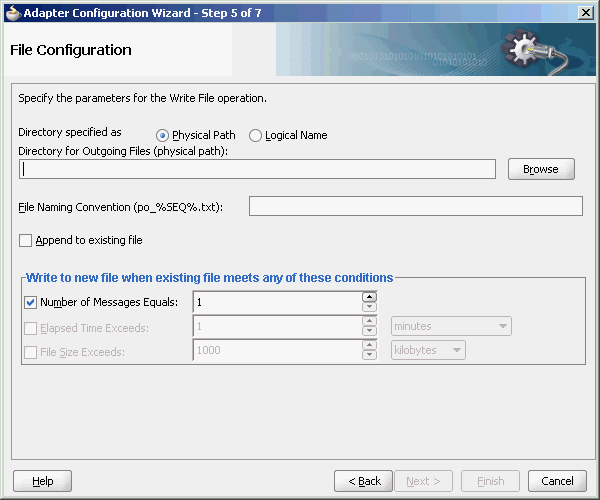
Description of "Figure 4-9 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Configuration Page"
Batching option is disabled if "Append" is chosen in the wizard. In addition, the following error message is displayed if the user specifies a dynamic file naming convention as opposed to a static file naming convention:
You can not choose to Append Files and use a dynamic file naming convention at the same time
If you are using the "Append" functionality in Oracle FTP Adapter, ensure that the FTP server supports the "APPE" command.
4.2.21 Recursive Processing of Files Within Directories in Oracle FTP Adapter
In earlier versions of the Oracle SOA Suite, the inbound Oracle FTP Adapter used the NLST (Name List) FTP command to read a list of file names from the FTP server. However, the NLST command does not return directory names and therefore does not allow recursive processing within directories. In the 11g release, the Oracle FTP Adapter uses the LIST command, instead.
However, the response from the LIST command is different for different FTP servers. To incorporate the subtle differences in results from the LIST command in a standard manner, the following parameters are added to the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter:
-
defaultDateFormat: This parameter specifies the default date format value. On the FTP server, this is the value for files that are older. The default value for this parameter is
MMM d yyyyas most UNIX-type FTP servers return the last modified time stamp for older files in theMMM d yyyyformat. For example,Jan 31 2006.You can find the default date format for your FTP server by using the
ls -lcommand by using a FTP command-line client. For example,ls -lon a vsftpd server running on Linux returns the following:-rw-r--r-- 1 500 500 377 Jan 22 2005 test.txt
For Microsoft Windows NT FTP servers, the
defaultDateFormatisMM-dd-yy hh:mma, for example,03-24-09 08:06AM <DIR> oracle. -
recentDateFormat: This parameter specifies the recent date format value. On the FTP server, this is the value for files that were recently created.
The default value for this parameter is
MMM d HH:mmas most UNIX-type FTP servers return the last modified date for recently created files inMMM d HH:mmformat, for example,Jan 31 21:32.You can find the default date format for your FTP server by using the
ls -lcommand from an FTP command-line client. For example,ls -lon a vsftpd server running on Linux returns the following:150 Here comes the directory listing. -rw-r--r-- 1 500 500 377 Jan 30 21:32 address.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 500 500 580 Jan 3121:32 container.txt .....................................................................................
For Microsoft Windows NT FTP servers, the
recentDateFormatparameter is in theMM-dd-yy hh:mma, format, for example,03-24-09 08:06AM <DIR> oracle. -
serverTimeZone: The server time zone, for example, America/Los_Angeles. If this parameter is set to blank, then the default time zone of the server running the Oracle FTP Adapter is used.
-
listParserKey: Directs the Oracle FTP Adapter on how it should parse the response from the
LISTcommand. The default value is UNIX, in which case the Oracle FTP Adapter uses a generic parser for UNIX-like FTP servers. Apart fromUNIX, the other supported values areWINandWINDOWS, which are specific to the Microsoft Windows NT FTP server.Note:
The locale language for the FTP server can be different from the locale language for the operating system. Do not assume that the locale for the FTP server is the same as the locale for the operating system it is running on. You must set theserverLocaleLanguage,serverLocaleCountry, andserverLocaleVariantparameters in such cases. -
serverLocaleLanguage: This parameter specifies the locale construct for language.
-
serverLocaleCountry: This parameter specifies the locale construct for country.
-
serverLocaleVariant: This parameter specifies the locale construct for variant.
Configure the Parameters in the Deployment Descriptor
The standard date formats of an FTP server are usually configured when the FTP server is installed. If your FTP server uses a format "MMM d yyyy" for defaultDateFormat and "MMM d HH:mm" for recentDateFormat, then your Oracle FTP Adapter must use the same formats in its corresponding deployment descriptor.
If you enter "ls -l" from a command-line FTP, then you can see the following:
200 PORT command successful. Consider using PASV. 150 Here comes the directory listing. -rw-r--r-- 1 500 500 377 Jan 22 21:32 1.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 500 500 580 Jan 22 21:32 2.txt .................................................................................
This is the recentDateFormat parameter for your FTP server, for example MMM d HH:mm (Jan 22 21:32). Similarly, if your server has an old file, then the server does not show the hour and minute part and it shows the following:
-rw-r--r-- 1 500 500 377 Jan 22 2005 test.txt
This is the default date format, for example MMM d yyyy (Jan 22 2005).
Additionally, the serverTimeZone parameter is used to by the Oracle FTP Adapter to parse time stamps for FTP server running in a specific time zone. The value for this is either an abbreviation such as "PST" or a full name such as "America/Los_Angeles".
Additionally, the FTP server might be running on a different locale. The serverLocaleLanguage, serverLocaleCountry, and serverLocaleVariant parameters are used to construct a locale from language, country, variant where
-
language is a lowercase two-letter ISO-639 code, for example, en
-
country is an uppercase two-letter ISO-3166 code, for example, US
-
variant is a vendor and browser-specific code.
If these locale parameters are absent, then the Oracle FTP Adapter uses the system locale to parse the time stamp.
Additionally, if the FTP server is running on a different system than the SOA suite, then you must handle the time zone differences between them. You must convert the time difference between the FTP server and the system running the Oracle FTP Adapter to milliseconds and add the value as a binding property:"timestampOffset" in the composite.xml.
For example, if the FTP server is six hours ahead of your local time, you must add the following endpoint property to your service or reference:
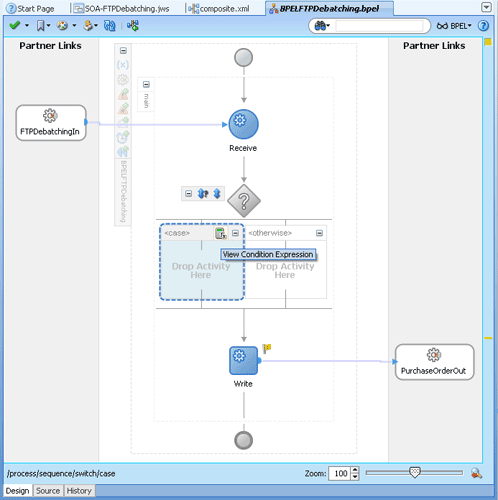
<service name="FTPDebatchingIn">
<interface.wsdl
interface="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/ftp/FTPDebatchingIn/#wsdl.interface(Get_ptt)"/>
<binding.jca config="DebatchingIn_ftp.jca">
<property name=" timestampOffset" type="xs:string" many="false" source="" override="may"> 21600000</property>
</binding.jca>
</service>.
Some FTP servers do not work well with the LIST command. In such cases, use the NLST command for listing, but you cannot process directories recursively with NLST.
If you want to use the NLST command, then you must add the following property to the JCA file, for example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<adapter-config name="FTPDebatchingIn" adapter="Ftp Adapter"
xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/Ftp/FtpAdapter" UIincludeWildcard="*.txt"
adapterRef=""/>
<activation-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.ftp.inbound.FTPActivationSpec">
…………………………………………..
…………………………………………..
<property name="UseNlst" value="true"/>
</activation-spec>
</endpoint-activation>
</adapter-config>
4.2.22 Securing Enterprise Information System Credentials
When a resource adapter makes an outbound connection with an Enterprise Information System (EIS), it must sign on with valid security credentials. In accordance with the J2CA 1.5 specification, Oracle WebLogic Server supports both container-managed and application-managed sign-on for outbound connections. At runtime, Oracle WebLogic Server determines the chosen sign-on mechanism, based on the information specified in either the invoking client component's deployment descriptor or the res-auth element of the resource adapter deployment descriptor. This section describes the procedure for securing the user name and password for Oracle JCA Adapters by using Oracle WebLogic Server container-managed sign-on.
Both, Oracle WebLogic Server and EIS maintain independent security realms. A container-managed sign-on enables you to sign on to Oracle WebLogic Server and also be able to use applications that access EIS through a resource adapter without having to sign on separately to the EIS. Container-managed sign-on in Oracle WebLogic Server uses credential mappings. The credentials (user name/password pairs or security tokens) of Oracle WebLogic security principals (authenticated individual users or client applications) are mapped to the corresponding credentials required to access EIS. You can configure credential mappings for applicable security principals for any deployed resource adapter.
To configure credential mappings, you can specify the user names and passwords in the weblogic-ra.xml file for the corresponding adapter or perform the following procedure by accessing the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:
-
Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Click Deployments in the Domain Structure pane. The deployed applications and adapters are displayed, as shown in Figure 4-10.
Figure 4-10 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Summary of Deployments Page
Description of "Figure 4-10 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Summary of Deployments Page"
-
Click the adapter for which you must create the security credentials. For example, click
FtpAdapter. The Settings for FtpAdapter page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-11.Figure 4-11 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FTPAdapter Page
Description of "Figure 4-11 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FTPAdapter Page"
-
Click the Security tab. The Settings for FTPAdapter page with the Stand-Alone Resource Adapter Roles pane displayed, as shown in Figure 4-12.
Figure 4-12 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FTPAdapter Page
Description of "Figure 4-12 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FTPAdapter Page"
-
Click the Credential Mappings tab.
-
Click New in the Credential Mappings pane. The Create a New Security Credential Mapping page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-13.
Figure 4-13 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page
Description of "Figure 4-13 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page"
-
Select eis/Ftp/FtpAdapter (JNDI for Oracle FTP Adapter) to create a security credential map entry for Oracle FTP Adapter, as shown in Figure 4-14.
Figure 4-14 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page
Description of "Figure 4-14 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page"
-
Click Next. The Create a New Security Credential Mapping – WebLogic Server User page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-15.
Figure 4-15 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page
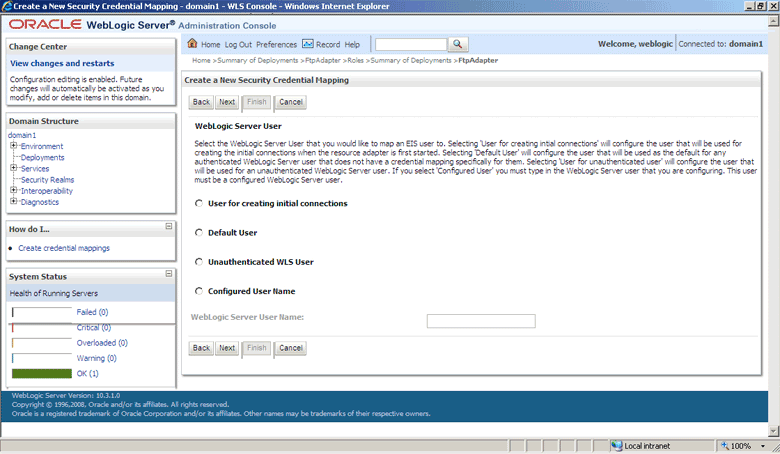
Description of "Figure 4-15 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page"
Note:
Credential mapping is not supported for the User for creating initial connections and Unauthenticated WLS User options. -
Select Configured User Name and enter the Oracle WebLogic Server user name in the WebLogic Server User Name field, as shown in Figure 4-16. For example, enter
weblogic, which is the default user name.Figure 4-16 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page
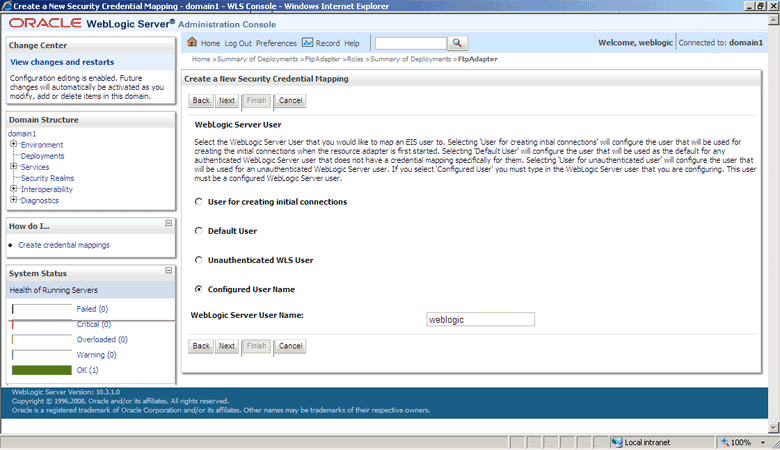
Description of "Figure 4-16 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page"
-
Click Next. The Create a New Security Credential Mapping – EIS User Name and Password page is displayed.
-
Enter the EIS user name in the EIS User Name field, the EIS password in the EIS Password field, and then reenter the EIS password in the Confirm Password field to confirm the password, as shown in Figure 4-17.
Figure 4-17 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page
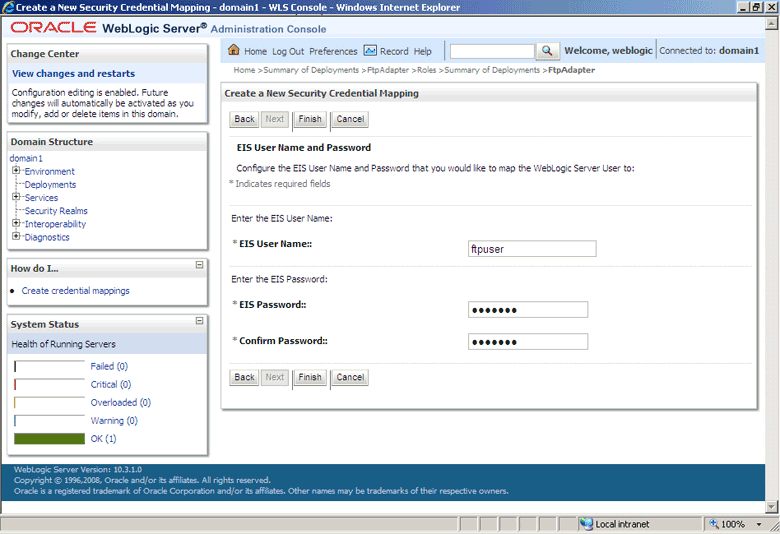
Description of "Figure 4-17 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Create a New Security Credential Mapping Page"
-
Click Finish. The new security credential mapping is created, as shown in Figure 4-18.
Figure 4-18 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FTPAdapter Page
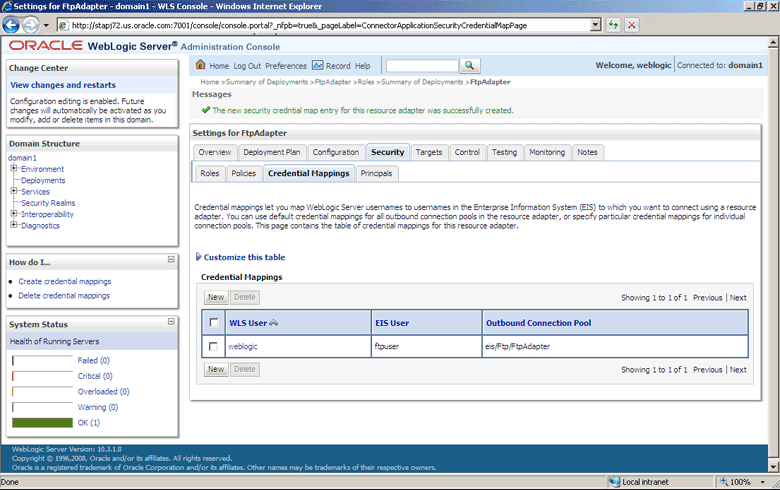
Description of "Figure 4-18 The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FTPAdapter Page"
4.3 Oracle File and FTP Adapter Concepts
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters concepts are discussed in the following sections:
-
Section 4.3.3, "Oracle File Adapter Synchronous Read Concepts"
-
Section 4.3.7, "Oracle FTP Adapter Synchronous Get File Concepts"
4.3.1 Oracle File Adapter Read File Concepts
In the inbound direction, the Oracle File Adapter polls and reads files from a file system for processing. This section provides an overview of the inbound file reading capabilities of the Oracle File Adapter. You use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to configure the Oracle File Adapter for use with a BPEL process or a Mediator. Configuring the Oracle File Adapter creates an inbound WSDL and JCA file pair.
The following sections describe the Oracle File Adapter read file concepts:
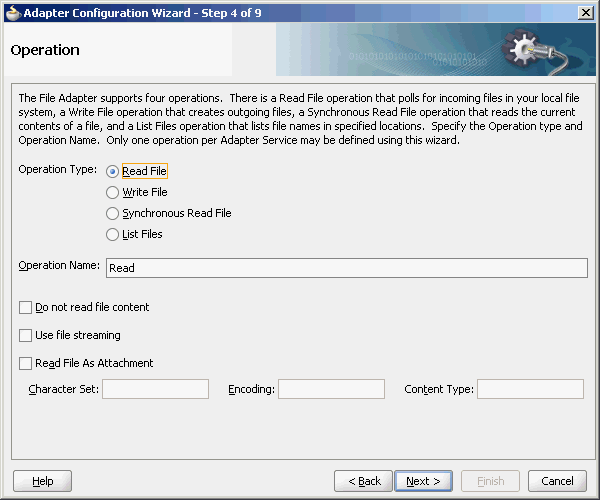
4.3.1.1 Inbound Operation
For inbound operations with the Oracle File Adapter, select the Read File operation, as shown in Figure 4-19.
Figure 4-19 Selecting the Read File Operation
Description of "Figure 4-19 Selecting the Read File Operation"
4.3.1.2 Inbound File Directory Specifications
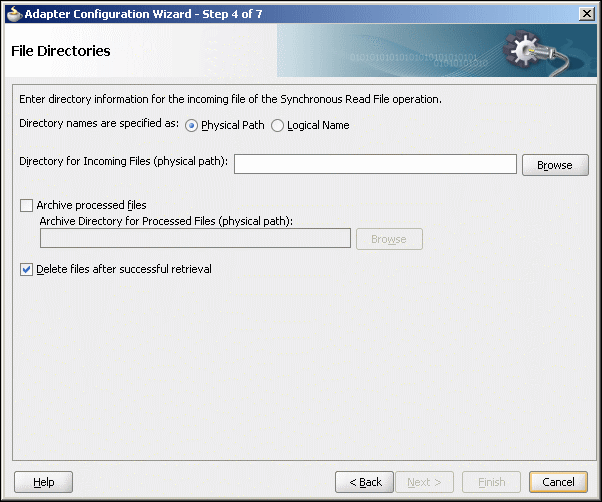
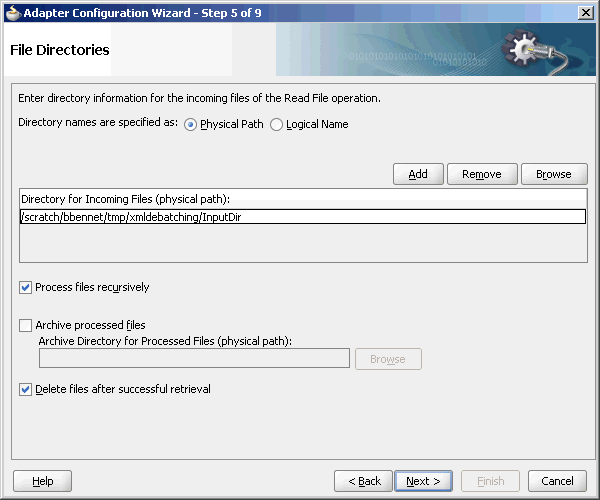
The File Directories page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard shown in Figure 4-20 enables you to specify information about the directory to use for reading inbound files and the directories in which to place successfully processed files. You can choose to process files recursively within directories. You can also specify multiple directories.
Figure 4-20 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Specifying Incoming Files
Description of "Figure 4-20 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Specifying Incoming Files"
The following sections describe the file directory information to specify:
4.3.1.2.1 Specifying Inbound Physical or Logical Directory Paths in SOA Composite
You can specify inbound directory names as physical or logical paths in the composite involving Oracle BPEL PM and Mediator. Physical paths are values such as c:\inputDir.
Note:
If the inbound Oracle File Adapter is configured for polling multiple directories for incoming files, then all the top-level directories (inbound directories where the input file appears) must exist before the file reader starts polling these directories.In the composite, logical properties are specified in the inbound JCA file and their logical-physical mapping is resolved by using binding properties. You specify the logical parameters once at design time, and you can later modify the physical directory name as needed.
For example, the generated inbound JCA file looks as follows for the logical input directory name InputFileDir.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<adapter-config name="FlatStructureIn" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" UIincludeWildcard="*.txt" adapterRef=""/>
<endpoint-activation operation="Read">
<activation-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.inbound.FileActivationSpec">
<property name="UseHeaders" value="false"/>
<property name="LogicalDirectory" value="InputFileDir"/>
<property name="Recursive" value="true"/>
<property name="DeleteFile" value="true"/>
<property name="IncludeFiles" value=".*\.txt"/>
<property name="PollingFrequency" value="10"/>
<property name="MinimumAge" value="0"/>
<property name="OpaqueSchema" value="false"/>
</activation-spec>
</endpoint-activation>
</adapter-config>
In the composite.xml file, you then provide the physical parameter values (in this case, the directory path) of the corresponding logical ActivationSpec or InteractionSpec. This resolves the mapping between the logical directory name and actual physical directory name.
<service name="FlatStructureIn">
<interface.wsdl interface="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/FlatStructureIn/#wsdl.interface(Read_ptt)"/>
<binding.jca config="FlatStructureIn_file.jca">
<property name=" InputFileDir" type="xs:string" many="false" source="" override="may"> /home/user/inputDir</property>
</binding.jca>
</service>
4.3.1.2.2 Archiving Successfully Processed Files
This option enables you to specify a directory in which to place successfully processed files. You can also specify the archive directory as a logical name. In this case, you must follow the logical-to-physical mappings described in Section 4.3.1.2.1, "Specifying Inbound Physical or Logical Directory Paths in SOA Composite."
4.3.1.2.3 Deleting Files After Retrieval
This option enables you to specify whether to delete files after a successful retrieval. If this check box is not selected, processed files remain in the inbound directory but are ignored. Only files with modification dates more recent than the last processed file are retrieved. If you place another file in the inbound directory with the same name as a file that has been processed but the modification date remains the same, then that file is not retrieved.
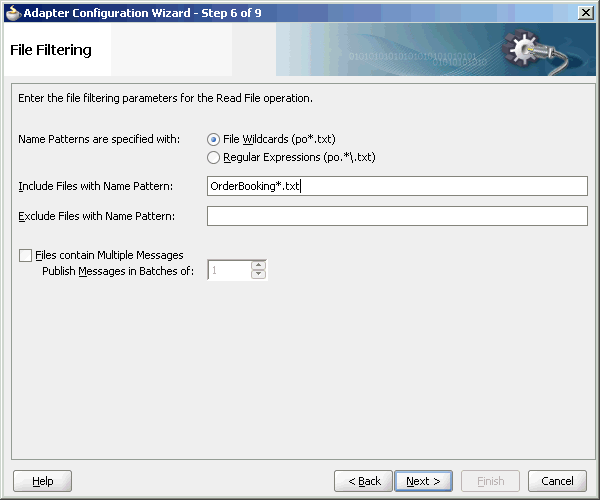
4.3.1.3 File Matching and Batch Processing
The File Filtering page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard shown in Figure 4-21 enables you to specify details about the files to retrieve or ignore.
The Oracle File Adapter acts as a file listener in the inbound direction. The Oracle File Adapter polls the specified directory on a local or remote file system and looks for files that match specified naming criteria.
Figure 4-21 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-File Filtering Page
Description of "Figure 4-21 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-File Filtering Page"
The following sections describe the file filtering information to specify:
4.3.1.3.1 Specifying a Naming Pattern
Specify the naming convention that the Oracle File Adapter uses to poll for inbound files. You can also specify the naming convention for files you do not want to process. Two naming conventions are available for selection. The Oracle File Adapter matches the files that appear in the inbound directory.
-
File wildcards (
po*.txt)Retrieves all files that start with
poand end with.txt. This convention conforms to Windows operating system standards.
-
Regular expressions (
po.*\.txt)Retrieves all files that start with
poand end with.txt. This convention conforms to Java Development Kit (JDK) regular expression (regex) constructs.
Notes:
-
If you later select a different naming pattern, ensure that you also change the naming conventions you specify in the Include Files and Exclude Files fields. The Adapter Configuration Wizard does not automatically make this change for you.
-
Do not specify *.* as the convention for retrieving files.
-
Be aware of any file length restrictions imposed by your operating system. For example, Windows operating system file names cannot be more than 256 characters in length (the file name, plus the complete directory path). Some operating systems also have restrictions on the use of specific characters in file names. For example, Windows operating systems do not allow characters such as
backslash(\), slash (/), colon (:), asterisk (*), left angle bracket (<), right angle bracket (>), or vertical bar(|).
4.3.1.3.2 Including and Excluding Files
If you use regular expressions, the values you specify in the Include Files and Exclude Files fields must conform to JDK regular expression (regex) constructs. For both fields, different regex patterns must be provided separately. The Include Files and Exclude Files fields correspond to the IncludeFiles and ExcludeFiles parameters, respectively, of the inbound WSDL file.
Note:
The regex pattern complies with the JDK regex pattern. According to the JDK regex pattern, the correct connotation for a pattern of any characters with any number of occurrences is a period followed by a plus sign(.+). An asterisk (*) in a JDK regex is not a placeholder for a string of any characters with any number of occurrences.If you want the inbound Oracle File Adapter to pick up all file names that start with po and which have the extension txt, then you must specify the Include Files field as po.*\.txt when the name pattern is a regular expression. In this regex pattern example:
-
A period (
.)indicates any character. -
An asterisk (
*) indicates any number of occurrences. -
A backslash followed by a period (\.) indicates the character period (.) as indicated with the backslash escape character.
The Exclude Files field is constructed similarly.
If you have Include Files field and Exclude Files field expressions that have an overlap, then the exclude files expression takes precedence. For example, if Include Files is set to abc*.txt and Exclude Files is set to abcd*.txt, then you will not receive any abcd*.txt files.
Note:
You must enter a name pattern in the Include Files with Name Pattern field and not leave it empty. Otherwise, the inbound adapter service reads all the files present in the inbound directory, resulting in incorrect results.Table 4-3 lists details of Java regex constructs.
Note:
Do not begin JDK regex pattern names with the following characters: plus sign (+), question mark (?), or asterisk (*).Table 4-3 Java Regular Expression Constructs
| Matches | Construct |
|---|---|
|
Characters |
- |
|
The character |
|
|
The backslash character |
|
|
The character with octal value |
|
|
The character with octal value |
|
|
The character with octal value |
|
|
The character with hexadecimal value |
|
|
The character with hexadecimal value |
|
|
The tab character |
|
|
The new line (line feed) character |
|
|
The carriage-return character |
|
|
The form-feed character |
|
|
The alert (bell) character |
|
|
The escape character |
|
|
The control character corresponding to |
|
|
- |
- |
|
Character classes |
- |
|
|
|
|
Any character except |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
Predefined character classes |
- |
|
Any character (may or may not match line terminators) |
- |
|
A digit: |
|
|
A nondigit: |
|
|
A white space character: |
|
|
A nonwhitespace character: |
|
|
A word character: |
|
|
A nonword character: |
|
|
Greedy quantifiers |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For details about Java regex constructs, go to
4.3.1.3.3 File Include and Exclude
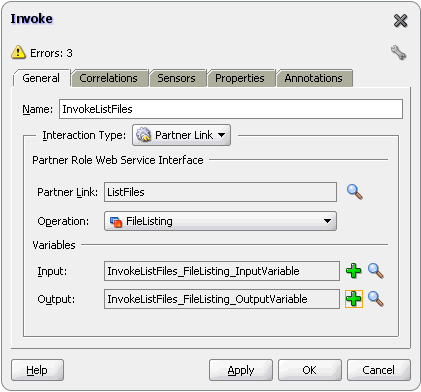
The FileList operation does not expose the java.file.IncludeFiles property. This property is configured while designing the adapter interaction and cannot be overridden via headers, for example:
<adapter-config name="ListFiles" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" UIincludeWildcard="*.txt" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="FileListing_ptt" operation="FileListing"> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileListInteractionSpec"> <property name="PhysicalDirectory" value="%INP_DIR%"/> <property name="PhysicalDirectory" value="%INP_DIR%"/> <property name="Recursive" value="true"/> <property name="Recursive" value="true"/> <property name="IncludeFiles" value=".*\.txt"/> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config>
In this example, IncludeFiles, once set, cannot be changed.
4.3.1.3.4 Debatching Multiple Inbound Messages
You can select whether incoming files have multiple messages, and specify the number of messages in one batch file to publish. When a file contains multiple messages and this check box is selected, this is referred to as debatching. Nondebatching is applied when the file contains only a single message and the check box is not selected. Debatching is supported for native and XML files.
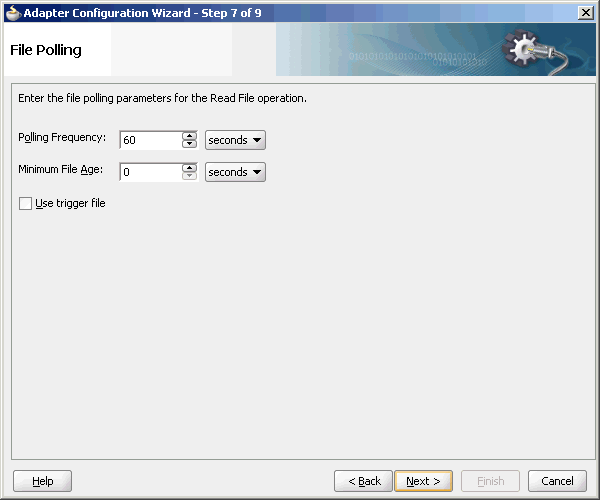
4.3.1.4 File Polling
The File Polling page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard shown in Figure 4-22 enables you to specify the following inbound polling parameters:
-
The frequency with which to poll the inbound directory for new files to retrieve.
-
The minimum file age of files to retrieve. For example, this polling parameter enables a large file to be completely copied into the directory before it is retrieved for processing. The age is determined by the last modified time stamp. For example, if you know that it takes three to four minutes for a file to be written, then set the minimum age to five minutes. If a file is detected in the input directory and its modification time is less than five minutes older than the current time, then the file is not retrieved because it is still potentially being written to.
Figure 4-22 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-File Polling Page
Description of "Figure 4-22 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-File Polling Page"
Note:
You must not manually change the value of polling parameters inJCA files. You must use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to modify this parameter.By default, polling by inbound Oracle File and FTP Adapters start as soon as the endpoint is activated. However, if you want more control over polling, then you can use a file-based trigger. Once the Oracle File or FTP Adapter finds the specified trigger file in a local or remote directory, it starts polling for the files in the inbound directory.
For example, a BPEL process is writing files to a directory and a second BPEL process is polling the same directory for files. If you want the second process to start polling the directory only after the first process has written all the files, then you can use a trigger file. You can configure the first process to create a trigger file at the end. The second process starts polling the inbound directory once it finds the trigger file.
The trigger file directory can be the same as the inbound polling directory or different from the inbound polling directory. However, if your trigger file directory and the inbound polling directory are the same, then you should ensure that the name of the trigger file is not similar to the file filter specified in the Adapter Configuration page shown in Figure 4-21.
The content of a trigger file is never read and therefore should not be used as payload for an inbound receive activity.
Table 4-4 lists the parameters that you must specify in the inbound service JCA file:
Table 4-4 Trigger File Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
or
|
The physical or logical name of the directory in which the Oracle File and FTP Adapters look for the trigger file. The |
|
|
|
The name of the trigger file. |
|
|
|
Strategy that is used as the triggering mechanism. The value can be one of the following: EndpointActivation: The adapter looks for the trigger file every time the composite is activated. Note: The composite gets activated every time you start the container or redeploy the application, or retire or activate the composite application from Oracle Enterprise Manager. Every time you restart the container, the composite application is not triggered until it sees the trigger file in the specified directory. OnceOnly: The adapter looks for the trigger file only once in its lifetime. Once it finds the trigger file, it remember that across restarts and redeployments. EveryTime: The adapter looks for the trigger file on each polling cycle.The default value for |
|
The following is a sample JCA file for the inbound service:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <adapter-config name="FlatStructureIn" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" UIincludeWildcard="*.txt" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-activation operation="Read"> <activation-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.inbound.FileActivationSpec"> <property.../> <property name="TriggerFilePhysicalDirectory" value="/tmp/flat/ArchiveDir"/> </activation-spec> </endpoint-activation> </adapter-config>
4.3.1.5 Postprocessing
The Oracle File Adapter supports several postprocessing options. After processing the file, files are deleted if specified in the File Polling page shown in Figure 4-22. Files can also be moved to a completion (archive) directory if specified in the File Directories page shown in Figure 4-20.
4.3.1.6 Native Data Translation
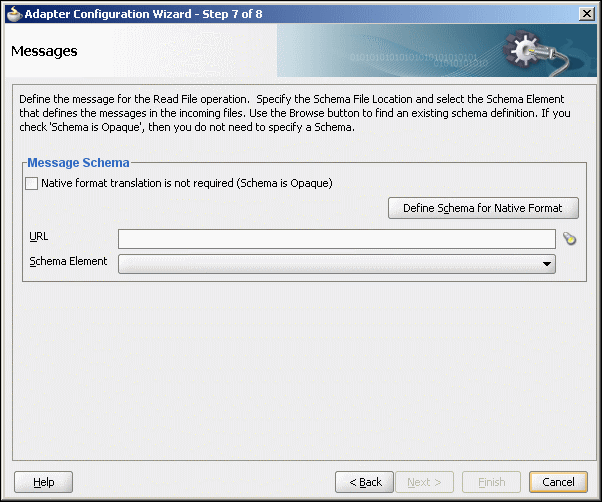
The next Adapter Configuration Wizard page that appears is the Messages page shown in Figure 4-23. This page enables you to select the XSD schema file for translation.
Figure 4-23 Specifying the Schema - Messages Page
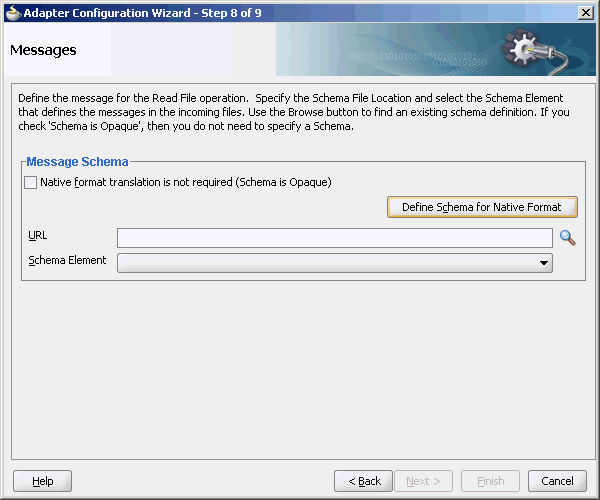
Description of "Figure 4-23 Specifying the Schema - Messages Page"
If native format translation is not required (for example, a JPG or GIF image is being processed), then select the Native format translation is not required check box. The file is passed through in base-64 encoding.
XSD files are required for translation. If you want to define a new schema or convert an existing data type definition (DTD) or COBOL Copybook, then select Define Schema for Native Format. This starts the Native Format Builder wizard. This wizard guides you through the creation of a native schema file from file formats such as comma-separated value (CSV), fixed-length, DTD, and COBOL Copybook. After the native schema file is created, the Messages page is displayed, with the Schema File URL and Schema Element fields filled in. For more information, see Section 6.1, "Creating Native Schema Files with the Native Format Builder Wizard."
4.3.1.7 Inbound Service
When you finish configuring the Oracle File Adapter, a JCA file is generated for the inbound service. The file is named after the service name you specified on the Service Name page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard. You can rerun the wizard later to change your operation definitions.
The ActivationSpec parameter holds the inbound configuration information. The ActivationSpec and a set of inbound Oracle File Adapter properties are part of the inbound JCA file.
Table 4-5 lists the properties of a sample inbound JCA file.
Table 4-5 Sample JCA Properties for Inbound Service
| Property | Sample Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The ActivationSpec property values are specified in the Adapter Configuration Wizard during design time and, as shown in Table 4-5. The inbound Oracle File Adapter uses the following configuration properties:
-
PollingFrequency -
MinimumAge -
PhysicalDirectory -
LogicalDirectory -
PublishSize -
PhysicalArchiveDirectory -
LogicalArchiveDirectory -
IncludeFiles -
ExcludeFiles -
UseHeaders -
ListSorter -
ThreadCount -
Recursive -
MaxRaiseSize
For a description of these configuration properties, see Appendix A of this book.
4.3.1.8 Inbound Headers
Apart from the payload, Oracle File Adapter publishes the following header metadata, from the inbound service, as shown in Figure 4-24:
-
jca.file.FileName: file name -
jca.file.Directory: directory name -
jca.file.Batch: a unique name for a batch in case of debatching -
jca.file.BatchIndex: the batch index for each message within the batch for debatching -
jca.file.Size: the file size -
jca.file.LastModifiedTime: the last modified time for the file
4.3.2 Oracle File Adapter Write File Concepts
In the outbound direction, the Oracle File Adapter receives messages from the service engine and writes the messages to a file in a file system. This section provides an overview of the outbound file writing capabilities of the Oracle File Adapter. You use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to configure the Oracle File Adapter for use with a BPEL process or a Mediator Service. This creates an outbound WSDL and a JCA file pair.
This section includes the following topics:
4.3.2.1 Outbound Operation
For outbound operations with the Oracle File Adapter, select the Write File operation, as shown in Figure 4-25.
Figure 4-25 Selecting the Write File Operation
Description of "Figure 4-25 Selecting the Write File Operation"
The Add Output Header checkbox is visible when you select File Write. When you select this checkbox, the adapter WSDL will have an output message pointing to a header schema, shown by the bold highlight below.
<wsdl:definitions name="fileout3"
targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/SOAApp1/NewJCAFmwk/ fileout3"
xmlns:jca="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/wsdl/jca/"
xmlns:FILEAPP="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:tns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/SOAApp1/NewJCAFmwk/ fileout3"
xmlns:plt="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2003/05/partner-link/">"
xmlns:opaque="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/opaque/"
<plt:role name="Write_role" >
<plt:portType name="tns:Write_ptt" />
</plt:role>
</plt:partnerLinkType>"
<wsdl:types>
<schema TargetNamespace="http://xlmns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/opaque/"
xmlns:opaque="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/opaque/"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" >
<element name="opaqueElement" type="base64Binary" />
</schema>
<schema targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
attributeFormDefault="qualified"
<element name="OutboundFileHeaderType" >
<complexType>
<sequence>
<element name="filename" type="string" />
<element name="directory" type="string" />
</sequence>
</complexType>
</element>
</schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:message name="Write_msg">
<wsdl:part name="opaque" element="opaque:opaqueElement"/>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:message name="Output_msg">
<wsdl:part name="body" element="FILEAPP:OutboundFileHeaderType"/>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:portType name="Write_ptt">
<wsdl:operation name="Write">
<wsdl:input message="tns:Write_msg"/>
<wsdl:output message="tns:Output_msg"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:portType>
</wsdl:definitions>
You can select the 'Update Output Header' checkbox in edit mode, and the output message/ header schema will be removed from the adapter WSDL.
4.3.2.2 Outbound File Directory Creation
For the outbound operation, you can specify the outbound directory, outbound file naming convention to use, and, if necessary, the batch file conventions to use.
The File Configuration page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard shown in Figure 4-26 enables you to specify the directory for outgoing files and the outbound file naming convention.
Figure 4-26 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-Parameters for Outgoing Files
Description of "Figure 4-26 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-Parameters for Outgoing Files"
The following sections describe the file configuration information to specify:
-
Section 4.3.2.2.1, "Specifying Outbound Physical or Logical Directory Paths in Oracle BPEL PM"
-
Section 4.3.2.2.4, "Specifying the Outbound File Naming Convention"
-
Section 4.3.2.2.5, "Specifying a Dynamic Outbound File Name"
4.3.2.2.1 Specifying Outbound Physical or Logical Directory Paths in Oracle BPEL PM
You can specify outbound directory names as physical or logical paths. Physical paths are values such as c:\outputDir.
If you specify logical parameters, then the generated JCA file looks as follows for the logical outbound directory name OutputFileDir.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<adapter-config name="FlatStructureOut" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" adapterRef=""/>
<endpoint-interaction operation="Write">
<interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileInteractionSpec">
<property name="LogicalDirectory" value="OutputFileDir"/>
<property name="FileNamingConvention" value="%yyMMddHHmmssSS%_%SEQ%_%yyyyMMdd%_%SEQ%.out.%SEQ%"/>
<property name="Append" value="false"/>
<property name="NumberMessages" value="1"/>
<property name="OpaqueSchema" value="false"/>
</interaction-spec>
</endpoint-interaction>
</adapter-config>
Select the outbound adapter in the "External References" swim lane in JDeveloper wizard (it is present in the composite.xml tab). Create a "Binding Property" in the Property Inspector for the outbound adapter (you must scroll down to find it). Once the Create Property box appears, enter OutputFileDir in the Name field and the actual output dir name, example, C:\outputDir in the Value field. The composite.xml file appears as follows:
<reference name="FlatStructureOut">
<interface.wsdl interface="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/FlatStructureOut/#wsdl.interface(Write_ptt)"/>
<binding.jca config="FlatStructureOut_file.jca">
<property name="OutputFileDir" type="xs:string" many="false"
override="may">C:\outputDir</property>
</binding.jca>
</reference>
Note:
Ensure that you limit the length of outbound file names (the file name, plus the complete directory path) to 200 characters. This is not an exact limit but rather a recommendation. When an outbound file name is long (for example, 215 characters), a blank file with that name is created in the outbound directory.4.3.2.2.2 Specifying Outbound Physical or Logical Directory Paths in Mediator
You can specify outbound directory names as physical or logical paths in Mediator. Physical paths are values such as c:\inputDir.
You can specify the logical names at design time in the File Directories page shown in Figure 4-20 and then provide logical-physical mapping by using the Endpoint properties. For example, WriteFile is an outbound adapter service. You have specified OutDir as the logical directory name at design time.
4.3.2.2.3 Specifying a Dynamic Outbound Directory Name
For outbound operation, you can specify a dynamic outbound directory name. You can set variables to specify dynamic outbound directory names.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<adapter-config name="ReadAddressChunk" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" adapterRef=""/>
<endpoint-interaction operation="ChunkedRead">
<interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.ChunkedInteractionSpec">
<property name="PhysicalDirectory" value="C:\foo"/>
<property name="FileName" value="dummy.txt"/>
<property name="ChunkSize" value="1"/>
</interaction-spec>
</endpoint-interaction>
</adapter-config>
In the preceding example, in the JCA file, the physical directory is set to "C:\foo" but during run time it is dynamically changed to the assigned value. In this example, the physical directory is dynamically changed to "C:\out". You must perform the following steps to specify the dynamic outbound directory name:
-
Double-click the invoke activity.
-
Click the Browse Variables icon.
-
In the Variable Chooser dialog, click the Create an Object icon.
-
Create a variable
MyDirof typexsd:string, as shown in Figure 4-27. -
Drag and drop an Assign activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the assign activity and click the Copy Operation tab.
-
Click Create and then Copy Operation. The Create Copy Operation dialog is displayed.
-
In the Create Copy Operation dialog, select Expression from Type and specify the directory name and path, as shown in Figure 4-28. The output file is written to this directory.
-
Click OK in the Create Copy Operation dialog and then click OK in the Assign dialog. The
.bpelpage is displayed. -
Double-click the invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Properties tab.
-
Select the
jca.file.Directoryproperty from the Properties column and set the Value asMyDir(the directory that you created in Step 4.) Ensure that the Type column is set toinput, as shown in Figure 4-29.
Note:
When using dynamic directories, ensure that parameters such asNumberMessages, ElapsedTime, and FileSize are not defined in the outbound adapter service WSDL file. These parameters are not supported with dynamic directories.4.3.2.2.4 Specifying the Outbound File Naming Convention
Specify the naming convention to use for outgoing files. You cannot enter completely static names such as po.txt. This is to ensure the uniqueness in names of outgoing files, which prevents files from being inadvertently overwritten. Instead, outgoing file names must be a combination of static and dynamic portions.
The prefix and suffix portions of the file example shown in Figure 4-26 are static (for example, po_ and .xml). The %SEQ% variable of the name is dynamic and can be a sequence number or a time stamp (for example, po_%yyMMddHHmmss%.xml to create a file with a time stamp).
If you choose a name starting with po_, followed by a sequence number and the extension txt as the naming convention of the outgoing files, then you must specify po_%SEQ%.txt.
If you choose a name starting with po_, followed by a time stamp with the pattern yyyy.MM.dd and the extension txt as the naming convention of the outgoing file, then you must specify po_%yyyy.MM.dd%.txt. For example, the outgoing file name can be po_2004.11.29.txt.
Additionally, you can combine file naming conventions. For example, you can specify the file naming convention as po_%SEQ%_%yyyy.MM.dd%_%SEQ%.txt.
Note:
When you use the time stamp pattern, the same time stamp may be generated on subsequent calls and you may lose messages. The workaround is to combine the time-stamp pattern with a sequence pattern. Alternatively, you can use a time-stamp pattern closest to a millisecond, in which case the adapter handles the uniqueness of the file names.You cannot use a regular expression for outbound synchronous reads. In these cases, the exact file name must be known.
A time stamp is specified by date and time pattern strings. Within date and time pattern strings, unquoted letters from 'A' to 'Z' and from 'a' to 'z' are interpreted as pattern letters representing the components of a date or time string. Text can be quoted using single quotation marks (') to avoid interpretation. The characters "''" represent single quotation marks. All other characters are not interpreted.
The Java pattern letters are defined in Table 4-6.
Table 4-6 Java Pattern Letters
| Letter | Date or Time Component | Presentation | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Era designator |
Text |
|
|
|
Year |
Year |
|
|
|
Month in year |
Month |
|
|
|
Week in year |
Number |
|
|
|
Week in month |
Number |
|
|
|
Day in year |
Number |
|
|
|
Day in month |
Number |
|
|
|
Day of week in month |
Number |
|
|
|
Day in week |
Text |
|
|
|
AM/PM marker |
Text |
|
|
|
Hour in day (0-23) |
Number |
|
|
|
Hour in day (1-24) |
Number |
|
|
|
Hour in AM/PM (0-11) |
Number |
|
|
|
Hour in AM/PM (1-12) |
Number |
|
|
|
Minute in hour |
Number |
|
|
|
Second in minute |
Number |
|
|
|
Millisecond |
Number |
|
|
|
Time zone |
General Time Zone |
|
|
|
Time zone |
RFC 822 Time Zone |
|
Different presentations in the pattern are as follows:
-
Text
For formatting, if the number of pattern letters is four or more, then the full form is used; otherwise, a short or abbreviated form is used if available. For parsing, both forms are accepted, independent of the number of pattern letters.
-
Number
For formatting, the number of pattern letters is the minimum number of digits, and shorter numbers are zero-padded to this number. For parsing, the number of pattern letters is ignored unless it is needed to separate two adjacent fields.
-
Year
For formatting, if the number of pattern letters is two, then the year is truncated to two digits; otherwise, it is interpreted as a number.
For parsing, if the number of pattern letters is more than two, then the year is interpreted literally, regardless of the number of digits. Using the pattern MM/dd/yyyy, 01/11/12 parses to Jan 11, 12 A.D.
For parsing with the abbreviated year pattern (y or yy), the abbreviated year is interpreted relative to some century. The date is adjusted to be within 80 years before and 20 years after the time instance is created. For example, using a pattern of MM/dd/yy and Jan 1, 1997 is created; the string 01/11/12 is interpreted as Jan 11, 2012, while the string 05/04/64 is interpreted as May 4, 1964. During parsing, only strings consisting of exactly two digits are parsed into the default century. Any other numeric string, such as a one-digit string, a three-or-more-digit string, or a two-digit string that is not all digits (for example, -1), is interpreted literally. So, 01/02/3 or 01/02/003 is parsed using the same pattern as Jan 2, 3 AD. Likewise, 01/02/-3 is parsed as Jan 2, 4 BC.
-
Month
If the number of pattern letters is
3or more, then the month is interpreted as text; otherwise, it is interpreted as a number. -
General time zone
Time zones are interpreted as text if they have names. For time zones representing a
GMToffset value, the following syntax is used:
GMTOffsetTimeZone:
GMT Sign Hours : Minutes
Sign: one of
+ -
Hours:
Digit
Digit Digit
Minutes:
Digit Digit
Digit: one of
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Hours must be between 0 and 23, and Minutes must be between 00 and 59. The format is locale-independent and digits must be taken from the Basic Latin block of the Unicode standard.
For parsing, RFC 822 time zones are also accepted.
For formatting, the RFC 822 4-digit time zone format is used:
RFC822TimeZone:
Sign TwoDigitHours Minutes
TwoDigitHours:
Digit Digit
TwoDigitHours must be between 00 and 23. Other definitions are the same as for general time zones.
For parsing, general time zones are also accepted.
4.3.2.2.5 Specifying a Dynamic Outbound File Name
For outbound operation, you can specify a dynamic outbound file name. You can set variables to specify dynamic outbound file names.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<adapter-config name="ReadAddressChunk" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" adapterRef=""/>
<endpoint-interaction operation="ChunkedRead">
<interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.ChunkedInteractionSpec">
<property name="PhysicalDirectory" value="C:\foo"/>
<property name="FileName" value="dummy.txt"/>
<property name="ChunkSize" value="1"/>
</interaction-spec>
</endpoint-interaction>
</adapter-config>
In the preceding example, in the JCA file, the physical directory is set to "C:\foo" but during run time it is dynamically changed to the assigned value. In this example, the physical directory is dynamically changed to "C:\out". You must perform the following steps to specify the dynamic outbound directory name:
-
Double-click the invoke activity.
-
Click the Browse Variables icon.
-
In the Variable Chooser dialog, click the Create an Object icon.
-
Create a variable
fileof typexsd:string, as shown in Figure 4-27. -
Drag and drop an Assign activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the assign activity and click the Copy Operation tab.
-
Click Create and then Copy Operation. The Create Copy Operation dialog is displayed.
-
In the Create Copy Operation dialog, select Expression from Type and specify the file name, as shown in Figure 4-28. The output file is written to this file.
-
Click OK till you exit the assign activity dialog.
-
Double-click the invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Properties tab.
-
Select the
jca.file.FileNameproperty from the Properties column and set the Value asfile(the file that you created in Step 4.) Ensure that the Type column is set toinput, as shown in Figure 4-30.
Note:
When using dynamic files, ensure that parameters such asNumberMessages, ElapsedTime, and FileSize are not defined in the outbound adapter service WSDL file. These parameters are not supported with dynamic files.4.3.2.2.6 Batching Multiple Outbound Messages
In the simplest scenario, you specify writing a single file to a single message. You can also specify the outbound method for batch file writing. This method enables you to specify the number of messages to publish in one batch file. The following batch file settings are provided in the File Configuration page shown in Figure 4-26:
-
Number of Messages Equals
Specify a value which, when equaled, causes a new outgoing file to be created.
-
Elapsed Time Exceeds
Specify a time which, when exceeded, causes a new outgoing file to be created.
Note:
The Elapsed Time Exceeds batching criteria is evaluated and a new outgoing file is created, only when an invocation happens.For example, if you specify that elapsed time exceeds 15 seconds, then the first message that is received is not written out, even after 15 seconds, as batching conditions are not valid. If a second message is received, then batching conditions become valid for the first one, and an output file is created when the elapsed time exceeds 15 seconds.
-
File Size Exceeds
Specify a file size which, when equaled, causes an outgoing file to be created. For example, assume that you specify a value of
3for the number of messages received and a value of 1 MB for the file size. When you receive two messages that when combined equal or exceed 1 MB, or three messages that are less than 1 MB, an output file is created.
Note:
You must not manually change the file configurations specified in the preceding list in theJCA files. You must use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to modify these configurations.If the Oracle File Adapter encounters some problem during batching, then it starts batching at the point at which it left off on recovery.
4.3.2.3 Native Data Translation
The next Adapter Configuration Wizard page that appears is the Messages page shown in Figure 4-31. This page enables you to select the XSD schema file for translation.
As with specifying the schema for the inbound direction, you can perform the following tasks in this page:
-
Specify whether native format translation is not required.
-
Select the XSD schema file for translation.
-
Start the Native Format Builder wizard to create an XSD file from file formats such as CSV, fixed-length, DTD, and COBOL Copybook.
For more information about Messages page, see Section 4.3.1.6, "Native Data Translation."
4.3.2.4 Outbound Service Files
When you complete configuration of the Oracle File Adapter with the Adapter Configuration Wizard, a WSDL and a JCA file pair is generated for the outbound operation. The files are named after the service name you specified on the Service Name page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard shown in Figure 3-8. You can rerun the wizard later to change your operation definitions.
A sample outbound JCA file includes the information listed in Table 4-7:
Table 4-7 Sample JCA Properties for Outbound Service
| Property | Sample Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The outbound Oracle File Adapter uses the following configuration parameters:
-
PhysicalDirectory -
LogicalDirectory -
NumberMessages -
ElapsedTime -
FileSize -
FileNamingConvention -
Append
For a description of these configuration properties, see Appendix A of this book.
4.3.3 Oracle File Adapter Synchronous Read Concepts
In the outbound direction, the Oracle File Adapter polls and reads the current contents of files. This section provides an overview of the outbound synchronous file reading capabilities of the Oracle File Adapter. For reading a file synchronously, you select Synchronous Read File operation, as shown in Figure 4-32.
Figure 4-32 Synchronous Read Operation Page
Description of "Figure 4-32 Synchronous Read Operation Page"
All the pages of the Adapter Configuration Wizard are similar to the Read File operation except the File Name page. You can specify the name of the file to be read in the File Name field, as shown in Figure 4-33.
4.3.4 Oracle File Adapter File Listing Concepts
This feature of the Oracle File Adapter lets you use a BPEL activity to retrieve a list of files from a target directory. This list of files is returned as an XML document and contains information such as file name, directory name, file size, and last modified time. This section provides an overview of the file listing capabilities of the Oracle File Adapter. You use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to configure the Oracle File Adapter for use with a BPEL process or a Mediator service. This creates an outbound WSDL and JCA file pair.
Note:
The file creation time property,creationTime, is not supported because the standard Java APIs do not provide a mechanism to retrieve the creation time. The value of the creationTime property is always displayed as 0.
For example,
<creationTime xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/file/FAListFiles/FAListFilesTest/ReadS/">0</creationTime>
This section includes the following topics:
4.3.4.1 Listing Operation
For listing files, you must select the List Files operation, as shown in Figure 4-34.
4.3.4.2 File Directory Specifications
The File Directories page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard shown in Figure 4-35 enables you to specify information about the directory to use for reading files names for the list operation. You can choose to list files recursively within directories.
Figure 4-35 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-Specifying Incoming Files
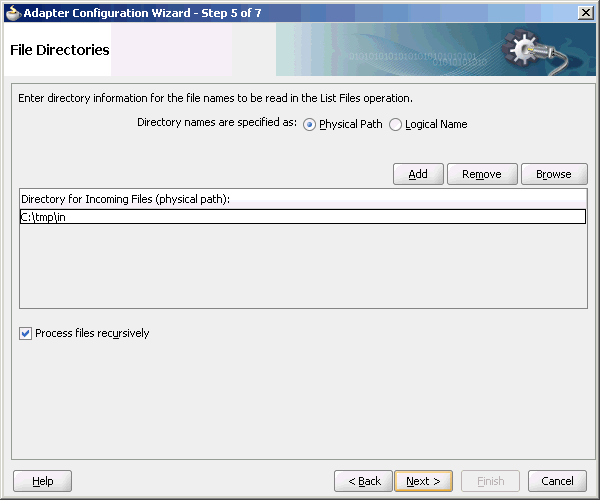
Description of "Figure 4-35 The Adapter Configuration Wizard-Specifying Incoming Files"
The following section describes the file directory information to specify:
4.3.4.2.1 Specifying Inbound Physical or Logical Directory Paths in SOA Composite
You can specify directory names as physical or logical paths for composites involving Oracle BPEL PM and Mediator. Physical paths are values such as C:\inputDir.
In the composite, logical properties are specified in the JCA file, and their logical-physical mapping is resolved by using binding properties. You specify the logical directory once at design time, and you can later modify the directory name as needed.
For example, the generated JCA file looks as follows for the logical input directory name C:\inputDir:
<adapter-config name="ListFiles" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" UIincludeWildcard="*.txt" adapterRef=""/>
<endpoint-interaction portType="FileListing_ptt" operation="FileListing">
<interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileListInteractionSpec">
<property name="PhysicalDirectory" value="C:\inputDir"/>
<property name="Recursive" value="true"/>
<property name="IncludeFiles" value=".*\.txt"/>
</interaction-spec>
</endpoint-interaction>
</adapter-config>
4.3.4.3 File Matching
The File Filtering page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard shown in Figure 4-36 enables you to specify details about the files to retrieve or ignore.
The Oracle File Adapter acts as a file listener and polls the specified directory on a local or remote file system and looks for files that match specified naming criteria.
Figure 4-36 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Filtering
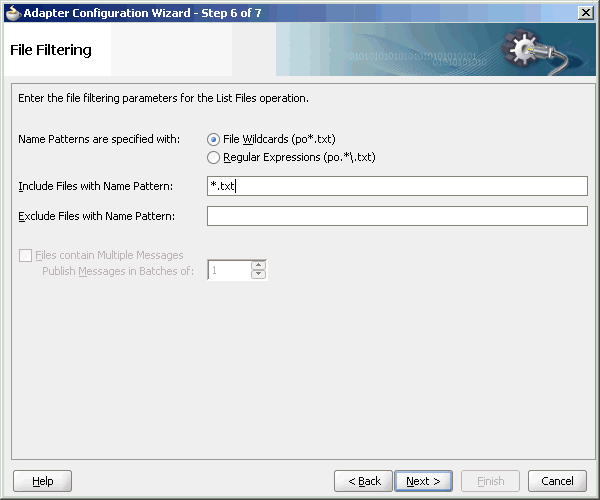
Description of "Figure 4-36 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Filtering"
The following sections describe the file filtering information to specify:
4.3.4.3.1 Specifying a Naming Pattern
Specify the naming convention that the Oracle File Adapter uses to poll for inbound files. You can also specify the naming convention for files you do not want to process. Two naming conventions are available for selection. The Oracle File Adapter matches the files that appear in the inbound directory.
-
File wildcards (
po*.txt)Retrieve all files that start with
poand end with.txt. This convention conforms to operating system standards.
-
Regular expressions (
po.*\.txt)Retrieve all files that start with
poand end with.txt. This convention conforms to Java Development Kit (JDK) regular expression (regex) constructs.
Notes:
-
If you later select a different naming pattern, ensure that you also change the naming conventions you specify in the Include Files and Exclude Files fields. The Adapter Configuration Wizard does not automatically make this change for you.
-
Do not specify *.* as the convention for retrieving files.
-
Be aware of any file length restrictions imposed by your operating system. For example, Windows operating system file names cannot be more than 256 characters in length (the file name, plus the complete directory path). Some operating systems also have restrictions on the use of specific characters in file names. For example, Windows operating systems do not allow characters such as
backslash(\), slash (/), colon (:), asterisk (*), left angle bracket (<), right angle bracket (>), or vertical bar(|).
4.3.4.3.2 Including and Excluding Files
If you use regular expressions, the values you specify in the Include Files and Exclude Files fields must conform to JDK regular expression (regex) constructs. For both fields, different regex patterns must be provided separately. The Include Files and Exclude Files fields correspond to the IncludeFiles and ExcludeFiles parameters, respectively, of the inbound WSDL file.
Note:
The regex pattern complies with the JDK regex pattern. According to the JDK regex pattern, the correct connotation for a pattern of any characters with any number of occurrences is a period followed by a plus sign(.+). An asterisk (*) in a JDK regex is not a placeholder for a string of any characters with any number of occurrences.If you want the inbound Oracle File Adapter to pick up all file names that start with po and which have the extension txt, you must specify the Include Files field as po.*\.txt when the name pattern is a regular expression. In this regex pattern example:
-
A period (
.)indicates any character. -
An asterisk (
*) indicates any number of occurrences. -
A backslash followed by a period (\.) indicates the character period (.) as indicated with the backslash escape character.
The Exclude Files field is constructed similarly.
If you have Include Files field and Exclude Files field expressions that have an overlap, then the exclude files expression takes precedence. For example, if Include Files is set to abc*.txt and Exclude Files is set to abcd*.txt, then you receive any files prefixed with abcd*.
Note:
Do not begin JDK regex pattern names with the following characters: plus sign (+), question mark (?), or asterisk (*).For details about Java regex constructs, go to
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/api
Note:
Files are not read and therefore there is no native data translation.4.3.5 Oracle FTP Adapter Get File Concepts
In the inbound direction, the Oracle FTP Adapter works the same way as the Read File operations of the Oracle File Adapter in that it polls and gets files from a file system for processing. The major difference is that the Oracle FTP Adapter is used for remote file exchanges. To configure the FTP adapter for remote file exchanges, the Adapter Configuration Wizard asks for connection information to an FTP server to be used later, as shown in Figure 4-37.
Figure 4-37 Specifying FTP Server Connection Information
Description of "Figure 4-37 Specifying FTP Server Connection Information"
The default adapter instance JNDI name is eis/Ftp/FtpAdapter, or use a custom name. This name connects to the FTP server during run time.
Note:
The Oracle FTP Adapter does not support the FTP commandsRESTART and RECOVERY during the transfer of large files.After logging in, you select the Get File (read) operation and the type of file to deliver. Figure 4-38 shows this selection.
Figure 4-38 Selecting the Get File Operation
Description of "Figure 4-38 Selecting the Get File Operation"
The serverType property in the deployment descriptor is used to determine line separators when you transfer data. You can specify unix, win, or mac as property values. These values represent the operating system on which the FTP server is running. By default, the serverType property contains unix.
When you specify mac as the value, \r is used as line separator. For unix, \n is used and for win, \r\n is used. You must note that this property is used by the NXSD translator component to write the line separator during an outbound operation.
From this point onwards, pages of the Adapter Configuration Wizard for the Get File operation are the same as those for the Read File operation of the file. Table 4-8 lists the pages that are displayed and provides references to sections that describe their functionality.
Table 4-8 Adapter Configuration Wizard Windows for Get File Operation
| Page | See Section... |
|---|---|
|
File Directories (Figure 4-20) |
|
|
File Filtering (Figure 4-21) |
|
|
File Polling (Figure 4-22) |
|
|
Messages (Figure 4-23) |
An additional Adapter Configuration Wizard page is also available for advanced users. This page is shown in Figure 4-39 and appears only after you make either or both of the following selections on the File Polling page shown in Figure 4-22:
-
Do not select the Delete Files After Successful Retrieval check box.
-
Set the value of the Minimum File Age field to a value greater than 0.
This page enables you to specify a method for obtaining the modification time of files on the remote FTP server:
Note:
The Oracle FTP Adapter uses theLIST command as opposed to NLST for listing and retrieves the time stamps because of which you need not specify the time formats. However, you must specify the time formats as shown below if you do any of the following:
-
If you specify
NLSTas the listing command (either through the mapping file or theUseNlst="true"parameter in the inboundJCAfile) -
If you want to use the File Name Substring option
This note is not applicable if your case does not fall under neither of these categories.
-
File System
This option enables you to obtain the date/time format of the file modification time with the file system listing command. However, this option is rarely used and is not supported by all FTP servers. See your FTP server documentation to determine whether your server supports the file system listing command, which command-line syntax to use, and how to interpret the output.
For example, if the file system listing command
quote mdtmfilenameis supported and returns the following information:213 20050602102633
specify the start index, end index, and date/time format of the file modification time in the Data/Time Format field as a single value separated by commas (for example, 4,18,yyyyMMddHHmmss).
Where:
-
4 is the start index of the file modification time.
-
18 is the end index of the file modification time.
-
yyyyMMddHHmmss is the data/time format of the file modification time obtained with the
quote mdtmfilenamecommand.
The resulting JCA file includes the following parameters and values:
<property name=" FileModificationTime " value=" FileSystem "/> <property name=" ModificationTimeFormat" value=" 4,18,yyyyMMddHHmmss "/>
To handle the time zone issue, you must also be aware of the time stamp difference. The time zone of the FTP server is determined by using the Windows date/time properties (for example, by double-clicking the time being displayed in the Windows task bar). You must then convert the time difference between the FTP server and the system on which the Oracle FTP Adapter is running to milliseconds and add the value as a binding property in the
composite.xmlfile:<binding.jca config="FlatStructureIn_file.jca"> <property name="timestampOffset" source="" type="xs:string" many="false" override="may">238488888</property--> </binding.jca>
-
-
Directory Listing
This option enables you to obtain the date/time format from the file modification time with the FTP directory listing command. For example, if the directory listing command (
ls -l) returns the following information:12-27-04 07:44AM 2829 NativeData2.txt
specify the start index, end index, and date/time format of the file modification time as a single value separated by commas in either the Old File Date/Time Format field or the Recent File Date/Time Format field (for example,
0,17,MM-dd-yy hh:mma).Where:
-
0is the start index of the file modification time. -
17is the end index of the file modification time. -
MM-dd-yy hh:mma is the date/time format of the file modification time obtained with the
ls -lcommand. For this example, the value is entered in the Recent File Date/Time Format field. This field indicates that the format is obtained from the most recent file adhering to the naming convention, whereas the Old File Date/Time Format field obtains the format from the oldest file.
The resulting JCA file includes the following parameters and values:
<property name=" FileModificationTime " value=" DirListing"/> <property name=" ModificationTimeFormat" value="0,17, MM-dd-yy hh:mma "/>
To handle the time zone issue, you must also be aware of the time stamp difference. The time zone of the FTP server is determined by using the Windows date/time properties (for example, by double-clicking the time being displayed in the Windows task bar). You must then convert the time difference between the FTP server and the system on which the Oracle FTP Adapter is running to milliseconds and add the value as a binding property in the
composite.xmlfile:<binding.jca config="FlatStructureIn_file.jca"> <property name="timestampOffset" source="" type="xs:string" many="false" override="may">238488888</property--> </binding.jca>
-
-
File Name Substring
This option enables you to obtain the modification time from the file name. For example, if the name of the file is
fixedLength_20050324.txt, you can specify the following values:-
The start index in the Substring Begin Index field (for example,
12) -
The end index in the End Index field (for example,
20) -
The date and time format in the Date/Time Format field conforming to the Java
SimpleDateFormatto indicate the file modification time in the file name (for example,yyyyMMdd)
The resulting JCA file includes the following parameters and values:
<property name=" FileModificationTime " value=" Filename"/> <property name=" FileNameSubstringBegin " value="12 "/> <property name=" FileNameSubstringEnd " value="20"/> <property name=" ModificationTimeFormat " value=" yyyyMMdd "/>
-
After the completion of the Adapter Configuration Wizard, configuration files are created in the Applications section of JDeveloper.
See Section 2.22, "Error Handling" for more information about error handling.
You must also add the DefaultDateFormat and the RecentDateFormat parameters to the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter, as shown in the following sample:
<non-managed-connection managedConnectionFactoryClassName="oracle.tip.adapter.ftp.FTPManagedConnection
Factory">
<property name="host" value="localhost"/>
<property name="port" value="21"/>
<property name="username" value="****"/>
<property name="password" value="****"/>
<property name="listParserKey" value="UNIX"/>
<property name="defaultDateFormat" value="MMM d yyyy"/>
<property name="recentDateFormat" value="MMM d HH:mm"/>
</non-managed-connection>
For more information on the DefaultDateFormat and the RecentDateFormat parameters, refer to Section 4.2.21, "Recursive Processing of Files Within Directories in Oracle FTP Adapter."
4.3.6 Oracle FTP Adapter Put File Concepts
In the outbound direction, the Oracle FTP Adapter works the same as the Write File operations of the Oracle File Adapter. The Oracle FTP Adapter receives messages from a BPEL process or a Mediator service and writes the messages in a file to a file system (in this case, remote). Because the messages must be written to a remote system, the Adapter Configuration Wizard prompts you to connect to the FTP server with the adapter instance JNDI name, as shown in Figure 4-37.
After logging in, you select the Put File (write) operation and the type of file to deliver. Figure 4-40 shows this selection.
Figure 4-40 Selecting the Put File Operation
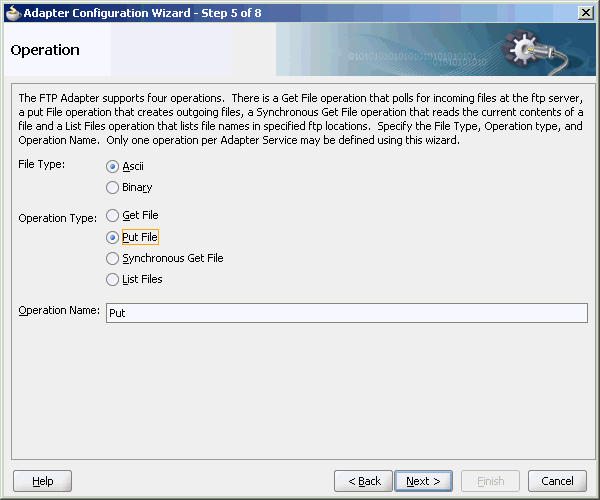
Description of "Figure 4-40 Selecting the Put File Operation"
From this point onwards, pages of the Adapter Configuration Wizard for the Put File operation are the same as those for the Write File operation of the Oracle File Adapter. Table 4-9 lists the pages that display and provide references to sections that describe their functionality.
Table 4-9 The Adapter Configuration Wizard Pages for Put File Operation
| Page | See Section... |
|---|---|
|
File Configuration (Figure 4-26) |
|
|
Messages (Figure 4-31) |
After the completion of the Adapter Configuration Wizard, configuration files are created in the Applications section of JDeveloper.
4.3.7 Oracle FTP Adapter Synchronous Get File Concepts
In the outbound direction, the Oracle FTP Adapter works the same way as the Synchronous Read File operations of the Oracle File Adapter in that it polls and gets files from a file system and reads the current contents of the file. The major difference is that the Oracle FTP Adapter is used for remote file exchanges. Because of this, the Adapter Configuration Wizard asks for connection information to an FTP server to be used later. For reading a file synchronously, you select Synchronous Get File operation, as shown in Figure 4-41.
Figure 4-41 Selecting the Synchronous Get File Operation
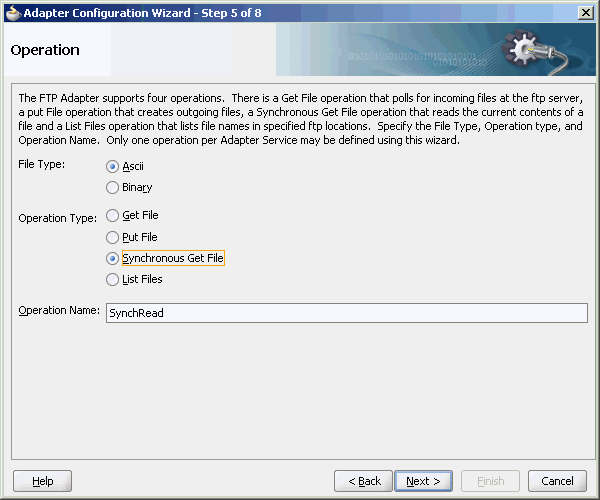
Description of "Figure 4-41 Selecting the Synchronous Get File Operation"
4.3.8 Oracle FTP Adapter File Listing Concepts
The Oracle FTP Adapter file listing concepts are similar to the Oracle File Adapter file listing concepts discussed in Section 4.3.4, "Oracle File Adapter File Listing Concepts." The Oracle FTP Adapter polls for files in a target directory and lists files from the target directory to specified FTP locations. The contents of the files are not read. This feature of the Oracle FTP Adapter lets you use an invoke activity to retrieve a list of files from a target directory. This list of files is returned as an XML document and contains information such as file name, directory name, file size, and last modified time.
Note:
The file creation time property,creationTime, is not supported for FTP because the standard Java APIs do not provide a mechanism to retrieve the creation time. The value of the creationTime property is always displayed as 0.
The creationTime property is supported for SFTP only.
You use the Adapter Configuration Wizard to configure the Oracle FTP Adapter for use with a BPEL process or a Mediator service. This creates an outbound WSDL and JCA file pair.
For listing files, you must select the List Files operation from the Operation Type page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard. In the File Directories page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard, you must specify information about the directory to use for reading file names for the list operation. You can choose to list files recursively within directories. The File Filtering page of the Adapter Configuration Wizard enables you to specify details of the files to retrieve or ignore.
The Oracle FTP Adapter acts as a listener and polls the specified directory on a local or remote file system and looks for files that match specified naming criteria.
4.4 Configuring Oracle File and FTP Adapters
Various configuration tasks for Oracle File and FTP Adapters are discussed in the following sections:
-
Section 4.4.1, "Configuring the Credentials for Accessing a Remote FTP Server"
-
Section 4.4.2, "Configuring Oracle File and FTP Adapters for High Availability"
-
Section 4.4.3, "Using Secure FTP with the Oracle FTP Adapter"
-
Section 4.4.5, "Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter for HTTP Proxy"
4.4.1 Configuring the Credentials for Accessing a Remote FTP Server
To access a remote FTP server, you must configure the following credentials:
-
User name: the user name to use on the remote FTP server.
-
Password: the password to use on the remote FTP server.
-
Port: 21
-
Host: the IP address of the remote FTP server.
You must configure these credentials by modifying the weblogic-ra.xml file using the Oracle WebLogic Server console.
To do so, in the Oracle WebLogic Server Admin Console:
-
Select Deployments from the Navigation pane on the left.
-
Select FtpAdapter from the table of Deployments shown on the right.
-
Select the Configuration subtab for the FtpAdapter and then Outbound Connection Pools.
-
Expand
javax.resource.cci.ConnectionFactoryand then select the instance that you are modifying. (For example, choose theeis/Ftp/FtpAdapterinstance for the non-HA use case.)
4.4.2 Configuring Oracle File and FTP Adapters for High Availability
The requirements and procedure to configure the Oracle File and FTP Adapters for high availability for an active-active topology are discussed in the following sections:
4.4.2.1 Prerequisites for High Availability
Before you configure the Oracle File or FTP Adapter for high availability, you must ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
-
Clustered processes must use the same physical directory.
-
Connection-factories must specify the same shared directory as the control directory, and their names must match. For example, if the deployment descriptor for one connection factory has
/shared/control_diras the value forcontrolDir, then the other deployment descriptor must also have the same value. -
Fault-policies and fault-bindings must be created for remote faults to ensure that the adapter acts correctly. For more information on fault-policies and fault-bindings, see Section 2.22, "Error Handling."
-
The
MaxRaiseSizeproperty must be set in the inbound JCA file.
Note:
For large payloads, you must increase the transaction time-out for theSOADataSource by adding the following:
<xa-set-transaction-timeout>true</xa-set-transaction-timeout> <xa-transaction-timeout>1000</xa-transaction-timeout>
Note:
For Windows platforms, you must ensure that the input and output directories are canonicalized. For example, you must useC:\bpel\input instead of c:\bpel\input. Note the use of capitalized drive letter C: instead of c:.Note:
On all platforms, you must not end input or output directory names with the Java system property file.separator value. For example,/tmp/file/in/ is invalid but /tmp/file/in is valid.4.4.2.2 High Availability in Inbound Operations
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters must ensure that only one node processes a particular file in a distributed topology. You can use the database table as a coordinator to ensure that Oracle File and FTP Adapters are highly available for inbound operations.
Using Database Table as a Coordinator
You must use the following procedure to make an inbound Oracle File or FTP Adapter service highly available by using database table as a coordinator:
Note:
You must increase global transaction timeouts if you use database as a coordinator.-
Create Database Tables
You are not required to perform this step because the database schemas are pre-created as a part of soainfra.
-
Modify Deployment Descriptor for Oracle File Adapter
Modify Oracle File Adapter deployment descriptor for the connection-instance corresponding to
eis/HAFileAdapterfrom the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:-
Log in to your Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. To access the console, navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/console. -
Click Deployments in the left pane for Domain Structure.
-
Click FileAdapter under Summary of Deployments on the right pane.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Click the Outbound Connection Pools tab, and expand javax.resource.cci.ConnectionFactory to see the configured connection factories, as shown in Figure 4-42:
Figure 4-42 Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FileAdapter Page
Description of "Figure 4-42 Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FileAdapter Page"
-
Click eis/HAFileAdapter. The Outbound Connection Properties for the connection factory corresponding to high availability is displayed.
-
Update the connection factory properties, as shown in Figure 4-43.
Figure 4-43 Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for javax.resource.cci.ConnectionFactory Page
Description of "Figure 4-43 Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for javax.resource.cci.ConnectionFactory Page"
The new parameters in connection factory for Oracle File and FTP Adapters are as follows:
controlDir- Set it to the directory structure where you want the control files to be stored. You must set it to a shared location if multiple WebLogic Server instances run in a cluster.inboundDataSource- Set the value tojdbc/SOADataSource. This is the data source, where the schemas corresponding to high availability are pre-created. The pre-created schema file can be found under$BEA_HOME/AS11gR1SOA/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/adapter/createschema_adapter_oracle.sql. If you want to create the schemas elsewhere, use this script. You must set the inboundDataSource property accordingly if you choose a different schema. -
Configure BPEL Process or Mediator Scenario to use the connection factory, as shown in the following example:
<adapter-config name="FlatStructureIn" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/HAFileAdapter" UIincludeWildcard="*.txt" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-activation portType="Read_ptt" operation="Read"> <activation-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.inbound.FileActivationSpec"../> <property../> <property../> </activation-spec> </endpoint-activation> </adapter-config>
Note:
The location attribute is set toeis/HAFileAdapterfor the connection factory.
-
4.4.2.3 High Availability in Outbound Operations
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters must ensure that if multiple references write to the same directory, then these do not overwrite each other. The following locking capabilities can be used to make Oracle File and FTP Adapters highly available for outbound operations:
-
Database mutex
-
User-defined mutex
You must use the following procedure to make an outbound Oracle File or FTP Adapter service highly available by using database table as a coordinator:
Note:
You must increase global transaction timeouts if you use the database as a coordinator.-
Create Database Tables
You are not required to perform this step as the database schemas are precreated as a part of soainfra.
-
Modify Deployment Descriptor for Oracle File Adapter
Modify Oracle File Adapter deployment descriptor for the connection-instance corresponding to
eis/HAFileAdapterfrom the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:-
Log in to your Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. To access the console, navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/console. -
Click Deployments in the left pane for Domain Structure.
-
Click FileAdapter under Summary of Deployments on the right pane.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Click the Outbound Connection Pools tab, and expand javax.resource.cci.ConnectionFactory to see the configured connection factories, as shown in Figure 4-42.
-
Click eis/HAFileAdapter. The Outbound Connection Properties page is displayed with the connection factory corresponding to high availability.
-
Update the connection factory properties, as shown in Figure 4-44.
Figure 4-44 Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for javax.resource.cci.Connectionfactory Page

Description of "Figure 4-44 Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for javax.resource.cci.Connectionfactory Page"
The new parameters in connection factory for Oracle File and FTP Adapters are as follows:
controlDir- Set it to the directory structure where you want the control files to be stored. You must set it to a shared location if multiple WebLogic Server instances run in a cluster.inboundDataSource- Set the value tojdbc/SOADataSource. This is the data source, where the schemas corresponding to high availability are precreated. The precreated schemas can be found under$BEA_HOME/AS11gR1SOA/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/adapter/createschema_adapter_oracle.sql. If you want to create the schemas elsewhere, then use this script. You must set the inboundDataSource property accordingly if you choose a different schema.outboundDataSource- Set the value tojdbc/SOADataSource. This is the data source where the schemas corresponding to high availability are precreated. The precreated schemas can be found under$BEA_HOME/AS11gR1SOA/rcu/integration/soainfra/sql/adapter/createschema_adapter_oracle.sql. If you want to create the schemas elsewhere, then use this script. You must set the outboundDataSource property if you choose to do so.outboundLockTypeForWrite- Set the value tooracleif you are using Oracle Database. By default the Oracle File and FTP Adapters use an in-memory mutex to lock outbound write operations. You must choose from the following values for synchronizing write operations:memory- The Oracle File and FTP Adapters use an in-memory mutex to synchronize access to the file system.oracle - The adapter uses the Oracle Database sequence.
db- The adapter uses a precreated database table (FILEADAPTER_MUTEX) as the locking mechanism. You must use this option only if you are using a schema other than the Oracle Database schema.user-defined- The adapter uses a user-defined mutex. To configure the user-defined mutex, you must implement the mutex interface"oracle.tip.adapter.file.Mutex"and then configure a new binding-property with the name"oracle.tip.adapter.file.mutex"and value as the fully qualified class name for the mutex for the outbound reference. -
Configure BPEL Process or Mediator Scenario to use the connection factory, as shown in the following example:
<adapter-config name="FlatStructureOut" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/HAFileAdapter" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="Write_ptt" operation="Write"> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileInteractionSpec"> <property../> <property../> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config>
Note:
The location attribute is set toeis/HAFileAdapterfor the connection factory.
-
4.4.3 Using Secure FTP with the Oracle FTP Adapter
The Oracle FTP Adapter supports the use of the secure FTP feature on Windows, Solaris, and Linux. For Windows, this feature is certified on FileZilla FTP server with OpenSSL. This section provides an overview of secure FTP functionality and describes how to install and configure this feature.
This section includes the following topics:
-
Section 4.4.3.2, "Installing and Configuring FTP Over SSL on Solaris and Linux"
-
Section 4.4.3.3, "Installing and Configuring FTP Over SSL on Windows"
4.4.3.1 Secure FTP Overview
In environments in which sensitive data is transferred to remote servers (for example, sending credit card information to HTTP servers), the issue of security is very important. Security in these cases primarily refers to two requirements:
-
Trust in the remote server with which you are exchanging data
-
Protection from third parties trying to intercept the data
Secure socket layer (SSL) certificates and encryption focus on satisfying these two security requirements. When SSL is used for FTP, the resulting security mechanism is known as FTPS (or FTP over SSL).
To gain the trust of clients in SSL environments, servers obtain certificates (typically, X.509 certificates) from recognized certificate authorities. When you set up the FTP server, you use openSSL to create a certificate for the server. Every client trusts a few parties, to begin with. If the server is one of these trusted parties, or if the server's certificate was issued by one of these parties, then you have established trust, even indirectly. For example, if the server's certificate was issued by authority A, which has a certificate issued by authority B, and the client trusts B, that is good enough. For the setup shown in Figure 4-45, the server's certificate is directly imported into the client's certificate store (or Oracle Wallet) as a trusted certificate.
You make the data being transferred immune to spying by encrypting it before sending it and decrypting it after receiving it. Symmetric encryption (using the same key to encrypt and decrypt data) is much faster for large amounts of data than the public key and private key approach. Symmetric encryption is the approach used by FTPS. However, before the client and server can use the same key to encrypt and decrypt data, they must agree on a common key. This client typically does this by performing the following tasks:
-
Generating a session key (to be used to encrypt and decrypt data)
-
Encrypting this session key using the server's public key that is part of the server's certificate
-
Sending the key to the server
The server decrypts this session key by using its private key and subsequently uses it to encrypt file data before sending it to the client.
4.4.3.2 Installing and Configuring FTP Over SSL on Solaris and Linux
The following subsections describe how to install and configure secure FTP for Solaris and Linux:
4.4.3.2.1 Installing and Configuring OpenSSL
OpenSSL is an open source implementation of the SSL protocol. OpenSSL implements basic cryptographic functions and provides utility functions. Install and configure OpenSSL on the Solaris or Linux host to be used as the FTP server.
-
Go to the following URL:
http://www.openssl.org/source
-
Locate
openssl-0.9.7g.tar.gzin the list of available files. For example:3132217 Apr 11 17:21:51 2005 openssl-0.9.7g.tar.gz (MD5) (PGP sign)
-
Download the following files:
-
openssl-0.9.7g.tar.gz -
openssl-0.9.7g.tar.gz.md5 (under the
MD5link) -
openssl-0.9.7g.tar.gz.asc (under the
PGP signlink
-
-
Unzip the following file using
gunzip.gunzip openssl-0.9.7g.tar.gz
-
Untar the following file:
tar xvf openssl-0.9.7g.tar
-
Change directories to the following location:
cd openssl-0.9.7g
-
Run the following command:
./config --prefix=/usr --openssldir=/usr/local/openssl
-
Change to the Bourne shell (if you are not using it):
sh
-
Configure and export the
PATHvariable:PATH=${PATH}:/usr/ccs/bin; export PATH -
Run the following command:
make
-
Exit the Bourne shell:
exit
-
Run the following command:
make test
-
Log in as the super user:
msu
-
Enter the password when prompted.
-
Run the following command:
make install
4.4.3.2.2 Installing and Configuring vsftpd
The vsftpd server is a secure and fast FTP server for UNIX systems. Install and configure vsftpd on the Solaris or Linux host to be used as the FTP server.
-
Go to the following location:
ftp://vsftpd.beasts.org/users/cevans/
-
Download
vsftpd-2.0.5(You need the tar and signature file (.ascfile)). For example:[BINARY] vsftpd-2.0.5.tar.gz. . . . . . . . . . . [Mar 19 21:26] 149K [FILE] vsftpd-2.0.5.tar.gz.asc. . . . . . . . . [Mar 19 21:26] 189B
-
Unzip the following file using
gunzip.gunzip vsftpd-2.0.5.tar.gz
-
Unzip the tar file:
tar xvf vsftpd-2.0.5.tar
-
Change directories to the following location:
cd vsftpd-2.0.5
-
Make the following change in the
builddefs.hfile:#undef VSF_BUILD_SSL
to
#define VSF_BUILD_SSL
-
Log in as the super user:
msu
-
Enter the password when prompted.
-
Create a file named
vsftpd.confwith the following settings in the/etcdirectory:# Standalone mode listen=YES max_clients=200 max_per_ip=4 # Access rights anonymous_enable=YES #chroot_local_user=YES #userlist_enable=YES ftp_username=ftp local_enable=YES write_enable=YES anon_upload_enable=YES anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES anon_other_write_enable=YES chown_uploads=YES chown_username=ftp # Security anon_world_readable_only=NO allow_anon_ssl=YES ssl_enable=YES connect_from_port_20=YES hide_ids=YES pasv_min_port=50000 pasv_max_port=60000 # Features ftpd_banner="Welcome to the FTP Service" xferlog_enable=YES ls_recurse_enable=NO ascii_download_enable=NO async_abor_enable=YES # Performance one_process_model=NO idle_session_timeout=120 data_connection_timeout=300 accept_timeout=60 connect_timeout=60 anon_max_rate=50000
Note:
Copies of thevsftpd.conffile appear in several locations in thevsftpd-2.0.5directory structure. If you use one of those files to create thevsftpd.conffile in the/etcdirectory, then ensure that it only includes the parameters and settings described in Step 9. -
Run the following commands:
mkdir /var/ftp useradd -d /var/ftp ftp chown root /var/ftp chmod og-w /var/ftp mkdir /usr/share/empty mkdir /usr/share/ssl mkdir /usr/share/ssl/certs
-
openssl req -x509 -nodes -newkey rsa:1024 -keyout /usr/share/ssl/certs/vsftpd.pem -out /usr/share/ssl/certs/vsftpd.pem
-
Run the
vsftpddaemon from thevsftpd-2.0.5directory:./vsftpd
4.4.3.2.3 Creating PKCS#12 Certificates and Keys"t
You can manage and edit security credentials by creating PKCS#12 certificates and keys.
-
Export the
vsftpd.pemfrom Step 11 of Section 4.4.3.2.2, "Installing and Configuring vsftpd" into PKCS#12 format:
openssl pkcs12 -export -out vsfptd.p12 -in vsfptd.pem -inkey vsftpd.pem
4.4.3.2.4 Setting Up the Oracle FTP Adapter
Perform the following tasks to set up the Oracle FTP Adapter:
-
On your Solaris or Linux host, run the following commands:
mkdir /var/ftp/inDir mkdir /var/ftp/outDir chmod 777 /var/ftp/inDir /var/ftp/outDir
-
Specify the FTP connection parameters in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor from the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Where... Is... useFtpsSet to True. This setting is required to use FTP over SSL. The default isFalse.walletLocationThe location of the PKCS12 file created in Section 4.4.3.2.3, "Creating PKCS#12 Certificates and Keys"t." walletPasswordThe password of the PKCS12 file. channelMaskThe type of channel: control channel or data channel. Possible values are both,control,data, ornone. The default isboth.securePortThe port for FTP over SSL. The default is 990.keyStoreProviderNameThe keystore provider class. The default is sun.security.provider.Sun.keystoreTypeThe keystore type. The default is PKCS12.keystoreAlgorithmThe keystore algorithm. The default is PKCS12enableCipherSuitsList of comma separated cipher suites. The default is blank, in which case the default list of cipher suites are used. For most cases, you are not required to change this. pkiProviderSet to blank. jsseProviderSet to blank. You have now installed and configured secure FTP and are ready to use this feature with the Oracle FTP Adapter.
4.4.3.3 Installing and Configuring FTP Over SSL on Windows
The FTPS feature is certified on FileZilla FTP server with OpenSSL. You must follow the procedure in the following subsections for installing and configuring OpenSSL for FileZilla on Windows:
-
Section 4.4.3.3.2, "Generating OpenSSL Server Key and Certificate"
-
Section 4.4.3.3.3, "Importing the Server Key and Certificate Into FileZilla Server"
-
Section 4.4.3.3.4, "Converting the Server Key From PEM to PKCS12 Format"
-
Section 4.4.3.3.5, "Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter Deployment Descriptor to Use the New Key"
4.4.3.3.1 Installing OpenSSL
OpenSSL is an open source implementation of the SSL protocol. OpenSSL implements basic cryptographic functions and provides utility functions. Perform the following steps to install and configure OpenSSL on the Windows host to be used as the FTP server.
-
Go to the following URL:
-
Download and install
Visual C++ 2008 Redistributables. -
Download and install
Win32 OpenSSL v0.9.8k Light.
4.4.3.3.2 Generating OpenSSL Server Key and Certificate
To create the server key and certificate files, you must perform the following steps:
-
Open the command prompt and browse to the
OpenSSL\bindirectory. -
Run the following command:
openssl req -new -x509 -keyout mykey.pem -out mycert.pem -days 365
A sample command output is as follows:
C:\OpenSSL\bin>openssl req -new -x509 -keyout mykey.pem -out mycert.pem -days 365 Loading 'screen' into random state - done Generating a 1024 bit RSA private key ..........++++++ .......++++++ writing new private key to 'mykey.pem' Enter PEM pass phrase: Verifying - Enter PEM pass phrase: ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:US State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:CA Locality Name (eg, city) []:Belmont Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:Test Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Test Common Name (eg, YOUR name) []:Test test Email Address []:test@test.com
-
Re-enter PEM pass phrase entered in step 3 for verification.
-
Enter the requested details.
The server key (
mykey.pem) and certificate (mycert.pem) are generated in theOpenSSL\bindirectory.
4.4.3.3.3 Importing the Server Key and Certificate Into FileZilla Server
To import the server key and certificate into FileZilla, you must perform the following steps:
-
Open a FileZilla Server interface from your Windows Start menu.
-
Click Edit, and then click Settings.
The FileZilla Server Options dialog is displayed.
-
Click SSL/TLS settings.
-
Enter the server key and certificate details as shown in Figure 4-46.
Figure 4-46 The FileZilla Server Options Dialog
Description of "Figure 4-46 The FileZilla Server Options Dialog"
Note:
In the Key password field, you must use the PEM pass phrase generated in Step 3 of Section 4.4.3.3.2, "Generating OpenSSL Server Key and Certificate."
4.4.3.3.4 Converting the Server Key From PEM to PKCS12 Format
You must convert the server key and the server certificate from the PEM format to the PKCS#12 format as the Oracle FTP Adapter does not recognize the PEM format. To convert the server key and certificate to the PKCS#12 format, you must perform the following steps:
-
Open the command prompt and browse to the
OpenSSL\bindirectory. -
Run the following command:
openssl pkcs12 -export -out mykeyz.p12 -in mycert.pem -inkey mykey.pem
The command output is as follows:
C:\OpenSSL\bin>openssl pkcs12 -export -out mykeyz.p12 -in mycert.pem -inkey mykey.pem Loading 'screen' into random state - done Enter pass phrase for mykey.pem: Enter Export Password: Verifying - Enter Export Password:
-
Enter a PEM pass phrase when prompted. This is the pass phrase that you created while generating OpenSSL server key and certificate in Section 4.4.3.3.2, "Generating OpenSSL Server Key and Certificate."
-
Re-enter the export password for verification.
-
Enter the requested details.
The
mykeyz.p12file is generated in theOpenSSL\bindirectory. -
Copy the
mykeyz.p12file to the managed Oracle WebLogic Server instance running the Oracle FTP Adapter.For example,
/scratch/$user/private/mykeyz.p12
4.4.3.3.5 Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter Deployment Descriptor to Use the New Key
You must perform the following steps to configure the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/console. -
Use the required credentials to open the home page of the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Select Deployments in the Domain Structure pane.
The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Summary of Deployments page is displayed.
-
Click FtpAdapter.
The Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - Settings for FtpAdapter page is displayed.
-
Click the Configuration tab, and then click the Outbound Connection Pools tab.
The Outbound Connection Pool Configuration table is displayed.
-
Select the JNDI name for the Ftp Adapter instance that you wish to configure. For example,
"eis/Ftp/FtpAdapter". -
Configure the deployment descriptors listed in Table 4-10:
Table 4-10 JCA Properties for Oracle File and FTP Adapters
Property Name Property Value useFtpsSet the value to
true.walletLocationSet it to the location of the PKCS#12 file in the managed Oracle WebLogic Server instance:
/scratch/$user/private/mykeyz.p12.walletPasswordSet the value to the export password generated in Step 4 of Section 4.4.3.3.4, "Converting the Server Key From PEM to PKCS12 Format."
keyStoreProviderNameSet the value to
sun.security.provider.SunkeystoreTypeSet the value to
PKCS12keystoreAlgorithmSet the value to
SunX509pkiProviderMust be left blank.
jsseProviderMust be left blank.
4.4.4 Using SFTP with Oracle FTP Adapter
SSH file transfer protocol (SFTP) is a network protocol that enables secure file transfer over a network. Oracle FTP Adapter supports the use of the SFTP feature on Windows and Linux. This section provides an overview of the SFTP functionality and describes how to install and configure this feature.
This section includes the following tasks:
4.4.4.1 SFTP Overview
FTP is the network protocol that enables clients to securely transfer files over the underlying SSH transport. SFTP is not similar to FTP over SSH or File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Figure 4-47 displays the communication process between an SSH client and an SSH server. SFTP is supported in Windows and Linux.
SFTP has the following features:
4.4.4.1.1 Encryption
The SSH protocol uses public key cryptography for encryption. This section explains how data is encrypted:
-
The SSH subsystem uses symmetric key ciphers such as Data Encryption Standard (DES) or Blowfish to generate a session key. The SSH protocol currently uses the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Algorithm to derive the symmetric key for the session.
-
The data is encrypted using the session key.
-
The session key is encrypted by using the recipient's public key. Because the recipient already has the private key, it can decrypt the message by using its preferred PKI algorithm such as Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) or Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA).
4.4.4.1.2 Authentication
The SSH protocol inherently supports password authentication by encrypting passwords or session keys as they are transferred over the network. In addition, the SSH protocol uses a mechanism known as 'known hosts' to prevent threats such as IP spoofing. When this mechanism is used, both the client and the server have to prove their identity to each other before any kind of communication exchange.
4.4.4.1.3 Integrity
The SSH protocol uses widely trusted bulk hashing algorithms such as Message Digest Algorithm 5 (MD5) or Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-1) to prevent insertion attacks. Implementation of data integrity checksum by using the algorithms mentioned in Section 4.4.4.1.1, "Encryption" prevents deliberate tampering of data during transmission.
4.4.4.1.4 Data Compression
The SSH protocol supports zlib, an open-source cross-platform algorithm for data compression. SSH uses zlib to compress in-flight data to reduce network bandwidth.
4.4.4.2 Install and Configure OpenSSH for Windows
OpenSSH for Windows is the free implementation of the SSH protocol on Windows. Perform the following steps to install and configure OpenSSH on Windows XP:
-
Log in as a user with Administrator privileges.
-
Download
setup.exefrom the following location:http://www.cygwin.com
-
Run
setup.exe. The Cygwin Net Release Setup window is displayed. -
Click Next. The Choose Installation type window is displayed.
-
Select Install from Internet as the download source and click Next. The Choose Installation Directory window is displayed.
-
Leave the root directory as C:\cygwin. Also, keep the default options for the Install For and the Default Text File Type fields.
-
Click Next. The Select Local Package Directory window is displayed.
-
Click Browse and select C:\cygwin as the local package directory.
-
Click Next. The Select Connection Type window is displayed.
-
Select a setting for Internet connection and click Next. The Choose Download Site(s) window is displayed.
-
Select a site from the Available Download Sites list and click Next. The Select Packages window is displayed.
-
Click View to see the complete list of packages available for installation.
-
Select openssh if it is not the default value.
-
Select the Binaries box for openssh.
-
Click Next to start the installation.
-
On Windows XP desktop, right -click My Computer and select Properties.
-
Click the Advanced tab and click Environment Variables.
-
Click New and enter
CYGWINin the Variable Name field andntsecin the Variable Value field. -
Add
C:\cygwin\binto the system path. -
Open the cygwin window.
-
Type
ssh-host-config. -
You are prompted with the following questions:
-
Shall privilege separation be used? (yes/no)Enter
yes. -
Shall this script create a local user 'sshd' on this machine?Enter
yes. -
Do you want to install sshd as service?(Say "no" if it's already installed as service) (yes/no)Enter
yes. -
Which value should the environment variable CYGWIN have when sshd starts? It's recommended to set at least "ntsec" to be able to change user context without password. Default is "binmode ntsec tty".Enter
ntsec.
-
-
Type
net start sshdto start the sshd service. -
Run the following command in the cygwin window to replicate the Windows local user accounts to cygwin:
mkpasswd --local > /etc/passwd mkgroup --local > /etc/group
-
To test the setup, type
ssh localhostin the cygwin window.
4.4.4.3 Set Up Oracle FTP Adapter for SFTP
To use the SFTP functionality, you must modify the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter.
Table 4-11 lists the properties for which you must specify a value in the deployment descriptor. The values of these properties depend on the type of authentication and the location of OpenSSH.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specify Mandatory: Yes Default value: |
|
|
Specify For password-based authentication, the user name and password specified in the For public key authentication, the Mandatory: Yes |
|
|
Specify This is an optional parameter where the user can select the default key exchange protocol for negotiating the session key for encrypting the message. Mandatory: No Default value: |
|
|
Specify This parameter enables the user to choose whether in-flight data should be compressed or not. Mandatory: No |
|
|
Specify This parameter enables the user to select the bulk-hashing algorithm for data integrity checks. Mandatory: No Default value: |
|
|
Specify This parameter enables the user to configure the asymmetric cipher for the communication. Mandatory: No Default value: |
|
|
Specify the path to the private key file. This is required if the Mandatory: No |
|
|
Specify a cipher from the following list:
Mandatory: No Default value: blowfish-cbc |
|
|
Specify Specify If you select HTTP, then you must provide values for the following parameters:
Mandatory: Yes |
4.4.4.3.1 Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter for Password Authentication
To set up the Oracle FTP Adapter for password authentication, the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter must specify the values of the properties listed in Table 4-11. Ensure that the authenticationType property is set to password.
Specify the following properties and values listed in Table 4-12:
Table 4-12 Sample SFTP Properties and Values
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.4.4.3.2 Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter for Public Key Authentication
For public key authentication, you must first configure OpenSSH and then set up the Oracle FTP Adapter. The Oracle FTP Adapter setup depends on whether the OpenSSH is running inside a firewall or outside a firewall. If OpenSSH is running inside the firewall, then see the following sections:
If OpenSSH is running outside the firewall, then see the following sections:
4.4.4.3.3 Configuring OpenSSH for Public-Key Authentication
Perform the following steps:
-
Go to the
C:\cygwin\etcdirectory. If required, configure thesshd_configfile to force public key authentication. For more information, see openssh help or manual. -
Go to the
C:\cygwin\bindirectory. -
Run the following command to generate the key pair:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
-
Enter
/etc/id_rsawhen prompted for the file in which the key should be saved. -
Enter the passphrase.
-
Enter the passphrase again.
-
Go to the
/etcdirectory and verify that both the public key file (id_rsa.pub) and the private key file (id_rsa) are generated. -
Run the following command to create a copy of the public key file:
cp id_rsa.pub authorized_keys
-
Create a copy of the private key file in a secured location such as
C:\my-secured-folder\. The Oracle FTP Adapter configuration refers to this private key file. -
Restart the OpenSSH server by running the following commands:
net stop sshd net start sshd
4.4.4.3.4 Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter for Public Key Authentication with OpenSSH Running Inside a Firewall
To set up the Oracle FTP Adapter for public key authentication, you must specify the values of the parameters listed in Table 4-11 in the deployment descriptor. Ensure that the authenticationType parameter is set to publickey and the transportProvider parameter is set to socket. The privateKeyFile parameters should contain the location of the private key file.
A sample list of public key authentication properties and their values is shown in Table 4-13.
Table 4-13 Sample SFTP Properties and Values
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C:\my-secured-folder\id_rsa |
|
|
blowfish-cbc |
|
|
|
4.4.4.3.5 Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter for Public Key Authentication with OpenSSH Running Outside a Firewall
Perform the following steps to set up the Oracle FTP Adapter for public key authentication when OpenSSH is running outside the firewall:
-
In the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter, you must specify the values of the properties listed in Table 4-11 in the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter. Ensure that the
authenticationTypeproperty is set topublickeyand thetransportProviderproperty is set toHTTP. TheprivateKeyFileproperty contains the location of the private key file. -
In the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter, also specify the following proxy-related properties:
-
proxyHost: The name of the proxy host. -
proxyPort: The port number of the proxy. -
proxyUsername: The user name for the proxy. -
proxyPassword: The password for the proxy. -
useProxy: Specifytrueto use proxy.
-
A sample list with public key authentication properties and proxy properties is shown in Table 4-14.
Table 4-14 Sample SFTP Properties and Values
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C:\my-secured-folder\id_rsa |
|
|
blowfish-cbc |
|
|
|
4.4.5 Configuring Oracle FTP Adapter for HTTP Proxy
The Oracle FTP Adapter provides proxy support for HTTP proxy only. The HTTP proxy support is available in the following two modes, plain FTP mode and SFTP mode. This section explains how to configure the Oracle FTP Adapter for running in plain FTP mode and SFTP mode. It contains following sections:
4.4.5.1 Configuring for Plain FTP Mode
For running the Oracle FTP Adapter in plain FTP mode, you must specify the value of certain parameters in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor. Table 4-15 lists the properties that you must modify.
Table 4-15 Plain FTP Mode Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The remote FTP server name. |
|
|
The FTP control port number. |
|
|
The FTP user name. |
|
|
The FTP password. |
|
|
The proxy host name. |
|
|
The proxy port number. |
|
|
The proxy user name. |
|
|
The proxy password. |
|
|
The proxy type. Only HTTP proxy type is supported. |
|
|
The absolute path of the proxy definition file. This parameter is not mandatary. See Section 4.4.5.1.1, "Proxy Definition File" for more information. |
|
|
Specify |
A sample list of Oracle FTP Adapter descriptor properties and their values is shown in Table 4-16.
Table 4-16 Sample Plain FTP Mode Properties and Values
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.4.5.1.1 Proxy Definition File
You can specify all proxy-specific information in a proxy definition file and configure the adapter to use this file with the proxyDefinitionFile property of the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor file. A proxy definition file is written in XML format and is based on XML schema. The XML schema for the proxy definition file is shown in Example 4-5. Your proxy definition file must be based on this XML schema.
Example 4-5 Proxy Definition File XML Schema
<?xml version = \"1.0\" encoding = \"UTF-8\"?>
<schema targetNamespace = "http://ns.oracle.com/ip/af/ftp/proxy" xmlns = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:proxy="http://ns.oracle.com/ip/af/ftp/proxy">
<element name="ProxyDefinitions" type="proxy:ProxyDefinitionsType"/>
<complexType name="ProxyDefinitionsType">
<sequence>
<element name="Proxy" type="proxy:ProxyDefinition"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
</complexType>
<complexType name="ProxyDefinition">
<sequence>
<element name="Step" type="proxy:StepType"
minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="key" type="ID" use="required"/>
<attribute name="description" type="string"
use="required"/>
<attribute name="type" type="proxy:Protocol"
use="optional"/>
</complexType>
<complexType name="StepType">
<simpleContent>
<extension base="string">
<attribute name="command" type="string" use="required"/>
<attribute name="args" type="string" use="required"/>
</extension>
</simpleContent>
</complexType>
<simpleType name="Protocol">
<restriction base="string">
<enumeration value="ftp" />
<enumeration value="http" />
</restriction>
</simpleType>
</schema>
A sample proxy definition file, based on the XML schema in Example 4-5, would look as shown in Example 4-6:
Example 4-6 Proxy Definition File
<?xml version = '1.0' standalone = 'yes'?> <proxy:ProxyDefinitions xmlns:proxy="http://ns.oracle.com/ip/af/ftp/proxy"> <Proxy key="http" description="http" type="http"> <Step command="USER" args="remote_username" /> <Step command="PASS" args="remote_password" /> </Proxy> </proxy:ProxyDefinitions>
When you use the file in Example 4-6, the Oracle FTP Adapter sends the following sequence of commands to log in:
-
USER remote_username
-
PASS remote_password
You can also direct the proxy definition file to pick values from the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter. You can use the following expressions for this:
-
$proxy.user: This corresponds to the value of theproxyUsernameparameter in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor. -
$proxy.pass: This corresponds to the value of theproxyPasswordparameter in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor. -
$remote.user: This corresponds to the value of theusernameparameter in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor. -
$remote.pass: This corresponds to the value of thepasswordparameter in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor. -
$remote.host: This corresponds to the value of thehostparameter in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor. -
$remote.port: This corresponds to the value of theportparameter in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor.
A sample proxy definition file based on the XML schema in Example 4-6 and taking values from the weblogic-ra.xml file is shown in Example 4-7:
Example 4-7 Proxy Definition File Taking Values from the Deployment Descriptor
<?xml version = '1.0' standalone = 'yes'?> <proxy:ProxyDefinitions xmlns:proxy="http://ns.oracle.com/ip/af/ftp/proxy"> <Proxy key="http" description="http" type="http"> <Step command="USER" args="$remote.user" /> <Step command="PASS" args="$remote.pass" /> </Proxy> </proxy:ProxyDefinitions>
4.4.5.2 Configuring for SFTP Mode
For running the Oracle FTP Adapter in SFTP mode, you must specify the value of certain properties in the Oracle FTP Adapter deployment descriptor. Table 4-17 lists the properties that you must modify.
Table 4-17 SFTP Mode Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The remote FTP server name. |
|
|
The FTP control port number. |
|
|
The SFTP user name. |
|
|
The SFTP password. |
|
|
The proxy server host name. |
|
|
The proxy port number. |
|
|
The proxy user name. |
|
|
The proxy password. |
|
|
Specify |
|
|
Specify either |
|
|
Specify |
A sample list of deployment descriptor properties is shown in Table 4-18.
4.5 Oracle File and FTP Adapters Use Cases
This section includes the following Oracle File and FTP Adapters use cases:
-
Section 4.5.6, "Oracle File Adapter Read File As Attachments"
-
Section 4.5.10, "Oracle FTP Adapter Dynamic Synchronous Read"
4.5.1 Oracle File Adapter XML Debatching
This is an Oracle File Adapter feature that debatches large XML documents into smaller individual XML fragments.
In this use case, the Debatching XML process uses the Oracle File Adapter to debatch an XML file containing a batch of employees occurring in the XML file as repeating nodes. These nodes are then processed and every individual node is written to separate output files.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.1.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.1.4, "Creating the Outbound File Adapter Service"
4.5.1.1 Prerequisites
To perform debatching, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-102FileAdapterXMLDebatching sample:
-
artifacts/input/emps.xml -
artifacts/schemas/employees.xsd
You can obtain the Adapters-102FileAdapterXMLDebatching sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and by selecting the Adapters tab.
4.5.1.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
SOA-XMLDebatchingin the Application Name field, as shown in Figure 4-48, and click Next. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed.Figure 4-48 The Generic Create Application - Name your application Page
Description of "Figure 4-48 The Generic Create Application - Name your application Page"
-
Enter
XMLDebatchingin the Project Name field. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list, as shown in Figure 4-49.
Figure 4-49 The Create Generic Application - Name your project Page
Description of "Figure 4-49 The Create Generic Application - Name your project Page"
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, as shown in Figure 4-50, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
Figure 4-50 The Create Generic Application - Configure SOA settings Page
Description of "Figure 4-50 The Create Generic Application - Configure SOA settings Page"
-
Enter
BPELXMLDebatchingin the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template box, as shown in Figure 4-51.Figure 4-51 The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process Page
Description of "Figure 4-51 The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process Page"
-
Click OK. The SOA-XMLDebatching application and the XMLDebatching project appear in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-52.
Figure 4-52 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-52 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Copy the
employees.xsdfile to the xsd directory in your project (see Section 4.5.1.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file).
4.5.1.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read the file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop the Oracle File Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
XMLDebatchingInin the Service Name field and, as shown in Figure 4-53.Figure 4-53 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Service Name Page

Description of "Figure 4-53 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - Service Name Page"
-
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File, as shown in Figure 4-54, and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
Figure 4-54 The Adapter Configuration Wizard Operation Page
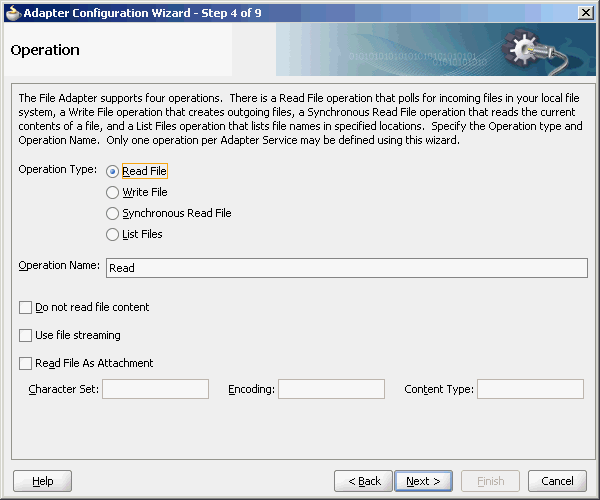
Description of "Figure 4-54 The Adapter Configuration Wizard Operation Page"
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory, as shown in Figure 4-55. The File Filtering page is displayed.
Figure 4-55 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Directories Page

Description of "Figure 4-55 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Directories Page"
-
Enter
*.xmlin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, select Files Contain Multiple Messages check box, specify1as the value for Publish Messages in Batches Of box, as shown in Figure 4-56.Figure 4-56 The Adapter Configuration Wizard File Filtering Page
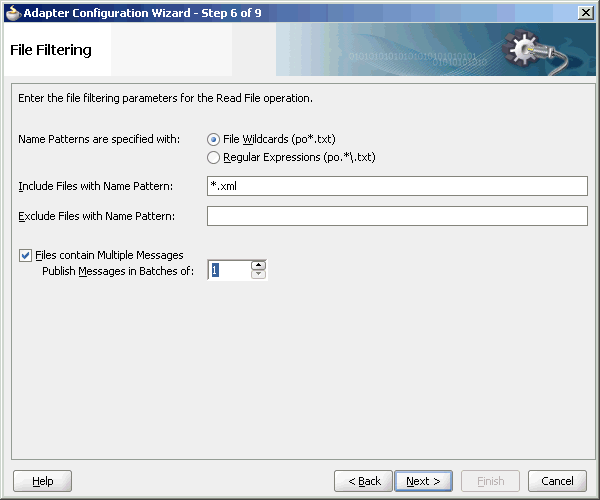
Description of "Figure 4-56 The Adapter Configuration Wizard File Filtering Page"
-
Click Next. The File Polling page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, employees.xsd, and employees, as shown in Figure 4-57.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the employees.xsd file, as shown in Figure 4-58.
Figure 4-58 The Adapter Configuration Wizard File Messages Page
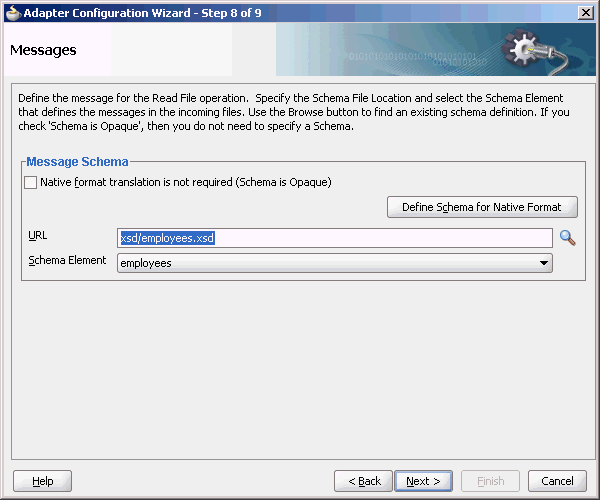
Description of "Figure 4-58 The Adapter Configuration Wizard File Messages Page"
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-59.
Figure 4-59 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-59 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.1.4 Creating the Outbound File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound file adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop the File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
XMLOutin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Write File, and click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the output directory and enter
emp_%SEQ%.xmlin the File Naming Convention (po_%SEQ%.txt) field, as shown in Figure 4-60. -
Select Number of Messages Equals option, if not already selected. The default value is
1.Figure 4-60 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Configuration Page
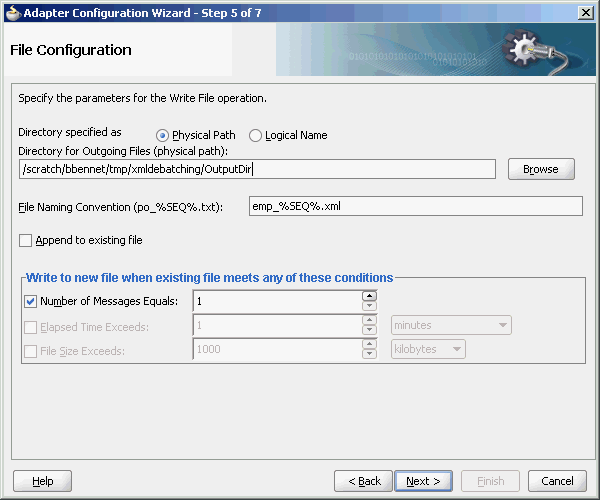
Description of "Figure 4-60 The Adapter Configuration Wizard - File Configuration Page"
-
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, employees.xsd, and employee, as shown in Figure 4-61.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the employees.xsd file, as shown in Figure 4-58.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-62.
Figure 4-62 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-62 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.1.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the XMLDebatchingIn in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the XMLOut in the External References area.
The JDeveloper Composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-63.
Figure 4-63 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
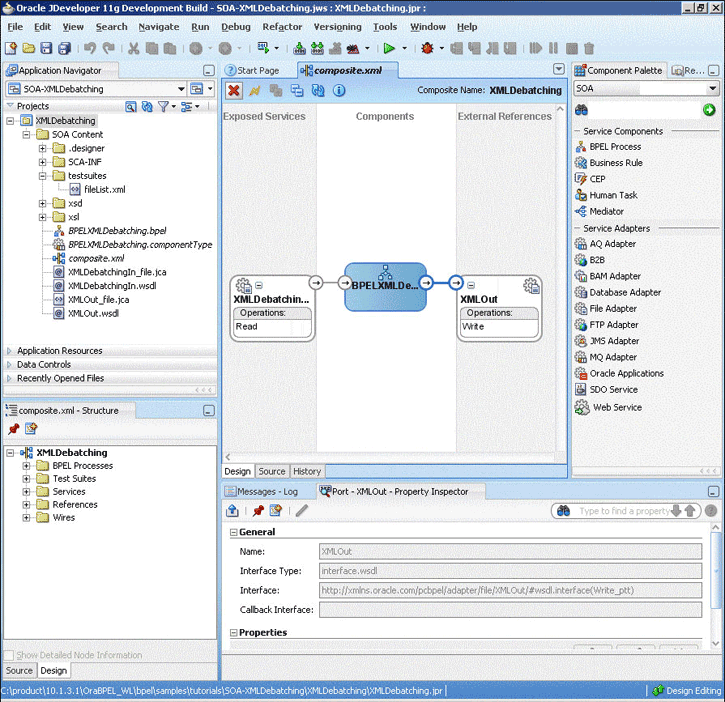
Description of "Figure 4-63 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELXMLDebatching. The BPELXMLDebatching.bpel page is displayed.
-
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
ReceiveEmployeein the Name field, as shown in Figure 4-64.Figure 4-64 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-64 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel"
-
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select XMLDebatchingIn, as shown in Figure 4-65, and click OK.
Figure 4-65 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog
Description of "Figure 4-65 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog"
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog, as shown in Figure 4-66. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance, and click OK. The JDeveloper BPELXMLDebatching.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-67.
Figure 4-67 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-67 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
WriteEmployeein the Name field, as shown in Figure 4-68. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select XMLOut, as shown in Figure 4-69, and click OK.
Figure 4-69 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog
Description of "Figure 4-69 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog"
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name. The Invoke dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-70.
-
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELXMLDebatching.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-71.
Figure 4-71 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-71 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel"
-
Drag and drop a Transform activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the Transform activity. The Transform dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
TransformPayloadin the Name field, as shown in Figure 4-72. -
Click the Transformation tab. The Transform dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-73.
Figure 4-73 The Transform Dialog - Transformation Tab
Description of "Figure 4-73 The Transform Dialog - Transformation Tab"
-
Click the Create... icon. The Source Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select ReceiveEmployee_Read_InputVariable in the Source Variable box, and select employees in the Source Part box, and then click OK. The Transform dialog is displayed with the Source and Part selected.
-
Select WriteEmployee_Write_InputVariable in the Target Variable list, select employee in the Target Part, as shown in Figure 4-74.
-
Click the Create Mapping icon. The XSL Editor page is displayed.
-
Drag employees from sources to employee in the target, as shown in Figure 4-75. The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
Figure 4-75 The JDeveloper - Transformation_2.xsl
Description of "Figure 4-75 The JDeveloper - Transformation_2.xsl"
-
Click OK.
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Close the XSL Editor page. The BPELXMLDebatching.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-76.
Figure 4-76 The JDeveloper - XML Debatching Complete
Description of "Figure 4-76 The JDeveloper - XML Debatching Complete"
4.5.1.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.1.7 Monitoring Using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control Console (Fusion Middleware Control Console)
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using the Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the emps.xml file to the input directory and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created.
-
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow.
-
Click an activity to display the activity details.
4.5.2 Flat Structure for Oracle BPEL PM
This use case demonstrates how a flat structure business process uses the Oracle File Adapter to process address book entries from a Comma Separated Value (CSV) file. This is then transformed and written to another file in a Fixed Length format.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.2.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.2.4, "Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.2.7, "Monitoring Using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.2.1 Prerequisites
To perform the flat structure business process, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-101FileAdapterFlatStructure sample:
-
artifacts/input/address-csv.txt -
artifacts/schemas/address-csv.xsd -
artifacts/schemas/address-fixedLength.xsd -
artifacts/xsl/addr1Toaddr2.xsl
You can obtain the Adapters-101FileAdapterFlatStructure sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and selecting the Adapters tab.
4.5.2.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
SOA-FlatStructurein the Application Name field, and click OK. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
FlatStructurein the Project Name. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPELFlatStructurein the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template box. -
Click OK. The SOA-FlatStructure application and the FlatStructure project appear in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-77.
Figure 4-77 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-77 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Copy the address-csv.xsd and address-fixedLength.xsd files to the schema directory in your project (see Section 4.5.2.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file).
-
Copy addr1Toaddr2.xsl to the xsl directory of your project (see Section 4.5.2.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file).
4.5.2.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read the file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
FlatStructureInin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File, and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory. Check Archive Processed Files.
-
Enter the physical path for the archive directory for processed files.
-
Click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.txtin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, click Next. The File Polling page is displayed. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-csv.xsd, and Root-Element.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the
address-csv.xsdfile. -
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and
composite.xmlappears, as shown in Figure 4-78.Figure 4-78 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-78 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.2.4 Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle File Adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
FlatStructureOutin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Write File, and click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the output directory and enter
address_%SEQ%.datain the File Naming Convention(po_%SEQ%.txt) field. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-fixedLength.xsd, and Root-Element.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the address-fixedLength.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-79.
Figure 4-79 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-79 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.2.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the FlatStructureIn in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the FlatStructureOut in the External References area.
The JDeveloper Composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-80.
Figure 4-80 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
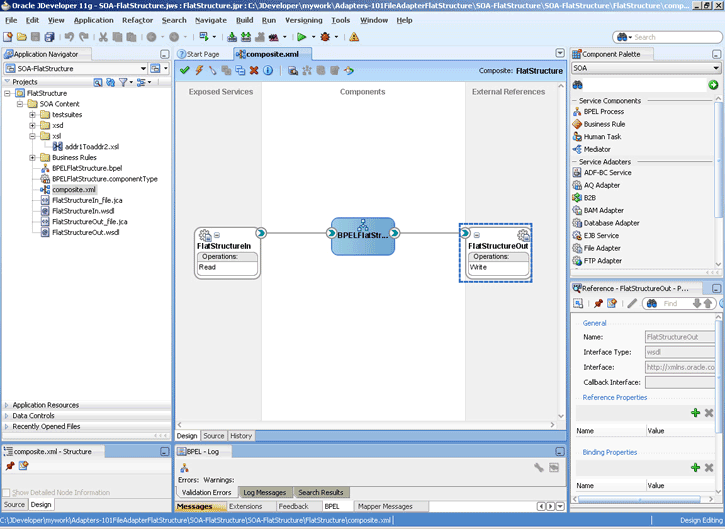
Description of "Figure 4-80 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELFlatStructure. The BPELFlatStructure.bpel page is displayed.
-
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
ReceiveCSVin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select FlatStructureIn, and click OK.
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance, and click OK. The JDeveloper BPELFlatStructure.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-81.
Figure 4-81 The JDeveloper - BPELFlatStructure.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-81 The JDeveloper - BPELFlatStructure.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
InvokeWritein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select FlatStructureOut, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELFlatStructure.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-82.
Figure 4-82 The JDeveloper - BPELFlatStructure.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-82 The JDeveloper - BPELFlatStructure.bpel"
-
Drag and drop a Transform activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the Transform activity. The Transform dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
TransformPayloadin the Name field. -
Click the Transformation tab. The Transform dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Source Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select ReceiveCSV_Read_InputVariable in the Source Variable box, and select body in the Source Part box, and then click OK. The Transform dialog is displayed with the Source and Part selected.
-
Select InvokeWrite_Write_InputVariable in the Target Variable list, select body in the Target Part.
-
Click the Browse button at the end of the Mapper File field and select addr1Toaddr2.xsl file from the xsl directory in your project.
-
Click OK.
-
Click File, Save All. The BPELFlatStructure.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-83.
Figure 4-83 The JDeveloper - BPELFlatStructure.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-83 The JDeveloper - BPELFlatStructure.bpel"
4.5.2.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.2.7 Monitoring Using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the address-csv.txt file to the input directory and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created.
-
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow. Additionally, click an activity (such as invoke, receive) to view the details of an activity.
-
Click ReceiveCSV to display the activity details.
4.5.3 Flat Structure for Mediator
In this use case, Mediator receives the customer data from a file system as a text file, through an inbound Oracle File Adapter service named ReadFile. The ReadFile adapter service sends the message to a routing service named ReadFile_RS. The ReadFile_RS sends the message to the outbound adapter service WriteFTP. The WriteFTP service delivers the message to its associated external application.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.3.2, "Creating a Mediator Application and Project"
-
Section 4.5.3.3, "Importing the Schema Definition (.XSD) Files"
-
Section 4.5.3.4, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.3.5, "Creating the Outbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service"
4.5.3.1 Prerequisites
This example assumes that you are familiar with basic Mediator constructs, such as services, routing service, and JDeveloper environment for creating and deploying Mediator services.
To perform the flat structure for Mediator business process, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-101FileAdapterFlatStructure sample:
-
artifacts/schemas/address-csv.xsd
You can see the = Adapters-101FileAdapterFlatStructure sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and selecting the Adapters tab.
4.5.3.2 Creating a Mediator Application and Project
To create an application and a project for the use case, follow these steps:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
FileFTP_RWin the Application Name field and click Next. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
FileRead_FTPWritein the Project Name field. -
In the Available list in the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Create Generic Application - Configure SOA settings page is displayed.
-
Select Composite With Mediator in the Composite Template box.
-
Click Finish. The Create Mediator - Mediator Component page is displayed.
-
Enter
FileRead_RSin the Name field. -
Select Define Interface Later in the Template list, and then click OK. The
FileFTP_RWapplication and theFileRead_FTPWriteproject appear in the design area.
4.5.3.3 Importing the Schema Definition (.XSD) Files
Perform the following steps to import the XSD files that define the structure of the messages:
-
Create a
Schemadirectory and copy theaddress-csv.xsdfile to this directory (see Section 4.5.3.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file). -
In the Application Navigator, select FileRead_FTPWrite.
-
From the File menu, select Import. The Import dialog is displayed.
-
From the Select What You Want to Import list, select Web Source, and then click OK. The Web Source dialog is displayed.
-
To the right of the Copy From field, click Browse. The Choose Directory dialog is displayed.
-
Navigate to the Schema directory and click Select. The Web Source dialog with the directory is displayed.
-
Click OK.
4.5.3.4 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read the file from a local directory
-
Drag a File Adapter service from Components Palette to the design area. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
ReadFilein the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
-
Select Physical Path option, and click Browse and select a polling directory.
-
Click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.txtin the Include Files with Name Pattern field and click Next. The File Polling page is displayed. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click the Browse For Schema File button at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select Project Schema Files, address-csv.xsd, and then Root-Element.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Next in the Messages page. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. A ReadFile adapter service is created.
4.5.3.5 Creating the Outbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle FTP Adapter service to write the file to an FTP server:
-
Drag an FTP Adapter service from Components Palette to the design area. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
WriteFTPin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The FTP Server Connection page is displayed.
-
Specify the JNDI Name of the FTP Server in the FTP Server JNDI Name field and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Ascii option as File Type.
-
Select Put File option as the Operation Type and click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed.
-
Specify the directory to which file must be written in the Directory for Outgoing Files (physical path) field.
-
Specify the naming convention for the output file name in the File Naming Convention field. For example,
po_%SEQ%.txt. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click the Browse For Schema File button at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select Project Schema Files, address-csv.xsd, and then Root-Element.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Next in the Messages page. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. A WriteFTP adapter service is created.
4.5.3.6 Wiring Services
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound Oracle File Adapter service, Mediator component, Outbound Oracle FTP Adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the ReadFile in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the Mediator component in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the Mediator component in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the WriteFTP in the External References area. The JDeveloper composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-84.
Figure 4-84 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
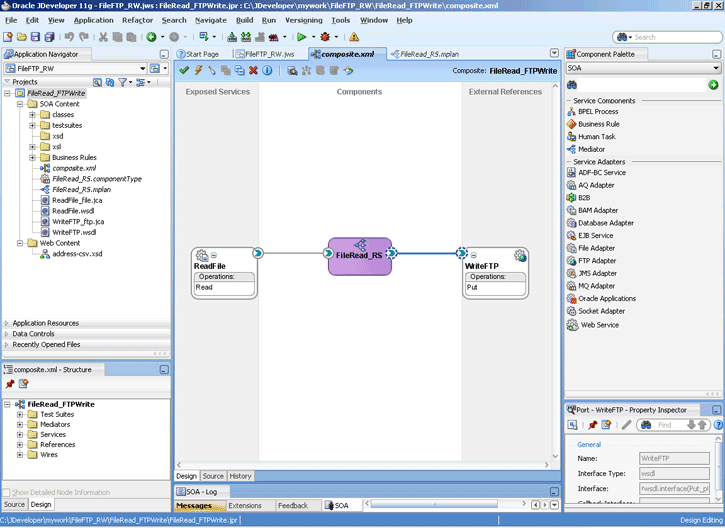
Description of "Figure 4-84 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.3.7 Creating the Routing Rule
Perform the following steps to create a routing service:
-
Double-click the ReadFile_RS routing service. The Read operation is listed in the Operations pane, as shown in Figure 4-85.
Figure 4-85 The JDeveloper - ReadFile_RS Routing Service Page
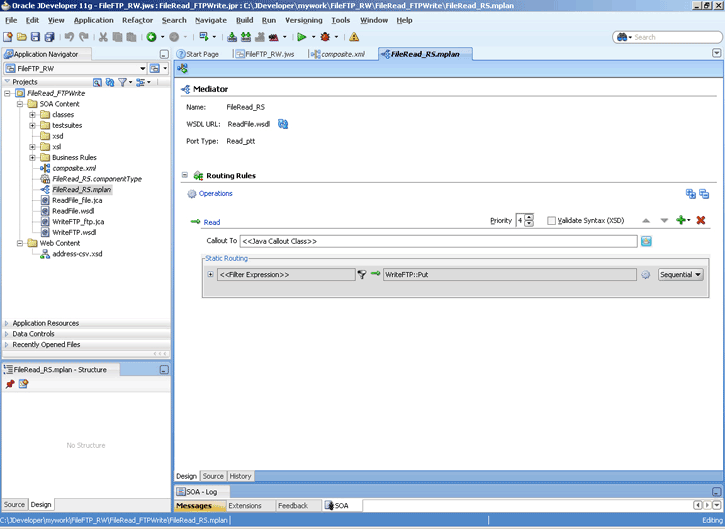
Description of "Figure 4-85 The JDeveloper - ReadFile_RS Routing Service Page"
-
Click the + sign to the left of <<Filter Expression>>to expand the routing rule.
-
Click the icon that appears at the end of the Transform Using field. The Request Transformation Map dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-86.
Figure 4-86 The Request Transformation Map Dialog
Description of "Figure 4-86 The Request Transformation Map Dialog"
-
Select Create New Mapper File and click OK.
A Root-Element_To_Root-Element.xsl tab is added to JDeveloper. This tab enables you to graphically create a document transformation file to convert the structure of the file data to a canonical data structure.
-
Drag and drop the imp1:Address source element to the imp1:Address target element. The Auto Map Preferences dialog is displayed.
-
From the During Auto Map options, deselect Match Elements Considering their Ancestor Names.
-
Click OK.
-
From the File menu, click Save.
4.5.3.8 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.3.9 Run-Time Task
At run time, copy a text file to the polling directory. Once the Oracle File Adapter picks the file, the file is written to the directory that you specified at design time.
4.5.4 Oracle File Adapter Scalable DOM
This use case demonstrates how a scalable DOM process uses the streaming feature to copy/move huge files from one directory to another.
The streaming option is not supported with DB2 hydration store.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.4.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.4.4, "Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.4.7, "Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.4.1 Prerequisites
To perform the streaming large payload process, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-103FileAdapterScalableDOM sample:
-
artifacts/schemas/address-csv.xsd -
artifacts/input/address-csv-large.txt
You can obtain the Adapters-103FileAdapterScalableDOM sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and by selecting Adapters tab:
4.5.4.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
SOA-ScalableDOMin the Application Name field, and click Next. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
ScalableDOMin the Project Name field. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The SOA-ScalableDOM application and ScalableDOM project appears in the Application Navigator and the Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPELScalableDOMin the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template box. -
Click OK. The SOA-ScalableDOM application and the ScalableDOM project appears in the design area.
-
Copy the address-csv.xsd file to the xsd directory in your project (see Section 4.5.4.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file).
4.5.4.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read the file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
ScalableDOMInin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File, and check Use File Streaming, and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.txtin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, click Next. The File Polling page is displayed. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-csv.xsd, and Root-Element, as shown in Figure 4-87.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the
address-csv.xsdfile. -
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-88.
Figure 4-88 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-88 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.4.4 Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle File Adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
ScalableDOMOutin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Write File, and click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the output directory and enter
address-csv_%SEQ%.xmlin the File Naming Convention (po_%SEQ%.txt) field. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-csv.xsd, and Root-Element.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the
address-csv.xsdfile. -
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-89.
Figure 4-89 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
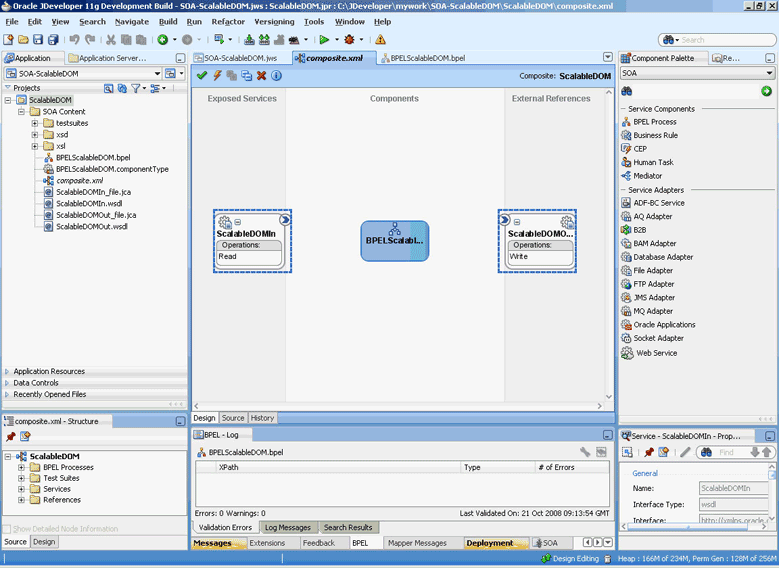
Description of "Figure 4-89 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.4.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the ScalableDOMIn in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the ScalableDOMOut in the External References area.
The JDeveloper composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-90.
Figure 4-90 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
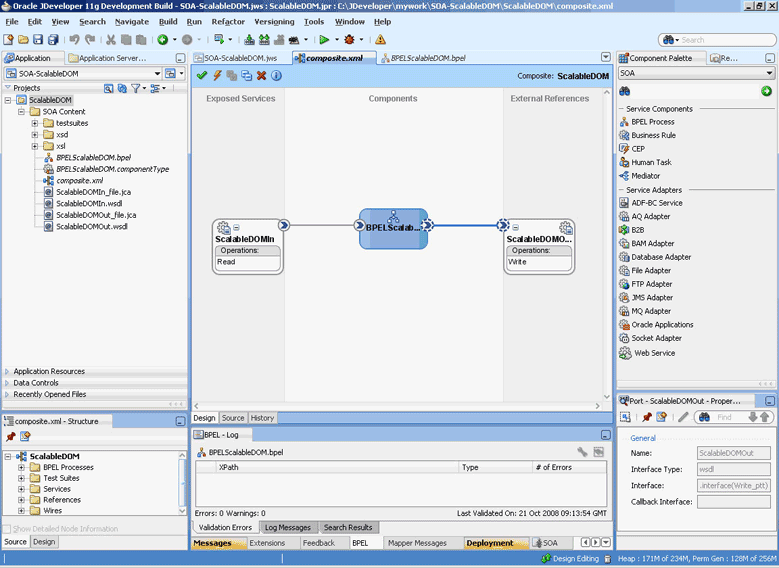
Description of "Figure 4-90 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELScalableDOM. The BPELScalableDOM.bpel page is displayed.
-
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
ReceiveFilein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select ScalableDOMIn, as shown in Figure 4-91, and click OK.
Figure 4-91 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog
Description of "Figure 4-91 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog"
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance, and click OK. The JDeveloper composite.xml page appears, as shown in Figure 4-92.
Figure 4-92 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-92 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
WriteFilein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select ScalableDOMOut, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Input variable field is populated with the default variable name. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELScalableDOM.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-93.
Figure 4-93 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel Page
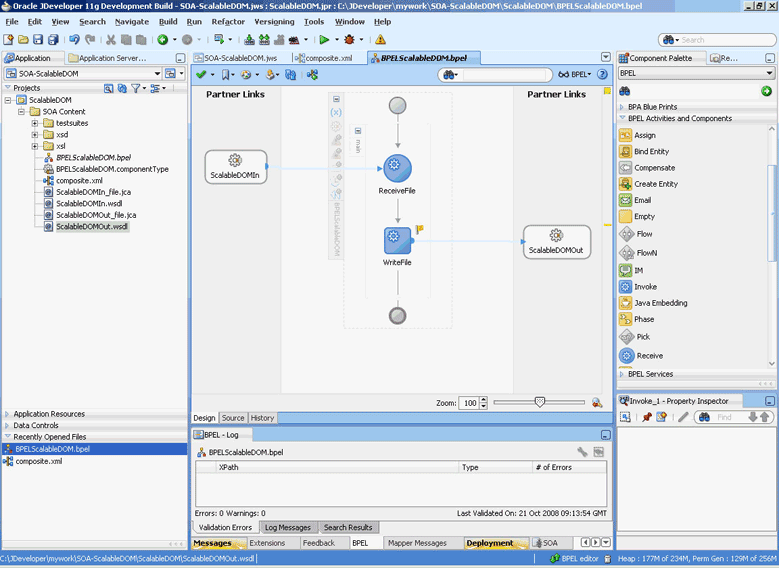
Description of "Figure 4-93 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel Page"
-
Drag and drop an Assign activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the Assign activity. The Assign dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
AssignPayloadin the Name field. -
Click the Copy Operation tab. The Assign dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-94.
Figure 4-94 The Assign Dialog - Copy Operation Tab
Description of "Figure 4-94 The Assign Dialog - Copy Operation Tab"
-
Select Copy Operation. The Create Copy Operation dialog is displayed.
-
Expand the variables in the From and To panes, as shown in Figure 4-95.
Figure 4-95 The Create Copy Operation Dialog
Description of "Figure 4-95 The Create Copy Operation Dialog"
-
Click OK. The Assign dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-96.
-
Click OK, the JDeveloper BPELScalableDOM.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-97.
Figure 4-97 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-97 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel"
-
Click File, Save All.
4.5.4.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.4.7 Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the
address-csv-large.txtfile to the input directory and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created. -
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow. Additionally, click an activity to view the details of an activity.
4.5.5 Oracle File Adapter ChunkedRead
This is an Oracle File Adapter feature that uses an invoke activity within a while loop to process the target file. This feature enables you to process arbitrarily large files.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.5.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.5.4, "Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.5.7, "Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.5.1 Prerequisites
To perform the Oracle File Adapter ChunkRead, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-106FileAdapterChunkedRead sample:
-
artifacts/schemas/address-csv.xsd -
artifacts/schemas/address-fixedLength.xsd -
artifacts/xsl/addr1Toaddr2.xsl -
artifacts/input/address-csv.txt
You can obtain the Adapters-106FileAdapterChunkedRead sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and selecting the Adapters tab.
4.5.5.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
SOA-ChunkedReadin the Application Name field, and click Next. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
ChunkedReadin the Project Name field. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPELChunkedReadin the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template box. -
Click OK. The SOA-ChunkedRead application and the ChunkedRead project appears in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-98.
Figure 4-98 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
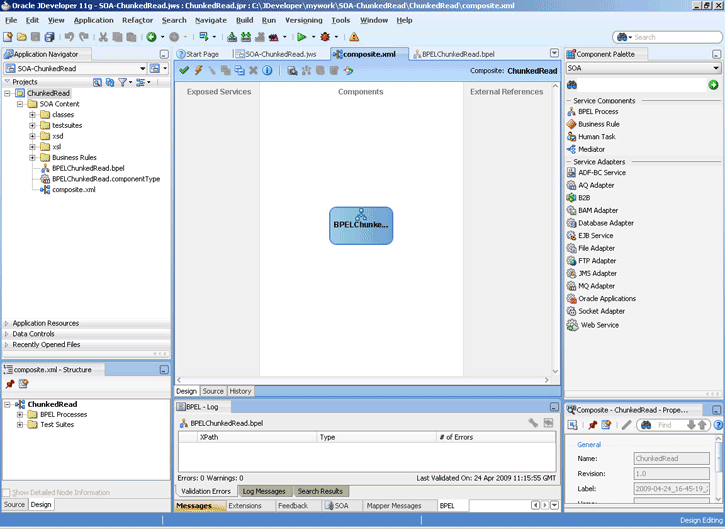
Description of "Figure 4-98 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Copy the address-csv.xsd and address-fixedLength.xsd files to the xsd directory in your project (see Section 4.5.5.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of these files).
-
Copy addr1Toaddr2.xsl to the xsl directory of your project (see Section 4.5.5.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of these files).
4.5.5.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read the file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
FileInNoPayloadInin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File, check Do Not Read File Content box, and then click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory. Check Process Files Recursively.
-
Click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.txtin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, click Next. The File Polling page is displayed. -
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-99.
Figure 4-99 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
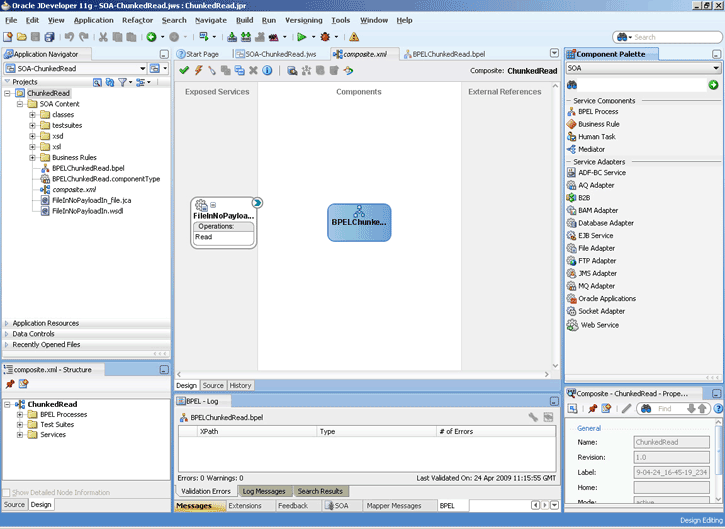
Description of "Figure 4-99 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.5.4 Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle File Adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
ReadAddressChunkin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Synchronous Read File, enter
ChunkedReadin the Operation Name field, and then click Next. The File Directories page is displayed. -
Enter the physical path for the output directory and select Delete Files After Successful Retrieval.
-
Click Next. The File Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
dummy.txtin the File Name field. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-csv.xsd, and Root-Element.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the
address-csv.xsdfile. -
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and
composite.xmlappears, as shown in Figure 4-100.Figure 4-100 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
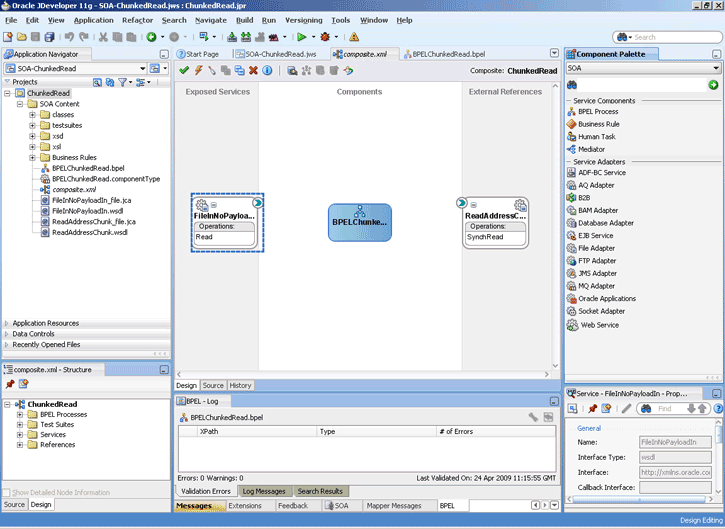
Description of "Figure 4-100 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Manually edit the metadata to incorporate the chunked read feature.
Open
ReadAddressChunk_file.jcafile and modify the metadata as shown below:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <adapter-config name="ReadAddressChunk" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="ChunkedRead_ptt" operation="ChunkedRead"> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.ChunkedInteractionSpec"> <property name="PhysicalDirectory" value="/tmp/chunked/in"/> <property name="FileName" value="dummy.txt"/> <property name="ChunkSize" value="1"/> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config> -
Click File, Save All.
Add Another Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
AppendChunkin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Write File, enter
Writein the Operation Name field, and then click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed. -
Enter the physical path for the output directory, enter
dummy.txtin the File Naming Convention (po_%SEQ%.txt) and select Append to Existing File. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-fixedLength.xsd, and Root-Element.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the
address-fixedLength.xsdfile. -
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-101.
Figure 4-101 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
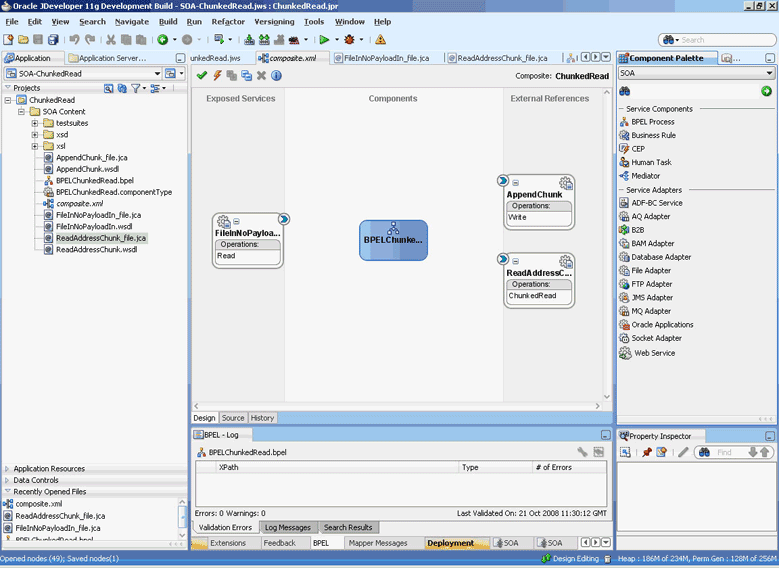
Description of "Figure 4-101 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.5.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, two Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the FileInNoPayloadIn in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the ReadAddressChunk in the External References area and also to the green triangle in the AppendChunk in the External References area.
The JDeveloper
composite.xmlappears, as shown in Figure 4-102.Figure 4-102 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
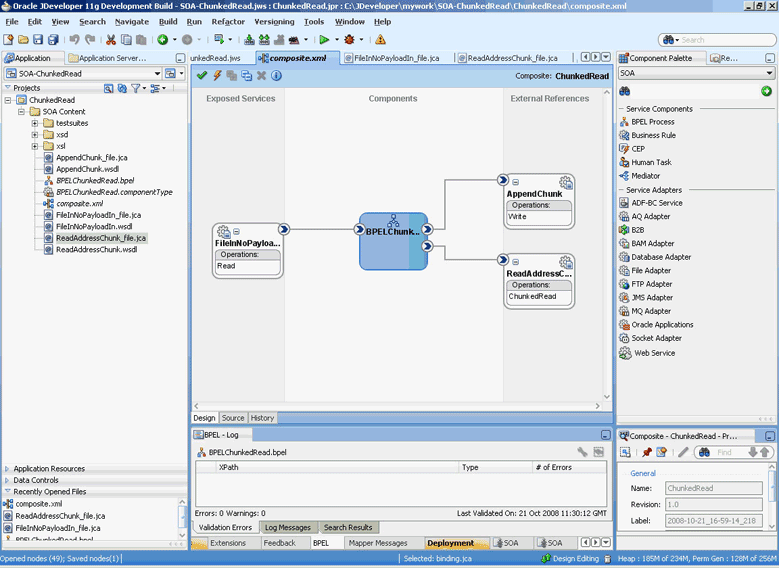
Description of "Figure 4-102 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELChunkedRead. The BPELChunkedRead.bpel page is displayed.
-
Click the Variables... icon represented by (x). The Variables dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Create the following variables, as shown in Figure 4-103. You will use these variables later:
<variable name="dir" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="file" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="outIsEOF" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="outLineNumber" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="outColumnNumber" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="returnIsEOF" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="returnLineNumber" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="returnColumnNumber" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="returnIsMessageRejected" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="returnRejectionReason" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="returnNoDataFound" type="xsd:string"/>Note:
All variables are Simple Types of type xsd:string. -
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
ReceiveFileDetailsin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select FileInNoPayloadIn, and click OK.
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance.
-
Click the Properties tab. The properties and the corresponding value column is displayed.
-
Select jca.file.Directory property. Double-click in the corresponding value column. The Adapter Property value dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Browse Variables icon. The Variable XPath Builder dialog is displayed.
-
Expand Variables, select dir, and then click OK. The value of the
jca.file.Directoryis set todir. -
Repeat the same for
jca.file.FileNameproperty and set the value to file. The Receive dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-104. -
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELChunkedRead.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-105
Figure 4-105 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-105 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Assign activity from the Component Palette after the Receive activity in the design area.
-
Double-click the Assign activity. The Assign dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
AssignChunkedReadin the Name field. -
Click the Copy Operation tab. The Assign dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-94.
-
Select Copy Operation. The Create Copy Operation dialog is displayed.
-
Set the default values for the headers, as shown in Figure 4-106.
-
Click OK, the JDeveloper BPELChunkedRead.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-107.
Figure 4-107 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-107 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity below the Assign Activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
InvokeReadAddressin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select ReadAddressChunk, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name. The Invoke dialog is displayed with input variable populated.
-
Repeat the same to select the output variable. The Invoke dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-108.
-
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELChunkedRead.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-109.
Figure 4-109 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-109 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel"
-
Click the Source tab for the BPELChunkedRead.bpel page, and add the following properties for the invoke activity that you just created:
<bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.Directory" variable="dir"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.FileName" variable="file"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.LineNumber" ="outLineNumber"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.ColumnNumber" variable="outColumnNumber"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.IsEOF" variable="outIsEOF"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.LineNumber" variable="returnLineNumber"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.ColumnNumber" variable="returnColumnNumber"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.IsEOF" variable="returnIsEOF"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.IsMessageRejected" variable="returnIsMessageRejected"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.RejectionReason" variable="returnRejectionReason"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.NoDataFound" variable="returnNoDataFound"/>
The invoke activity appears as follows:
<invoke name="InvokeReadAddress" inputVariable="InvokeReadAddress_SynchRead_InputVariable" outputVariable="InvokeReadAddress_SynchRead_OutputVariable" partnerLink="ReadAddressChunk" portType="ns3:SynchRead_ptt" operation="SynchRead"> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.Directory" variable="dir"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.FileName" variable="file"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.LineNumber" variable="outLineNumber"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.ColumnNumber" variable="outColumnNumber"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.IsEOF" variable="outIsEOF"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.LineNumber" variable="returnLineNumber"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.ColumnNumber" variable="returnColumnNumber"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.IsEOF" variable="returnIsEOF"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.IsMessageRejected" variable="returnIsMessageRejected"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.RejectionReason" variable="returnRejectionReason"/> <bpelx:outputProperty name="jca.file.NoDataFound" variable="returnNoDataFound"/> </invoke>
-
Add an assign activity called
CopyHeaders, as given in Add an Assign Activity, to copy the return parameters from the invoke activity. The Assign dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-110. -
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELChunkedRead.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-111.
Figure 4-111 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel
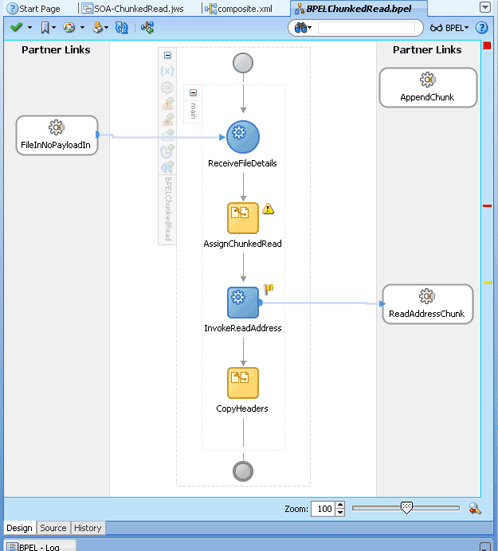
Description of "Figure 4-111 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel"
-
Drag and drop a Switch activity below the CopyHeaders Assign activity.
-
Double-click <case> in the Switch activity. The Switch Case dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
DATA FOUNDin the Name field and select the returnNoDataFound expression in the Expression box. The Switch Case dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-112. -
Drag and drop an Invoke activity in the <Case DATA FOUND> for Switch Activity.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
InvokeAppendin the Name field. -
Select AppendChunk in the Partner Link field.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name. The Invoke dialog is displayed with input variable populated.
-
Click the Properties tab and select file variable, as shown in Figure 4-113.
-
Click OK.
-
Drag and drop a Transform activity in the <case DATA FOUND> section just before the InvokeAppend activity.
-
Double-click the Transform activity.
-
Enter
TransformPayloadin the Name field. -
Click the Transformation tab.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Source Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select InvokeReadAddress_SyncRead_InputVariable, and click OK.
-
Select InvokeAppend_Write_InputVariable from the Target Variable list.
-
Click Browse at the end of the Mapper File field, and select the addr1Toaddr2.xsl file.
-
Click OK.
-
Drag and drop an Empty activity in the <otherwise> section in the Switch activity. The BPELChunkedRead.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-114.
Figure 4-114 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel
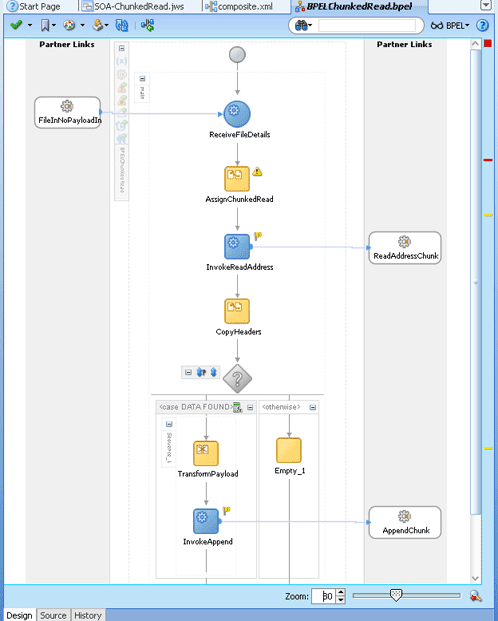
Description of "Figure 4-114 The JDeveloper - BPELChunkedRead.bpel"
-
Click File, Save All.
4.5.5.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.5.7 Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the
address-csv.txtfile to the input directory (see Section 4.5.5.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file) and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created. -
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow. Additionally, click an activity to view the details of an activity.
4.5.6 Oracle File Adapter Read File As Attachments
This is an Oracle File Adapter feature to opaquely copy or move large amount of data, from a source directory on your file system to a destination directory, as attachments. For example, you can transfer large MS Word documents, images, and PDFs without processing their content within the composite application. The read file as attachment feature is available only when the Read File option is chosen.
This use case demonstrates the ability of the Oracle File Adapter to process a large *.doc file as an attachment. This feature of reading files as attachments is very similar to Opaque translation. However, attachments can be of the order of gigabytes depending on database limitations.
-
Section 4.5.6.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.6.4, "Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.6.7, "Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.6.1 Prerequisites
To perform Oracle File Adapter read file as attachments, you require a large MS Word document (*.doc file).
4.5.6.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
AttachmentAppin the Application Name field, and click Next. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
Attachmentin the Project Name field. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPELAttachmentin the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template list. -
Click OK. The
AttachmentAppapplication and theAttachmentproject appear in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-115.Figure 4-115 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-115 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.6.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read a large file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
AttachmentInin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File as the Operation Type and select Read File As Attachment, as shown in Figure 4-116, and then click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
Note:
You must ignore Character Set, Encoding, and Content Type fields. These fields must be populated with values only if you are using third-party applications that must read this attachment. The attachment in this use case is finally consumed by an outbound Oracle File Adapter, hence these values are not required.Figure 4-116 The Adapter Configuration Wizard Operation Page
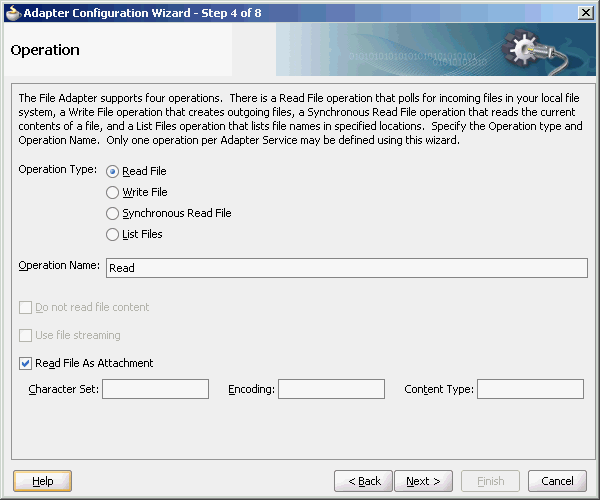
Description of "Figure 4-116 The Adapter Configuration Wizard Operation Page"
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory, as shown in Figure 4-55 and click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.docin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, as shown in Figure 4-56. -
Click Next. The File Polling page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-117.
Figure 4-117 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
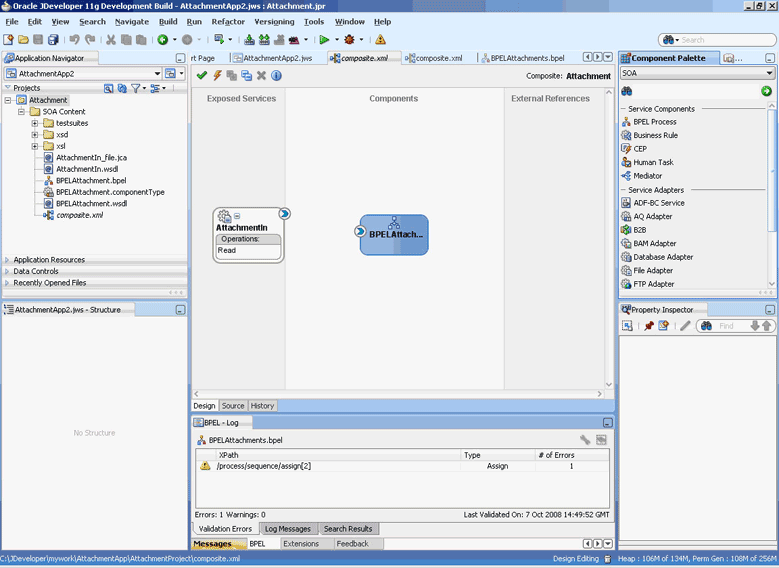
Description of "Figure 4-117 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.6.4 Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle File Adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
AttachmentOutin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Write File, and click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the output directory and enter
attachment_%SEQ%.docin the File Naming Convention(po_%SEQ%.txt) field, as shown in Figure 4-60. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project WSDL Files, AttachmentIn.wsdl, Inline Schemas, and attachmentElement, as shown in Figure 4-118.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with AttachmentIn.wsdl.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-119.
Figure 4-119 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
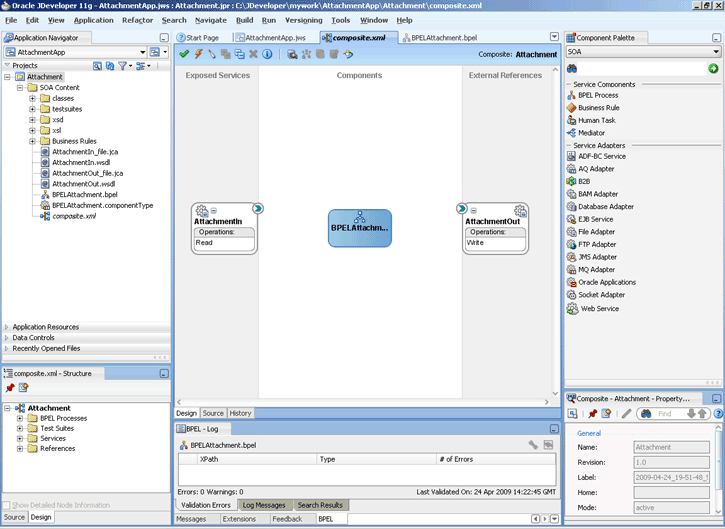
Description of "Figure 4-119 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.6.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the AttachmentIn in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the AttachmentOut in the External References area.
The JDeveloper composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-120.
Figure 4-120 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
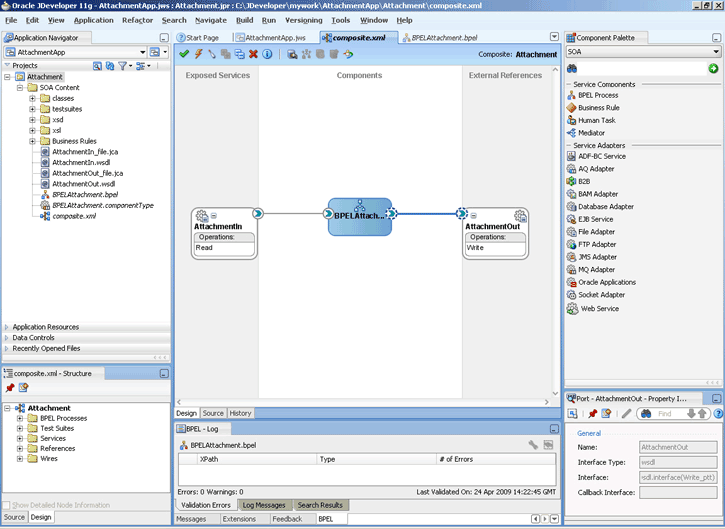
Description of "Figure 4-120 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELAttachment. The BPELAttachment.bpel page is displayed.
-
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
ReceiveInputin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select AttachmentIn, as shown in Figure 4-121 and click OK.
Figure 4-121 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog
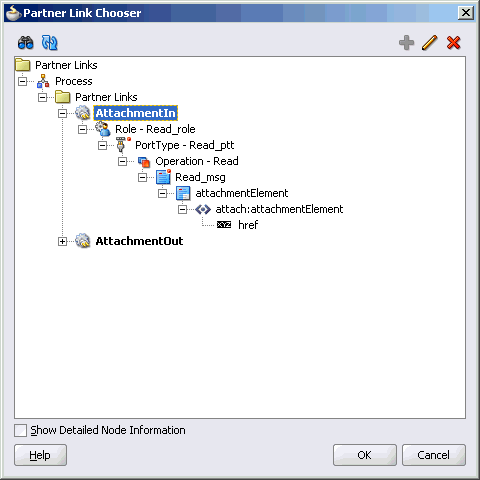
Description of "Figure 4-121 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog"
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog, as shown in Figure 4-122. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance, and click OK. The JDeveloper BPELAttachment.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-123.
Figure 4-123 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel
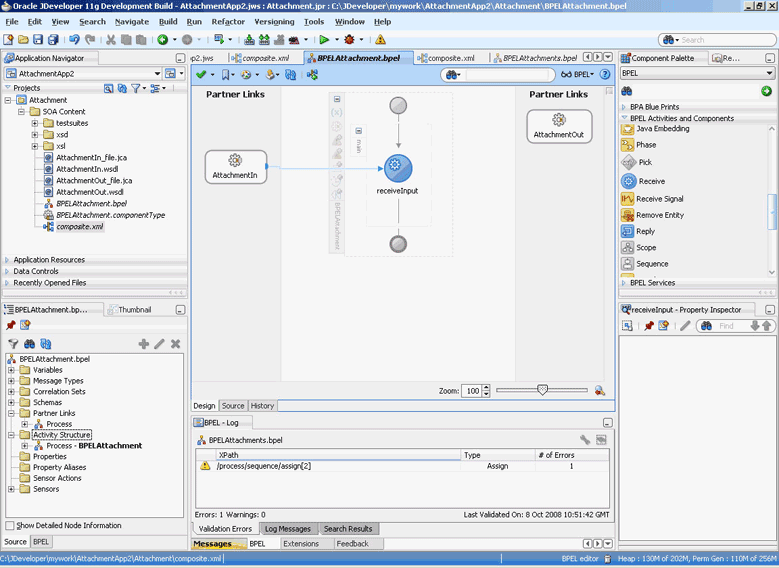
Description of "Figure 4-123 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
Write_Attachmentin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select AttachmentOut, as shown in Figure 4-124, and click OK.
Figure 4-124 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog
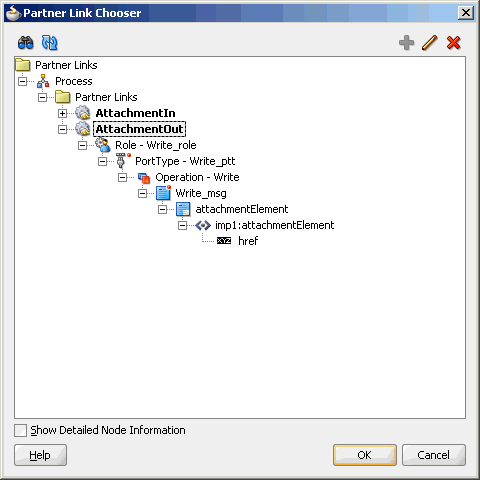
Description of "Figure 4-124 The Partner Link Chooser Dialog"
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name. The Invoke dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-125.
-
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELAttachment.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-126.
Figure 4-126 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel
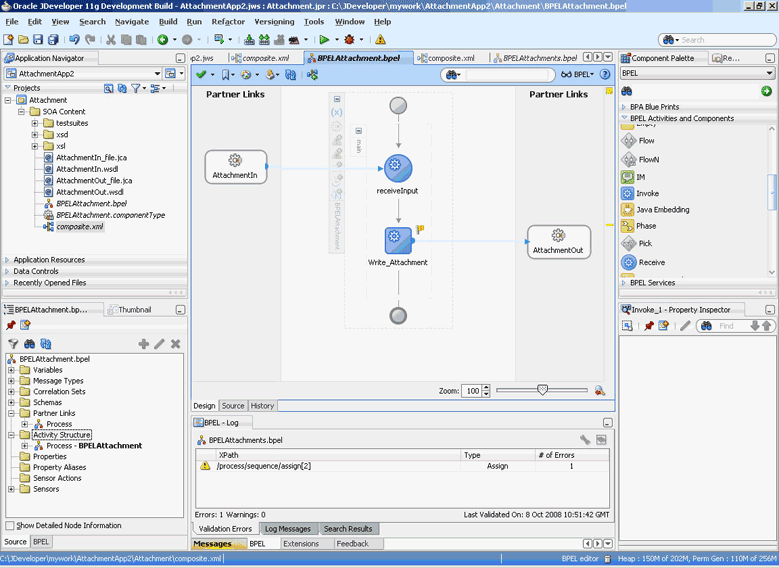
Description of "Figure 4-126 The JDeveloper - BPELXMLDebatching.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Assign activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the Assign activity. The Assign dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
AssignReferencein the Name field. -
Click the Copy Operation tab. The Assign dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-127.
Figure 4-127 The Assign Dialog - Copy Operation Tab
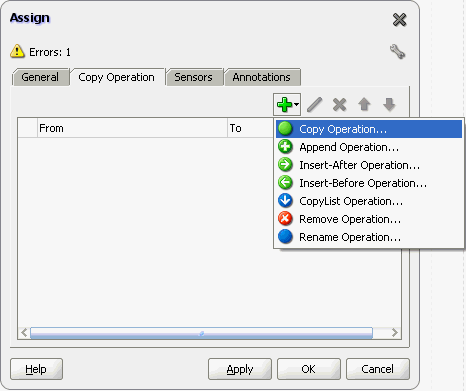
Description of "Figure 4-127 The Assign Dialog - Copy Operation Tab"
-
Select Copy Operation. The Create Copy Operation dialog is displayed.
-
Expand the variables in the From and To panes, as shown in Figure 4-128.
Figure 4-128 The Create Copy Operation Dialog
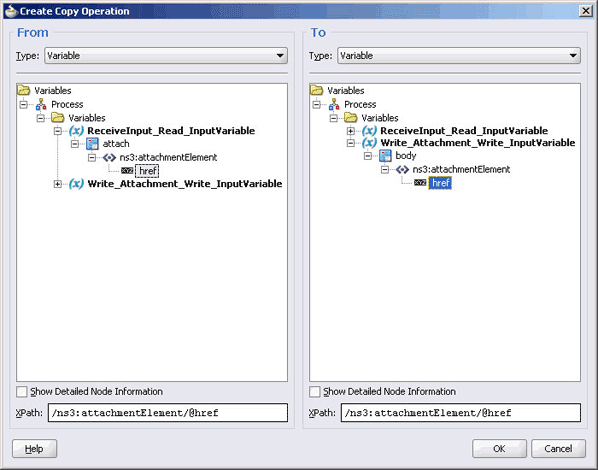
Description of "Figure 4-128 The Create Copy Operation Dialog"
Note:
In the case of variables defined by reference to an element, both the source and the target must be the same element. -
Click OK. The Assign dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-129.
-
Click OK, the JDeveloper BPELAttachment.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-130.
Figure 4-130 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-130 The JDeveloper - BPELScalableDOM.bpel"
-
Click File, Save All.
4.5.6.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.6.7 Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using the Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the
attachment.docfile to the input directory (see Section 4.5.6.1, "Prerequisites" for details) and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created. -
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow. Additionally, click an activity to view the details of an activity.
4.5.7 Oracle File Adapter File Listing
This is an Oracle File Adapter feature that lets you use an invoke activity to retrieve a list of files from a target directory. This list of files is returned as an XML document and contains information such as file name, directory name, file size, and last modified time.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.7.3, "Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.7.6, "Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.7.1 Prerequisites
To perform Oracle File Adapter Listing, you require *.txt files. You must create and save the *.txt files in the target directory.
4.5.7.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
FileListingAppin the Application Name field, and click Next. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
FileListingin the Project Name field. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPELFileListingin the Name field, select One Way BPEL Process from the Template box. -
Click OK. The FileListingApp application and the FileListing project appears in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-131.
Figure 4-131 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-131 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.7.3 Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle File Adapter service to list the file from a target directory:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
ListFilesin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select List Files, enter
FileListingin the Operation Name field, and then click Next. The File Directories page is displayed. -
Enter the physical path for the input directory, as shown in Figure 4-55.
-
Click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.txtin the Include Files with Name Pattern field. -
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-132.
Figure 4-132 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-132 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
4.5.7.4 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the two components that you have created: BPEL process, and the Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in ListFiles in the External References area.
The JDeveloper Composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-133.
Figure 4-133 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
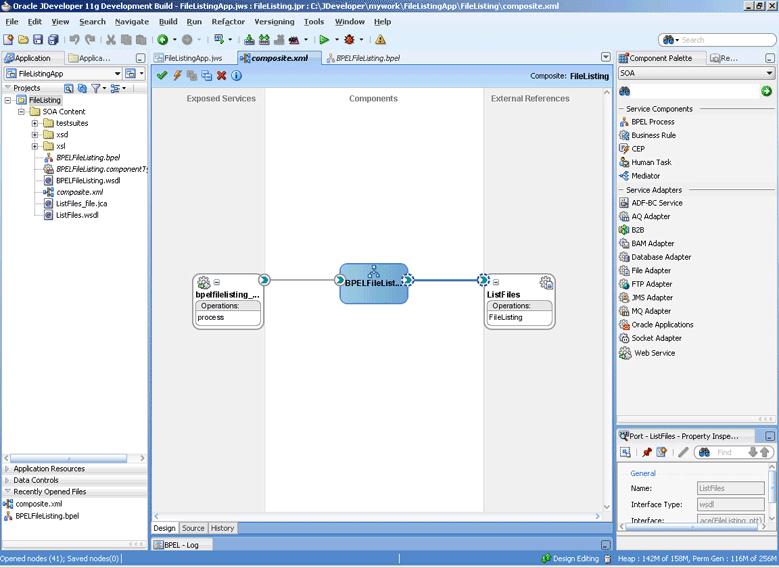
Description of "Figure 4-133 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELFileListing. The BPELFileListing.bpel page is displayed.
-
Click the Variables... icon represented by (x). The Variables dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Create a variable,
MyDirof typexsd:string, as shown in Figure 4-134. You will use these variables later. -
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELFileListing.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-135
Figure 4-135 The JDeveloper - BPELFileListing.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-135 The JDeveloper - BPELFileListing.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity below the receive Activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
InvokeListFilesin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select ListFiles, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name. The Invoke dialog is displayed with input variable populated.
-
Repeat the same to select the output variable. The Invoke dialog is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-136.
-
Click the Properties tab. The properties and the corresponding value column is displayed.
-
Select jca.file.Directory property. Double-click in the corresponding value column. The Adapter Property Value dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Browse Variables icon. The Variable XPath Builder dialog is displayed.
-
Expand Variables, select MyDir, and then click OK. The value of the
jca.file.Directoryis set toMydir. -
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELFileListing.bpel page appears, as shown in Figure 4-137.
Figure 4-137 The JDeveloper - BPELFileListing.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-137 The JDeveloper - BPELFileListing.bpel"
-
Drag and drop an Assign activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive activities and the Invoke activity in the design area.
-
Double-click the Assign activity. The Assign dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
AssignDirNamein the Name field. -
Click the Copy Operation tab. The Assign dialog is displayed.
-
Select Copy Operation. The Create Copy Operation dialog is displayed.
-
Set the values for the headers, as shown in Figure 4-138.
-
Click OK, the JDeveloper BPELFileListing.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-139.
Figure 4-139 The JDeveloper - BPELFileListing.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-139 The JDeveloper - BPELFileListing.bpel"
-
Click File, Save All.
4.5.7.5 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.7.6 Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the
*.txtfiles to the input directory (see Section 4.5.7.1, "Prerequisites" for details) and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created. -
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow. Additionally, click an activity to view the details of an activity.
4.5.8 Oracle File Adapter Complex Structure
This use case demonstrates the ability of the Oracle File Adapter to process native data defined in a custom format. In this sample, the custom format represents an invoice defined in invoice-nxsd.xsd. The Oracle File Adapter processes the invoice.txt file and publishes this to the ComplexStructure BPEL process. This is then transformed to a PurchaseOrder and written out as an xml file.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.8.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.8.4, "Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.8.7, "Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.8.1 Prerequisites
To perform the complex structure business process, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-104FileAdapterComplexStructure sample:
-
artifacts/schemas/invoice-nxsd.xsd -
artifacts/schemas/po.xsd -
artifacts/xsl/InvToPo.xsl -
artifacts/input/invoice.txt
You can obtain the Adapters-104FileAdapterComplexStructure sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and selecting the Adapters tab.
4.5.8.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
SOA-ComplexStructurein the Application Name field, and click Next. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
ComplexStructurein the Project Name field. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPEComplexStructurein the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template box. -
Click OK. The SOA-ComplexStructure application and the ComplexStructure project appears in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-140.
Figure 4-140 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-140 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Copy the invoice-nxsd.xsd and po.xsd files to the schema directory in your project (see Section 4.5.8.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of these files).
-
Copy InvToPo.xsl to the xsl directory of your project (see Section 4.5.8.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file).
4.5.8.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read the file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
Complex Structure Inin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File, and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory and click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.txtin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, click Next. The File Polling page is displayed. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, invoice-nxsd.xsd, and invoice.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the invoice-nxsd.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-141.
Figure 4-141 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-141 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.8.4 Creating the Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle File Adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop the Oracle File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
ComplexStructureOutin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Write File, and click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the output directory and enter
invoice_%SEQ%.txtin the File Naming Convention(po_%SEQ%.txt) field. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, po.xsd, and po.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the po.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-142.
Figure 4-142 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
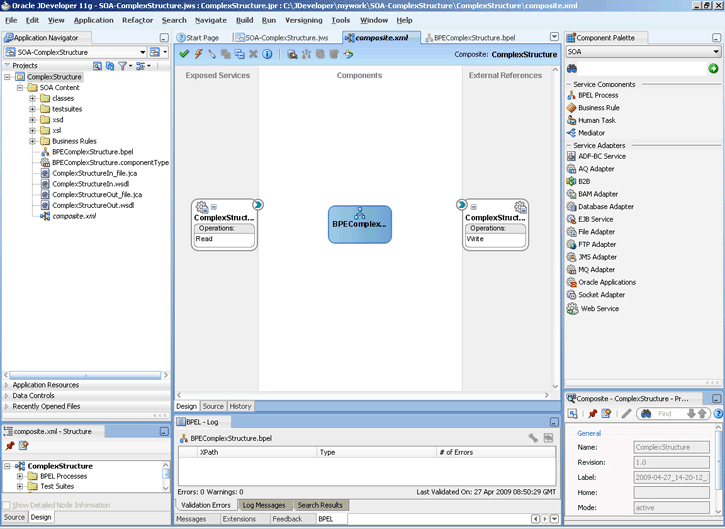
Description of "Figure 4-142 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.8.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the ComplexStructureIn service in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the ComplexStructureOut reference in the External References area.
The JDeveloper Composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-143.
Figure 4-143 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-143 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELComplexStructure. The BPELComplexStructure.bpel page is displayed.
-
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
ReceiveInvoicein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select ComplexStructureIn, and click OK.
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance, and click OK. The JDeveloper BPELComplexStructure.bpel page appears.
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
InvokeWritein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select ComplexStructureOut, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
InvokeWrite_Write_OutputVariablein the variable name field and click OK. The Invoke dialog is displayed. -
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELComplexStructure.bpel page appears.
-
Drag and drop a Transform activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the Transform activity. The Transform dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
TransformPayloadin the Name field. -
Click the Transformation tab. The Transform dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Source Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select ReceiveInvoice_Read_InputVariable in the Source Variable box, and select body in the Source Part box, and then click OK. The Transform dialog is displayed with the Source and Part selected.
-
Select InvokeWrite_Write_OutputVariable in the Target Variable list, select body in the Target Part.
-
Click the Browse Mapping icon at the end of the Mapper File field and select InvToPo.xsl file from the xsl directory in your project.
-
Click OK.
-
Click File, Save All. The BPELComplexStructure.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-144.
Figure 4-144 The JDeveloper - BPELComplexStructure.bpel
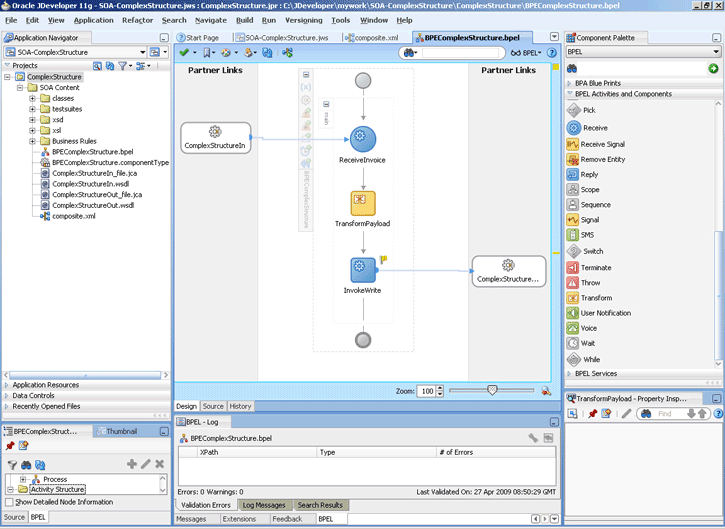
Description of "Figure 4-144 The JDeveloper - BPELComplexStructure.bpel"
4.5.8.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.8.7 Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the
invoice.txtfile to the input directory (see Section 4.5.8.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file) and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created. -
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow.
-
Click ReceiveInvoice to display the activity details
4.5.9 Oracle FTP Adapter Debatching
This is an Oracle FTP Adapter feature that debatches a large XML document into smaller individual XML fragments. This use case demonstrates how the debatching business process sample uses the Oracle FTP Adapter to process a file containing a batch of business records such as one or more invoice and purchase orders. The PurchaseOrders (POs) are then debatched and written to separate output files.
This use case includes the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.9.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.9.4, "Creating the Outbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.9.7, "Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.9.1 Prerequisites
To perform the complex structure business process, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-101FTPAdapterDebatching sample:
-
artifacts/schemas/container.xsd -
artifacts/schemas/po.xsd -
artifacts/xsl/InvToPo.xsl -
artifacts/xsl/PoToPo.xsl -
artifacts/input/container.txt
You can obtain the Adapters-101FTPAdapterDebatching sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and selecting the Adapters tab.
4.5.9.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
SOA-FTPDebatchingin the Application Name field, and click OK. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
FTPDebatchingin the Project Name. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPELFTPDebatchingin the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template box. -
Click OK. The SOA-FTPDebatching application and the FTPDebatching project appears in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-145.
Figure 4-145 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-145 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Copy the
container.xsdandpo.xsdfiles to thexsddirectory of your project (see Section 4.5.9.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of these files). -
Copy the
InvToPo.xslandPoToPo.xslfiles to the xsl directory of your project (see Section 4.5.9.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of these files).
4.5.9.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle FTP Adapter service to read the file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop the Oracle FTP Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
FTPDebatchingInin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The FTP Server Connection page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-146.
Note:
Ensure that you have configured the jndi-name in the deployment descriptor for Oracle FTP Adapter before deploying this application.Figure 4-146 The Adapter Configuration Wizard FTP Server Connection Page

Description of "Figure 4-146 The Adapter Configuration Wizard FTP Server Connection Page"
-
Click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Get File, as shown in Figure 4-147, and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
Figure 4-147 The Adapter Configuration Wizard Operation Page

Description of "Figure 4-147 The Adapter Configuration Wizard Operation Page"
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory, and click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.txtin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, select Files Contain Multiple Messages check box, specify1as the value for Publish Messages in Batches Of box. -
Click Next. The File Polling page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, container.xsd, and container.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the container.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-148.
Figure 4-148 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-148 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.9.4 Creating the Outbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle FTP Adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop the FTP Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
PurchaseOrderOutin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The FTP Server Connection page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Put File, and click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the output directory and enter
po_%SEQ%.txtin the File Naming Convention(po_%SEQ%.txt) field. -
Select Number of Messages Equals option, if not already selected. The default value is
1. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, po.xsd, and po.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the po.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-149.
Figure 4-149 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-149 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.9.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the FTPDebatchingIn service in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the PurchaseOrderOut reference in the External References area.
The JDeveloper Composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-150.
Figure 4-150 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
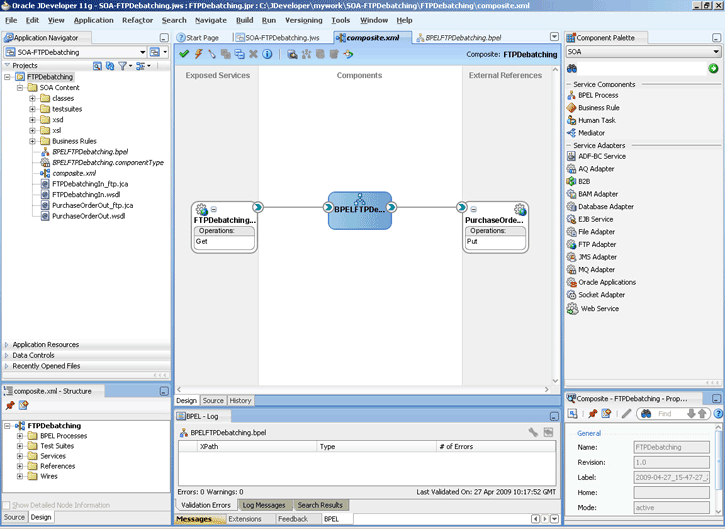
Description of "Figure 4-150 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELFTPDebatching. The
BPELFTPDebatching.bpelpage is displayed. -
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
Receivein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select FTPDebatchingIn, and click OK.
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance, and click OK. The JDeveloper
BPELFTPDebatching.bpelpage appears with the Receive activity added.
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
Writein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select PurchaseOrderOut, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Receive dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
Write_Put_OutputVariablein the Variable field and click OK. The Invoke dialog is displayed. -
Click OK. The JDeveloper
BPELFTPDebatching.bpelpage appears with the invoke activity added.
-
Drag and drop a Switch activity from the Component Palette in between the Receive and Invoke activities in the design area.
-
Expand the Switch activity. This displays a screen to enter the values for <case> and <otherwise>.
-
In the
<case>section, click the View Condition Expression icon, as shown in Figure 4-151. The Condition Expression pop-up window is displayed. -
Click the Xpath Expression Builder icon in the pop-up window. The Expression Builder dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
starts-with(local-name(ora:getNodes('receive_Get_InputVariable','body','/ns3:container/child::*[position()=1]')),'invoice')as the expression, as shown in Figure 4-152, and click OK. The screen returns to the Condition Expression pop-up window.Figure 4-152 The Expression Builder Dialog
Description of "Figure 4-152 The Expression Builder Dialog"
-
Add two transformation activities, one each for <case> and <otherwise> sections.
-
Drag and drop a Transform activity in the <case> section.
-
Double-click the Transform activity.
-
Enter
InvToPoin the Name field. -
Click the Transformation tab.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Source Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Accept the defaults and click OK.
-
Select Write_Put_OutputVariable in the Target Variable list.
-
Click the Browse Mappings icon at the end of the Mapper File field, and select the InvToPo.xsl file.
-
Click OK.
-
Repeat the same process for the second transformation. Select
PoToPo.xslas the Mapper File for this transform activity.
The BPELFTPDebatching.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-153.
Figure 4-153 The BPELFTPDebatching.bpel Page
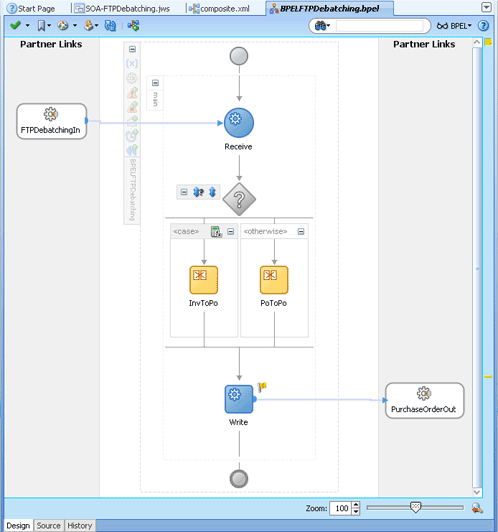
Description of "Figure 4-153 The BPELFTPDebatching.bpel Page"
-
-
Click File, Save All.
4.5.9.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.9.7 Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the
container.txtfile to the input directory (see Section 4.5.9.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file) and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created. -
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow. Additionally, click an activity (such as invoke, receive) to view the details of an activity.
4.5.10 Oracle FTP Adapter Dynamic Synchronous Read
This use case demonstrates the ability of the Oracle FTP Adapter to perform a mid-process synchronous read operation using an Invoke activity. This use case illustrates the following adapter functionality:
-
Oracle File Adapter (Read Operation)
-
Oracle FTP Adapter (Synchronous Read operation)
Ability to specify the file name to be read during run-time
-
Oracle File Adapter (Write Operation)
The process is initiated by the presence of a trigger file appearing in a local directory monitored by the inbound Oracle File Adapter. The trigger file contains the name of the file to be read by the synchronous read operation. This file name is passed through headers to the adapter. This can be done using the Properties tab for the Invoke activity. This synchronous read file operation is performed against a remote directory on a FTP server. The result of the read is then transformed and written out to a local directory through the outbound Oracle File Adapter. This section includes the following topics:
-
Section 4.5.10.3, "Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.10.4, "Creating the Outbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service"
-
Section 4.5.10.7, "Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console"
4.5.10.1 Prerequisites
To perform FTP Dynamic Synchoronous Read, you require the following files from the artifacts.zip file contained in the Adapters-102FTPAdapterDynamicSynchronousRead sample:
-
artifacts/schemas/address-csv.xsd -
artifacts/schemas/address-fixedLength.xsd -
artifacts/schemas/trigger.xsd -
artifacts/xsl/addr1Toaddr2.xsl -
artifacts/input/address_csv.txt -
artifacts/input/trigger.trg
You can obtain the Adapters-102FTPAdapterDynamicSynchronousRead sample by accessing the Oracle SOA Sample Code site, and selecting the Adapters tab.
4.5.10.2 Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. To create an application and a project for the use case, perform the following:
-
In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. The Create Generic Application - Name your application page is displayed.
-
Enter
SOA-FTPDynamicSynchronousReadin the Application Name field, and click OK. The Create Generic Application - Name your project page is displayed. -
Enter
FTPDynamicSynchronousReadin the Project Name. -
In the Available list under the Project Technologies tab, double-click SOA to move it to the Selected list.
-
Click Next. The Configure SOA settings dialog appears.
-
Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
-
Enter
BPELDynamicSynchronousReadin the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template box. -
Click OK. The SOA-FTPDynamicSynchronousRead application and FTPDynamicSynchronousRead project appears in the design area, as shown in Figure 4-154.
Figure 4-154 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-154 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Copy the
address-csv.xsd,address-fixedLength.xsd,andtrigger.xsdfiles to the xsd directory of your project (see Section 4.5.10.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of these files). -
Copy the
addr1Toaddr2.xslfile to the xsl directory of your project (see Section 4.5.10.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file).
4.5.10.3 Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read the file from a local directory:
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the Exposed Services swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
ReadTriggerin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Read File, and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the input directory and click Next. The File Filtering page is displayed.
-
Enter
*.trgin the Include Files With Name Pattern field, click Next. The File Polling page is displayed. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, trigger.xsd, and trigger.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the trigger.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The inbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-155.
Figure 4-155 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
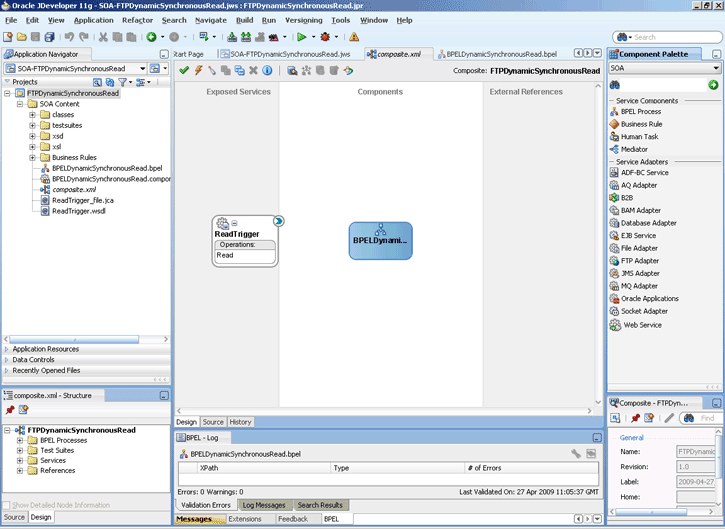
Description of "Figure 4-155 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.10.4 Creating the Outbound Oracle FTP Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle FTP Adapter service to write the file from a local directory to the FTP server:
-
Drag and drop FTP Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
SyncReadin the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The FTP Server Connection page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Synchronous Get File, and click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.
-
Enter the physical path for the output directory.
-
Click Next. The File Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
dummy.txtin the File Name field and click Next. The Messages page is displayed. -
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-csv.xsd, and Root-Element.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the address-csv.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle FTP Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-156.
Figure 4-156 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
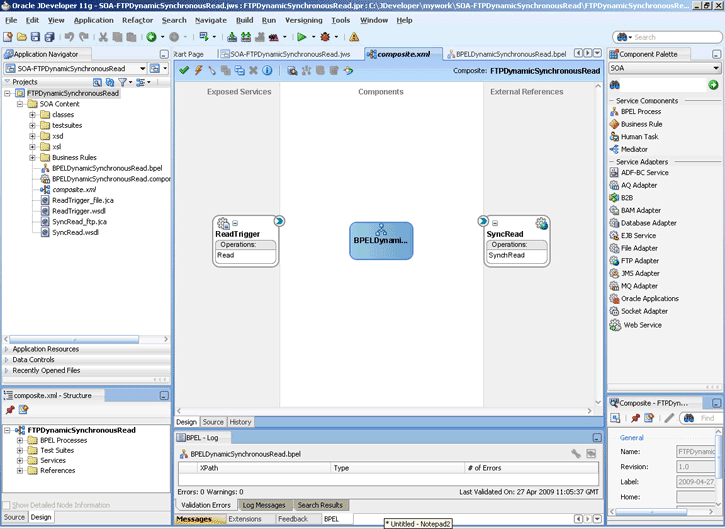
Description of "Figure 4-156 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
Add An Outbound Oracle File Adapter Service
-
Drag and drop the Oracle File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter
WriteFilein the Service Name field. -
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Write File, enter
Writein the Operation Name field, and then click Next. The File Configuration page is displayed. -
Enter the physical path for the output directory, enter
address_%SEQ%.txtin the File Naming Convention (po_%SEQ%.txt). -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Click Browse For Schema File that appears at the end of the URL field. The Type Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Click Project Schema Files, address-fixedLength.xsd, and Root-Element.
-
Click OK. The URL field in the Messages page is populated with the address-fixedLength.xsd file.
-
Click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured and composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-157.
Figure 4-157 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-157 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
4.5.10.5 Wiring Services and Activities
You have to assemble or wire the four components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, BPEL process, two Outbound adapter references. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
-
Drag the small triangle in the ReadTrigger in the Exposed Services area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in the SyncRead in the External References area and to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in WriteFile.
The JDeveloper Composite.xml appears, as shown in Figure 4-158.
Figure 4-158 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml
Description of "Figure 4-158 The JDeveloper - Composite.xml"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Double-click BPELDynamicSynchronousRead. The BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel page is displayed.
-
Drag and drop a Receive activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Receive activity. The Receive dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
ReceiveTriggerin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select ReadTrigger, and click OK.
-
Click the Auto-Create Variable icon to the right of the Variable field in the Receive dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Check Create Instance, and click OK. The JDeveloper BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel page appears.
Create a Variable and add an Invoke Activity
-
Click the Variables... icon represented by (x). The Variables dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Create a variable called file of type xsd:string, as shown in Figure 4-159.
-
Click OK to return to BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel page.
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
Invoke_SyncReadin the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select SyncRead, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Input variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Repeat the same for the Output Variable field.
-
Click the Properties tab. The properties and the corresponding value column is displayed.
-
Select
jca.ftp.FileNameproperty. Double-click in the corresponding value column. The Adapter Property value dialog is displayed. -
Click the Browse variables icon. The Variable XPath Builder dialog is displayed.
-
Expand Variables, select file, and then click OK. The value of the
jca.ftp.FileNameis set tofile. -
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel page appears.
-
Drag and drop an Invoke activity from the Component Palette to the design area.
-
Double-click the Invoke activity. The Invoke dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
InvokeWritein the Name field. -
Click Browse Partner Links at the end of the Partner Link field. The Partner Link Chooser dialog is displayed.
-
Select WriteFile, and click OK.
-
Click the Automatically Create Input Variable icon to the right of the Input variable field in the Invoke dialog. The Create Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select the default variable name and click OK. The Variable field is populated with the default variable name.
-
Click OK. The JDeveloper BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel page appears, as shown in .
Figure 4-160 The JDeveloper - BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel Page
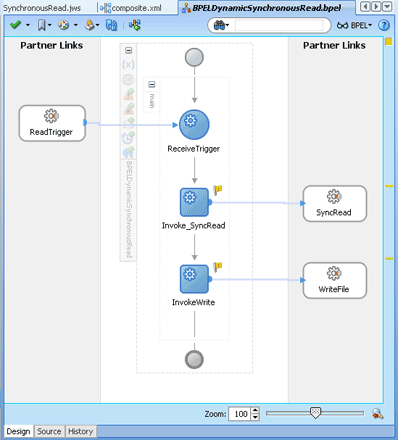
Description of "Figure 4-160 The JDeveloper - BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel Page"
-
Drag and drop an Assign activity from the Component Palette in between the ReceiveTrigger and Invoke_SyncRead activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the Assign activity. The Assign dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
AssignFileNamein the Name field. -
Click the Copy Operation tab. The Assign dialog is displayed.
-
Select Copy Operation. The Create Copy Operation dialog is displayed.
-
Create the copy operation between the trigger file name and the file variable, as shown in Figure 4-161.
Figure 4-161 The Create Copy Operation Dialog
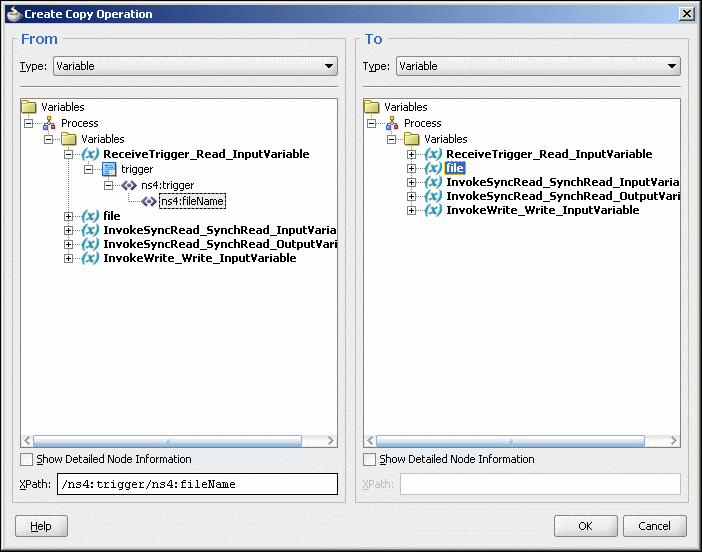
Description of "Figure 4-161 The Create Copy Operation Dialog"
-
Click OK in the Create Copy Operation dialog.
-
Click OK to return to the JDeveloper BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel page, as shown in Figure 4-162.
Figure 4-162 The JDeveloper - BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-162 The JDeveloper - BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel"
-
Click File, Save All.
-
Drag and drop a Transform activity from the Component Palette in between the Invoke_SyncRead and InvokeWrite activities in the design area.
-
Double-click the Transform activity. The Transform dialog is displayed.
-
Enter
TransformPayloadin the Name field. -
Click the Transformation tab. The Transform dialog is displayed.
-
Click the Create... icon. The Source Variable dialog is displayed.
-
Select InvokeSyncRead_SyncRead_OutputVariable in the Source Variable box, and select body in the Source Part box, and then click OK. The Transform dialog is displayed with the Source and Part selected.
-
Select InvokeWrite_Write_InputVariable in the Target Variable list, select body in the Target Part.
-
Click the Browse Mappings icon at the end of the Mapper File field and select
addr1Toaddr2.xslfile from the xsl directory in your project. -
Click OK.
-
Click File, Save All. The BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel page is displayed, as shown in Figure 4-163.
Figure 4-163 The JDeveloper - BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel
Description of "Figure 4-163 The JDeveloper - BPELDynamicSynchronousRead.bpel"
4.5.10.6 Deploying with JDeveloper
You must deploy the application profile for the SOA project and the application you created in the preceding steps. To deploy the application profile using JDeveloper, perform the following steps:
-
Create an application server connection. For more information, see Section 2.7, "Creating an Application Server Connection for Oracle JCA Adapters."
-
Deploy the application. For more information, see Section 2.8, "Deploying Oracle JCA Adapter Applications from JDeveloper."
4.5.10.7 Monitoring Using Fusion Middleware Control Console
You can monitor the deployed SOA composite using Fusion Middleware Control Console. Perform the following steps:
-
Navigate to
http://servername:portnumber/em. The composite you deployed appears in the application navigator. -
Copy the
address-csv.txtfile to the input directory (see Section 4.5.10.1, "Prerequisites" for the location of this file) and ensure it gets processed. Check the output directory to ensure that an output file has been created. -
Click the SOA composite that you deployed. The Dashboard is displayed.
Note your Instance ID in the Recent Instances area.
-
Click the Instances tab. The Instance IDs of the SOA composite are listed.
-
Click the Instance ID that you noted in Step 3. The Flow Trace page is displayed.
-
Click your BPEL process instance. The Audit Trail of the BPEL process instance is displayed.
-
Expand a payload node to view payload details.
-
Click the Flow tab to view the process flow.
-
Click ReceiveTrigger to display the activity details.
4.5.11 Copying, Moving, and Deleting Files
The Oracle File and FTP Adapters let you copy or move a file from one location to another, or delete a file from the target directory. Additionally, the Oracle FTP Adapter lets you move or copy files from a local file system to a remote file system and from a remote file system to a local file system. This feature is implemented as a interaction specification for outbound services. So, this feature can be accessed either by using a BPEL invoke activity or a Mediator routing rule.
At a high level, you must create an outbound service and configure this service with the source and target directories and file names.
The following use cases demonstrate the new functionality supported by Oracle File and FTP Adapters that allow you to copy, move, and delete files by using an outbound service:
-
Section 4.5.11.3, "Deleting a File from a Local File System Directory"
-
Section 4.5.11.8, "Moving a File from One FTP Server to another FTP Server"
4.5.11.1 Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to Another Local Directory
You can model only a part of this procedure by using the wizard because the corresponding Adapter Configuration Wizard is not available. You must complete the remaining procedure by manually configuring the generated JCA file.
You must perform the following steps to move a file from a local directory on the file system to another local directory:
-
Create an empty BPEL process.
-
Drag and drop File Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter a service name in the Service Name field.
-
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Select Define from operation and schema (specified later), and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Synchronous Read File, enter
FileMovein the Operation Name field, and then click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.Note:
You have selected Synchronous Read File as the operation because theWSDLfile that is generated as a result of this operation is similar to the one required for the file I/O operation. -
Enter a dummy physical path for the directory for incoming files, and then click Next. The File name page is displayed.
Note:
The dummy directory is not used. You must manually change the directory in a later step. -
Enter a dummy file name, and then click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
Note:
The dummy file name you enter is not used. You must manually change the file name in a later step. -
Select Native format translation is not required (Schema is opaque), and then click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in
FileMovein the External References area. The BPEL component is connected to the Oracle File Adapter outbound service. -
Create an invoke activity for the
FileMoveservice that you just created by selecting the default settings.The next step is to modify the generated
WSDLfile forMoveFileServiceservice and configure it with the new interaction specification for the move operation. -
Open the
FileMove_file.jcafile and modify the endpoint interaction, as shown in the following example.You must configure the JCA file with the source and target directory and file details. You can either hardcode the source and target directory and file details in the JCA file or use header variables to populate them. In this example, header variables are used.
<adapter-config name="FileMove" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="FileMove_ptt" operation="FileMove"> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileIoInteractionSpec"> <property name="SourcePhysicalDirectory" value="foo1"/> <property name="SourceFileName" value="bar1"/> <property name="TargetPhysicalDirectory" value="foo2"/> <property name="TargetFileName" value="bar2"/> <property name="Type" value="MOVE"/> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config>Note:
You have modified theclassNameattribute, and addedSourcePhysicalDirectory,SourceFileName,TargetPhysicalDirectory,TargetFileNameandType. Currently, the values for the source and target details are dummy. You must populate them at run-time. You can also hardcode them to specific directories or file names.The
Typeattributes decides the type of operation. Apart fromMOVE, the other acceptable values for theTypeattribute areCOPYandDELETE. -
Map the actual directory and file names to the source and target file parameters by performing the following procedure:
-
Create 4 string variables with appropriate names. You must populate these variables with the source and target directory details. The BPEL source view shows you this:
<variables> <variable name="InvokeMoveOperation_FileMove_InputVariable" messageType="ns1:Empty_msg"/> <variable name="InvokeMoveOperation_FileMove_OutputVariable" messageType="ns1:FileMove_msg"/> <variable name="sourceDirectory" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="sourceFileName" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="targetDirectory" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="targetFileName" type="xsd:string"/> </variables> -
Create an assign activity to assign values to
sourceDirectory,sourceFileName,targetDirectory, andtargetFileNamevariables. The assign operation appears in the BPEL source view as in the following example:<assign name="AssignFileDetails"> <copy> <from expression="'/home/alex'"/> <to variable="sourceDirectory"/> </copy> <copy> <from expression="'input.txt'"/> <to variable="sourceFileName"/> </copy> <copy> <from expression="'/home/alex'"/> <to variable="targetDirectory"/> </copy> <copy> <from expression="'output.txt'"/> <to variable="targetFileName"/> </copy> </assign>In the preceding example,
input.txtis moved from/home/alextooutput.txtin/home/alex.Note:
The source and target details are hardcoded in the preceding example. You can also provide these details as run-time parameters. -
Pass these parameters as headers to the invoke operation. The values in these variables override the parameters in the JCA file.
<invoke name="InvokeMoveOperation" inputVariable="InvokeMoveOperation_FileMove_InputVariable" outputVariable="InvokeMoveOperation_FileMove_OutputVariable" partnerLink="FileMove" portType="ns1:FileMove_ptt" operation="FileMove"> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.SourceDirectory" variable="sourceDirectory"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.SourceFileName" variable="sourceFileName"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.TargetDirectory" variable="targetDirectory"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.TargetFileName" variable="targetFileName"/> </invoke>
-
-
Finally, add an initial receive or pick activity.
You have completed moving a file from a local directory on the file system to another local directory.
4.5.11.2 Copying a File from a Local Directory on the File System to Another Local Directory
Perform the following procedure to copy a file from a local directory on the file system to another local directory:
-
Follow steps 1 through 12 of Section 4.5.11.1, "Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to Another Local Directory".
-
Change the value of the
TYPEattribute toCOPYinstead ofMOVEin the endpoint interaction, in Step 14 of Section 4.5.11.1, "Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to Another Local Directory" as shown in the following example:<adapter-config ...> <connection-factory .../> <endpoint-interaction ...> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileIoInteractionSpec"> <property .../> <property name="Type" value="COPY"/> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config>
4.5.11.3 Deleting a File from a Local File System Directory
To delete a file, you require TargetPhysicalDirectory and TargetFileName parameters.
Note:
You do not requireSourcePhysicalDirectory and SourceFileName to delete a file from a local file system directory.To delete a file, delete_me.txt, from /home/alex directory, you must perform the following:
-
Follow steps 1 through 12 in Section 4.5.11.1, "Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to Another Local Directory"
-
Change the value of the
TYPEattribute toDELETEin the endpoint interaction in Step 14 of Section 4.5.11.1, "Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to Another Local Directory", as shown in the following example:<adapter-config name="FileDelete" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="FileDelete_ptt" operation="FileDelete"> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileIoInteractionSpec"> <property name="TargetPhysicalDirectory" value="/home/alex"/> <property name="TargetFileName" value="delete_me.txt"/> <property name="Type" value="DELETE"/> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config>
4.5.11.4 Using a Large CSV Source File
Consider the following scenario, where you have a large CSV file of size 1 gigabyte coming on the source directory, and you must perform the following:
-
Translate the CSV into XML.
-
Transform the resulting XML using XSL.
-
Translate the result from the transform operation into a fixed length file.
This use case is similar to the FlatStructure sample in the BPEL samples directory. The difference is that the three steps occur in a single File I/O interaction.
Note:
All the three steps occur in a single File I/O interaction. This works only if all the records in the data file are of the same type.To use a large CSV file and perform the operations listed in the preceding scenario, you must perform the following steps:
-
Copy the
address-csv.xsdandaddress-fixedLength.xsdfiles from the FlatStructure sample into thexsddirectory of your project. -
Copy
addr1Toaddr2.xslfrom the FlatStructure sample into thexsldirectory of your project. -
Configure the File I/O interaction, as shown in the following example. At a high level, you must specify the source schema, the target schema, and the XSL in the interaction specification along with the source and target directory or file details, as shown in the following example:
<adapter-config name="FileMove" adapter="File Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/FileAdapter" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="FileMove_ptt" operation="FileMove"> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.file.outbound.FileIoInteractionSpec"> <property name="SourcePhysicalDirectory" value="foo1"/> <property name="SourceFileName" value="bar1"/> <property name="SourceSchema" value="xsd/address-csv.xsd"/> <property name="SourceSchemaRoot value="Root-Element"/> <property name="SourceType" value="native"/> <property name="TargetPhysicalDirectory" value="foo2"/> <property name="TargetFileName" value="bar2"/> <property name="TargetSchema" value="xsd/address-fixedLength.xsd"/> <property name="TargetSchemaRoot value="Root-Element"/> <property name="TargetType" value="native"/> <property name="Xsl value="xsl/addr1Toaddr2.xsl"/> <property name="Type" value="MOVE"/> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config>Note that you have provided the following additional parameters:
-
SourceSchema: Relative path to the source schema. -
SourceSchemaRoot: The root element in the source schema. -
SourceType: The type of data. The other possible type is XML. -
TargetSchema: Relative path to the target schema. -
TargetSchemaRoot: The root element in the target schema. -
TargetType: The type of data. The other possible type is XML. -
Xsl: Relative path to the Xsl file.
-
4.5.11.5 Moving a File from One Remote Directory to Another Remote Directory on the Same FTP Server
The I/O use cases for the Oracle FTP Adapter are very similar to those for Oracle File Adapter. However, there are a few nuances that need attention.
In this use case you will move a file within the same directory, which is similar to a rename operation on the same server. Most FTP servers support the RNFR/RNTO FTP commands that let you rename a file on the FTP server.
However, even if the RNFR/RNTO commands are not supported, moving a file within the same directory is still possible because of a binding property, UseNativeRenameOperation. By default, this property is set to TRUE, and in this case the Oracle FTP Adapter uses the native RNFR/RNTO commands. However, if this property is set to FALSE, then the Oracle FTP Adapter uses the Get and Put commands followed by a Delete command to emulate a move operation.
You can model only a part of this procedure by using the wizard because the corresponding Adapter Configuration Wizard is not available. You must complete the remaining procedure by manually configuring the generated JCA file.
You must perform the following steps to move a file from a remote directory to another remote directory on the same FTP server:
-
Create an empty BPEL process.
-
Drag and drop FTP Adapter from the Component Palette to the External References swim lane. The Adapter Configuration Wizard Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The Service Name page is displayed.
-
Enter a service name in the Service Name field.
-
Click Next. The Adapter Interface page is displayed.
-
Click Next. The FTP Server Connection page is displayed.
-
Enter the JNDI name for the FTP server, and click Next. The Operation page is displayed.
-
Select Synchronous Get File, enter
FTPMovein the Operation Name field, and then click Next. The File Directories page is displayed.Note:
You have selected Synchronous Get File as the operation because theWSDLfile that is generated as a result of this operation is similar to the one required for the file I/O operation. -
Enter a dummy physical path for the directory for incoming files, and then click Next. The File name page is displayed.
Note:
The dummy directory is not used. You must manually change the directory in a later step. -
Enter a dummy file name, and then click Next. The File Name page is displayed.
Note:
The dummy file name you enter is not used. You must manually change the file name in a later step. -
Click Next. The Messages page is displayed.
-
Select Native format translation is not required (Schema is opaque), and then click Next. The Finish page is displayed.
-
Click Finish. The outbound Oracle File Adapter is now configured.
-
Drag the small triangle in the BPEL process in the Components area to the drop zone that appears as a green triangle in
FTPMovein the External References area. The BPEL component is connected to the Oracle FTP Adapter outbound service. -
Click File, Save All.
-
Create an invoke activity for the
FTPMoveservice that you just created.The next step is to modify the generated
WSDLfile forFTPMoveservice and configure it with the new interaction specification for the move operation. -
Open the
FTPMove_ftp.jcafile and modify theinteraction-spec, as shown in the following example.You must configure the JCA file with the source and target directory and file details. You can either hardcode the source and target directory and file details in the JCA file or use header variables to populate them. In this example, header variables are used.
<adapter-config name="FTPMove" adapter="Ftp Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata"> <connection-factory location="eis/Ftp/FtpAdapter" adapterRef=""/> <endpoint-interaction portType="FTPMove_ptt" operation="FTPMove"> <interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.ftp.outbound.FTPIoInteractionSpec"> <property name="SourcePhysicalDirectory" value="foo1"/> <property name="SourceFileName" value="bar1"/> <property name="TargetPhysicalDirectory" value="foo2"/> <property name="TargetFileName" value="bar2"/> <property name="Type" value="MOVE"/> </interaction-spec> </endpoint-interaction> </adapter-config>Note:
You have modified theclassNameattribute, and addedSourcePhysicalDirectory,SourceFileName,TargetPhysicalDirectory,TargetFileName, andType. Currently, the values for the source and target details are dummy. You must populate them at run-time. You can also hardcode them to specific directories or file names.The
Typeattributes decides the type of operation. Apart fromMOVE, the other acceptable values for theTypeattribute areCOPYandDELETE. -
Map the actual directory and file names to the source and target file parameters by performing the following procedure:
-
Create 4 string variables with appropriate names. You must populate these variables with the source and target directory details. The BPEL source view shows you this:
<variables> <variable name="InvokeMoveOperation_FileMove_InputVariable" messageType="ns1:Empty_msg"/> <variable name="InvokeMoveOperation_FileMove_OutputVariable" messageType="ns1:FileMove_msg"/> <variable name="sourceDirectory" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="sourceFileName" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="targetDirectory" type="xsd:string"/> <variable name="targetFileName" type="xsd:string"/> </variables> -
Create an assign activity to assign values to
sourceDirectory,sourceFileName,targetDirectory, andtargetFileNamevariables. The assign operation appears in the BPEL source view as in the following example:<assign name="AssignFTPFileDetails"> <copy> <from expression="'/home/ftp'"/> <to variable="sourceDirectory"/> </copy> <copy> <from expression="'input.txt'"/> <to variable="sourceFileName"/> </copy> <copy> <from expression="'/home/ftp/out'"/> <to variable="targetDirectory"/> </copy> <copy> <from expression="'output.txt'"/> <to variable="targetFileName"/> </copy> </assign>In the preceding example,
input.txtis moved or renamed from/home/ftptooutput.txtin/home/ftp/out.Note:
The source and target details are hardcoded in the preceding example. You can also provide these details as run-time parameters. -
Pass these parameters as headers to the invoke operation. The values in these variables override the parameters in the JCA file.
<invoke name="InvokeRenameService" inputVariable="InvokeRenameService_RenameFile_InputVariable" partnerLink="RenameFTPFile" portType="ns2:RenameFile_ptt" operation="RenameFile"> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.SourceDirectory" variable="returnDirectory"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.SourceFileName" variable="returnFile"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.TargetDirectory" variable="returnDirectory"/> <bpelx:inputProperty name="jca.file.TargetFileName" variable="targetFile"/> </invoke>
-
-
Finally, add an initial receive or pick activity.
You have completed moving or renaming a file from a remote directory to another remote directory on the same FTP server.
Note:
If the FTP server does not support theRNFR/RNTO FTP commands, then you must set UseNativeRenameOperation to FALSE and define the property in composite.xml, as shown in the following example:
<reference name="FTPMove" ui:wsdlLocation="FTPMove.wsdl">
<interface.wsdl interface="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/ftp/SOAFtpIO/SOAFtpIO/FTPMove/#wsdl.interface(FTPMove_ptt)"/>
<binding.jca config="FTPMove_ftp.jca">
<property name="UseNativeRenameOperation" type="xs:string" many="false" override="may">false</property>
</binding.jca>
</reference>
4.5.11.6 Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to a Remote Directory on the FTP Server
The steps for this use case are the same as the steps for the use case in Section 4.5.11.5, "Moving a File from One Remote Directory to Another Remote Directory on the Same FTP Server" except that you must configure the source directory as local and the target directory as remote.
Use the SourceIsRemote and TargetIsRemote properties to specify whether the source and target file are on the local or remote file system, as shown in the following example:
<adapter-config name="FTPMove" adapter="Ftp Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/Ftp/FtpAdapter" adapterRef=""/>
<endpoint-interaction portType="FTPMove_ptt" operation="FTPMove">
<interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.ftp.outbound.FTPIoInteractionSpec">
<property name="SourcePhysicalDirectory" value="foo1"/>
<property name="SourceFileName" value="bar1"/>
<property name="SourceIsRemote" value="false"/>
<property name="TargetPhysicalDirectory" value="foo2"/>
<property name="TargetFileName" value="bar2"/>
<property name="Type" value="MOVE"/>
</interaction-spec>
</endpoint-interaction>
</adapter-config>
Note:
In this example, you have configuredSourceIsRemote as false. In this case, the FTP input and output operation assumes that the source file comes from a local file system. Also, notice that you did not specify the parameter for target because TargetIsRemote is set to true by default.4.5.11.7 Moving a File from a Remote Directory on the FTP Server to a Local Directory on the File System
The steps for this use case are the same as the steps for the use case in Section 4.5.11.6, "Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to a Remote Directory on the FTP Server" except that you must configure the source directory as remote and the target directory as local, as shown in the following example:
<adapter-config name="FTPMove" adapter="Ftp Adapter" xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/Ftp/FtpAdapter" adapterRef=""/>
<endpoint-interaction portType="FTPMove_ptt" operation="FTPMove">
<interaction-spec className="oracle.tip.adapter.ftp.outbound.FTPIoInteractionSpec">
<property name="SourcePhysicalDirectory" value="foo1"/>
<property name="SourceFileName" value="bar1"/>
<property name="TargetPhysicalDirectory" value="foo2"/>
<property name="TargetFileName" value="bar2"/>
<property name="TargetIsRemote" value="false"/>
<property name="Type" value="MOVE"/>
</interaction-spec>
</endpoint-interaction>
</adapter-config>
Note:
In this example, you have configuredTargetIsRemote as false. In this case, the FTP I/O assumes that the source file comes from a remote file system whereas the target is on a local file system. Also, notice that you did not specify the parameter for source because SourceIsRemote is set to true by default.4.5.11.8 Moving a File from One FTP Server to another FTP Server
To move a file from one FTP server to another FTP server you must sequentially perform the use cases documented in the following sections:
-
Section 4.5.11.7, "Moving a File from a Remote Directory on the FTP Server to a Local Directory on the File System" to upload the file from the local directory to another FTP server
-
Section 4.5.11.6, "Moving a File from a Local Directory on the File System to a Remote Directory on the FTP Server" to download the file from the FTP server to a local directory