| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.4.0) E10148-12 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.4.0) E10148-12 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter explains how to integrate the Search service in a WebCenter Portal application at design time.
For more information about managing and including search, see:
"Managing Oracle SES Search in WebCenter" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter
"Working with the Search Service" in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Spaces
This chapter includes the following sections:
WebCenter search provides a unified, extensible framework that enables the discovery of information through an intuitive user interface. It honors application security settings by returning only the results a user is authorized to view. Users can save their searches for reuse, including searches with complex search refinement conditions.
WebCenter provides two ways of searching your application:
Oracle Secure Enterprise Search (SES) adapter
Oracle WebCenter live search adapters
In addition, the Documents service provides its own search engine for file searches. This saves time and increases the relevancy of results by narrowing the scope of a search to files.
|
See Also: Section 13.4, "Using Portal Navigation to Create a Sitemap" for information about integrating an external search engine in your application |
With WebCenter Portal applications, Oracle Secure Enterprise Search (SES) is set as the default and preferred search platform. Oracle SES provides unified ranking results for the following resources:
Documents, including wikis and blogs
Announcements and Discussions
Spaces, lists, pages, and people resources in WebCenter Spaces
|
Note: Oracle WebCenter Spaces applications include the Oracle SES crawler that indexes Spaces, lists, pages, and people resources in WebCenter Spaces. This crawler is not supported in WebCenter Portal applications. |
Oracle SES search is beneficial for the following reasons:
Oracle SES search provides unified ranking results, with the most relevant items appearing first.
Oracle SES search allows search of repositories outside of WebCenter. Oracle SES results appear in the same result set as WebCenter search results.
Oracle SES search supports the Search service REST APIs and data control for customizing your search interface.
Oracle SES 11.1.2 is provided on the Oracle WebCenter companion CD. Supported versions include Oracle SES 10.1.8.4 and later. You can register multiple Oracle SES connections, but only one of them is active at a time.
Search with Oracle SES requires additional configuration in Oracle SES Administration, Oracle Content Server, and Oracle Discussions Server.
Although Oracle SES is the preferred search platform for best performance, you can manually override search with Oracle SES and have WebCenter Portal applications search using the original WebCenter search adapters. WebCenter search adapters span all enabled and searchable services, such as documents, tags, people, and pages.
If no resource action handling is specified in the WebCenterPortal application, then the default action when a search result is clicked is to render the search result in a new browser window. Also, results from services that provide resource viewers, such as Documents, Discussions or Announcements, open in their resource viewers. For more information about resource viewers and the Resource Action Handling framework, see Section 7.3, "Extending Your Application with Custom Components."
At run time, users can perform global (application-wide) searches from the Search task flow or from the Search toolbar and refine and save searches.
For more information about the WebCenter search at runtime, see Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Spaces.
This section provides the steps for adding the Search service to your application. It includes the following subsections:
If you override search with Oracle SES to use the original WebCenter search adapters, then no connections are required.
To search with Oracle SES, you must add the Oracle SES connection in the WebCenter Portal application. For more information, see Section 40.3.4, "Configuring Search with the Oracle SES Adapter."
|
Note: You can create a connection to Oracle SES to search repositories outside WebCenter and override using Oracle SES as the default search crawler with Fusion Middleware Control or WLST. This allows users to search other WebCenter Portal application resources, such as people. |
Add the search toolbar to a page, following Section 40.2.2, "Adding the Search Service at Design Time."
Set up a connection to Oracle SES. In the Application Navigator, expand Application Resources. Right-click the Connections node, select New Connection, and then Oracle Secure Enterprise Search.
In Oracle WebCenter, select to create the connection in either the Application Resources or IDE connections. A connection in Application Resources is available only for that application, while a connection in IDE connections is available for all applications you create. If you plan to use the connection in other applications, then select IDE connections to avoid the need to re-create it.
|
Note: If you create the connection in IDE, then the connection must be added to the application later. For example, in the Resource Palette under IDE connections, right-click the connection and select Add to Application. |
Enter values for the fields in the dialog. For example:
For Connection Name, enter a meaningful name, for example, SESconnection. This name cannot be changed after it is created. (To use a different connection name, create a new connection.)
For SOAP URL, enter the URL for the Oracle SES Web Services endpoint, for example:
http://host:port/search/query/OracleSearch
Under Federation Trusted Entity, for Entity Name, enter the trusted entity defined for this application on the Oracle SES instance; for example, wcsearch.
A trusted entity allows the WebCenter application to authenticate itself to Oracle SES and assert its users when making queries on Oracle SES. This trusted entity can be any user that either exists on the identity management server behind Oracle SES or is created internally in Oracle SES. You can find (or create) the trusted entity on the Global Settings - Federation Trusted Entities page of Oracle SES.
For Entity Password, enter the password of the Federation Trusted Entity user.
Under Application Configuration, select the box for Set as default connection for the Search service.
This ensures that your application uses that connection to access Oracle SES. The Search service uses only one Oracle SES connection.
|
Note: After you create a connection as the default connection, you cannot edit it so that it is not the default. To use a different default connection, you must create a new connection and mark that as the default connection. |
For Source Group, enter the Oracle SES source group in which to search. If a value is not provided, then all crawl sources in the Oracle SES instance are searched.
|
Note: Source groups present a good way to segment your searchable data on Oracle SES. Given an Oracle SES instance that keeps a search index on all corporate data, you can use source groups to make only a portion of your corporate data available to a WebCenter search. For more information on creating source groups, see Oracle SES Administrator's Guide. |
Under Testing, for User name, enter the name of a user present in both the Oracle Identity Management server configured for your WebCenter Portal application and the Oracle Identity Management server configured for Oracle SES.
You should see something similar to Figure 40-1.
Figure 40-1 Create Oracle SES Connection Dialog
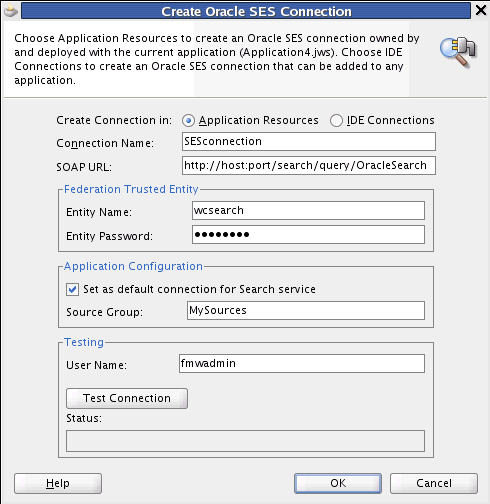
Click Test Connection and check the status.
If the connection is successful, then click OK.
After you have included the Oracle SES connection in your application, you should see it in your Application Resources panel, as shown in Figure 40-2.
Figure 40-2 Oracle SES Connection in Application Resources
The Oracle SES connection is now included in the connections.xml file and is the default connection in the adf-config.xml file, as shown in Example 40-1.
Example 40-1 Oracle SES Connection in adf-config.xml
<ses-properties> <connection>SESconnection</connection> <data-group>MySources</data-group> </ses-properties>
|
Note: After a WebCenter Portal application has been deployed to an Oracle WebLogic managed server, you can configure it using WLST or Fusion Middleware Control. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter. |
This section describes the Search service task flows and explains how to integrate the Search service into your application. It includes the following subsections:
Section 40.2.2.2, "How to Add the Search Service to Your Page"
Section 40.2.2.3, "How to Modify the Search Service Task Flow Parameters"
Table 40-1 lists the Search service task flows.
Table 40-1 Search Service Task Flows
| Task Flow | Definition |
|---|---|
|
This task flow provides a rich search experience with features for refining and saving search results. |
|
|
This task flow enables you to create a simple launch pad for running saved searches within the application. |
|
|
This task flow enables users to select which WebCenter services to search. |
|
|
This task flow enables users to enter simple search criteria and run the search from the application. Search results are rendered as links. |
The Search Toolbar task flow offers the easiest way to add the Search service to your application. To add the Search Toolbar task flow to your WebCenter Portal application:
Follow the steps described in Chapter 3, "Preparing Your Development Environment" to create a customizable page in your application.
|
Note: ADF security is configured by default if you created your application using the WebCenter Portal Application template. For information about configuring ADF security, see Section 63.3, "Configuring ADF Security." |
Open the page on which to add the Search service.
In the Resource Palette, expand My Catalogs, WebCenter Services Catalog, and Task Flows.
Drag and drop the Search Toolbar task flow onto the page.
When prompted, select Region as the way to create the task flow.
If a prompt to confirm the ADF library appears, click Add Library.
Run your page with the search toolbar on it.
In the Application Navigator, right-click this application and select Run. It may take a few moments for the operation to complete.
Enter the user name and credentials that you created when you defined security.
|
Note: To return results, the Search service requires that other WebCenter services are included in the application. |
Some Search service task flows have optional task flow binding parameters.
In addition to providing values for successful task flow rendering, you can use task flow parameters to customize the appearance and behavior of a task flow instance. For example, you can use adjust the value of the searchBoxSize parameter to change the size of the search box.
To see and adjust task flow binding parameter values after you have placed a task flow on a page:
Navigate to the Edit Task Flow Binding dialog by clicking the Bindings tab at the bottom of the page containing the task flow (next to the Source tab).
Under Executables, you'll see the task flow you added. Figure 40-3 shows an example of a Search task flow in the Executables section.
Select the task flow, and next to the Executables heading, click the Edit selected element (pencil) icon.
In the Edit Task Flow Binding dialog Figure 40-4, revise the binding parameter value by double-clicking the field and either changing the existing value or adding a new one.
Figure 40-4 Edit Task Flow Binding Dialog for Search Task Flow
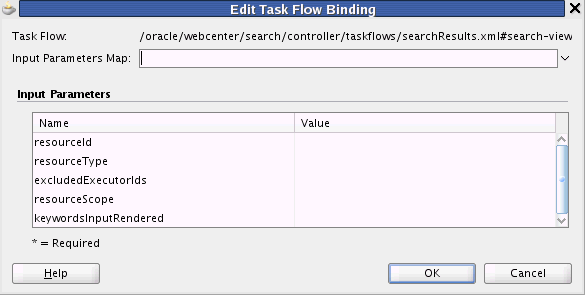
When you are finished, click OK.
Save and run your page to see the results.
Table 40-2 describes the properties that are unique to the Search service task flows.
Table 40-2 Search Service Task Flow Parameters
| Property | Description | Task Flow |
|---|---|---|
|
Either search keywords or the saved search GUID. This parameter is intended for internal use only. Do not change this value unless you want coded search main views. If you do change this value, then you must also specify |
Search |
|
|
A marker specifying whether the This value is set automatically and is for internal use only. Do not change it unless you want coded search main views. |
Search |
|
|
A list of IDs of services or executors to omit when displaying search results. This value is set automatically and is for internal use only. |
Search |
|
|
Unique ID to limit the search scope. To limit the search to a particular Space, set this to the GUID of the Space. For example: |
Search |
|
|
Show or hide the input box. Set to true (default) to show the input box, or set to false to hide it. |
Search |
|
|
Unique ID to limit the search scope. To limit the search to a particular Space, set this to the GUID of the Space. |
Search Toolbar |
|
|
Value to limit the size of the search box. The default value is 42. Enter a lower number (for example, 30) to shorten the length of the search box. This also changes the size of the search box in the Search task flow. |
Search Toolbar |
|
Note: The All Saved Searches and the Search Preferences task flows do not have any unique properties. |
The Oracle SES adapter must be configured with an identity management system to validate and authenticate users. This is necessary for searches to return only results that the user is allowed to view based on access privileges. Because WebCenter uses identity propagation when communicating with Oracle SES, WebCenter's user base must match that in Oracle SES. One way this can happen is by configuring WebCenter and Oracle SES to the same identity management system. For detailed information, see the section "Oracle SES - Configuration" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter.
The original WebCenter search adapters rely on individual services to ensure that the user performing the search can view results. Search results are returned based on user privileges. When unauthenticated, queries return only public content. Only authenticated users of an ADF-secured WebCenter Portal application can save searches.
ADF security is configured by default if you created your application using the WebCenter Portal Application template. For information about configuring ADF security, see Section 63.3, "Configuring ADF Security."
This section describes optional features available with this service. It includes the following subsections:
Section 40.3.2, "Adding the Search - Saved Searches Task Flow"
Section 40.3.4, "Configuring Search with the Oracle SES Adapter"
Section 40.3.5, "Configuring Search with WebCenter Search Adapters"
Section 40.3.10, "Customizing the Search UI Without the Search Service APIs"
|
Note: The Search service REST APIs and data controls are available only for search using Oracle SES. They are not supported with search using the original WebCenter search adapters. |
To add the Search task flow to your WebCenter Portal application, follow the instructions provided for the Search Toolbar task flow in Section 40.2.2, "Adding the Search Service at Design Time," but instead, drag and drop the Search task flow onto the page.
To run the page with the Search view:
In the Application Navigator, right-click the page and select Run. As long as the application has been ADF-secured, you should see a login page. It may take a few moments for the operation to complete.
If you configured ADF security, then enter the user name and password that you provided and click Submit.
Enter some search criteria in the field and click the Search icon. You may get few, if any, results if the application is not populated with much besides the Search service itself.
You can add the Search - Saved Searches task flow to provide a simple launch pad for running saved searches within the application. To add this task flow to your WebCenter Portal application, follow the instructions provided for the Search Toolbar task flow in Section 40.2.2, "Adding the Search Service at Design Time," but instead, drag and drop the Search - Saved Searches task flow onto the page.
The task flow renders links that, when clicked, run a saved search.
The Search Preferences task flow enables users to control which WebCenter services are searched. By default, all enabled services are selected to be searched. Users can disable any service from which they do not want to see search results. Users also can select the order of services in their search results. For example, they may find that search results from the Documents service prove more useful that search results from other services.
To add the Search Preferences task flow to your WebCenter Portal application, follow the instructions provided for the Search Toolbar task flow in Section 40.2.2, "Adding the Search Service at Design Time," but instead, drag and drop the Search Preferences task flow onto the page.
WebCenter Portal applications automatically set Oracle Secure Enterprise Search (SES) as the default search adapter, but additional configuration is required in Oracle SES Administration, Oracle Content Server, and Oracle Discussions Server. See the section "Managing the Search Service" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter for detailed information about the steps to set up search with the Oracle SES adapter.
After you have completed all configuration steps, validate the inclusion of Oracle SES results in WebCenter search.
In the Application Navigator, right-click the page you created with the Search Toolbar, and click Run.
As long as the application has been ADF-secured, you should see a login page. It may take a few moments for the operation to complete.
Enter the user name and credentials that you created when you defined security.
Click Submit.
When the page loads, you should see your search toolbar.
Figure 40-5 shows a sample results page for the search term webcenter, before Oracle SES has crawled anything.
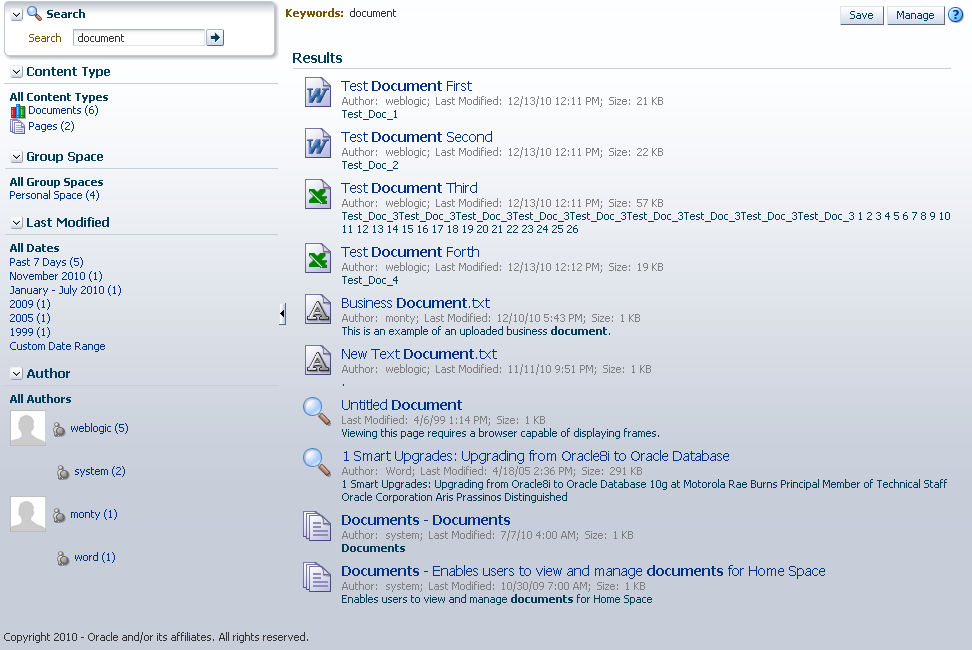
Figure 40-6 shows a sample results page after Oracle SES has been configured and crawled.
Figure 40-6 Search Results after Crawling
|
See Also: Oracle SES documentation provided on the Oracle Fusion Middleware documentation library (in the WebCenter product area) |
You can manually override search with Oracle SES and have WebCenter Portal applications search using the original WebCenter search adapters. WebCenter search adapters span all enabled and searchable services, such as documents, tags, people, and pages.
To enable search with the WebCenter search adapters, edit the adf-config.xml file either to change all enable attributes in crawl-properties to false (Example 40-2) or to comment out the crawl-properties entirely (Example 40-3).
Example 40-2 Crawl Properties in adf-config.xml Set to False
<searchC:adf-search-config
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/search/config">
<display-properties>
<common numSavedSearches="5"/>
<region-specific>
<usage id="simpleSearchResultUIMetadata" numServiceRows="5"/>
<usage id="searchResultUIMetadata" numServiceRows="5"/>
<usage id="localToolbarRegion" numServiceRows="5"/>
</region-specific>
</display-properties>
<execution-properties timeoutMs="7000" prepareTimeoutMs="3000"/>
<crawl-properties fullCrawlInterval="P5D" enableWcServicesCrawl="false"
enableWcDiscussionsCrawl="false" enableWcUcmCrawl="false"/>
<ses-properties>
<connection/>
<data-group/>
</ses-properties>
</searchC:adf-search-config>
Example 40-3 Crawl Properties in adf-config.xml Commented Out
<searchC:adf-search-config
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/search/config">
<display-properties>
<common numSavedSearches="5"/>
<region-specific>
<usage id="simpleSearchResultUIMetadata" numServiceRows="5"/>
<usage id="searchResultUIMetadata" numServiceRows="5"/>
<usage id="localToolbarRegion" numServiceRows="5"/>
</region-specific>
</display-properties>
<execution-properties timeoutMs="7000" prepareTimeoutMs="3000"/>
<!--
<crawl-properties fullCrawlInterval="P5D" enableWcServicesCrawl="true"
enableWcDiscussionsCrawl="true" enableWcUcmCrawl="true"/>
-->
<ses-properties>
<connection/>
<data-group/>
</ses-properties>
</searchC:adf-search-config>
Custom components can implement Search service APIs to expose their content to a WebCenter search.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle WebCenter.
Oracle WebCenter provides REST APIs to support the Search service. Use the Search service REST APIs to post, read, update, and delete searches. You can specify keywords and the scope of the search; for example, the iPhone could search for "smith" in all Spaces, documents and wiki pages. The API also lets you build a customized search user interface on top of the Search service.
This section describes the REST APIs associated with the Search service. It includes the following subsections:
For an introduction to the REST APIs, see Chapter 51, "Using Oracle WebCenter REST APIs."
|
Note: REST APIs do not work out of the box. Before you can use REST APIs, you must take the configuration steps outlined in the following section: Section 51.2, "Before You Begin: Performing Required Configurations." |
Each REST service has a link element within the resource index that provides the entry point for that service. To find the entry point for the Search service, find the link element with a resourceType of:
urn:oracle:webcenter:search
The corresponding href or template element provides the URI entry point. The client sends HTTP requests to this entry point to work with the Search service.
For more information about the resource index, see Section 51.6.1, "The Resource Index."
For more information about resource types, see Section 51.6.2.1, "Resource Type."
When the client has identified the entry point, it then can navigate through the resource type taxonomy to perform the required operations. For more information about the individual resource types, see the appropriate section in Section 51.6.2.1, "Resource Type."
The taxonomy for the Search service is:
urn:oracle:webcenter:search urn:oracle:webcenter:search:results
Beyond the service entry points, URL templates allow clients to pass query parameters to customize their requests and control the form of returned data.
Collection resources in the search resources support pagination (startIndex and itemsPerPage). Other query parameters are not supported (that is, search and projection).
Authentication is required before using Search REST API methods.
For general security considerations, see Section 51.9, "Security Considerations for WebCenter REST APIs."
This section provides information about each resource type. It includes the following subsection:
Use this resource type to identify the URI to use to read (GET) a query containing keywords and attribute-specific criteria.
The request is represented by the URL and the response is a list of search results, each with metadata to help the end user choose an item to drill down, as well as cross links to the owning REST services, if available. If the owning REST service is unavailable, then an HREF link is provided.
The response XML can be paginated with standard URL parameters, and appropriate previous and next links provided along with a general template (with the query prepopulated) for the consuming application to do its own custom pagination.
Navigation Paths to results
This section shows how the client can navigate through the hypermedia to access this resource:
resourceindex search
resourceindex
spaces
spaces:resourceindex
spaces:search
Supported Methods for results
The following methods are supported by this resource:
GET
request - body: none, Parameters: serviceId, q, scopeGuid, refiners, startIndex (pagination), itemsPerPage (pagination)
response - body: search results, and refiners (if refiners=true)
where:
serviceId={serviceId}
Optional: The service ID of the item. If omitted, this searches across all services; for example, oracle.webcenter.doclib searches only documents.
q={queryString}
Searches may be specified using the following format
[[field1:[operand]][:]value1[;field2:operand:value2]]
Where multiple clauses are joined by an implicit AND and are syntactically separated by the ";" semicolon. Square brackets [] denote optional values. Each clause can be one of the following types:
keywords - simple string with no ":" colon separator
attribute1:value1 - shortcut for a clause meaning attribute1 equals value1
attribute1:operand1:value1 - a clause capturing a Boolean condition between attribute1 and value1
Search refinement attributes include the following:
title - Name or title of the item
description - Description of the item
creator - Creator or contributors of the item
date - Date on which the item was last modified
tags - Tag words that the item may have (applicable to pages)
Legal operands:
equals - Strings and Numbers
contains - Strings
gt (greater than) - Numbers
gte (greater than or equals) - Numbers
lt (less than) - Numbers
lte (less than or equals) - Numbers
scopeGuid={...}
Optional: The GUID associated with the scope.
refiners={true|false}
Optional: Whether to fetch refiners. If omitted, the default value is false.
For more information, see Section 51.6.2.5, "Templates."
Writable Elements for results
Table 40-3 lists the writable elements for this resource.
Table 40-3 Writable Elements for results
| Element | Type | Required | Constraints | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
String |
1 or more characters |
Name of the query author |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
String |
No |
1 or more characters |
Description of the query |
|
|
||||
|
|
Resource Types Linked to From results
Table 40-4 lists the resource types that the client can link to from this resource.
Use the Search service data control to build a customized search user interface with a WebCenter Portal application or a custom task flow. Deploying this task flow into an ADF library allows for a portable consumption of the task flow; for example, you could add it to a WebCenter Spaces application Resource Catalog to build site templates.
The Search data control contains the searchSes method. Table 40-5 describes its parameters for setting search refiners and limiting the scope of the search.
Table 40-5 searchSes Input Parameters
| Parameter | Required? | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
No |
String |
GUID value to filter results by Spaces. |
|
|
No |
String |
The service ID of the item. If omitted, this searches across all services; for example, oracle.webcenter.doclib searches only documents. |
|
|
Yes |
String |
Search terms. |
|
|
No |
List |
Collection of predicates. |
|
|
No |
Boolean |
Whether to fetch refiners. If omitted, the default value is false. |
|
|
Yes |
Integer |
Specifies the index of the first matching result that should be included in the result set (0-n ... zero based). This is used for pagination. |
|
|
Yes |
Integer |
Number of results to display. |
The searchSes method returns:
Collection of SearchServiceDCRows objects
Collection of SearchServiceDCRefiner objects
author
comments
createDate
description
iconPath
language
largeIconPath
lastModifiedDate
resourceId
scopeGuid
serviceId
size
tagWords
title
type
urlSearchServiceDCRefiner
element
keywords
scopeGuid
serviceId
Collection of predicates
To use the Search data control:
In JDeveloper, create a WebCenter Portal application with an Oracle SES connection. After the connection is available, the Search Data Control is listed in the Data Controls palette.
Drag and drop the searchSes method from SearchServiceDC.
Choose ADF Parameter Form, and the Edit Form Fields dialog opens. Click OK.
Drag the rows accessor, from the SearchServiceDCResult return object type, onto the form, and choose Table - ADF Read-only Table. Click OK.
Run the page, enter appropriate values. For example:
keywords: any search term
startIndex: 0
itemsPerPage: 10
For information about adding WebCenter data controls to your application, see Section 7.1.2, "Understanding WebCenter APIs."
You can use search adapters to add other sources to your search results. WebCenter framework automatically discovers these search adapters and consolidates them in formulating search results in your WebCenter Portal application. Subsequently, when you expose your custom component to the Search service in your application, it is included in the federated search.
This section describes how to extend WebCenter search through search adapters. It includes the following subsections:
To add a new search source, you must create Java classes for the new source to manage the incoming queries and return search results. After you add the necessary Java classes to your application, you must register them with the Search service.
When performing a search, the search framework calls QueryManager.createRowQueryHandler with a query object and a List<QName> that describes the columns sought. In return, the framework receives a QueryHandler<Row>.
A QueryHandler can be a QueryFederator or a QueryExecutor. A QueryFederator is just a collection of other QueryHandlers. With the QueryFederator, the framework can get a list of the child QueryHandlers and keep recursing until all QueryExecutors are found.
The framework calls the execute method on the QueryExecutor to get a QueryResult<Row>, which is an extension of java.util.Iterator<Row> that iterates and retrieves rows of results.
One possible implementation would be to create these classes:
SampleQueryManager ...
SampleRowQueryExecutor ...
SampleRowQueryResult ...
SampleRow ...
To add a new search source with a similar query manager:
In Oracle JDeveloper, open the application in which to add the search source.
Confirm that the WebCenter Common library is included in your project:
Right-click your ViewController project and select Project Properties and then Libraries and Classpath.
If the WebCenter Common library is not included, as shown in Figure 40-7, then click Add Library and select it.
Click OK.
Create a class called SampleQueryManager.java (Example 40-4).
Example 40-4 SampleQueryManager.java
package mycompany.myproduct.myapp.mycomponent.query;
import java.util.List;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QName;
import oracle.webcenter.search.Query;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QueryExecutor;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QueryManager;
import oracle.webcenter.search.Row;
public class SampleQueryManager
implements QueryManager
{
public SampleQueryManager()
{
}
public QueryExecutor<Row> createRowQueryHandler(Query query,
List<QName> columns)
{
return new SampleRowQueryExecutor(query, columns);
}
}
Create a class called SampleRowQueryExecutor.java (Example 40-5).
Example 40-5 SampleRowQueryExecutor.java
package mycompany.myproduct.myapp.mycomponent.query;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_EXTENT;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_MODIFIED;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_CREATOR;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_TITLE;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_URI;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_IDENTIFIER;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.WPSAPI_ICON_PATH;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QName;
import oracle.webcenter.search.Query;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QueryExecutor;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QueryHandler;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QueryResult;
import oracle.webcenter.search.Row;
public class SampleRowQueryExecutor
implements QueryExecutor<Row>
{
private static final int PRESET_ESTIMATED_RESULT_COUNT = 10;
private static final int PRESET_VALUES_BATCH_SIZE = 5;
private static final int MAX_RESULT_LIMIT = 100;
private int m_resultStart;
private int m_resultLimit;
private Query m_query;
private List<QName> m_columns;
private Map<String, String> m_properties;
public SampleRowQueryExecutor(Query query, List<QName> columns)
{
m_query = query;
m_columns = columns;
m_properties = new HashMap<String, String>();
// In actuality you may want to make sure this string is translatable
m_properties.put(QueryHandler.TITLE, "Sample");
}
/**
* Create several rows for "batchRepeat" times.
*/
private static void createRows(List<Row> rows, int batchRepeat)
{
while (batchRepeat-- > 0)
{
rows.add(new SampleRow("23847", "Initial Sorting of Tables",
"Bar", "2006-06-08", 5120));
rows.add(new SampleRow("4827445", "Support for facelets?",
"Foo", "2006-04-17", 1400000));
rows.add(new SampleRow("952787", "For Thomas Kincade's validation demo",
"Tiger", "2006-01-09", 1300000));
rows.add(new SampleRow("4394588", "Page not showing in WYSIWYG fashion",
"Ken Swartz", "2006-04-27", 3000));
rows.add(new SampleRow("3920", "Tree table",
"Scott", "2006-03-24", 1200));
}
}
/**
* Instead of doing a query execution here,
* just create a bunch of rows.
*/
public QueryResult<Row> execute()
{
List<Row> rows = new ArrayList<Row>();
// To hit a certain count here but not go over the max
int realLimit = Math.min(MAX_RESULT_LIMIT, m_resultLimit);
createRows(rows, (realLimit / PRESET_VALUES_BATCH_SIZE));
// Create the QueryResult
QueryResult<Row> ret = new SampleRowQueryResult(rows.iterator());
ret.getProperties().put(QueryResult.ESTIMATED_RESULT_COUNT,
Integer.toString(PRESET_ESTIMATED_RESULT_COUNT));
return ret;
}
/**
* Remember the result start.
*/
public void setResultStart(int resultStart)
{
m_resultStart = resultStart;
}
/**
* Store away the result limit to use in the execute
* to only get that number of results back.
*/
public void setResultLimit(int resultLimit)
{
m_resultLimit = resultLimit;
}
/**
* Expose our properties map containing our title.
*/
public Map<String, String> getProperties()
{
return m_properties;
}
}
Create a class called SampleRowQueryResult.java (Example 40-6).
Example 40-6 SampleRowQueryResult.java
package mycompany.myproduct.myapp.mycomponent.query;
import java.util.Iterator;
import oracle.webcenter.search.util.WrapperQueryResult;
import oracle.webcenter.search.Row;
public class SampleRowQueryResult extends WrapperQueryResult<Row>
{
public SampleRowQueryResult(Iterator<Row> rows)
{
super(rows);
}
}
Create a class called SampleRow.java (Example 40-7).
Example 40-7 SampleRow.java
package mycompany.myproduct.myapp.mycomponent.query;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import oracle.webcenter.search.QName;
import oracle.webcenter.search.Row;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_EXTENT;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_MODIFIED;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_CREATOR;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_TITLE;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_URI;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_IDENTIFIER;
import static oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.WPSAPI_ICON_PATH;
public class SampleRow implements Row
{
private Map<QName, Object> m_storage = new HashMap<QName, Object>();
private DateFormat m_dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
SampleRow(String id, String title,
String creator, String lastModified,
int size)
{
m_storage.put(DCMI_IDENTIFIER, id);
// Only if you have an external URL to go to
// m_storage.put(DCMI_URI, "http://my.external.url");
m_storage.put(DCMI_TITLE, title);
m_storage.put(DCMI_CREATOR, creator);
// The below path points to a path accessible in the classpath to an icon
m_storage.put(WPSAPI_ICON_PATH, "/adf/webcenter/search_qualifier.png");
try
{
Date date = m_dateFormat.parse(lastModified);
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.setTime(date);
m_storage.put(DCMI_MODIFIED, cal);
}
catch (ParseException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
m_storage.put(DCMI_EXTENT, new Long(size));
}
public Object getObject(QName columnName)
{
return m_storage.get(columnName);
}
public Iterator<QName> getColumns()
{
return m_storage.keySet().iterator();
}
}
To register your query manager with the Search service, you must edit the service-definition.xml file. The SampleQueryManager line exposes the custom adapter's query manager implementation to the Search service so that the custom adapter is included with any search user interface.
The entry should be similar to Example 40-8.
Example 40-8 Sample Query Manager Entry in service-definition.xml
<service-definition id="mycompany.myproduct.myapp.mycomponent"
version="11.1.1.0.0">
<resource-view taskFlowId="/somepath/somefile.xml#someId"
authorizerClass="some.service.id.Authorizer1"/>
<name>Custom Component 1</name>
<description>Description for Custom Component 1</description>
<search-definition xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/search"
id="mycompany.myproduct.myapp.mycomponent.query" version="11.1.1.0.0">
<query-manager-class>
mycompany.myproduct.myapp.mycomponent.query.SampleQueryManager
</query-manager-class>
</search-definition>
</service-definition>
For more information about the resource-view tag (and Oracle WebCenter's Resource Action Handling framework), see Section 7.3, "Extending Your Application with Custom Components."
This section describes the attributes available for searching a service. It includes the following subsections:
The WebCenter search user interface exposes searches based on three fields: keywords, date, and person. Each service, in its own search implementation, honors these fields to the best of its capabilities. At minimum, it supports the keywords field. When you define your own search adapter, you must honor these fields to the best of your adapter's capabilities, as described in Section 40.3.9.3.8, "Selectable Attributes."
By default, the keyword field is in oracle.webcenter.search.TextPredicate. The field can comprise multiple words, with the service determining how to interpret multiple words. The WebCenter Search service does not tokenize before the call comes to the service, but here are some guidelines:
If two or more tokens are enclosed within quotes, then they should be interpreted as one word.
Unless the OR operator is explicitly set, it is assumed that the default conjunction among the words in the keywords field is AND.
For the Search service to support filtering of query results by last modified date, the service implementation of the WPSAPI must support the use of oracle.webcenter.search.AttributePredicate, accessible from the query object, that uses oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_MODIFIED. The supported comparators must include the following:
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.GREATER_THAN
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQUALS
They may also include the following:
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.EQUALS
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.NOT_EQUALS
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.LESS_THAN
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.LESS_THAN_OR_EQUALS
The literals for comparison should be of type java.util.Calendar.
You can use the BETWEEN clause for dates. The complex date condition, instead of being a simple AttributePredicate, is a ComplexPredicate that contains one GREATER_THAN AttributePredicate and one LESS_THAN AttributePredicate with an AND conjunction operator. This ComplexPredicate must apply the AND operator with the rest of the fields (that is, keywords and person).
To differentiate between this case and the default case, service authors must check on the type of the predicate that is meant for the date condition. If it is an AttributePredicate, then it is the default case. If it is a ComplexPredicate, then it is a special case.
For the Search service to support filtering of query results by person, the service implementation of the WPSAPI must support oracle.webcenter.search.AttributePredicate, accessible from the query object, that uses oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.WPSAPI_MODIFIER.
The comparators supported must include the following:
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.EQUALS
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.CONTAINS
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.STARTS_WITH
oracle.webcenter.search.ComparatorConstants.ENDS_WITH
The literals for comparison should be of type java.lang.String.
Service authors must check on the type of predicate that is meant for the person condition. An AttributePredicate is the default case.
The Search service (as a caller) expects that the query's getPredicate() method likely returns an oracle.webcenter.search.ComplexPredicate that joins an oracle.webcenter.search.TextPredicate holding the keyword, and an oracle.webcenter.search.ComplexPredicate holding the date condition, and an oracle.webcenter.search.AttributePredicate holding the person condition.
The following selectable attributes/columns should be supported by your search adapter in its search implementation:
Title (Required)
For each resource returned, the Search service user interface can display the title column, if provided. It is strongly recommended that the title column comes with the QName AttributeConstants.DCMI_TITLE.
Resource ID (Required)
For resources to communicate a unique identifier that allows the Search service to render a link to navigate to the resource view (or any declared views) of the service, the column with the name oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_IDENTIFIER must be returned as a column accessible from a row within the QueryResult<Row>.
The Search service extracts the DCMI_IDENTIFIER column and feeds it into the resource viewer as the value of the resourceId parameter when the link is clicked.
If your resource view (or any declared views) requires multiple columns in the primary key, then try to bundle all of them into a composite string value for the oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_IDENTIFIER column. The Search service treats that opaquely and passes it to your resource view, within which it may deconstruct the string into the various parts of the primary key.
Resource Type
For each resource returned, the Search service user interface can display the type column, if provided. The type column comes with the QName AttributeConstants.DCMI_TYPE. If the DCMI_TYPE column is not found, then the value of the DCMI_FORMAT column is used in its place. In your resource viewer, you can make use of the resource type to aid in the rendering of a resource.
Resource URL (in place of Resource ID)
In the absence of an oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_IDENTIFIER column, the Search service constructs the link from the value of the column specified by oracle.webcenter.search.AttributeConstants.DCMI_URI. With absolute URLs, the DCMI_URI can launch a link from the search results to the URL.
This allows for services, such as the Documents service and the Page service, to invoke the browser plug-in to render various results link targets, instead of invoking a resource view.
Last Modified Date
For each resource returned, the Search service user interface can display the last modified date column, if provided. To mirror the searchable attribute of the last modified date, it is important that users can see the last modified date as a returned column in the search result.
For most users, the last modified date is more relevant than the creation date. To have better consistency between the searchable attributes and the selectable attributes (so that users know what date to search with after seeing some values in the columns), it is strongly recommended that service authors return AttributeConstants.DCMI_MODIFIED rather than AttributeConstants.DCMI_CREATED. The last modified date is of type java.util.Calendar.
Creator
For each resource returned, the Search service user interface can display the creator and last modified by column, if provided. The search user interface combines them in the same column as a list of contributors for the found resource. The QNames to use are AttributeConstants.DCMI_CREATOR and AttributeConstants.WPSAPI_MODIFIED, respectively. The creator is of type java.lang.String.
Icon
For each resource returned, the Search service user interface can display the icon column, if provided. The icon column comes with the QName AttributeConstants.WPSAPI_ICON_PATH and corresponds to a valid path to an icon file that is accessible in the class path. The icon path is of type java.lang.String.
Size
For each resource returned, the Search service user interface can display the size column, if provided. The size column comes with the QName AttributeConstants.DCMI_EXTENT and corresponds to the size of the resource found. The size is of type java.lang.Number.
When you perform a search from the main view or toolbar, it should seamlessly include your new search source. For testing purposes, be sure to enter criteria that yields a result in your newly-added search source.
The Search service invokes a resource viewer using the Resource Action Handling framework. For information about registering a resource viewer to allow custom components to be found using Search, see Section 7.3, "Extending Your Application with Custom Components."
You can develop a custom search user interface in a WebCenter Portal application without the Search service API, but still with Oracle SES as the application's search engine by using the Oracle SES Web Service Query API to do search functions. Also, action handling for search results can be managed with WebCenter Resource Action Handling so that when a WebCenter resource (for example, a document) is clicked in the search results, the resource is shown in the viewer of the resource (for example, the Documents resource viewer). Moreover, if the application uses WebCenter Navigation, then certain resource types can be shown in the navigation node of the resource.
This section describes the required steps to enable WebCenter Resource Action Handling for handling search result action.
Use the Document Service Manager provided by WebCenter to crawl documents.
|
See Also: Section "Setting Up Oracle SES to Search Documents" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter |
The Document Services Manager creates an attribute called wc_url in the Oracle SES index for each document. The value of the wc_url attribute is a URL that goes to the Resource Action Handling module of the WebCenter Portal application. The URL uses the value of the WebCenter URL Prefix parameter in the Document Service instance as the prefix.
Set the parameter value as the host and port where the WebCenter application is deployed, plus the context root; for example:
http://myhost:8888/DocumentsServer
Use the wc_url attribute for action handling in the search UI.
Typically, the search UI uses the URL attribute for action handling. To use WebCenter Resource Action Handling for action handling of search results of the Documents resource type, use the wc_url attribute. Note that only search results with the Documents resource type have the wc_url attribute. Therefore, this must be done conditionally in the search UI code.
Specify the WebCenter Resource Action Handling class for click action of search result.
When a search result is clicked, the resource is rendered in the resource viewer of the resource, if available. The current search results page is over-written. Use Resource Action Framework to change this behavior.
Update the adf-config.xml file of the WebCenter Portal application to specify the WebCenter Resource Action Handling class to use.
Example 40-9 shows how to use PopUpResourceActionViewHandler to show the resource in a popup window when a search result is clicked.
Example 40-9 Specifying PopUp Behavior Handler
xmlns:wpsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/framework/service"
<wpsC:adf-service-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/framework/service">
<resource-handler class="oracle.webcenter.framework.resource.view.PopUpResourceActionHandler"/>
</wpsC:adf-service-config>
Example 40-10 shows how to use NavigationResourceActionHandler to show the resource in the navigation node of the resource when a search result is clicked.
Example 40-10 Specifying the Navigation Handler
xmlns:wpsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/framework/service"
<wpsC:adf-service-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/webcenter/framework/service">
<resource-handler class="oracle.webcenter.portalframework.sitestructure.handler.NavigationResourceActionHandler"/>
</wpsC:adf-service-config>
This section describes common problems and solutions for the Search service.
Problem
There is a set timeout for querying each service. If a particular service does not return search results in the allotted time, then it times out. The Announcements and Discussions services are susceptible to timeouts. (In WebCenter Spaces, pages and Spaces could have timeouts from search execution.)
Solution
To improve performance at design time, you can increase the values (in milliseconds) of timeoutMs and prepare TimeoutMs in adf-config.xml. The following is the relevant fragment of adf-config.xml, found in the Application Resources panel in the ADF META-INF folder:
<execution-properties timeoutMs="3000"prepare TimeoutMs="1000"/>
At runtime, you can configure timeouts using WLST or Enterprise Manager.