| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster Concepts Guide Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.0 |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
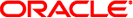
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster Concepts Guide Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.0 |
2. Key Concepts for Hardware Service Providers
Oracle Solaris Cluster System Hardware and Software Components
Software Components for Cluster Hardware Members
Logging Into the Cluster Remotely
SPARC: Oracle Solaris Cluster Topologies
SPARC: Clustered Pair Topology
SPARC: N*N (Scalable) Topology
SPARC: Oracle VM Server for SPARC Software Guest Domains: Cluster in a Box Topology
SPARC: Oracle VM Server for SPARC Software Guest Domains: Clusters Span Two Different Hosts Topology
SPARC: Oracle VM Server for SPARC Software Guest Domains: Redundant I/O Domains
3. Key Concepts for System Administrators and Application Developers
A topology is the connection scheme that connects the cluster nodes to the storage platforms that are used in the cluster. Oracle Solaris Cluster supports any topology that adheres to the following guidelines.
Oracle Solaris Cluster software supports from one to eight cluster nodes in a cluster. Different hardware configurations impose additional limits on the maximum number of nodes that you can configure in a cluster composed of x86 based systems. See x86: Oracle Solaris Cluster Topologies for the supported node configurations.
Shared storage devices must connect to nodes.
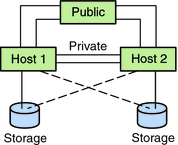
Oracle Solaris Cluster does not require you to configure a cluster by using specific topologies. The following clustered pair topology, which is a topology for clusters that are composed of x86 based nodes, is described to provide the vocabulary to discuss a cluster's connection scheme. This topology is a typical connection scheme.
The following section includes a sample diagram of the topology.
A clustered pair topology consists of two cluster nodes that operate under a single cluster administrative framework. In this configuration, failover occurs only between a pair. However, all nodes are connected by the cluster interconnect and operate under Oracle Solaris Cluster software control. You might use this topology to run a parallel database or a failover or scalable application on the pair.
The following figure illustrates a clustered pair configuration.
Figure 2-12 x86: Clustered Pair Topology
An N+1 topology includes some number of primary cluster nodes and one secondary node. You do not have to configure the primary nodes and secondary node identically. The primary nodes actively provide application services. The secondary node need not be idle while waiting for a primary node to fail.
The secondary node is the only node in the configuration that is physically connected to all the multihost storage.
If a failure occurs on a primary node, Oracle Solaris Cluster fails over the resources to the secondary node. The secondary node is where the resources function until they are switched back (either automatically or manually) to the primary node.
The secondary node must always have enough excess CPU capacity to handle the load if one of the primary nodes fails.
The following figure illustrates an N+1 configuration.
Figure 2-13 x86: N+1 Topology
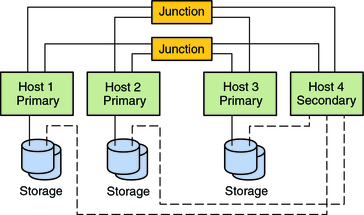
An N*N topology enables every shared storage device in the cluster to connect to every cluster node in the cluster. This topology enables highly available applications to fail over from one node to another without service degradation. When failover occurs, the new node can access the storage device by using a local path instead of the private interconnect.
The following figure illustrates an N*N configuration.
Figure 2-14 SPARC: N*N Topology