A User Interface
Dynamic Converter includes administrative pages that you use to create and administer your dynamic conversion environment:
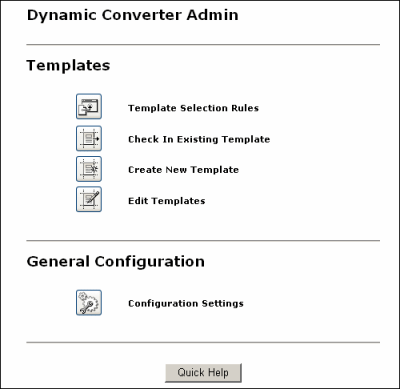
A.1 Dynamic Converter Admin Page
If you click either of the Dynamic Converter Admin links (see "Dynamic Converter Admin Link"), the Dynamic Converter Admin page is displayed.
You can do the following on the Dynamic Converter Admin page:
-
Create and manage template selection rules (see Chapter 3, "Template Rules")
-
Check in existing templates (see Chapter 4, "Conversion Templates")
-
Create new templates (see Chapter 5, "HTML Conversion Templates")
-
Edit existing templates (see Chapter 5, "HTML Conversion Templates")
-
Configure Dynamic Converter settings (see Chapter 2, "Configuring Dynamic Converter")
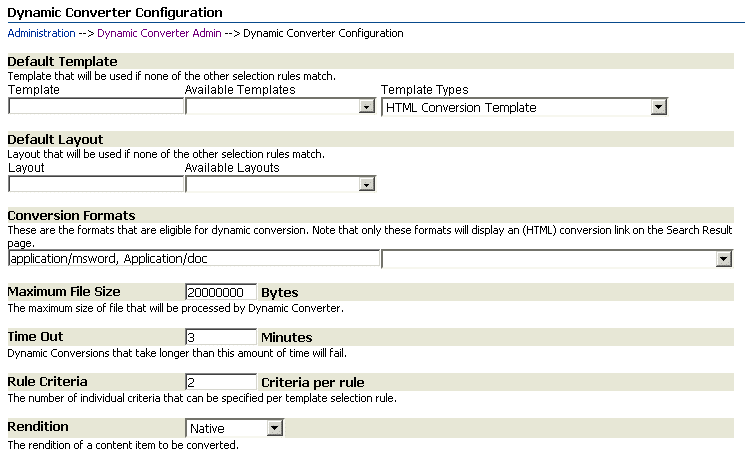
A.2 Dynamic Converter Configuration Page
There are several configuration settings that determine how Dynamic Converter handles source documents. You can specify the default template to use for source documents, the file types to convert, the number of criteria fields available on the template selection rules page, and a number of other Dynamic Converter translation options.
You set these configuration options on the Dynamic Converter Configuration page, which you access by clicking Configuration Settings on the Dynamic Converter Admin page (see "Dynamic Converter Admin Page").
This page is presented in several sections:
When you are done, click the Update button at the bottom of the page to apply any configuration changes you made. Changes made on the Dynamic Converter Configuration page take effect immediately and do not require a restart of the Content Server.
A.2.1 General Conversion Settings
The general settings section of the Dynamic Converter Configuration page enables you to set a number of conversion settings, such as the default template and layout, the supported conversion formats, etc.
The following options are available (for each page section):
| Option | Definition |
|---|---|
| Template | This is the name of the template that is applied to source documents that fall outside of your template selection rules. A default template can be especially useful when you are still setting up your template selection rules. You might, for example, create a blank, or stripped-down, template as the default. |
| Available Templates | This is a list of all the available templates currently stored in the Content Server. |
| Template Types | This is a list of the different types of templates: HTML Conversion Template, Classic HTML Conversion Template, and Script Template. When you choose a template type, a list of available templates of that type are displayed in the Available Templates field.
For more information, see "Template Types". |
| Option | Definition |
|---|---|
| Layout | This is the name of the layout template that is applied to source documents that fall outside of your template selection rules. This only applies to Classic HTML Conversion templates. You might create a default layout template that includes the Content Server borders and navigation. |
| Available Layouts | This is a list of all the available layout templates currently stored in the Content Server. |
| Option | Definition |
|---|---|
| Formats | These are the supported file formats that are converted by Dynamic Converter and as a result, will include an (HTML) link next to them. A file format is the same as a MIME type, and it can be specified using the same comma delimited values (application/rtf, application/msword, etc.). It is important to note that this Format setting serves a different purpose than the Format field on the Template Selection Rules page (see "Template Selection Rules Page"), which assigns templates to source documents based on their file type.
When Dynamic Converter is used with Inbound Refinery (or another conversion add-on), a list of file formats similar to the Available Templates list may be available. If Dynamic Converter is used as a stand-alone system, the list may be empty, and you will need to manually add them. For more information, see "Adding File Formats For Dynamic Conversion". |
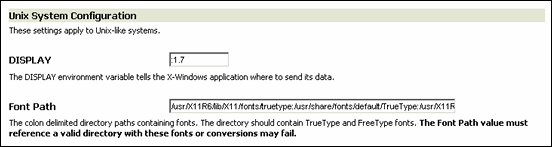
A.2.2 UNIX Configuration Settings
The UNIX System Configuration section on the configuration page enables you to configure a number of UNIX-specific settings. These settings do not appear on the configuration page if you are running Dynamic Converter on a Windows system.
A.2.3 Classic HTML Template Conversion Configuration Settings
Figure A-4 Classic HTML Template Conversion Configuration Settings on Dynamic Converter Configuration Page

The Classic HTML Template Conversion Configuration section on the configuration page enables you to configure a number of settings related to the conversion of Classic HTML Conversion templates (for more information, see Chapter 5, "HTML Conversion Templates").
A.2.4 Script Template Conversion Configuration Settings
Figure A-5 Script Template Conversion Configuration Settings on Dynamic Converter Configuration Page
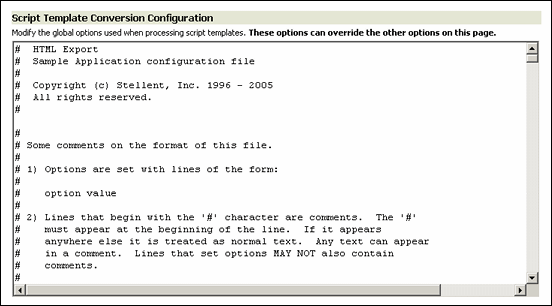
The Script Template Conversion Configuration section on the configuration page enables you to directly access the global script template settings (for more information, see Chapter 7, "Script Templates"). Any changes you make by adding or commenting out parts of this file will override other conversion options. This file contains comments that explain each of the available options.
Text in this box is not verified for correct syntax.
A.2.5 Conversion and Caching Optimizations
The Conversion and Caching Optimizations settings have been present in the config.cfg file, but are now exposed on the configuration page. The authoritative location for these settings is on the configuration page. If you had these set in a previous config.cfg, those values will be used to populate the values on the configuration page.
| Option | Definition |
|---|---|
| Dated Cache Interval Days | This option defines the frequency (in days) with which the conversion cache is evaluated and cached items may be considered for deletion, depending on how long they have been in the cache and their conversion status.
The default is 7 days (i.e., the cache is evaluated once a week). This setting applies to a number of Content Server related products (not just Dynamic Converter). |
| Conversion Cache Expiration Period | This option defines the number of days that must pass before converted items in the cache may be considered for deletion. Date expiration only applies to cached items for documents that are no longer present and to cached items that were not generated by forced conversion (for more information, see "Forced Conversions").
The default is 7 days (i.e., cached items are not considered for deletion unless they are more than one week old). |
| Max. Conversion Cache Size | This option defines the number of megabytes of the file cache that is allowed for dynamic conversions. If it is exceeded, then during the next clean-up cycle (which, by default, is seven days) the caches that have not been accessed for the longest period of time are deleted first. (The list for deleting is sorted by the "last accessed" date in ascending order.) If the cache size limit is not exceeded, then the caches are examined for potential deletion in the same order, but caches that are forced conversions of existing documents are not deleted.
The default is 10,000 (about 9.8 GB). |
| Use Upfront and Forced Conversions | Choose whether all upfront conversion and forced conversions should be enabled (for more information, see "Upfront Conversions" and "Forced Conversions"). |
| Reevaluate conversion rules during re-indexing | Choose whether all upfront and forced conversions should be re-evaluated during a re-index cycle. You might temporarily enable this Element, for example, to re-translate all relevant content items using a new conversion rule that you created. To do so, enable this option, rebuild the Content Server index, and then disable this option again. |
| Reconvert when metadata is updated | Choose whether to convert items again if their metadata is updated. For more information, see "Metadata Changes". |
| Timestamp Check Frequency | Specify the frequency with which Dynamic Converter checks the timestamp of converted content items. For more information, see "Timestamp Checking Frequency". |
| Use database method to determine if content items need reconversion | This option is available only if the "Reconvert when metadata is updated" option is enabled.
It allows you to specify that the database method should be used to determine if a content item's metadata has been updated. For more information, see "Metadata Changes". |
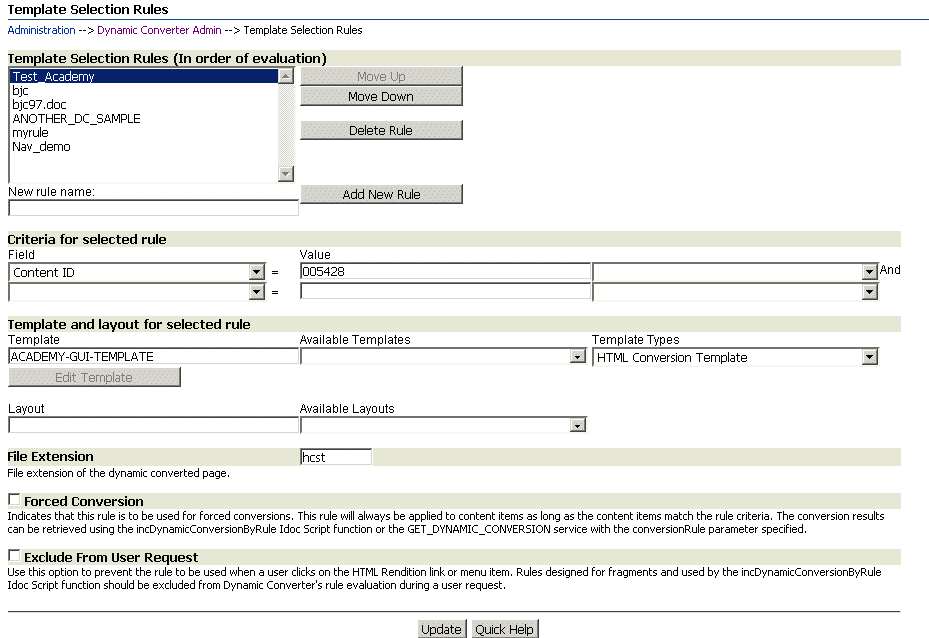
A.3 Template Selection Rules Page
Use the Template Selection Rules page to add, remove, and re-order rules. To access this page, click Template Selection Rules on the Dynamic Converter Admin page (see "Dynamic Converter Admin Page").
Rules are processed from the top down. When a user requests a source document in Content Server, the rule that appears first in this list is processed. If the rule does not apply (for example, the source document might contain metadata not specified in the rule), then the next rule is processed. This process continues until it reaches the last rule in your list.
Once a rule has been added, you can use the criteria section to define or target your rule toward the source documents stored in the Content Server. You might, for example, choose "Type" as a category and "Report" as the name so that your rule applies to all documents with the type "Report."
Lastly, you will choose a template for your rule. In a second template field, you can specify a layout template that complements a Classic HTML Conversion template by establishing a consistent page layout (borders, navigation, scripting, etc.) for your converted documents.
Note:
Rules that were created in a Dynamic Converter version prior to 6.1 appear as a numbered rule in this version of Dynamic Converter. You can continue using that rule or delete it and re-create the rule in Dynamic Converter 11gR1 (you cannot rename a rule).The following options are available (for each page section):
| Option | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Field | These are the metadata fields that you can base a template selection rule on (all fields are case-sensitive). The number of criteria that you can specify for each rule is controlled by a setting on the Dynamic Converter Configuration page (see "Dynamic Converter Configuration Page").
The following metadata fields are available:
If you have added custom metadata to the Content Server, those values will appear in this list too. |
| Value | This is the specific metadata value for your criteria. Source documents are converted with the associated template if their metadata value matches the value listed here.
You can select the desired metadata from the menu to the right of the Value field. You can also use wildcards in the Value field (for example *report*). An * (asterisk) wildcard represents any number of characters, and a ? (question mark) represents a single character. For example, the value report* includes report2001, reporting, and reports. The value report? includes reports and report8, but it does not include report10. |
Template and Layout for Selected Rule
| Option | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Template | This is the name (content ID) of the template that you want to apply to source documents matching the above criteria. |
| Available Templates | This is a list of all the available templates currently stored in the Content Server. |
| Template Types | This is a list of the different types of templates: HTML Conversion Template, Classic HTML Conversion Template, and Script Template. When you choose a template type, a list of available templates of that type will display in the Available Templates field.
For more information, see Chapter 4, "Conversion Templates." |
| Edit Template | This button is activated once you enter a recognized template in the Template text box. Click this button to open the Template Editor. (The Template Editor contains a suite of editing options, all in a graphical user interface.) The first time you click this button, you are prompted to download the Template Editor.
For more information, see "Classic HTML Conversion Template Editor". |
| Layout | This is the name of the layout template. This only applies for the Classic HTML Conversion templates. A layout template is commonly used along with another template to control the placement of items on a web page, in particular, the areas outside of the converted content (borders, navigation, company logo, custom script, etc.). |
| Available Layouts | This is a list of all the available layout templates currently stored in Content Server. |
| Option | Definitions |
|---|---|
| File Extension | Set the file extension of converted pages that use this rule. |
| Forced Conversion | Indicates that this rule is to be used for forced conversion (see "Forced Conversions"). This rule will always be applied to content items as long as the content items match the rule criteria. The conversion results can be retrieved using the incDynamicConversionByRule Idoc Script function or the GET_DYNAMIC_CONVERSION service with the conversionRule parameter specified. |
| Exclude From User Request | Indicates that the rule should not be used when a user clicks on the HTML rendition link or menu item. Rules designed for fragments (see "Fragment-Only Conversions") and used by the incDynamicConversionByRule Idoc Script function should be excluded from Dynamic Converter's rule evaluation during a user request. |
| Update | Click this button to apply any changes that you have made to the Template Selection Rules page. |
| Quick Help | Click this button to display context-sensitive help information about this page. |
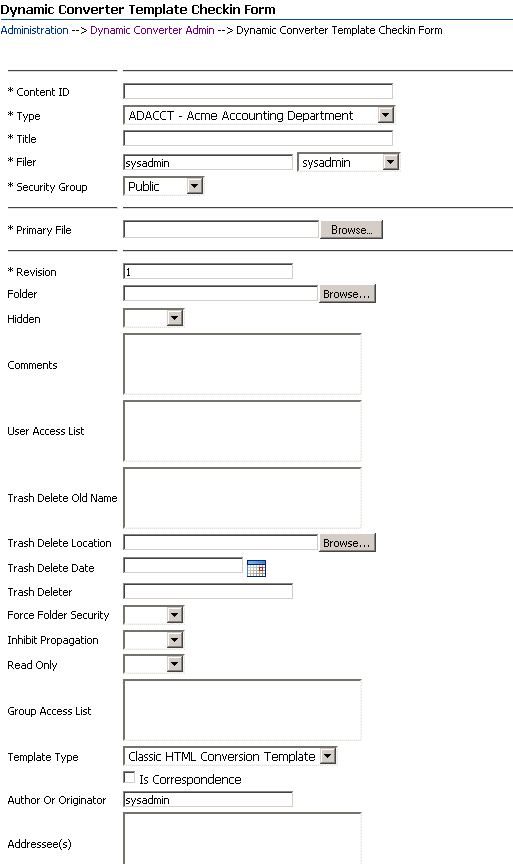
A.4 Template Check-In Form
Use this page to check in an existing Dynamic Converter template file. To access this page, click Check In Existing Template on the Dynamic Converter Admin page (see "Dynamic Converter Admin Page").
This page is very similar to a typical Content Server check-in form. The main difference is the option to choose a template type. It is very important to select the appropriate template type (for more information, see "Template Types") so that your Dynamic Converter menus and the Template Editor function properly.
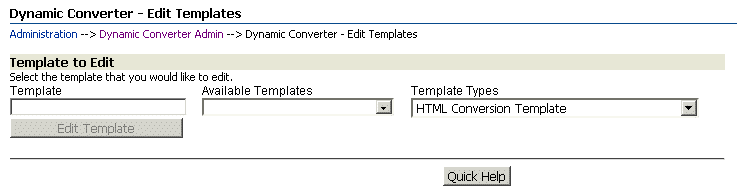
A.5 Edit Templates Page
Use this page to edit an existing template (that is, one that is already checked into the Content Server). To access this page, click Edit Existing Template on the Dynamic Converter Admin page (see "Dynamic Converter Admin Page").
You can either type the content ID of an existing template or, much easier, you can select from the list of templates in the Content Server.
If a known template is not included in the list of available templates, then it was most likely not assigned the correct Template type when it was checked into the Content Server (for more information, see "Checking In a Template"). You then need to open the content information page of the checked-in template and update its template type.
After you specify a template, the Edit Template button becomes available. Click this button to open the Template Editor (for more information, see "About Templates"). The HTML Conversion Editor will be downloaded to your machine.
With some browsers, such as Firefox, you may be prompted for how to handle the file dc_hcmapedit.jnlp. The correct way to open this file is with Java(TM) Web Start Launcher (default).
Note:
The Template Editor comes with its own extensive help system, which can be called from the application's user interface.