2 Using TopLink with WebLogic Server
This chapter introduces how TopLink can be used as the persistence provider for TopLink Java Persistence API (JPA) 2.0 applications deployed to WebLogic Server.
This chapter contains the following sections:
2.1 Understanding TopLink and WebLogic Server
WebLogic Server is a scalable, enterprise-ready Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) application server. WebLogic Server's complete implementation of the Java EE 5.0 specification provides a standard set of APIs for creating distributed Java applications that can access a wide variety of services, such as databases, messaging services, and connections to external enterprise systems. In addition to the Java EE implementation, WebLogic Server enables enterprises to deploy mission-critical applications in a robust, secure, highly available, and scalable environment. These features allow enterprises to configure clusters of WebLogic Server instances to distribute load, and provide extra capacity in case of hardware or other failures. For more details about these and other WebLogic Server features, see Introduction to WebLogic Server.
2.1.1 Advantages to Using TopLink with WebLogic Server
While WebLogic Server can use other persistence providers and TopLink can be used with other application servers, using WebLogic Server with TopLink provides a number of advantages:
-
TopLink is included in all WebLogic Server distributions, and WebLogic Server can be configured so that TopLink is the default persistence provider for WebLogic Server domains, with support for JPA 2.0. See Section 2.3.1, "Task 1: Set TopLink as the Default JPA Provider (WebLogic Server 11g),"and Section 2.3.2, "Task 2: Apply the Patch to Support JPA 2.0 in WebLogic Server 11g."
-
Oracle WebLogic Suite includes Oracle Coherence, which is a Java-based in-memory data-grid product that provides data caching, data replication, and distributed computing services. WebLogic Server and Coherence are tightly integrated and allow applications to use Coherence data caches. WebLogic Server applications can use TopLink Grid, which is an integration between TopLink and Coherence that allows TopLink to use Coherence as a level 2 (L2) cache and persistence layer for entities. How to use these integrations is beyond the scope of this documentation. See Oracle Coherence Developer's Guide and Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle TopLink with Coherence Grid for more information.
Note:
You can also obtain Coherence as a separately-licensed product to use WebLogic Server Standard Edition and WebLogic Server Enterprise Edition. See the links above for more information.
-
TopLink logging integration in WebLogic Server provides a comprehensive, integrated logging infrastructure. See Section 2.3.5, "Task 5: Use or Reconfigure the Logging Integration."
-
WebLogic Server supports the Oracle Application Framework (ADF), an end-to-end Java EE framework, based on Struts and JavaServer Faces (JSF). ADF simplifies application development by providing infrastructure services and a visual and declarative development experience. TopLink and ADF together provide a complete Java EE application infrastructure. How to use ADF is beyond the scope of this documentation. See Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
-
WebLogic Server, TopLink, and ADF are all integrated with JDeveloper, Oracle's integrated development environment (IDE) that provides end-to-end support for modeling, developing, debugging, optimizing, and deploying Java EE applications, including applications that use TopLink as the persistence provider and that are deployed to WebLogic Server. How to use JDeveloper is beyond the scope of this documentation. See
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/jdev/overview/index.htmlfor general information about JDeveloper. For information about JDeveloper tasks, see the JDeveloper online help in the JDeveloper IDE.
2.1.2 The Relationship of TopLink to Other Fusion Middleware Products
Figure 2-1 shows how WebLogic Server and TopLink are related to and used with other Oracle products. You can: use JDeveloper (or Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse or NetBeans) to develop Java EE applications; use TopLink as the persistence provider; use Oracle Coherence (via TopLink Grid integration) for data caching, data replication and distributed computing services; use WebLogic as the application server; and use the Oracle database for persisting data from TopLink JPA applications or XML for persisting data from TopLink MOXy applications.
Figure 2-1 Relationship of WebLogic Server, TopLink, and Related Products
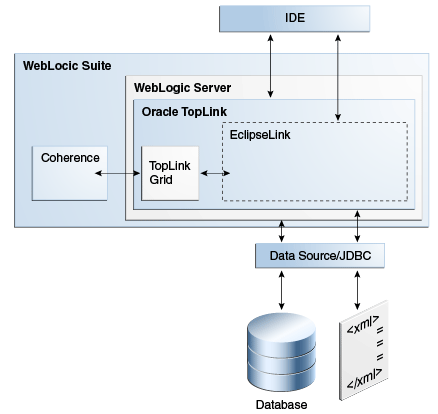
Description of "Figure 2-1 Relationship of WebLogic Server, TopLink, and Related Products "
2.2 What You Need to Start
To develop and deploy TopLink applications to Oracle WebLogic Server, you need:
-
WebLogic Server. This documentation is based on Oracle WebLogic Server release 11gR1 (10.3.6).
For more information and downloads, see
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/weblogic/overview/index.htmlon the Oracle Technology Network.
-
Any compliant JDBC database including Oracle, Oracle Express, MySQL, etc.
For the Oracle database, see
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/enterprise-edition/overview/index.html. For Oracle Express Edition, seehttp://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/express-edition/overview/index.html. For MySQL, seehttp://www.oracle.com/us/products/mysql/index.html. -
While it is not required, you may want to use a Java development environment (IDE) for convenience during development. For example JDeveloper, Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse (OEPE), and Oracle NetBeans all provide sophisticated Java EE development tools. Both JDeveloper and OEPE include embedded versions of WebLogic Server, although this documentation describes a standalone instance of WebLogic Server.
For JDeveloper, see
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/jdev/downloads/index.html. For OEPE, seehttp://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/eclipse/overview/index.html. For NetBeans, seehttp://www.oracle.com/us/products/tools/050845.html.
2.3 Main Tasks
To run TopLink JPA applications in WebLogic server, you must configure WebLogic Server and coordinate certain settings in the server and your application, as described in the following steps.
-
Task 1: Set TopLink as the Default JPA Provider (WebLogic Server 11g)
-
Task 2: Apply the Patch to Support JPA 2.0 in WebLogic Server 11g
-
Task 3: Update the Version of EclipseLink in WebLogic Server
-
Task 6: Add Persistence to Your Java Application Using TopLink
-
Task 8: Extend the Domain to Use Advanced Oracle Database Features
-
Task 12: Configure and Monitor Persistence Settings in WebLogic Server
2.3.1 Task 1: Set TopLink as the Default JPA Provider (WebLogic Server 11g)
You can specify in a JPA application's persistence.xml file which JPA persistence provider to use for each entity. However, if no persistence provider is specified, the domain-wide default provider specified in WebLogic Server is used.
Note:
Oracle TopLink is the default JPA persistence provider in WebLogic Server 12c, so you do not have to do anything further to use it as the default provider in that release and later.
Oracle TopLink is not set as the default JPA persistence provider in WebLogic Server 11g (10.3.n), so you must set it to be the default provider in those releases.
Note:
The reason that TopLink is not the default persistence provider is to maintain backwards-compatibility with previous versions of WebLogic Server 10.3. This allows you to upgrade your version of WebLogic Server to future 10.3 patch sets, without changing the persistence provider.
Changing the default provider does not affect applications that are already deployed. The setting takes effect when the server is restarted or the application is manually redeployed.
To specify TopLink as the default JPA provider in the WebLogic Server Administration Console:
-
Start WebLogic Server and start the Administration Console.
-
If you have not already done so, in the Change Center of the Administration Console, click Lock & Edit.
-
In the left pane of the Console, under Domain Structure, select the domain name.
-
Select Configuration > General > JPA.
-
From the Default JPA Provider list, select TopLink.
-
Click Save.
-
To activate these changes, in the Change Center of the Administration Console, click Activate Changes.
2.3.2 Task 2: Apply the Patch to Support JPA 2.0 in WebLogic Server 11g
WebLogic Server 11gR1 (10.3.6) supports JPA 1.0 by default. However, you can apply a patch to provide support for JPA 2.0. For complete instructions, see "Using JPA 2.0 with TopLink in WebLogic Server" in Programming Enterprise JavaBeans for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Note:
JPA 2.0 is backwards compatible so it can support applications that use the JPA 1.0 API.
Note:
WebLogic Server 12c supports JPA 2.0 by default.
2.3.3 Task 3: Update the Version of EclipseLink in WebLogic Server
TopLink includes all the EclipseLink libraries, which provide the support for JPA, MOXy, DBWS, and other persistence and transformation services. The version of EclipseLink in TopLink may not be the most current available from the Eclipse Foundation. However, you can upgrade the EclipseLink version by using the WebLogic Server FilteringClassLoader and the shared library feature.
For what is supported in various releases, see the following:
-
"Oracle TopLink: JPA Certification" at
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/ias/jpa-082702.html#eclipselink -
"Oracle TopLink and WebLogic Support" at
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/ias/weblogic-086699.html
The FilteringClassLoader provides a mechanism for configuring deployment descriptors to specify that certain packages are always loaded from the application, rather than being loaded by the system classloader. You can use this mechanism to specify that a newer version of EclipseLink be used by an application. For more information about filtering classloader, see "Using a Filtering Classloader" in Developing Applications for Oracle WebLogic Server.
A shared library is a Java EE module that can be shared by multiple enterprise applications. A shared library is deployed to a WebLogic Server target, and it can then be referenced by applications. Upon deployment, WebLogic Server merges the contents of the shared library with the application. In addition, because shared libraries can be packaged as standard Java EE archives, any descriptors are also merged with the application at deployment. For more information about WebLogic Server shared libraries, see "Creating Shared Java EE Libraries and Optional Packages" in Developing Applications for Oracle WebLogic Server.
To update the version of EclipseLink used by applications deployed to WebLogic Server, do the following:
-
Download the
eclipselink-version_no.zipfor the EclipseLink version you want from the EclipseLink web site athttp://www.eclipse.org/eclipselink/downloads/index.php. -
Prepare the shared library as a standard Java EE Enterprise Archive (EAR), named, for example,
eclipselink-shared-lib.ear, containing the following items:META-INF/weblogic-application.xml META-INF/application.xml lib/eclipselink.jar
For more information about creating EARs, see, for example, "Creating and Configuring Web Applications" in Developing Web Applications, Servlets, and JSPs for Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
In the application's
weblogic-application.xmldescriptor file, add aprefer-application-packageselement, with the subelement<package-name>org.eclipse.persistence.*</package-name>, as shown below:<weblogic-application> <prefer-application-packages> <package-name>org.eclipse.persistence.*</package-name> </prefer-application-packages> </weblogic-application> -
Create an
application.xmlfile for the application. This file is necessary to support the runtime library merging. The minimum configuration is as follows:<application> <display-name>eclipselink-shared-lib</display-name> <module> <java></java> </module> </application> -
Add extension name, specification version, and implementation version to the EAR's
META-INF/MANIFEST.MFfile. For example, if you are using ant, you can do the following:<target name="package" depends="prepare"> <jar destfile="dist/${ant.project.name}.ear"> <metainf dir="etc" includes="*.xml"/> <manifest> <attribute name="Extension-Name" value="eclipselink"/> <attribute name="Specification-Version" value="2.0"/> <attribute name="Implementation-Version" value="2.2.0"/> </manifest> <fileset dir="build" includes="**/*"/> </jar> </target>At deployment time, WebLogic Server uses the attributes as metadata for the deployed shared-library.
The final EAR file should look like this:
META-INF/ META-INF/MANIFEST.MF META-INF/application.xml META-INF/weblogic-application.xml lib/ lib/eclipselink.jar
-
Deploy
eclipselink-shared-lib.earto WebLogic Server. This results in a new library being available on the server,eclipselink#2.0@2.2.0. -
In the
weblogic-application.xmlfile of any applications that will use the updated version of EclipseLink, add a reference to the shared library, as shown below:<weblogic-application> <library-ref> <library-name>eclipselink</library-name> <specification-version>2.0</specification-version> <implementation-version>2.2.0</implementation-version> </library-ref> </weblogic-application>
2.3.4 Task 4: Configure JMX MBean Extensions in WebLogic Server
WebLogic Server uses Java Management Extensions (JMX) MBeans to configure, monitor, and manage WebLogic Server resources. For TopLink applications, MBeans are used to monitor and configure aspects of persistence units and are also used for logging.
Note:
When deployed to WebLogic Server, TopLink applications deploy MBeans when they connect to the database, not at deployment time.
For information about how MBeans are used in WebLogic Server, see Developing Custom Management Utilities With JMX for Oracle WebLogic Server and Developing Manageable Applications With JMX for Oracle WebLogic Server.
For information about TopLink logging in WebLogic Server, see Section 2.3.5, "Task 5: Use or Reconfigure the Logging Integration."
By default, when you deploy an EclipseLink application to Oracle WebLogic Server, the EclipseLink runtime deploys the following Java Management Extensions (JMX) MBeans to the Oracle WebLogic Server JMX service for each EclipseLink session:
-
org.eclipse.persistence.services.DevelopmentServices- This class is meant to provide facilities for managing an EclipseLink session internal to EclipseLink over JMX. -
org.eclipse.persistence.services.RuntimeServices- This class is meant to provide facilities for managing an EclipseLink session external to EclipseLink over JMX.
Use the API that this JMX MBean exposes to access and configure your TopLink sessions at run time, using JMX code that you write, or to integrate your TopLink application with a third-party JMX management application, such as JConsole.
To obtain information about accessing information about custom MBeans, you must first enable anonymous lookup and then use a separate tool to access the MBean information.
To enable honeymooner lookup in the Administration Console, do the following:
-
If you have not already done so, in the Change Center of the Administration Console, click Lock & Edit.
-
In the left pane, select your domain to open the Settings page for your domain.
-
Expand Security > General.
-
Select Anonymous Admin Lookup Enabled.
-
To activate these changes, in the Change Center of the Administration Console, click Activate Changes.
For the instructions on how to access the MBean information using various tools, see "Accessing Custom MBeans," in Developing Manageable Applications With JMX for Oracle WebLogic Server.
For information about monitoring custom MBeans in the WebLogic Server Administration Console, see "Monitor Custom MBeans" in Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
2.3.5 Task 5: Use or Reconfigure the Logging Integration
By default, TopLink logging is integrated into the WebLogic Server logging infrastructure. Details about the integration works and how to override it are described in the following sections. For detailed information about WebLogic Server logging, see the following:
-
Using Logging Services for Application Logging for Oracle WebLogic Server
-
Configuring Log Files and Filtering Log Messages for Oracle WebLogic Server
-
The logging topics in Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help
For information about configuring logging for JPA persistence units, see "How to Configure Logging" in the EclipseLink documentation at http://wiki.eclipse.org/EclipseLink/Examples/JPA/Logging.
2.3.5.1 How the Logging Integration Works
By default, the WebLogic Server logging implementation is injected into the persistence context, which results in all TopLink logging messages being output according to the WebLogic Server logging configuration.
As a result of this integration, TopLink logging levels are converted to WebLogic Server logging levels as shown in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 Mapping of TopLink Logging Levels to WebLogic Server Logging Levels
| TopLink Logging Levels | WebLogic Server Logging Levels |
|---|---|
|
ALL, FINEST, FINER, FINE |
DEBUG |
|
CONFIG |
INFO |
|
INFO |
NOTICE |
|
WARNING |
WARNING |
|
SEVERE |
ALERT |
|
OFF |
OFF |
WebLogic Server logging levels are mapped to TopLink levels as shown in Table 2-2.
2.3.5.2 Viewing Persistence Unit Logging Levels in the Administration Console
You can see the TopLink logging level defined for the persistence unit in the Administration Console, as described in Section 2.3.11, "Task 12: Configure and Monitor Persistence Settings in WebLogic Server." However, be aware that this logging level, set in persistence.xml is overridden when the default WebLogic Server/ TopLink logging integration is used. For instructions on overriding the integration, see the next section, Section 2.3.5.3, "Overriding the Default Logging Integration."
When the default integration is used, the EJB logging options for persistence are mapped through and control TopLink's logging output in the Administration Console.
2.3.5.3 Overriding the Default Logging Integration
You set TopLink logging levels in the persistence.xml file. However, when you accept the default logging integration with WebLogic Sever, those settings are ignored, and the logging configuration set in WebLogic Server is used. The TopLink logging levels are used only when you use the native TopLink logging implementation.
You can override the default logging integration by setting eclipselink.logging.logger property name to a different setting, for example:
To enable the default TopLink logging set the eclipselink.logging.logger property as follows:
<property name="eclipselink.logging.logger" value="DefaultLogger"/>
You can also use java.util.logging to use a different logging implementation for TopLink message, for example java.util.logging:
<property name="eclipselink.logging.logger" value="JavaLogger"/>
2.3.5.4 Configuring WebLogic Server to Expose TopLink Logging
If you use the native TopLink logging implementation, you can still display TopLink logging messages in the WebLogic Server domain's log files by configuring WebLogic Server to redirect Java Virtual Machine (JVM) output to the registered log destinations.
For more information and instructions for configuring the redirect, see "Redirecting JVM Output" in Configuring Log Files and Filtering Log Messages for Oracle WebLogic Server. To set this option in the Administration Console, see "Redirect JVM output" in Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
2.3.5.5 Other Considerations
You should be aware of these other considerations:
-
The message ID
2005000is used for all TopLink log messages. -
Some logging messages handled by WebLogic Server's integrated logger may show up in the WebLogic Server console or the server log (depending on the settings of logging levels) during deployment, even though at runtime the application's entity manager factory will use only the TopLink logging infrastructure and only the TopLink logging settings.
-
If you use a different version of EclipseLink than the version bundled in your WebLogic Server installation (by using a filtering classloader), trying to using the default integrated logging can lead to errors, due to classloading conflicts. To work around this issue, explicitly set the
eclipselink.logging.loggerproperty to something other than the integrated WebLogic Server logger.
2.3.6 Task 6: Add Persistence to Your Java Application Using TopLink
Using TopLink JPA to provide persistence for an application is the fundamental task presumed by all the other tasks described in this chapter; yet the actual JPA programming practice is mostly outside the scope of this documentation. WebLogic Server imposes no special requirements on your TopLink application, other than the details described in this chapter.
That is because TopLink is based on EclipseLink, the open source persistence project from the Eclipse Foundation. EclipseLink 2.n is the reference implementation of the Java Persistence API, Version 2.0 specification. TopLink includes all of the EclipseLink jars, plus additional Oracle tools and features. Therefore, you can take advantage of the full range of features and functionality provided by JPA and EclipseLink when using TopLink to add the persistence layer to your Java applications.
This chapter describes features, settings, and tasks that are specific to using TopLink (runtime and API) with WebLogic Server. For information about developing, packaging, and deploying a Java application using JPA, see the following:
-
The EclipseLink project wiki at
http://wiki.eclipse.org/EclipseLink -
The EclipseLink Documentation Center at
http://wiki.eclipse.org/EclipseLink/Documentation_Center -
The Java Persistence API, Version 2.0 specification at
http://jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=317 -
"Part V, Persistence" in "The Java EE 5 Tutorial" at
https://download.oracle.com/javaee/5/tutorial/doc/bnbpy.html -
Any third-party book that describes programming Java applications using JPA
For more information about TopLink features and concepts, see Chapter 1, "Introduction" and Oracle Fusion Middleware Oracle TopLink Concepts.
For related WebLogic Server programming topics, see any book in the WebLogic Server documentation set (see Oracle Fusion Middleware Information Roadmap for Oracle WebLogic Server), in particular the following:
2.3.7 Task 7: Configure a Data Source
In WebLogic Server, you configure database connectivity by adding JDBC data sources to WebLogic Server domains. Each WebLogic data source contains a pool of database connections. Applications look up the data source on the JNDI tree or in the local application context and then reserve a database connection with the getConnection() method. Data sources and their connection pools provide connection management processes to keep the system running efficiently.
For information on using JDBC with WebLogic Server, see the following:
-
For complete documentation about working with JDBC in WebLogic Server, see Configuring and Managing JDBC Data Sources for Oracle WebLogic Server, in particular:
-
For information about working with JDBC data sources in the WebLogic Administration Console, see the topics under "Configure JDBC" in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
2.3.7.1 Ways to Configure Data Sources for JPA Applications
You can configure data sources for JPA applications deployed to WebLogic Server in a variety of ways, including the following:
2.3.7.2 Configure a Globally-Scoped JTA Data Source
The most common data source configuration is a globally-scoped JNDI data source, using JTA for transaction management, specified in the persistence.xml file. Configuration is straightforward, and multiple applications can access the data source.
Do the following:
2.3.7.2.1 Create the Data Source in WebLogic Server
To set up a globally-scoped JNDI data source in the WebLogic Server Administration Console, do the following:
-
Create a new data source, as described in "Configure JDBC generic data sources" in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
Note:
TopLink is compatible with any WebLogic Server data source that can be accessed using standard JNDI data source lookup by name. These instructions describe the wizard for a generic data source.
-
Enter values in the Create a New JDBC data source wizard, according to your needs. See "Create a JDBC Data Source" in Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help. for more information.
Important:
The value used for JNDI Name (on the JDBC Datasource Properties page must be the same as the value used for the
<jta-data-source>element inpersistence.xml. -
Configure connection pools, as described in "Configuring Connection Pool Features" in Configuring and Managing JDBC Data Sources for Oracle WebLogic Server. The connection pool configuration can affect TopLink's ability to handle concurrent requests from the application. Properties should be tuned in the same way any connection pool would be tuned to optimize resources and application responsiveness.
2.3.7.2.2 Configure persisence.xml
In the persistence.xml file, specify that the transaction-type is JTA, and provide the name of the data source in the jta-data-source element (prefaced by jdbc/ or not), as shown in Example 2-1, below:
Example 2-1 persistence.xml File With JNDI Data Source Using JTA
... <persistence-unit name="example" transaction-type="JTA"> <provider>org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider</provider> <jta-data-source>JDBC Data Source-1</jta-data-source> <class>org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.business.Cell</class> <class>org.eclipse.persistence.example.jpa.server.business.CellAttribute</class> </persistence-unit>
2.3.7.3 Configure an Application-Scoped JTA Data Source
To configure an application-scoped data source that use JTA for transaction management, perform the following tasks:
-
"Add the JDBC Module to the WebLogic Application Configuration"
-
"Configure the JPA Persistence Unit to Use the JTA Data Source"
2.3.7.3.1 Specify That the Data Source Is Application-Scoped
To define an application-scoped data source, create a name-jdbc.xml JDBC module file and place it in the META-INF folder of the application's EAR archive. In that file, add <scope>Application</scope> to the jdbc-data-source-params section, as shown in Example 2-2.
Example 2-2 JDBC Data Source Defined in the name-jdbc.xml File
<jdbc-data-source ...>
...
<jdbc-data-source-params>
<jndi-name>SimpleAppScopedDS</jndi-name>
<scope>Application</scope>
</jdbc-data-source-params>
</jdbc-data-source>
Hint:
You can create the framework for the a name-jdbc.xml file by creating a globally scoped data source from the WebLogic Server Administration Console, as described in Section 2.3.7.2, "Configure a Globally-Scoped JTA Data Source," with these differences:
-
Do not associate the data source with a server
-
Add the
<scope>element manually
For more information about JDBC module configuration files and jdbc-data-source (including <jdbc-driver-params> and <jdbc-connection-pool-params>), see "Configuring WebLogic JDBC Resources" in Configuring and Managing JDBC Data Sources for Oracle WebLogic Server.
2.3.7.3.2 Add the JDBC Module to the WebLogic Application Configuration
Add a reference to the JDBC module in the /META-INF/weblogic-application.xml application deployment descriptor in the EAR archive, as shown in Example 2-3. This registers the data source for use in the application.
Example 2-3 JDBC Module Defined in weblogic-application.xml
<wls:module> <wls:name>SimpleAppScopedDS</wls:name> <wls:type>JDBC</wls:type> <wls:path>META-INF/simple-jdbc.xml</wls:path> </wls:module>
For more information about weblogic-application.xml application deployment descriptors, see "Understanding Application Deployment Descriptors" in Deploying Applications to Oracle WebLogic Server and "Enterprise Application Deployment Descriptor Elements" in Developing Applications for Oracle WebLogic Server.
2.3.7.3.3 Configure the JPA Persistence Unit to Use the JTA Data Source
To make it possible for TopLink runtime to lazily look up an application-scoped data source, you must specify an additional data source property in the definition of the persistence unit in persistence.xml. For a JTA data source, add a fully-qualified javax.persistence.jtaDataSource property, with the value java:/app/jdbc/data_source_name, as shown in Example 2-4.
The values of the <jta-data-source> and <javax.persistence.jtaDataSource> properties must match.
Example 2-4 JTA Data Source Definition in persistence.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?> <persistence xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_1_0.xsd" version="1.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"> <persistence-unit name="employee" transaction-type="JTA"> <provider>org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider</provider> <jta-data-source>java:/app/jdbc/SimpleAppScopedDS</jta-data-source> <properties> <property name="javax.persistence.jtaDataSource" value="java:/app/jdbc/SimpleAppScopedDS" /> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
2.3.7.4 Configure a non-JTA Data Source and Manage Transactions in the Application
To configure a non-JTA data source managed by the application, do the same as described in Section 2.3.7.3, "Configure an Application-Scoped JTA Data Source," but configure the JPA persistence unit to use a non-JTA data source by specifying a not-JTA data source, as shown in Example 2-5:
Example 2-5 non-JTA Data Source Definition in persistence.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<persistence xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_1_0.xsd"
version="1.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence">
<persistence-unit name="employee" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<provider>org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider</provider>
<non-jta-data-source>OracleDS</non-jta-data-source>
<properties>
<property name="javax.persistence.nonJtaDataSource"
value="OracleDS" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
Write the code in your application to handle the transactions, as described, for example, in "Transactions in EJB Applications" in Programming JTA for Oracle WebLogic Server.
2.3.7.5 Make Sure the Settings Match
Certain settings in the data source configuration must match certain settings in the application's ejbModule/META-INF/persistence.xml file. For the data source configuration in WebLogic Server, you can check the settings in the configuration files or in the Administration Console.
In the Administration Console, review settings as follows:
-
In the Domain Structure tree, expand Services, then select Data Sources.
-
On the Summary of JDBC Data Sources page, click the name of the data source.
-
On the Settings for data_source_name > Configuration > General page, find the value for JNDI Name, for example localDS. If using JTA, the name must match the
<jta-data-source>inpersistence.xml. -
On the Settings for data_source_name > Configuration > Connection Pool page, review these settings:
-
The value for URL must match the
javax.persistence.jdbc.urlvalue inpersistence.xml, for example,jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:XE
-
The value for Driver Class Name must match the
javax.persistence.jdbc.drivervalue inpersistence.xml, for example (for a JTA data source),oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource.
-
The following examples show the values that must be shared in the domain's config.xml file and the application's persistence.xml file.
2.3.8 Task 8: Extend the Domain to Use Advanced Oracle Database Features
To fully support Oracle Spatial and Oracle XDB mapping capabilities (in both standalone Oracle WebLogic Server and the Oracle JDeveloper integrated WebLogic Server), you must use the toplink-spatial-template.jar and toplink-xdb-template.jar to extend the WebLogic Server domain to support Oracle Spatial and XDB, respectively.
To extend your WebLogic Server domain:
-
Download the
toplink-spatial-template.jar(to support Oracle Spatial) andtoplink-xdb-template.jar(to support Oracle XDB) files from: -
Launch the Config Wizard (
WL_HOME/common/bin/config.sh(or.bat). -
Select Extend an existing WebLogic domain.
-
Browse and select your WebLogic Server domain.
-
Select Extend my domain using an existing extension template.
-
Browse and select the required template JAR (
toplink-spatial-template.jarfor Oracle Spatial,toplink-xdb-template.jarfor Oracle XDB). -
Complete the remaining pages of the wizard.
For information about using WebLogic Server domain templates, see Domain Template Reference.
2.3.9 Task 10: Start WebLogic Server and Deploy the Application
For information about deploying to WebLogic Server see Deploying Applications to Oracle WebLogic Server See also "Deploying Fusion Web Applications" in Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
2.3.10 Task 11: Run the Application
For instructions for starting a deployed application from the WebLogic Administration Console, see "Start and stop a deployed Enterprise application" in Administration Console Online Help.
2.3.11 Task 12: Configure and Monitor Persistence Settings in WebLogic Server
In the WebLogic Server Administration Console, you can configure a persistence unit and configure JTA and non-JTA data sources of a persistence unit, as described below:
-
If you have not already done so, in the Change Center of the Administration Console, click Lock & Edit.
-
In the left pane of the Administration Console, select Deployments.
-
In the right pane, select the application or module you want to configure
-
Select Configuration.
-
Select Persistence.
-
Select the persistence unit you want to configure from the table.
-
Review and edit properties on the configuration pages. For help on any page, click the Help link at the top of the Administration Console.
Properties that can be viewed include:
-
Name
-
Provider
-
Description
-
Transaction type
-
Data cache time out
-
Fetch batch size
-
Default schema name
-
Name
-
Values of persistence unit properties defined in the
persistence.xmlfile, for example,eclipselink.session-name,eclipselink.logging.level, andeclipselink.target-server.
You can also set attributes related to the transactional and non-transactional data sources of a persistence unit, on the Data Sources configuration page.
-
-
To activate these changes, in the Change Center of the Administration Console, click Activate Changes.
For links to other help topics about working with persistence in the Administration Console, search for "Persistence" in the Table of Contents of the Administration Console Online Help.
2.4 Additional Resources
See the following links for more information about Oracle TopLink and Oracle WebLogic Server:
-
EclipseLink Documentation Center at
-
Oracle WebLogic Server documentation, for example,
Oracle Fusion Middleware Information Roadmap for Oracle WebLogic Server
2.4.2 Related Javadoc
For more information, see the following APIs in Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle TopLink.
-
org.eclipse.persistence -
org.eclipse.persistence.jpa.PersistenceProvider -
org.eclipse.persistence.services.mbean