 Optimization
Optimization
This chapter discusses:
Optimization.
PeopleSoft Optimization Framework components.
PeopleSoft Optimization Framework system architecture.
Optimization-based application development.
 Optimization
Optimization
In the context of PeopleSoft Optimization Framework, optimization means deciding on the best course of action given a range of alternatives. You use PeopleSoft Optimization Framework and the PeopleTools environment to build applications that use optimization-based decision-making.
PeopleSoft Optimization Framework enables applications to specify their business objectives, define the conditions, and set resource constraints. PeopleSoft Optimization Framework then applies advanced mathematical modeling and solution techniques to find solutions that meet input criteria. In contrast to sequential, query-based applications, which require users to analyze criteria and make decisions one by one, the solution generated by optimization exceeds, or at least matches, a solution generated by a person.
 PeopleSoft Optimization Framework Components
PeopleSoft Optimization Framework Components
PeopleSoft Optimization Framework contains the following main elements:
Optimization application tables.
PeopleSoft database tables that store source data, result data, control parameters, and user state information.
An instance of the optimization engine is a process managed by a type of PeopleSoft application server, called an Analytic Server. The optimization engine has a generic interface to bind with different optimization plug-ins to provide a variety of optimization services. It also brings data from the optimization application tables into memory. This in-memory data is synchronized with the database changes with each optimization transaction.
Within the analytic server, the optimization dispatcher provides a generic interface for application programmers to use PeopleCode to access the optimization engine.
An OPI is created specifically for optimization-based applications, such as consultant scheduling or supply chain planning and scheduling. The application knowledge and business logic of an optimization problem resides in the OPI. The OPI implements the optimization transactions that solve the problem using the source data as input and generating the result data as output. If your application is delivered with the Optimization PeopleCode plug-in, you are able to adapt the plug-in to a variety of optimization tasks.
Note. An OPI is created by PeopleTools development with support from PeopleSoft application development. An OPI is provided with the installed PeopleSoft applications that use PeopleSoft Optimization Framework. No OPI is in the PeopleTools installation. Your PeopleSoft application documentation discusses the available plugins and their required implementation steps and parameters.
 PeopleSoft Optimization Framework System Architecture
PeopleSoft Optimization Framework System Architecture
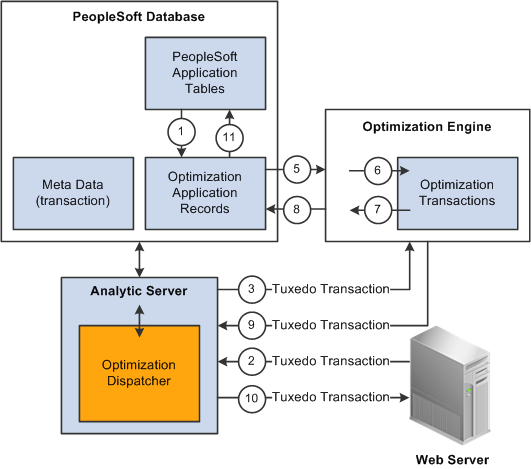
The following diagram illustrates PeopleSoft Optimization Framework architecture components and shows the sequence of use during a typical optimization transaction:
PeopleSoft Optimization Framework architecture
When an optimization-based application runs, the following actions occur:
The source data is loaded from PeopleSoft application tables into the optimization application records.
Depending on the amount of data, this can typically be done as a batch job.
A web server sends a request through Oracle Tuxedo to have the analytic server perform a PeopleSoft transaction using optimization.
Upon receiving the request, the optimization dispatcher, within the analytic server, locates the correct optimization engine and sends the optimization transaction to it through Oracle Tuxedo.
The optimization engine gets the metadata (optimization transaction name, parameters, and data types of the parameters) from the analytic type definition in the PeopleSoft application database.
It uses this information to check the integrity of the optimization transaction request. It also synchronizes the data in memory with changes in the optimization application tables.
The optimization engine reads the changed data (all the data, if this is the first time the data is being read) from the optimization application records into memory.
The optimization engine loads the appropriate OPI and passes the optimization transaction request to it.
The OPI is loaded during the first request to the optimization engine. It remains loaded until the optimization engine is shut down.
The OPI processes the transaction and provides result data in the form of output parameters to the optimization engine.
The OPI might also change data in memory to be saved to the database.
The optimization engine writes the changed data in memory to the optimization application tables.
The optimization engine returns the result data to the optimization dispatcher.
The application server completes the PeopleSoft transaction with the result data and returns a success code to the user and to the web server through Oracle Tuxedo.
After the user is satisfied with the optimization result data, the result data can be copied from the optimization application tables to the PeopleSoft application tables.
 Optimization-Based Application Development
Optimization-Based Application Development
To build an optimization-based application:
Design the analytic type definition.
Define the structure of the optimization application records and the specifications for the optimization transactions that you need for your application. Use PeopleSoft Application Designer to:
Create record definitions for the optimization application records and build them to create the database tables.
Create an analytic type definition, including the record definitions that you created and the specifications for the optimization transactions.
If needed, insert one or more optimization models into the analytic type definition.
Optimization models are developed specifically for, and delivered with, your PeopleSoft application. Each optimization model is a mathematical representation of the business problem for the optimization engine to solve.
Populate the application records with appropriate source data.
Using standard tools (such as PeopleCode, PeopleSoft Application Engine, and PeopleSoft Integration Broker), provide a mechanism to populate the optimization application records with source data. You can also use PeopleSoft application records directly instead of creating special optimization application records. By accessing the tables directly, you use fewer computer resources. However, accessing the application tables directly increases the dependency between the application design and the OPI design.
Note. Though you can populate the source data using PeopleSoft Integration Broker, you cannot actually access the analytic server or use analytic or optimization PeopleCode in a messaging PeopleCode program.
Build the application pages.
Using PeopleSoft Application Designer, build pages using the optimization application records to enable users to edit or view the source and result data and to interact with the optimization application. These pages use the PeopleCode OptEngine or AnalyticInstance class, provided by the optimization dispatcher, to send optimization transactions to the optimization engine. Building pages for optimization applications uses the same process as building pages for any PeopleSoft application.
Retrieve the result data.
Using standard PeopleTools, provide a mechanism to retrieve the result data in the optimization application records and copy it to the PeopleSoft application tables.
Note. If you rename any records or record fields that are used by your optimization-based application, the analytic type and optimization model definitions that use the record or field automatically reflect your changes. However, you must also ensure that any PeopleCode program, Application Engine program, or other tools account for those changes as well.