 Understanding PeopleSoft Open Query
Understanding PeopleSoft Open Query
This chapter provides an overview of PeopleSoft Open Query and discusses:
Supported Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) functions.
PeopleTools initialization procedures.
Connection procedures.
Information procedures.
Catalog procedures (metadata).
Using SQL execution procedures.
SQL execution procedures.
Execution models.
Using retrieval procedures.
Retrieval procedures.
Status and error retrieval procedures.
Transaction and connection termination procedures.
ODBC compliance.
ODBC to RDM data types.
PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC API example.
 Understanding PeopleSoft Open Query
Understanding PeopleSoft Open Query
The PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC driver and API enable third-party reporting tools or applications to access PeopleSoft data in conformance with the PeopleSoft Query access architecture (the embedded SQL access intelligence provided by PeopleSoft Query). The PeopleSoft Query access architecture provides the following key features:
Multiple levels of security
Query authorization
Operator security
Operator profile
Record level
Access group
Row level
Security record
Standard query data access
Access to all supported PeopleSoft databases.
Ability to run stored PeopleSoft queries.
Automatic use of table sets.
Effective-dated output.
Translate values.
International translations.

 Architecture
Architecture
This diagram illustrates the components involved in PeopleSoft Open Query architecture. The blocks containing boldface type represent PeopleSoft Open Query components:
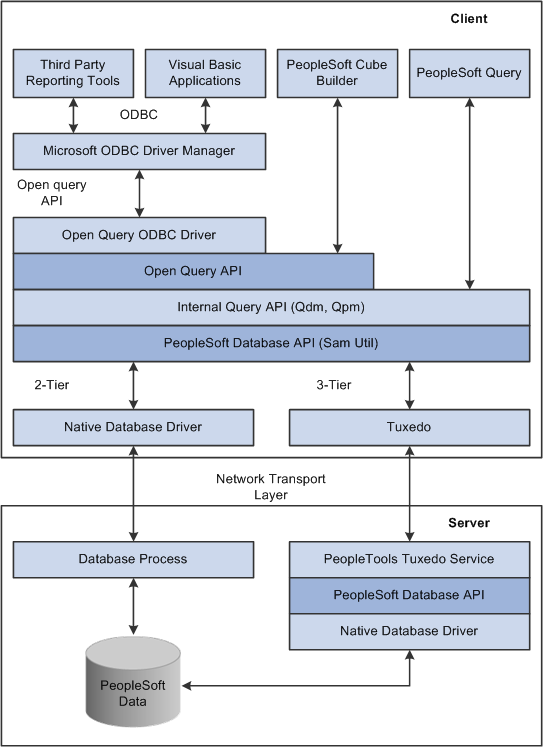
PeopleSoft Open Query architecture
This table describes PeopleSoft Open Query components:
|
Product |
Audience |
Purpose |
|
Open Query ODBC |
Third-party application vendors and implementation partners |
Open, documented API providing access to PeopleSoft Query as a data source. Primary means of achieving programmatic interface to PeopleSoft data. |
|
Open Query API |
PeopleTools development |
PeopleSoft proprietary. Exposes Query definition and runtime functions for use within PeopleTools. API used by ODBC driver and online analytical processing (OLAP). |

 PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC Driver
PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC DriverThe PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC driver is the external means for extracting data from a PeopleSoft database.
Using ODBC as our external API has several advantages:
Third-party tools do not need special information about PeopleSoft data.
Most third-party reporting and query tools already support ODBC.
Custom integration with PeopleTools is no longer required.
Proprietary interface drivers (namely P2SPS.DLL) are eliminated.
ODBC is supported by other application development tools, such as Visual Basic and PowerBuilder.
Connectivity to PeopleSoft data is maintained by the PeopleSoft security architecture.
Extension or modification of driver behavior is allowed by way of the ODBC standard.
The ODBC driver does not have any intrinsic knowledge of PeopleSoft data structures. Only the interface components exposed by way of PeopleSoft Open Query API are required to extract query data for a particular purpose.
This layer provides only the data modification and conversion code necessary to comply with the ODBC software development kit (SDK) standards. None of the PeopleTools structures are exposed at this level.

 PeopleSoft Open Query API
PeopleSoft Open Query API
The ODBC driver presents a stable interface to external applications. The PeopleSoft Open Query API is constantly under construction and therefore is not useful in this capacity. Because modifying behavior between releases presents a challenge when dealing with third-party applications, we created an intermediate layer between the ODBC driver and the underlying PeopleTools manager code. This wrapper code reduces the number of method calls to an acceptable level and allows the PeopleTools development team some leeway when new functionality is required or when the underlying code base is modified.
The PeopleSoft Open Query API enables the external driver (ODBC) and PeopleTools applications to focus solely on providing PeopleSoft data in the formats described by those products. It also abstracts the underlying connective architecture from the upper levels of the interface.
Because the architecture of this API is fluid, it is available only to PeopleTools development.
Note. You cannot use PeopleSoft Open Query APIs to write direct SQL, such as SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE, and so on, against the database. You can use them only to execute stored procedures.

 External Reporting Tools
External Reporting Tools
The PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC driver enables third-party reporting tools or ODBC-enabled development applications to access a PeopleSoft database. The driver enforces user, table, and row-level security through internal PeopleTools APIs. A user can leverage PeopleSoft Query to easily create platform-independent queries that run against any supported PeopleSoft database platform.

 Internet
Internet
The PeopleSoft Open Query API is a valuable link to all external data access mechanisms, including data over the internet.
 Supported ODBC Functions
Supported ODBC Functions
This quick-reference summary lists the ODBC API calls supported by the ODBC driver. API calls that are not supported return a SQL_ERROR. Each call is discussed in further detail in the following sections.
|
ODBC Call |
Function |
|
SQLAllocEnv |
Allocates an environment handle for the ODBC connection. |
|
SQLAllocConnect |
Allocates a connection; returns a connection handle. |
|
SQLAllocStmt |
Allocates a statement handle for the specified connection. |
|
SQLBindCol |
Provides the buffer address for an answer column about to be fetched. |
|
SQLBindParameter |
Provides the value of a parameter (prompt variable) defined in the query. |
|
SQLColAttributes |
Returns result-column descriptor information for a result set. |
|
SQLConnect |
Connects to a PeopleSoft database. |
|
SQLDescribeCol |
Provides descriptors (data type and so on) for a result column. |
|
SQLDescribeParam |
Describes a parameter marker in a statement. |
|
SQLDisconnect |
Disconnects from the data source. |
|
SQLDriverConnect |
Connects to a PeopleSoft database, prompting the user for any login parameters not provided by the caller. |
|
SQLError |
Retrieves information about an error that occurred on a previous call. |
|
SQLExecDirect |
Prepares and executes a query. Note. Only the stored procedure syntax is supported. |
|
SQLExecute |
Executes a previously prepared query. |
|
SQLFetch |
Fetches a row of the answer set into the bound columns. |
|
SQLFreeConnect |
Closes the database connection and frees all resources that are associated with it. |
|
SQLFreeStmt |
Discards all resources that are associated with a previously prepared statement. |
|
SQLGetData |
Retrieves data for a specific column of the current fetched row. (Useful for long data, images, and so on.) |
|
SQLGetFunctions |
Tells applications which ODBC functions this driver supports. |
|
SQLGetInfo |
Retrieves information about the data source. |
|
SQLGetRowCount |
Returns the number of rows affected by the last execution. |
|
SQLGetTypeInfo |
Returns information about data types supported by the data source. |
|
SQLNumParams |
Returns the number of parameters in a statement. |
|
SQLNumResultCols |
Returns the number of result columns in the answer set of a prepared query. |
|
SQLPrepare |
Prepares a query for execution. |
|
SQLProcedureColumns |
Provides a list of queries and result columns available to the current operator and matching the specified qualifiers. |
|
SQLProcedures |
Retrieves a list of available stored procedures (queries). |
|
SQLTransact |
Commits or rolls back the current transaction. |
The ODBC functions in the following table are supported calls with no underlying functionality. These functions exist to ensure compatibility with ODBC applications:
|
ODBC Call |
Function |
|
SQLColumns |
Retrieves column information from the database. |
|
SQLForeignKeys |
Retrieves database information concerning foreign keys. |
|
SQLGetConnectOption |
Gets connection option information. |
|
SQLGetCursorName |
Gets the name of the cursor. |
|
SQLGetStmtOption |
Gets statement option information. |
|
SQLMoreResults |
Returns whether or not another result set is pending. |
|
SQLPrimaryKeys |
Retrieves database information on primary keys. |
|
SQLSetConnectOption |
Sets database connection options. |
|
SQLSetCursorName |
Sets the name of the cursor to be used with the statement. |
|
SQLSetScrollOptions |
Sets options to control cursor scrolling. |
|
SQLSetStmtOption |
Sets options for the statement. |
|
SQLSpecialColumns |
Retrieves information about optimal keys or automatically incremented columns. |
|
SQLStatistics |
Retrieves statistics in tables and indices from the database. |
|
SQLTables |
Retrieves a list of tables or views in the database. |
 PeopleTools Initialization Procedures
PeopleTools Initialization Procedures
This section discusses the PeopleTools initialization procedures in alphabetical order.

 SQLAllocEnv
SQLAllocEnv
Syntax
RETCODE SQLAllocEnv(phenv)
Description
SQLAllocEnv allocates memory for an environment handle and initializes the ODBC call level interface for use by an application.
Parameters
This table describes the parameter:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
phenv |
HENV FAR * |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the environment handle. |

 SQLAllocConnect
SQLAllocConnect
Syntax
RETCODE SQLAllocConnect(henv, phdbc)
Description
SQLAllocConnect allocates memory for a connection handle within the environment, identified by henv. This is called after SQLAllocEnv.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
henv |
HENV |
Input |
Environment handle. |
|
phdbc |
HDBC FAR * |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the connection handle. |

 SQLFreeEnv
SQLFreeEnv
Syntax
RETCODE SQLFreeEnv(henv)
Description
SQLFreeEnv releases an environment handle and frees all memory that is associated with the handle. This is called after SQLFreeConnect.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
henv |
HENV |
Input |
Environment handle. |
 Connection Procedures
Connection Procedures
This section discusses the PeopleTools connection procedures in alphabetical order.
ODBC uses an abstraction that maps a single name (called the data source name or DSN) to all the necessary underlying software components required to access the data. The data source name is chosen by an end user or a system administrator and should express the kind of data that the DSN represents. ODBC data source mapping information is maintained in the registry in Microsoft Windows.
In order to connect to a PeopleSoft data source, several pieces of information are needed. With the introduction in PeopleTools of multiple sign-on capabilities, users must be prompted for required log in information. By default, PeopleTools installs an ODBC data source with the name PeopleSoft PeopleTools. This DSN has no references to PeopleSoft connection information. It is in effect an empty data source. Using this data source forces the underlying PeopleSoft security mechanisms to present the user with a sign-on dialog box. The user completes this as for a normal PeopleSoft application.
As per the ODBC standard, the PeopleSoft driver enables the user to create a data source that provides the information necessary to log in. If the information matches a current session, the user is not prompted to log in again.
The connection environment is affected by the workstation settings for PeopleSoft Process Scheduler. The values for the DBBIN and TOOLBIN are searched for the necessary support files required to log in to a database. Hence these values need to be valid. In the case of a three-tier logon, the value for DBBIN should be set empty.
Note. ODBC supports three connection functions: SQLConnect, SQLDriverConnect, and SQLBrowseConnect. SQLBrowseConnect is not supported by the PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC driver.

 SQLConnect
SQLConnect
Syntax
RETCODE SQLConnect(hdbc, szDSN, cbDSN, szUID, cbUID, szAuthStr, cbAuthStr)
Description
SQLConnect loads a driver and establishes a connection to a data source. The connection handle references storage of all information about the connection, including status, transaction state, and error information.
This function assumes that a connection may be completed by supplying only a DSN, user, and password. It further assumes that the application will either prompt the end user for security information, the security information is hard-coded, or the security information can be obtained from a centralized security server, such as Kerberos.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle. |
|
szDSN |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
Data source name. |
|
cbDSN |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szDSN |
|
szUID |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
User identifier. |
|
cbUID |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szUID. |
|
szAuthStr |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
Authentication string (typically the password). |
|
cbAuthStr |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szAuthStr. |

 SQLDriverConnect
SQLDriverConnect
Syntax
RETCODE SQLDriverConnect(hdbc, hwnd, szConnStrIn, cbConnStrIn, szConnStrOut, cbConnStrOutMax, pcbConnStrOut, fDriverCompletion)
Description
SQLDriverConnect handles the entire connection process for an application, prompting the end user for any information to complete the connection. The programmer can specify as much or as little about the connection as necessary. The following example illustrates the simplest case, in which the application does not specify any information at all about the connection. It supplies the connection handle returned from SQLAllocConnect, a window handle, and option specification of SQL_DRIVER_COMPLETE, and zero or NULL for the rest of the arguments.
rc = SQLDriverConnect(hdbc, hwnd, NULL, 0, NULL, 0, 0, SQL_DRIVER_COMPLETE);
The following keywords are used and supported by the PeopleSoft ODBC driver:
DSN: Data source name required by ODBC.
APPNAME: Application server name used for three-tier logon only.
DBTYPE: Database type of login can be any of the following values:
DB2: DB2 using Centura SQL network.
DB2400: DB2 on AS/400 using client access.
DB2ODBC: DB2 using the IBM ODBC driver.
DB2UNIX: DB2 UNIX driver.
ORACLE: Oracle using the OCI interface.
INFORMIX: Native Informix.
SYBASE: Native Sybase.
MICROSFT: SQL Server using ODBC.
APPSRV: Used to indicate that the database name is actually an application server name.
DBNAME: Name of the database or alias.
DBQ: Used to combine values separated by a slash (/), such as APPNAME/DBTYPE/DBNAME. The APPNAME value and the following slash are dropped when not in three-tier.
SERVER: Name of the database server, used by Sybase and Informix.
UID: PeopleSoft user ID.
PWD: Password associated with the PeopleSoft user.
The driver uses any information it retrieves from the ODBC.INI file or registry to augment the information passed to it in the connection string. If the information in the ODBC.INI file or registry duplicates information in the connection string, the driver uses the information in the connection string.
The existing PeopleSoft database connection dialog box prompts the user for any required connection information.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle. |
|
hwnd |
HWND |
Input |
Window handle. The application can pass the handle of the parent window, if applicable, or a null pointer if either the window handle is not applicable or if SQLDriverConnect does not present any dialog boxes. |
|
szConnStrIn |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
A full connection string, a partial connection string, or an empty string. |
|
cbConnStrIn |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szConnStrIn. |
|
szConnStrOut |
UCHAR FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the completed connection string. Upon successful connection to the target data source, this buffer contains the completed connection string. Applications should allocate at least 255 bytes for this buffer. |
|
cbConnStrOutMax |
SWORD |
Input |
Maximum length of the szConnStrOut buffer. |
|
pcbConnStrOut |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to the total number of bytes returned in szConnStrOut. If the number of bytes is greater than or equal to cbConnStrOutMax, the completed connection string in szConnStrOut is truncated to cbConnStrOutMax -1. |
|
fDriverCompletion |
UWORD |
Input |
Flag that indicates whether the Driver Manager or the driver must prompt for more connection information: SQL_DRIVER_PROMPT, SQL_DRIVER_COMPLETE, SQL_DRIVER_COMPLETE_REQUIRED, or SQL_DRIVER_NOPROMPT. |
 Information Procedures
Information Procedures
ODBC defines these functions as a means for the application to get information about the ODBC driver and data source. Typically, the application calls these functions passing a value of the particular type of information of interest. These values are numerous and are defined in the Microsoft ODBC SDK reference manual.

 SQLGetInfo
SQLGetInfo
Syntax
RETCODE SQLGetInfo(hdbc, fInfoType, rgbInfoValue, cbInfoValueMax, pcbInfoValue)
Description
SQLGetInfo returns general information about the driver and data source that is associated with a connection handle.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle. |
|
fInfoType |
UWORD |
Input |
Type of information. FInfoType must be a value representing the type of interest. |
|
rgbInfoValue |
PTR |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the information. Depends on the fInfoType requested. |
|
cbInfoValueMax |
SWORD |
Input |
Maximum length of the rgbInfoValue buffer. |
|
pcbInfoValue |
SWORD FAR * |
Output |
The total number of bytes (excluding the null termination byte for character data) available to return in rgbInfoValue. |

 SQLFunctions
SQLFunctions
Syntax
RETCODE SQLGetFunctions(hdbc, fFunction, pfExists))
Description
SQLGetFunctions returns information about whether a driver supports a specific ODBC function.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle. |
|
fFunction |
UWORD |
Input |
SQL_API_ALL_FUNCTIONS or a #define value that identifies the ODBC function of interest. |
|
pfExists |
UWORD FAR * |
Output |
If fFunction is SQL_API_ALL_FUNCTIONS, pfExists points to a UWORD array with 100 elements. The array is indexed by #define values that are used by fFunction to identify each ODBC function; some elements of the array are unused and reserved for future use. An element has a value of True if it identifies an ODBC function that is supported by the driver. It has a value of False if it identifies an ODBC function that is not supported by the driver or does not identify an ODBC function. |

 SQLGetTypeInfo
SQLGetTypeInfo
Syntax
RETCODE SQLGetTypeInfo(hstmt, fSqlType)
Description
SQLGetTypeInfo returns information about data types that are supported by the data source. The driver returns the information in the form of a SQL result set.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle for the result set. |
|
fSqlType |
SWORD |
Input |
The SQL data type. |
 Catalog Procedures (Metadata)
Catalog Procedures (Metadata)
ODBC listing procedures supply the client with catalog table information. The PeopleSoft ODBC driver supports listings of queries and columns using PeopleSoft metadata.

 SQLProcedures
SQLProcedures
Syntax
RETCODE SQLProcedures(hstmt, szProcQualifier, cbProcQualifier, szProcOwner, cbProcOwner, szProcName, cbProcName)
Description
SQLProcedures returns the list of procedure names that are stored in a specific data source. Procedure is a generic term used to describe executable objects or named entities that can be invoked using input and output parameters and that can return result sets similar to the results returned by SQL Select statements.
This function is typically used before statement execution to retrieve information about procedures available from the data source catalog.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
szProcQualifier |
UCHAR FAR * |
Input |
Procedure qualifier. |
|
cbProcQualifier |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szProcQualifier.. |
|
szProcOwner |
UCHAR FAR * |
Input |
String search pattern for procedure owner names. |
|
cbProcOwner |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szProcOwner. |
|
szProcName |
UCHAR FAR * |
Input |
String search pattern for procedure names. |
|
cbProcName |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szProcName. |
SQLProcedures returns the results as a standard result set (when SQLFetch is called), ordered by PROCEDURE_QUALIFIER, PROCEDURE_OWNER, PROCEDURE_NAME, PROCEDURE_REMARKS, and PROCEDURE_TYPE.
This table lists the columns that are in the PeopleSoft result set:
|
Column Name |
Data Type |
Description |
|
PROCEDURE_QUALIFIER |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
‘’ |
|
PROCEDURE_OWNER |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
‘QUERY’ |
|
PROCEDURE_NAME |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
Query name with punctuation and spaces converted to underscore |
|
REMARKS |
SQL_CHAR(256) |
Description of the Query, currently unused |
|
PROCEDURE_TYPE |
SQL_INT |
SQL_PT_PROCEDURE |

 SQLProcedureColumns
SQLProcedureColumns
Syntax
RETCODE SQLProcedureColumns(hstmt, szProcQualifier, cbProcQualifier, szProcOwner, cbProcOwner, szProcName, cbProcName, szColumnName, cbColumnName)
Description
SQLProcedureColumns returns a list of input and output parameters, as well as the columns that make up the result set for the specified procedures. The driver returns the information as a result set on the specified statement handle.
This function is typically used before statement execution to retrieve information about procedure parameters and columns from the data source’s catalog.
The PeopleSoft driver returns information for the first query that is requested only. It does not return results for multiple queries. The driver will the new query API functions QpmDescribeParm and QpmDescribeCol. QpmDescribeParm walks the query definition that is stored in hstmt and for each prompt variable returns a SQLProcedureColumns result row of COLUMN_TYPE equal to SQL_PARM_INPUT. QpmDescribeParm walks the same query definition and for each result column returns a SQLProcedureColumns result row of COLUMN_TYPE equal to SQL_RESULT_COL. The szProcQualifier and szProcOwner criteria are ignored. The result set returned is for the current user ID. The result set columns for Procedure Qualifier and Procedure Remarks do not apply and are set to NULL with a one-byte column length. The Procedure Owner column is set to either the user ID or Public.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle |
|
szProcQualifier |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
Procedure qualifier name |
|
cbProcQualifier |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szProcQualifier |
|
szProcOwner |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
String search pattern for procedure owner names |
|
cbProcOwner |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szProcOwner |
|
szProcName |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
String search pattern for procedure names |
|
cbProcName |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szProcName |
|
szColumnName |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
String search pattern for column names |
|
cbColumnName |
SWORD |
Input |
Length of szColumnName |
SQLProcedureColumns returns the results as a standard result set (when SQLFetch is called), ordered by PROCEDURE_QUALIFIER, PROCEDURE_OWNER, PROCDURE_NAME, and COLUMN_TYPE.
This table lists the columns in the result set:
|
Column Name |
Data Type |
Description |
|
PROCEDURE_QUALIFIER |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
N/A |
|
PROCEDURE_OWNER |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
N/A |
|
PROCEDURE_NAME |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
Procedure identifier |
|
COLUMN_NAME |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
Procedure column identifier |
|
COLUMN_TYPE |
SQL_INT |
SQL_PARAM_INPUT or SQL_RESULT_COL |
|
DATA_TYPE |
SQL_INT |
SQL data type |
|
TYPE_NAME |
SQL_CHAR(128) |
Data type name of procedure column |
|
PRECISION |
SQL_INT |
Precision of the procedure column |
|
LENGTH |
SQL_INT |
Length in bytes of data transferred on a SQLGetData or SQLFetch operation |
|
SCALE |
SQL_INT |
Scale of procedure column |
|
RADIX |
SQL_INT |
N/A |
|
NULLABLE |
SQL_INT |
Whether the procedure column accepts a NULL value |
|
REMARKS |
SQL_CHAR(256) |
A description of the procedure column |
 Using SQL Execution Procedures
Using SQL Execution Procedures
The minimum ODBC SQL conformance level requires the driver to support:
Data Manipulation Language (DML): simple Select, Insert, Update Searched, and Delete Searched.
Expressions: simple (such as A > B + C).
Data types: Char, Varchar, or Long Varchar.
The PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC driver does not support the minimum SQL conformance level even though it reports supporting extended syntax. PeopleSoft Open Query supports only the ODBC extended SQL grammar for stored procedures. The stored procedure syntax is:
{[? = ] call procedure_name [ (param, ...)]}
The stored procedure execution model supports the independent creation of a SQL statement. Independent creation is done through PeopleSoft Query. However, instead of a stored procedure, the result is a PeopleSoft Query object.
A statement handle references statement information, such as network information, SQLSTATE values and error messages, cursor names, number of result set columns, and status information for SQL statement processing. Before an application can execute a SQL statement, it must allocate a statement handle for the statement. To allocate a statement handle, an application declares a variable of type hstmt and passes its address to SQLAllocStmt.
See Also
 SQL Execution Procedures
SQL Execution ProceduresThis section discusses the SQL execution procedures in alphabetical order.

 SQLAllocStmt
SQLAllocStmt
Syntax
RETCODE SQLAllocStmt(hdbc, phstmt)
Description
SQLAllocStmt allocates memory for a statement handle and associates the statement handle with the connection that is specified by the connection handle.
If the application calls SQLAllocStmt with a pointer to a valid statement handle, the driver overwrites the statement handle without regard to its previous contents.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle. |
|
phstmt |
HSTMT FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the statement handle. |

 SQLExecDirect
SQLExecDirect
Syntax
RETCODE SQLExecDirect(hstmt, szSqlStr, cbSqlStr)
Description
SQLExecDirect executes a preparable statement, using the current values of the parameter marker variables if any parameters exist in the statement. The application calls SQLExecDirect to send a SQL statement to the data source. The driver modifies the statement to use the form of SQL used by the data source, then submits it to the data source. In particular, the driver modifies the escape clauses that are used to define ODBC-specific SQL grammar extensions.
The application can include one or more parameter markers in the SQL statement. To include a parameter marker, the application embeds a question mark (?) into the SQL statement at the appropriate position. It is unnecessary to use any parameter markers, as PeopleSoft Query objects know the exact number of prompt values. The PeopleSoft driver prompts the user for input values if no values were supplied through the input or the SQLBindParameter function.
Only stored procedures (predefined queries) are supported.
In addition to the ODBC error conditions, the PeopleSoft driver returns an error condition if the following conditions are true:
A valid PeopleSoft query name cannot be found or loaded.
Prompt values cannot be satisfied using a prompting page.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle |
|
szSqlStr |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
SQL statement to be executed. |
|
cbSqlStr |
SDWORD |
Input |
Length of szSqlStr. |

 SQLPrepare
SQLPrepare
Syntax
RETCODE SQLPrepare(hstmt, szSqlStr, cbSqlStr)
Description
SQLPrepare prepares a SQL string for execution. The application calls SQLPrepare to send a SQL statement to the data source for preparation. The application can include one or more parameter markers in the SQL statement. To include a parameter marker, the application embeds a question mark (?) into the SQL string at the appropriate position. After a statement is prepared, the application uses hstmt to refer to the statement in later function calls. The prepared statement that is associated with the hstmt may be executed again by calling SQLExecute until the application frees the hstmt with a call to SQLFreeStmt with the SQL_DROP option or until the hstmt is used in a call to SQLPrepare, SQLExecDirect, or one of the catalog functions (SQLColumns, SQLTables, and so on). After the application prepares a statement, it can request information about the format of the result set.
Only stored procedures (predefined queries) are supported.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
szSqlStr |
UCHAR FAR* |
Input |
SQL statement to be executed. |
|
cbSqlStr |
SDWORD |
Input |
Length of szSqlStr. |

 SQLExecute
SQLExecute
Syntax
RETCODE SQLExecute(hstmt)
Description
SQLExecute executes a prepared statement, using the current values of the parameter marker variables if any parameter markers exist in the statement. SQLExecute executes a statement prepared by SQLPrepare. After the application processes or discards the results from a call to SQLExecute, the application can call SQLExecute again with new parameter values.
To execute a Select statement more than once, the application must call SQLFreeStmt with the SQL_CLOSE parameter before reissuing the Select statement.
As in the SQLExecDirect function, the PeopleSoft ODBC driver prompts the user for input values if they have not been supplied.
Note. For applications to be flexible enough for using SQL for a particular purpose, you must provide the application a means to query the ODBC driver for information pertaining to required storage and data types. This is done using descriptive functions defined by the ODBC specification. ODBC-enabled applications use these functions to dynamically query the driver for information about the result set and the input and output values.
Parameters
This table describes the parameter:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |

 SQLColAttributes
SQLColAttributes
Syntax
RETCODE SQLColAttributes(hstmt, icol, fDescType, rbgDesc, cbValueMax, pcbValue)
Description
SQLColAttributes returns descriptor information for a column in a result set; it cannot be used to return information about the bookmark column (column 0). Descriptor information is returned as a character string, a 32-bit descriptor-dependent value, or an integer value.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
icol |
UWORD |
Input |
Column number of result data. |
|
fDescType |
UWORD |
Input |
Valid descriptor type. |
|
rbgDesc |
PTR |
Output |
Pointer to storage for descriptor information. |
|
cbValueMax |
SWORD |
Input |
Maximum buffer size. |
|
pcbValue |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Output length of data in buffer. |

 SQLDescribeCol
SQLDescribeCol
Syntax
RETCODE SQLDescribeCol(hstmt, icol, szColName, cbColNameMax, pcbColName, pfSqlType, pcbColDef, pibScale, pfNullable)
Description
SQLDescribeCol returns the result descriptor, column name, type, precision, scale, and nullability for one column in the result set. An application typically calls SQLDescribeCol after a call to SQLPrepare and before or after the associated call to SQLExecute. An application can also call SQLDescribeCol after a call to SQLExecDirect.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
icol |
UWORD |
Input |
Column number of result data. |
|
szColName |
UCHAR FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the column name. |
|
cbColNameMax |
SWORD |
Input |
Maximum length of the szColName buffer. |
|
pcbColName |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Total number of bytes available to return in szColName. |
|
pfSqlType |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
The SQL data type of the column. |
|
pcbColDef |
UDWORD FAR* |
Output |
The precision of the column on the data source. |
|
pibScale |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
The scale of the column on the data source. |
|
pfNullable |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Indicates whether the column allows NULL values. |

 SQLDescribeParam
SQLDescribeParam
Syntax
RETCODE SQLDescribeParam(hstmt, ipar, pfSqlType, pcbColDef, pibScale, pfNullable)
Description
SQLDescribeParam returns the description of a parameter marker that is associated with a prepared SQL statement. In terms of PeopleSoft Query objects, this is the description of the prompt values required to fulfill the query keys.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
ipar |
UWORD |
Input |
Marker number. |
|
pfSqlType |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the SQL type. |
|
pcbColDef |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to storage for precision of value. |
|
pibScale |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to storage for scale of value. |
|
pfNullable |
UDWORD FAR* |
Output |
Pointer to storage for nullable flag. |

 SQLGetRowCount
SQLGetRowCount
Syntax
RETCODE SQLRowCount(hstmt, pcrow)
Description
SQLRowCount returns the number of rows affected by an Update, Insert, or Delete statement or by a SQL_UPDATE, SQL_ADD, or SQL_DELETE operation in SQLSetPos. If SQLRowCount is called during a fetch cycle, the value returned is the number of rows returned to the application at the current position.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
pcrow |
SDWORD FAR * |
Input |
Pointer to storage of the row counter. |

 SQLNumParams
SQLNumParams
Syntax
RETCODE SQLNumParams(hstmt, pccol)
Description
SQLNumParams returns the number of parameters in a SQL statement.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle |
|
pccol |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Number of parameters in the statement. |

 SQLNumResultCols
SQLNumResultCols
Syntax
RETCODE SQLNumResultCols(hstmt, pccol)
Description
SQLNumResultCols returns the number of columns in the result set. SQLNumResultCols can be called successfully only when the statement handle is in the prepared or executed state. An application typically would use the value returned in pccol in a loop and call SQLDescribeCol for each column in the result set.
An application retrieves an entire row of values using a technique called binding. Binding associates the data from the data source with variables in the application program. There are two directions of binding: input and output. Input data must always be bound. On output, when a result column is bound, the variable receives the value for that column each time a new row is fetched. The following example shows how this technique differs from SQLGetData:
/* for all columns in the current result set */ for (i = 0; i < columns; i++) SQLBindCol(hstmt, ...,&value[i], ...) while (SQL_SUCCESS == (rc = SQLFetch(hstmt))) /* value[ i .. n] contains data for current row */
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle |
|
pccol |
SWORD FAR* |
Output |
Number of columns in the result set. |

 SQLBindCol
SQLBindCol
Syntax
RETCODE SQLBindCol(hstmt, icol, fCType, rbgValue, cbValueMax, pcbValue)
Description
SQLBindCol assigns the storage and data type for a column in a result set.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
icol |
UWORD |
Input |
Column number of result data. |
|
fCType |
SWORD |
Input |
The C data type of the result data. |
|
rbgValue |
PTR |
Both |
A pointer to storage for the result column. |
|
cbValueMax |
SDWORD |
Input |
Maximum length of the rgbValue buffer. |
|
pcbValue |
SDWORD FAR* |
Both |
A pointer to a buffer for the SQL_NULL_DATA or the number of bytes available to return in rgbValue prior to calling SQLFetch. |

 SQLBindParameter
SQLBindParameter
Syntax
RETCODE SQLBindParameter(hstmt, ipar, fParamType, fCType, fSqlType, cbColDef, ibScale, rbgValue, cbValueMax, pcbValue)
Description
An application calls SQLBindParameter to bind each parameter marker in a SQL statement. Bindings remain in effect until the application calls SQLBindParameter again or until the application calls SQLFreeStmt with the SQL_DROP or SQL_RESET_PARAMS option.
An application can use SQLBindParameter to supply the prompt values for a PeopleSoft query. SQLBindParameter calls the new function, ODBCBindParm. ODBCBindParm converts the ODBC C data type, fCType, to the ODBC SQL data type, fSqlType. It then maps the ODBC SQL data type to a supported PeopleSoft RDM data type and calls the appropriate internal bind function.
An ODBC driver is required to support conversions from all ODBC C data types to the ODBC SQL data types that they support.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle |
|
ipar |
UWORD |
Input |
Parameter number, ordered sequentially left to right, starting at 1. |
|
fParamType |
SWORD |
Input |
The type of the parameter. |
|
fCType |
SWORD |
Input |
The C data type of the parameter. |
|
fSqlType |
SWORD |
Input |
The SQL data type of the parameter. |
|
cbColDef |
UDWORD |
Input |
The precision of the column or expression of the corresponding parameter marker. |
|
ibScale |
SWORD |
Input |
The scale of the column or expression of the corresponding parameter marker |
|
rbgValue |
PTR |
Both |
A pointer to a buffer for the parameter’s data. |
|
cbValueMax |
SDWORD |
Input |
Maximum length of the rgbValue buffer. |
|
pcbValue |
SDWORD FAR* |
Both |
A pointer to a buffer for the parameter’s length. |
An application may also supply prompt values as literal strings embedded in the SQL statement string. For example:
SQLExecDirect(hstmt, "{call query.myquery(8001, NEWGN)}", SQL_NTS);
If prompt values are not provided, PeopleSoft Query prompts the user for each required value at the time of statement execution.
See Also
 Execution Models
Execution Models
ODBC supports three execution models. Each accomplishes the same tasks but differs from the others with regard to when and where (on the client or on the server) each step is performed.
In this model, the SQL statement is specified, sent to the server, and executed all in one step. This model is best suited for SQL statements for a particular purpose or SQL statements that are executed only once. Parameters can be used, but they act merely as placeholders that the driver replaces with the parameter values before it sends the SQL statement to the server.
The DBMS discards the optimization information that is used to execute the SQL statement after execution is complete. If the same statement is specified again with SQLExecDirect, the entire process of parsing and optimizing happens again.
In this model, the SQL statement is prepared (sent to the server, parsed, and optimized) first and executed later. When the statement is executed, what flows to the server is not the SQL statement itself, but a way of referencing the statement so that the access plan can be executed immediately. Parameters are often used in these SQL statements, so the only items that flow to the server are the reference to the access plan and the parameter values, not the entire SQL statement.
The Prepare/Execute model should be used when repeated execution of the same SQL statement is needed and when the SQL statement must be constructed dynamically during runtime. To use this model, the application calls SQLPrepare and then (presumably in a loop) calls SQLExecute.
The stored procedure model is like the Prepare/Execute model except that with stored procedures, the preparation step can be done independently from the application and the stored procedure persists beyond the runtime of the application. To use stored procedures in ODBC, the application calls SQLExecDirect but uses the SQL statement to specify the stored procedure name, as illustrated in the following example:
SQLExecDirect(hstmt, "{call query.proc1(?,?,?)}", SQL_NTS);
 Using Retrieval Procedures
Using Retrieval Procedures
For row-returning statements, such as Select statements or stored procedures, ODBC provides three ways to retrieve data. Using a single function call, an application can retrieve a single value, an entire row of values, or multiple rows of values. The PeopleSoft driver supports only the first two methods: single value and entire row.
One way that an application can retrieve data is by using a function call (SQLGetData) for every column in every row. The application supplies function arguments that specify the column number and a variable in which to receive the data. After the function call has been successfully executed, the value for the given column is returned in the variable. The application uses two loops to retrieve an entire result set, as in this example:
/* For all rows */ while (SQL_SUCCESS == (rc = SQLFetch(hstmt))) /* for all columns in current results set */ for (colnum = 1; colnum <= columns; colnum++) SQLGetData(hstmt, colnum, ..., &value, ..)
SQLGetData is also used for the piecemeal retrieval of large text and binary data (such as images). It is often difficult or impossible for an application to allocate a single piece of memory big enough to hold a large data object, such as a 50-page document or a high-density bitmap.
 Retrieval Procedures
Retrieval ProceduresThis section discusses the retrieval procedures in alphabetical order.

 SQLFetch
SQLFetch
Syntax
RETCODE SQLFetch(hstmt)
Description
SQLFetch fetches a row of data from a result set. The driver returns data for all columns that were bound to storage locations with SQLBindCol. SQLFetch positions the cursor on the next row of the result set. When the cursor is positioned to the last row of the result set, SQLFetch returns SQL_NO_DATA_FOUND.
If the application called SQLBindCol to bind columns, SQLFetch stores data in the locations specified by the calls to SQLBindCol. If the application does not call SQLBindCol to bind any columns, SQLFetch does not return any data; it just moves the cursor to the next row. An application can call SQLGetData to retrieve data not previously bound to a storage location.
Parameters
This table describes the parameter:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle |

 SQLGetData
SQLGetData
Syntax
RETCODE SQLGetData(hstmt, icol, fCType, rbgValue, cbValueMax, pcbValue)
Description
SQLGetData returns result data for a single unbound column in the current row. The application must call SQLFetch to position the cursor on a row of data before it calls SQLGetData. You can use SQLBindCol for some columns and use SQLGetData for others within the same row. This function can be used to retrieve character or binary data values in parts from a column with a character, binary, or data-source-specific data type (for example, data from SQL_LONGVARBINARY or SQL_LONGVARCHAR columns).
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle. |
|
icol |
UWORD |
Input |
Column number of result data. |
|
fCType |
SWORD |
Input |
The C data type of the result data. |
|
rbgValue |
PTR |
Both |
A pointer to storage for the result column. |
|
cbValueMax |
SDWORD |
Input |
Maximum length of the rgbValue buffer. |
|
pcbValue |
SDWORD FAR* |
Both |
A pointer to a buffer for the SQL_NULL_DATA or the number of bytes available to return in rgbValue prior to calling SQLFetch. |
 Status and Error Retrieval Procedures
Status and Error Retrieval Procedures
When any ODBC call fails, the driver retains error information until the next ODBC call. The error state and error text is retrieved from the driver with the SQLError function.

 SQLError
SQLError
Syntax
RETCODE SQLError(henv, hdbc, hstmt, szSqlState, pfNativeError, szErrorMsg, cbErrorMsgMax, pcbErrorMsg)
Description
SQLError returns error or status information. An application typically calls SQLError when a previous call to an ODBC function returns SQL_ERROR or SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO. The application can, however, call SQLError after any ODBC function call.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
henv |
HENV |
Input |
Environment handle or SQL_NULL_HENV. |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle or SQL_NULL_HDBC. |
|
hstmt |
HSTMT |
Input |
Statement handle or SQL_NULL_HSTMT. |
|
szSqlState |
UCHAR FAR * |
Output |
SQLSTATE as null terminated string. |
|
pfNativeError |
SDWORD FAR * |
Output |
Native error code (specific to the data source). |
|
szErrorMsg |
UCHAR FAR * |
Output |
Pointer to storage for the error message text. |
|
cbErrorMsgMax |
SWORD |
Input |
Maximum length of the szErrorMsg buffer. This must be less than or equal to SQL_MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH - 1. |
|
pcbErrorMsg |
SWORD FAR * |
Output |
Pointer to the total number of bytes (excluding the null termination byte) available to return in szErrorMsg. If the number of bytes available to return is greater than or equal to cbErrorMsgMax, the error message text in szErrorMsg is truncated to cbErrorMsgMax – 1 bytes. |
 Transaction and Connection Termination Procedures
Transaction and Connection Termination Procedures
Each query object that runs in ODBC creates a transaction. To ensure that all memory that is associated with a transaction is freed and locks are released, an application should call SQLTransact.

 SQLTransact
SQLTransact
Syntax
RETCODE SQLTransact(henv, hdbc, fType)
Description
SQLTransact requests a commit or rollback operation for all active operations on all statement handles that are associated with a connection. SQLTransact can also request that a commit or rollback operation be performed for all connections that are associated with the environment handle. In the case of query objects, the transaction is automatically closed upon termination of the statement handle.
Parameters
This table describes the parameters:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
henv |
HENV |
Input |
Environment handle or SQL_NULL_HENV. |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle or SQL_NULL_HDBC. |
|
fType |
UWORD |
Input |
Flag for SQL_COMMIT or SQL_ROLLBACK. |

 SQLDisconnect
SQLDisconnect
Syntax
RETCODE SQLDisconnect(hdbc)
Description
SQLDisconnect closes the connection that is associated with a specific connection handle.
If an application calls SQLDisconnect before it has freed all statement handles that are associated with the connection, the driver frees those statement handles after it successfully disconnects from the data source. However, if one or more of the statement handles that are associated with the connection are still executing asynchronously, SQLDisconnect will return SQL_ERROR.
Parameters
This table describes the parameter:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle. |

 SQLFreeConnect
SQLFreeConnect
Syntax
RETCODE SQLFreeConnect(hdbc)
Description
SQLFreeConnect releases a connection handle and frees all memory that is associated with the handle. This is called after SQLDisconnect.
Parameters
This table describes the parameter:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
hdbc |
HDBC |
Input |
Connection handle. |

 SQLFreeEnv
SQLFreeEnv
Syntax
RETCODE SQLFreeEnv(henv)
Description
SQLFreeEnv frees the environment handle and releases all memory that is associated with the environment handle.
Parameters
This table describes the parameter:
|
Argument |
Type |
Use |
Description |
|
henv |
HENV |
Input |
Environment handle. |
 ODBC Compliance
ODBC Compliance
The ODBC API defines a set of core functions that correspond to the functions in the X/Open and SQL Access Group Call Level Interface specification. ODBC also defines two extended sets of functionality, Level 1 and Level 2.
For the specific ODBC API descriptions and implementation details, refer to the Microsoft Open Database Connectivity Software Development Kit.
The following lists summarize the functionality that is included in each conformance level.
Core API functions allow the following:
Allocation and releasing of environment, connection, and statement handles.
Conversion to data sources. Use of multiple statements on a connection.
Preparation and immediate execution of SQL statements.
Assignment of storage for parameters in a SQL statement and result columns.
Retrieval of data from a result set. Retrieval of information about a result set.
Commit or rollback transactions.
Retrieval of error information.
The Level 1 API allows all the core functions, plus the following:
Connection to data sources with driver-specific dialog boxes.
Set and inquire values of statement and connection options.
Transmission of part or all of a parameter value (useful for long data).
Retrieval of part or all of a result column value (useful for long data).
Retrieval of catalog information (columns, special columns, statistics, and tables).
Retrieval information about driver and data source capabilities, such as supported data types, scalar functions, and ODBC functions.
The Level 2 API allows all the core and Level 1 functions, plus the following:
Ability to browse connection information and list available data sources.
Transmission of arrays of parameter values. Retrieval of arrays of result columns values.
Retrieval of the number of parameters and description of individual parameters.
Scrollable cursor.
Retrieval of the native form of a SQL statement.
Retrieval of catalog information (privileges, keys, and procedures).
Translation DLL calls.
To claim that it conforms to a given API or SQL conformance level, a driver must support all the functionality in that conformance level, regardless of whether that functionality is supported by the DBMS that is associated with the driver. However, conformance levels do not restrict drivers to the functionality in the levels to which they conform. Drivers support as much functionality as they can; applications can determine the functionality that is supported by a driver by calling SQLGetInfo, SQLGetFunctions, and SQLGetTypeInfo.
 ODBC to RDM Data Types
ODBC to RDM Data Types
The following table shows the mapping from ODBC C data types to ODBC SQL and PeopleSoft RDM data types:
|
RDM Type |
fSqlType |
Type |
|
RDM_CHAR |
SQL_CHAR |
Unsigned char FAR* |
|
RDM_LONG_CHAR |
SQL_VARCHAR |
Unsigned char FAR* |
|
RDM_NUMBER, RDM_SIGNED_NUMBER |
SQL_NUMERIC |
Unsigned char FAR* |
|
RDM_DATE |
SQL_DATE |
Struct tag DATE_STRUCT { UWORD year; UWORD month; UWORD day; } |
|
RDM_TIME |
SQL_TIME |
Struct TIME_STRUCT { UWORD hour; UWORD minute; UWORD second; } |
|
RDM_DATETIME |
SQL_TIMESTAMP |
Struct TIMESTAMP_STRUCT { SWORD year; UWORD month; UWORD day; UWORD hour; UWORD minute; UWORD second; UWORD fraction; } |
|
RDM_IMAGE |
SQL_LONGVARBINARY |
Unsigned char FAR * |
 PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC API Example
PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC API Example
The following example shows the ODBC API calls needed to execute a PeopleSoft query using the PeopleSoft Open Query ODBC driver. The following query requires two bind variables: business unit and department ID. The sample query returns an answer set of three columns: employee ID, name, and monthly rate.
/*********************************************************************** * Function: OpenQuerySample * * * * Description: Sample program illustrating the usage of PeopleSoft * * Open Query ODBC API. * * Sample code uses basic PeopleSoft Query ODBC interface * * functions. Most error checking is excluded to make * * code easier to follow; in a typical application, * * every return code would be checked. * * * * Returns: TRUE if successful * ***********************************************************************/ BOOL WINAPI OpenQuerySample(HWND hWnd) { HENV hEnv; // Environment handle for application HDBC hDbc; // Connection handle HSTMT hStmt; // Statement handle RETCODE retcode; // Return code char szConnectString[] = "DSN=PeopleSoft PeopleTools;DBTYPE=ORACLE;DBNAME=PTDMO7;UID=PTDMO;PWD=PTDMO;"; char szConnStringOut[256]; // completed connection string SWORD nConnStringLen; // length of completed connect string // Allocate environment, database connection retcode = SQLAllocEnv(&hEnv); if ((retcode = SQLAllocConnect(hEnv, &hDbc)) != SQL_SUCCESS) // error--this would normally abort program with message return(FALSE); // Connect to the database retcode = SQLDriverConnect(hDbc, hWnd, szConnectString, strlen(szConnectString), szConnStringOut, sizeof(szConnStringOut), &nConnStringLen, SQL_DRIVER_COMPLETE); retcode = SQLAllocStmt(hDbc, &hStmt); ProcessQuery(hStmt); // Close the connection, release resources retcode = SQLFreeStmt(hStmt); retcode = SQLDisconnect(hDbc); retcode = SQLFreeConnect(hDbc); retcode = SQLFreeEnv(hEnv); return(TRUE); } /*********************************************************************** * Function: ProcessQuery * * * * Description: Run a query and retrieve answer set. * * * * Returns: TRUE if successful, else FALSE * ***********************************************************************/ BOOL ProcessQuery(HSTMT hStmt) { RETCODE retcode; // Return code char szSelect[] = "{call query.myquery(?,?)"; // binding of input variables must occur before statement execution for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) retcode = SQLBindCol(hStmt, i, datatype, &value, sizeof(value), &valuelen); retcode = SQLExecDirect(hStmt, szSelect, strlen(szSelect)); while (retcode = SQLFetch(hStmt) == SQL_SUCCESS) // process data for a fetched row.... return(retcode == SQL_NO_DATA_FOUND); }