| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3 Overview Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3 Overview Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3 Information Library |
Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3 Overview
Introduction to Oracle Solaris Studio Software
Developer Workflow for Oracle Solaris Studio
Oracle Solaris Studio Compilers
OpenMP 3.1 for Parallel Programming
Sun Performance Library for Programs With Intensive Computation
dmake Utility for Building Applications
Tools for Debugging Applications
Tools for Verifying Applications
Discover Tool for Detecting Memory Errors
Uncover Tool for Measuring Code Coverage
Code Analyzer Tool For Integrated Error Checking
Tools for Tuning Application Performance
Collect Performance Data With the Collector
Examine Performance Data With the Performance Analyzer
Examine Performance Data With the er_print Utility
Analyze Multithreaded Application Performance With the Thread Analyzer
The Oracle Solaris Studio IDE is based on the NetBeans IDE, an open-source integrated development environment. The Oracle Solaris Studio IDE includes the core NetBeans IDE, the NetBeans C/C++ plugin module, and additional integrated Oracle Solaris Studio components that are not available in the open-source NetBeans IDE.
The Oracle Solaris Studio IDE uses the Oracle Solaris Studio C, C++, and Fortran compilers, the dmake build utility, and the dbx debugger. In addition, the IDE provides graphical profiling tools that use Oracle Solaris DTrace and Oracle Solaris Studio performance utilities invisibly to collect data on your running project.
Using the Oracle Solaris Studio IDE offers some advantages over development using text editors and the command line:
Code editing. Working with code can be more efficient with syntax highlighting, code completion, navigation between code elements, and integrated API documentation and man pages.
Code investigation. When you are trying to become familiar with some code or looking for a root cause of a bug, you might find useful such IDE features as Go to Symbol, Find Usages, the Classes window, the Include hierarchy, and the Call Graph.
Refactoring. You can find all usages of a variable or operation within a project, and rename all occurrences of the variable or operation and refactor throughout the product. Before performing the refactoring, you can preview the changes in a split-screen UI and approve them individually or all at once.
Remote development. You can run the IDE on a desktop system while using the Oracle Solaris Studio compilers and tools that are installed on a remote server. The tools run on the remote server while displaying back to your IDE which is running on your local system, with much better response time than typical remote display solutions.
To start the IDE, type the following command:
% solstudio
The following figure shows the IDE with the Quote sample project running.
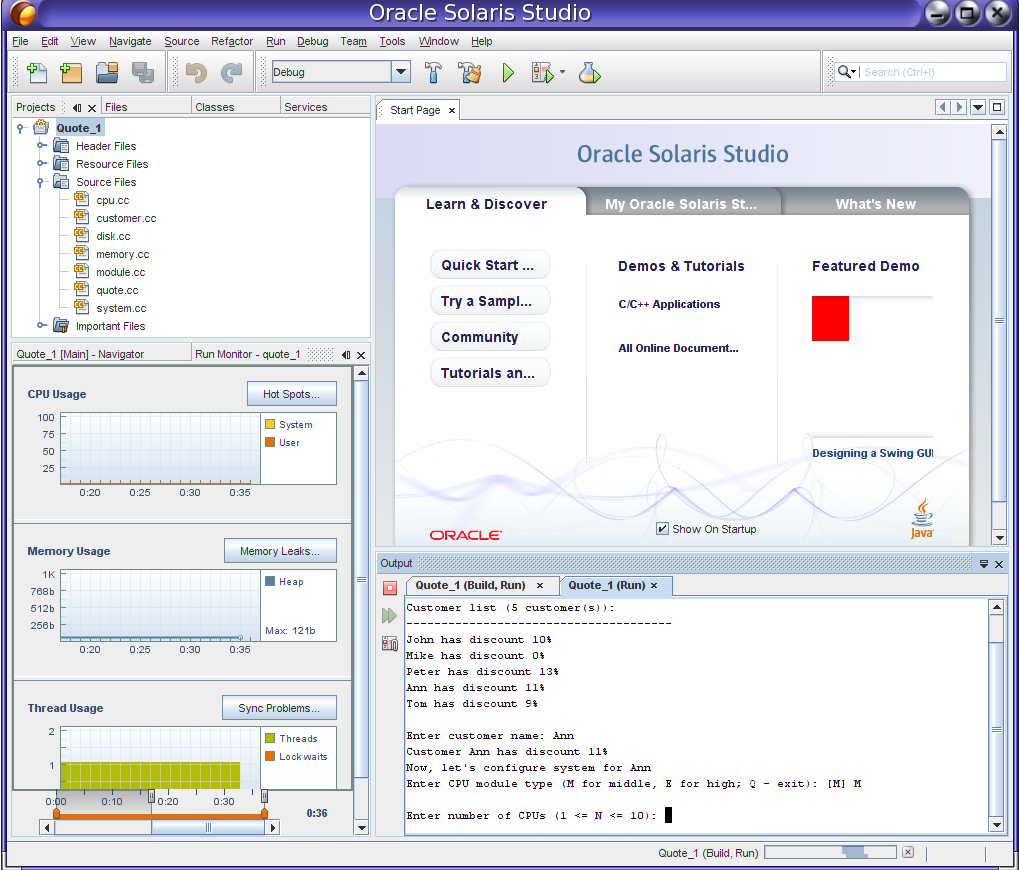
A C or C++ or Fortran project is a group of source files and associated information about how to compile and link the source files and run the resulting program. In the IDE, you always work inside a project even if your program is contained in a single source file. The IDE stores project information in a project folder that includes a makefile and metadata files. Your source directories do not need to be physically located in the project folder.
Each project (except a project created from an existing binary) must have a makefile so the IDE can build the project. A project's makefile can be generated by the IDE or you can use a makefile that was previously created outside the IDE. You can create projects from existing sources that already include a makefile, or that build a makefile when you run configure scripts.
You can build, run, and debug projects by clicking toolbar buttons, or by selecting menu commands. The IDE is preconfigured to use the Studio C, C++, and Fortran compilers, dmake, and dbx by default. However, if you have GNU compilers on your system, the IDE can usually find them if they are on your PATH. You can use the GNU tool collection by setting the Tool Collection in your project's properties.
You can learn about using the Oracle Solaris Studio IDE by reading the IDE's integrated help, which you can access through the IDE's Help menu or by pressing the F1 key. Many dialog boxes also have a Help button for information about how to use the dialog box.
The Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3: IDE Quick Start Tutorial shows how to get started using the IDE. In addition, the tutorials on the NetBeans IDE C/C++ Learning Trail can also be helpful for learning how to use the Oracle Solaris Studio IDE, although there are some differences between the user interfaces and features. In particular, NetBeans documentation about debugging does not apply to Oracle Solaris Studio IDE.