15 Installing Observer Libraries for ASP.NET
This topic provides instructions for installing and uninstalling observer libraries for monitoring ASP.NET services hosted in IIS 6.x.
Note:
For a list of the exact application server versions supported by this observer, refer to the Business Transaction Management (BTM) Certification Matrix. You can find this document online at http://support.oracle.com.The Observer Distribution File
The Business Transaction Management observers are distributed by way of ZIP files. Each ZIP file contains one type of observer that is suitable for installation into a particular application server. The ZIP file containing the observer for monitoring ASP.NET services is BTMObserver_Iis_6_Asp_*.zip.
Note:
In the complete ZIP file name, the asterisk (*) is replaced with the observer version number.Installing Observer Libraries for ASP.NET
-
Locate the observer distribution ZIP file for ASP.NET (BTMObserver_Iis_6_Asp_*.zip).
-
Unpack the ZIP file into a temporary directory (referred to henceforth as observer_temp).
Unpacking the ZIP file creates a nanoagent directory containing two subdirectories—config and lib.
-
Use gacutil.exe to copy all of the DLL files from C:\observer_temp\nanoagent\lib to the global application cache (GAC; normally located at C:\WINDOWS\assembly).
-
Copy C:\observer_temp\nanoagent\config\Web.config to your web site's home directory (the default home directory for the default web site is C:\Inetpub\wwwroot).
If you already have a Web.config in this directory, copy the contents of the provided Web.config into your existing Web.config. You should also back up your original Web.config in case you decide to uninstall the observer.
Copying the Web.config (or its contents) into the web site's home directory, enables monitoring on all of the applications installed in the web site. If you want to monitor only specific applications, copy the Web.config (or its contents) into the directories of those specific applications.
-
Open Web.config in a text editor and ensure that the version numbers of the AmberPoint assemblies in the GAC match the version number in Web.config, for example:
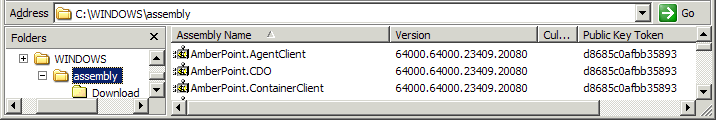
Description of the illustration gac.gif
<system.web> <webServices> <soapExtensionTypes> <add type="AmberPoint.NanoAgent.DotNet.AspNet.Handlers.SoapExtensionHandler, AmberPoint.NanoAgentAspNet, Version=64000.64000.23409.20080, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=d8685c0afbb35893" priority="1" group="0" /> </soapExtensionTypes> </webServices> </system.web>The version numbers must match for the assemblies to be found.
-
In Web.config, set the value of the AmberPoint:NanoConfigURL key to the URL of the monitor to which you want the observer to forward messages.
Use the following form, replacing Host:Port with the host name and port number of the monitor:
<add key="AmberPoint:NanoConfigURL" value="http://Host:Port/btmmonitor/agent/agent"/>This key associates the observer with the monitor whose URL you specify in the key. At startup, the observer retrieves its configuration from the specified monitor and begins sending observations to the monitor.
As an alternative to setting the monitor URL in the AmberPoint:NanoConfigURL key, you can create an environment variable named AP_NANO_CONFIG_URL and use it to set the monitor URL.
Notes:
If you are using replicated monitors, you must set the host and port portion of the URL to the host and port of your load balancer's HTTP virtual server. For example, if the HTTP virtual server's IP address is 10.147.46.152, and its port number is 5072, then you would set the URL to:http://10.147.46.152:5072/btmmonitor/agent/agent/
For more information about the load balancer's HTTP virtual server, see Configuring Your Load Balancer.
-
Also in Web.config, set the value of the AmberPoint:NanoLogBaseDir key to the location in which you want error logs created. Specify the location as an absolute path. If you want the directory created in case it doesn't exist, set the value of the AmberPoint:NanoCreateLogBaseDir key to true. For example:
<add key="AmberPoint:NanoLogBaseDir" value="C:/Inetpub/AmberPoint"/> <add key="AmberPoint:NanoCreateLogBaseDir" value="true"/>
The AmberPoint:NanoLogBaseDir key does not have a default value. If it is set to null, log files will not be generated.
In order for the observer to generate the log files, ensure that the user under which the observer is running has permission to write to the log directory. The observer runs as the user named NETWORK SERVICE.
For more information about configuring error logging, see Chapter 16, "Logging Observer Errors and Debugging Information."
-
Ensure that the monitor to which your observer forwards messages has an Observer Communication policy applied to it.
For information on applying an Observer Communication policy, see Applying an Observer Communication Policy.
Uninstalling the Observer Libraries for ASP.NET
-
Delete apobserver.configuration from the location specified in Web.config as the value of the AmberPoint:NanoConfig key (this key might use the deprecated name AmberPoint:NanoAgentConfigFile, depending on your version of the observer).
-
Revert your Web.config file to the state it was in before you installed the observer.
To perform this step, remove all observer-related content from the file. The observer-related content is:
-
The <sectionGroup> element with name AmberPoint
-
The <AmberPoint> element
-
The AmberPoint <add> element within the <soapExtensionTypes> element, for example:
<add type="AmberPoint.NanoAgent.DotNet.AspNet.Handlers.SoapExtensionHandler, AmberPoint.NanoAgentAspNet, Version=64000.64000.23409.20080, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=d8685c0afbb35893" priority="1" group="0" />
If the Web.config contains only observer-related content, you can delete the entire file.
-
-
Remove the observer DLLs from the GAC (unless they are being used by another observer on the machine).
The name of each observer DLL begins with the string “AmberPoint”. To remove a DLL, right-click it and choose Uninstall.
Note:
The observer for WCF uses many of the same DLLs as the observer for ASP.NET. If you have the observer for WCF installed on the machine, you must not remove the DLLs that are being used by it.