4 Configuring Oracle Site Guard
This chapter describes the tasks that you must follow to configure Oracle Site Guard.
It contains the following topics:
4.1 Overview
Before you create operation plans for disaster recovery, you must first configure Oracle Site Guard. After configuring Oracle Site Guard, you can create operation plans that use the configuration you have created.
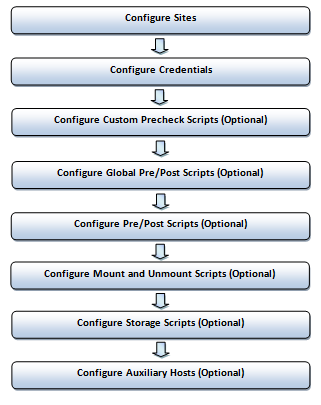
Figure 4-1 shows the roadmap for configuring Oracle Site Guard. Steps marked optional are required if the site topology and operation plans require a specific type of configuration. However, since most enterprise deployments are large and complex, they typically require all the configuration steps listed in the figure.
Note:
-
Before you configure Oracle Site Guard, ensure that you complete the tasks described in Section 3.2, "Prerequisites for Using Oracle Site Guard".
-
You must log in using the
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORrole privilege for performing the configuration tasks. Ensure that you have created the required user credentials as described in Section 3.2.2, "Creating Oracle Site Guard Administrator Users".
4.2 Configuring Sites
As the first step towards setting up a disaster-recovery configuration, you must configure sites, and designate roles to the configured sites. The configured sites must be designated as the primary (production) sites and standby sites.
Configure sites using one of the following methods:
4.2.1 Configuring Sites Using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console
To create an Oracle Site Guard configuration and associate a standby system with the primary system, complete the following steps:
-
Log in to Enterprise Manager as an
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORuser. -
From the Targets menu, click Systems.
The Systems page is displayed.
-
Click the name of the system (Generic System) for the primary site created as described in Section 3.2.3, "Creating Primary and Standby Sites".
The Generic System page for the primary site is displayed.
-
On the system's home page, from the Generic System menu, select Site Guard > Configure.
The Site Guard Configuration page is displayed.
-
On the General tab, in the Standby System(s) section, click Add.
The Search and Select: Standby Systems page is displayed.
-
Choose the standby system, and click Select.
-
Click Create. Or, if an Oracle Site Guard configuration already exists, click Save.
-
Click OK to confirm the action.
Site Guard saves the standby system configuration.
4.2.2 Configuring Sites Using EMCLI Commands
To add the configuration for the primary and standby sites, you must run the following emcli commands in the command-line interface:
Note:
For information about logging in toemcli, see chapter "Command Line Interface Concepts and Installation" in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface Guide.
emcli create_siteguard_configuration
-primary_system_name="system_name1"
-standby_system_name="system_name2"
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-primary_system_name |
Enter the name of your system, which is associated with the primary site. |
-standby_system_name |
Enter the name of your system, which is associated with the standby site. |
To display information about the association between existing primary and standby sites, run the following emcli commands in the command-line interface:
emcli get_siteguard_configuration
[-primary_system_name="name_of_the_primary_system"]
[-standby_system_name="name_of_the_standby_system"]
4.3 Creating Credential Associations
This section describes how to associate Site Guard managed targets and credentials that you created in Section 3.2.4, "Creating Credentials".
Note:
-
If you are using Named Credentials or Preferred Credentials, ensure that you have created all the necessary credentials for managing targets as described in Section 3.2.4, "Creating Credentials".
-
Ensure that you have created a user with
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORprivileges, as described in Section 3.2.2, "Creating Oracle Site Guard Administrator Users", and granted credential privileges to that user as described in Section 3.2.5, "Granting Credential Privileges to Oracle Site Guard Administrator Users".
It is essential that you set up named or preferred credential associations for the following targets:
-
Each host, where Oracle Fusion Middleware and Oracle Database are installed and configured (for normal user and users with root privileges)
-
Oracle WebLogic Administration Server
-
Oracle Database
4.3.1 Creating Named or Preferred Credential Associations
You can create Named or Preferred Credential associations using one of the following methods:
-
Creating Named or Preferred Credential Associations Using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console
-
Creating Named or Preferred Credential Associations Using EMCLI Commands
4.3.1.1 Creating Named or Preferred Credential Associations Using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console
To create named credentials using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console, complete the following steps:
-
Log in to Enterprise Manager as an
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORuser. -
From the Targets menu, click Systems.
-
On the Systems page, click the name of the system for which you want to configure credential associations.
-
On the system's home page, from the Generic System menu, select Site Guard > Configure.
-
Click the Credentials tab.
Associate the different types of credentials as described:
Associate Normal Host Credentials
Associate normal host credentials to run specific commands or scripts on the target host.
To associate normal host credentials, follow these steps:
-
In the Credential tab, in the Normal Host Credentials section, click Add.
The Add Normal Host Credentials dialog appears.
-
Select the target for which you want to associate normal host credentials. Select All to select all the systems in the list.
You can select the credentials set, by default, by selecting the Use Preferred Credentials option on the page. On selecting Use Preferred Credentials, the Named Credentials section is disabled. To select named credentials, deselect Use Preferred Credentials.
-
Click Save.
Associate Privileged Host Credentials
Associate privileged host credentials to mount or unmount storage on the target host.
To associate privileged host credentials, follow these steps:
-
In the Credential tab, in the Privileged Host Credentials section, click Add.
The Add Privileged Host Credentials dialog appears.
-
Select the target for which you want to associate privileged host credentials. Select All to select all the targets in the list.
You can select the credentials set, by default, by selecting the Use Preferred Credentials option on the page. On selecting Use Preferred Credentials, the Named Credentials section is disabled. To select named credentials, deselect Use Preferred Credentials.
-
Click Save.
Associate Oracle Node Manager Credentials
Associate Oracle Node Manager credentials to connect to manage node manager targets. You must also associate Oracle Node Manager credentials each sites that have a Oracle Weblogic Server target, however when you configure Oracle Node Manager credentials, you must configure using credentials for the type
HostNormalorHostPrivileged.To associate Oracle Node Manager credentials, follow these steps:
-
In the Credential tab, in the Oracle Node Manager Credentials section, click Add.
The Add Oracle Node Manager Credentials dialog appears.
-
Select the target host for which you want to associate Oracle Node Manager credentials. Select All to select all the target hosts in the list.
You can select the credentials set, by default, by selecting the Use Preferred Credentials option on the page. On selecting Use Preferred Credentials, the Named Credentials section is disabled. To select named credentials, deselect Use Preferred Credentials.
-
Click Save.
Associate Oracle WebLogic Administration Credentials
Associate Oracle WebLogic Administration credentials to connect to the administration server, or to start or stop managed servers.
To associate Oracle WebLogic administration credentials, follow these steps:
-
In the Credential tab, in the Oracle WebLogic Administration Credentials section, click Add.
The Add Oracle WebLogic Administration Credentials dialog appears.
-
Select the target for which you want to associate Oracle WebLogic administration credentials. Select All to select all the targets in the list.
You can select the credentials set, by default, by selecting the Use Preferred Credentials option on the page. On selecting Use Preferred Credentials, the Named Credentials section is disabled. To select named credentials, deselect Use Preferred Credentials.
-
Click Save.
Associate SYSDBA Database Credentials
Associate SYSDBA database credentials to perform switchover or failover operations through Data Guard Broker.
To associate database credentials, follow these steps:
-
In the Credential tab, in the SYSDBA Database Credentials section, click Add.
The Add Oracle WebLogic Administration Credentials dialog appears.
-
Select the target for which you want to associate SYSDBA Database credentials. Select All to select all the targets in the list.
You can select the credentials set, by default, by selecting the Use Preferred Credentials option on the page. On selecting Use Preferred Credentials, the Named Credentials section is disabled. To select named credentials, deselect Use Preferred Credentials.
-
Click Save.
-
4.3.1.2 Creating Named or Preferred Credential Associations Using EMCLI Commands
You can create a named or preferred credential associations for targets by running the credential framework EMCLI commands in the command-line interface:
emcli create_siteguard_credential_association
-system_name="name_of_the_system"
[-target_name="name_of_the_target"]
-credential_type="type_of_credential"
[-credential_name="name"]
[–use_preferred_credential="true_or_false"]
-credential_owner="owner"
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the name of the system. |
-target_name |
Specify the name of the target. This parameter is optional. |
-credential_type |
Specify the type of the credential. Example: HostNormal, HostPrivileged, NodeManager, WLSAdmin, or DatabaseSysdba.
Note: For Node Manager credential, specify the |
-credential_name |
Specify the name of the credential.
If the value for |
-credential_owner |
Specify the owner of the credential. |
–use_preferred_credential |
If you are using Preferred Credentials, then specify true. The default value is false. If you use the default value, then you must specify the -credential_name parameter to use named credentials. |
4.4 Configuring Scripts
Oracle Site Guard provides a mechanism for users to configure different types of scripts for managing disaster-recovery operations. Depending on their function, these scripts either come bundled with Oracle Site Guard, or they can be provided by the user. You must configure these scripts while configuring Oracle Site Guard. Note that these scripts must be added to the Enterprise Manager software library so that they can be automatically staged (deployed) on the hosts where they need to run. Scripts that are not part of the software library must be manually staged (deployed) on each host where they are defined to run.
You can configure the following types of scripts using Oracle Site Guard:
-
Custom Precheck Scripts
Custom Precheck scripts are used to extend the Precheck and Health Check functionality that Oracle Site Guard provides. For information about Precheck and Health Check functionality of Oracle Site Guard, see Section 2.3.1, "Extensibility."
-
Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, Global Pre Scripts, and Global Post Scripts
Pre scripts, Post Scripts, Global pre scripts, and Global Post Scripts are used for extending the functionality of Oracle Site Guard when executing operation plans. For more information, see Section 2.3.1, "Extensibility."
-
Mount and Unmount scripts
Mount and Unmount scripts as described in Section 2.3.3, "Storage Integration", are needed for files system mount and unmount operations that are performed during operations. You can use the scripts that are bundled with Oracle Site Guard, or you can provide your own scripts.
-
Storage scripts
Storage scripts as described in Section 2.3.3, "Storage Integration", are needed for storage management that must be performed during operations., You can use the scripts that are bundled with Oracle Site Guard, or you can provide your own scripts.
Note:
-
A user-defined script must be an executable script, and must have clearly defined return codes. The script must return
0on success, and non-zero values on failure. -
Ensure that you configure the required privileges to run all user-defined scripts.
This section contains the following topics:
4.4.1 Configuring Custom Precheck Scripts, Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, Global Pre Scripts, and Global Post Scripts
The following attributes are available for customizing a Pre Script, Post Script, Global Pre Script, and Global Post Script:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| script path | The file system path where the script resides. Note that the script must reside at the same path location on each host specified in the target hosts parameter. |
| component | Path to the entity in software library. If component is specified, path should contain only the file name and its parameters. This parameter is optional. |
| target hosts | The list of hosts where the script will run. |
| run on | Specifies whether the script should run on Any or All of the hosts specified in the target hosts parameter. |
| operation type | The operation type that the script is configured for (switchover, failover, start, or stop). |
| role | Specifies the role of the site during which the script will run (primary or standby). For example, a script configured for a primary role will only run when the site has a primary role. |
| credential type | Specifies the type of credential to be used for executing the script on the specified hosts (Normal Host Credentials or Privileged Host Credentials).
For information about various types of credentials, see Section 4.3, "Creating Credential Associations" |
To configure Custom Precheck Scripts, Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, Global Pre Scripts, and Global Post Scripts, follow one of these methods:
4.4.1.1 Configuring Custom Precheck Scripts, Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, Global Pre Scripts, and Global Post Scripts Using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console
To configure Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, Global Pre Scripts, and Global Post Scripts for the primary site, complete the following steps:
-
Log in to Enterprise Manager as an
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORuser. -
From the Targets menu, click Systems.
The Systems page is displayed.
-
Select the system name (Generic System) for which the script must be configured.
The Generic System page for that site is displayed.
-
Click Generic System > Site Guard > Configure.
The Site Guard Configuration page is displayed.
-
Click the Pre/Post Scripts tab.
-
Click Add.
The Add Pre/Post Scripts page is displayed.
-
Enter the following details:
-
Software Library Path: Enter the path to the software library entity that contains the script. Alternately, browse for the entity in the software library by clicking on the icon. This only applies if the script has already been added to the Enterprise Manager software library.
The entity in the Software Library must be present in a folder which is not locked. The symbol,
 , indicates that the folder is locked.
, indicates that the folder is locked. -
Script Path: Enter the path to the script, or click the search icon and browse the file system for the script. You can also browse file systems on the remote host after specifying the login credentials.
-
Target Hosts: Select one or more target hosts, or select All to configure the script to run on all hosts.
-
Script Type: Select one of the following options depending on the type of script being configured:
-
Custom Precheck Script
-
Pre Script
-
Post Script
-
Global Pre Script
-
Global Post Script
-
-
Run On: Select All Hosts to run the script on all selected hosts, or to run the script on any one of the selected target hosts, select Any Host.
-
Operation Type: The operation during which this script will run. Choose from the options - Switchover, Failover, Start, or Stop.
-
Role: Select Primary or Standby based on the system role. The script only runs when the system has the specified role.
Note:
For Global Pre-Script and Global Post-Script script types, the site Role can only be selected when the operation type is Start or Stop. For Switchover and Failover operations, the Role parameter is selected by Oracle Site Guard and cannot be modified. -
Credential Type: Select one of the following credential types for executing the script:
-
Normal Host Credentials
Select the Normal (non-root) privileges configured for the script host
-
Privileged Host Credentials
Select the Privileged (root) privileges configured for the script host
-
Custom Host Credentials
Select an alternate set of named credentials. If this option is chosen, select the named credential from the Named Credential drop-down menu.
-
-
Named Credential: Select the named credential to use when executing the script. This selection is only applicable if Credential Type is set to Custom Host Credentials.
-
Runtime Script: Select whether this is a Runtime script that will only be available during operation execution. Normally, scripts that are part of the Software Library should be designated as Runtime scripts, however any user script may be designated a Runtime script.
Note:
During a Precheck or Health Check, Oracle Site Guard checks the existence of runtime scripts that have been added to the Software Library. However, if the scripts are not part of the Software Library, Oracle Site Guard does not check for their existence before an operation plan is executed. -
Credential Parameters: Select one or more configured credentials to pass as parameters to this script. To select the credentials to pass to the script, move those credentials from the Available Values column to the Selected Values column.
-
-
Click Save.
4.4.1.2 Configuring Custom Precheck Scripts, Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, Global Pre Scripts, and Global Post Scripts Using EMCLI Commands
To configure Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, Global Pre Scripts, and Global Post Scripts with Oracle Site Guard, run the following emcli commands in the command-line interface:
emcli create_siteguard_script
-system_name=name_of_the_system
-operation=name_of_the_operation
-script_type=type_of_the_script
[-host_name=name_of_the_host_where_the_scripts_are_run]
-path=path_of_the_script
[-component="path_of_the_entity_in_software_library"]
[-runtime_script="flag_to_specify_if_prechecks_to_check_availability_of_this_script"]
[-run_on=flag_specifying_the_host]
[-all_hosts=flag_to_run_script_on_all_the_hosts_in_the_system]
[-role=role_associated_with_the_system]
[-credential_type=type_of_the_credential]
[-credential_name="name_of_the_credential"]
[-target_storage_credential_name=target_storage_credential]
[-source_storage_credential_name=source_storage_credential]
[-credential_owner=credential_owner]
Note:
-
A parameter enclosed in
[ ]indicates that the parameter is optional. -
You can specify the
-host_nameparameter more than once. -
Specifying the value
truefor the parameter-all_hosts=trueoverrides any host selected using the-host_nameoption.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the name of the system. |
-operation |
Specify the name of the operation. Name of the operation:
|
-script_type |
Specify the type of the script. It can be Mount, UnMount, Global-Pre-Script, Global-Post-Script, Pre Script, Post-Script, Storage-Failover, or Storage-Switchover. |
-host_name |
Specify the name of the host where this script will be executed.
This parameter is optional and can be specified more than once. |
-path |
Specify the path to the script. |
-component |
Specify the path to the entity in the software library. If component is specified, path should contain only the file name and its parameters.
This parameter is optional. |
-runtime_script |
Specify the value as true or false. If the script is designated as a runtime script, Precheck will not verify the existence of script. This parameter is used when the script is dynamically mounted or generated as part of execution of operation plan.
By default, all scripts staged from the software library are designated as runtime scripts. The default value for scripts that are not staged from software library is This parameter is optional. |
-run_on |
Specify whether the script needs to be executed on only one of the available hosts (enter any) or on all hosts (enter all).
This parameter is optional and default value is all. |
-all_hosts |
Optional flag to allow the script to run on all the hosts in the system. This parameter overrides the host_name. Enter true or false. |
-role |
Optional flag to configure script based on the system role. By default, the script is configured for both primary and standby roles for a given system. For example: Primary or Standby. |
–credential_type |
Specify HostNormal or HostPrivileged if you have root privileges. |
-credential_name |
Specify the name of the credential that is used to execute this script.
If the value for the parameter |
-target_storage_credential_name |
Specify the named credential for target storage. If target_storage_credential_name is specified then source_storage_credential_name and credential_owner must be specified. |
-source_storage_credential_name |
Specify the named credential for source storage. If source_storage_credential_name is specified then target_storage_credential_name and credential_owner must be specified. |
-credential_owner |
Specify the owner of the credential. If target_storage_credential_name and source_storage_credential_name are specified then the attribute credential_owner must be specified. |
Note:
-
[ ]indicates that the parameter is optional. -
You may specify the option
host_namemore than once. -
Specifying
-all_hosts=trueoverrides any hosts selected using the-host_nameoption. -
The
-roleoption is only applicable for Pre-Script or Post-Script.
4.4.2 Configuring Mount and Unmount Scripts
Mount and Unmount scripts are storage scripts that come in two flavors:
-
Bundled
Oracle Site Guard provides a bundled script for handling file-system mount and unmount operations. The script,
mount_umount.sh, is part of the Enterprise Manager Software Library. Oracle Site Guard automatically deploys bundled scripts on all hosts on which the scripts are defined to run. -
User-defined
You can define your own custom script for the file system mount and unmount operations.
You can add your own scripts to the Enterprise Manager software library. If you do this, Oracle Site Guard will deploy your scripts to all configured hosts at runtime. This is similar to how Oracle Site Guard automatically deploys bundled scripts like
mount_umount.sh. However, if your scripts are not part of the software library, then you must deploy these scripts on all hosts where they need to run.
4.4.2.1 mount_umount.sh
This section provides the syntax and usage for the mount_umount.sh script.
For mounting and unmounting file systems, configure the bundled mount_umount.sh script as shown in Example 4-1.
Example 4-1 Usage of mount_umount.sh Script
sh mount_umount.sh [-o operation_type ][-f directories_to_mount_or_unmount]
Note:
-
If there are multiple directories to be mounted or unmounted, use commas to separate the directories. Ensure that there are no spaces between the directory names.
-
Ensure that the
/etc/fstabfile is updated with the entries that you want to mount or unmount. -
Ensure that you have the privileges to mount or unmount file systems.
To mount multiple directories, run the following command:
sh mount_umount.sh -o mount -f /u02/oracle/config,/u02/oracle/product,/u02/oracle/stage
To mount a single directory, run the following command:
sh mount_umount.sh -o mount -f /u01/app/oracle/product/test
To unmount multiple directories, run the following command:
sh mount_umount.sh -o umount -f /u02/oracle/config,/u02/oracle/product,/u02/oracle/stage
To unmount a single directory, run the following command:
sh mount_umount.sh -o umount -f /u01/app/oracle/product/test
Configure mount or unmount scripts using one of the following options:
4.4.2.1.1 Configuring Mount or Unmount Scripts Using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console
To configure a mount or unmount script using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console, follow these steps:
-
Log in to Enterprise Manager as an
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORuser. -
From the Targets menu, click Systems.
The Systems page is displayed.
-
Select the system name (Generic System) on which the script must be configured.
The Generic System page for that site is displayed.
-
Click Generic System > Site Guard > Configure.
The Site Guard Configuration page is displayed.
-
Click the Storage Scripts tab.
-
Click Add.
The Add Storage Scripts page is displayed.
-
Enter the following details:
-
Software Library Path: Enter the path to the software library entity that contains the script. Alternately, browse for the entity in the software library by clicking the search icon. This only applies if the script has already been added to the Enterprise Manager software library.
-
Script Path: Specify the bundled
mount_umount.shscript with the appropriate options (see Section 4.4.2.1, "mount_umount.sh"), or provide a path to your own user-defined script.To enter a user-defined script you can click the search icon, and browse the file system. You can also browse file systems on the remote host after specifying login credentials.
-
Target Hosts: Select one or more target hosts, or select All to configure the script to run on all hosts.
-
Script Type: Select one of the following options:
-
Mount
-
UnMount
-
-
Run On: This option is disabled. The value is set to All Hosts.
-
Operation Type: The operation during which this script will run. Choose from the options - Switchover or Failover
-
Runtime Script: Select whether this is a Runtime script that will only be available during operation execution. Normally, scripts that are part of the Software Library should be designated as Runtime scripts, however any user script may be designated a Runtime script.
Note:
During a Precheck or Health Check, Oracle Site Guard checks the existence of runtime scripts that have been added to the Software Library. However, if the scripts are not part of the Software Library, Oracle Site Guard does not check for their existence before an operation plan is executed. -
Credential Type: Select one of the following credential types while executing the script:
-
Normal Host Credentials: Select these credentials to use the Normal (non-root) privileges configured for that script host.
-
Privileged Host Credentials: Select these credentials to use the Privileged (
root) privileges configured for that script host. -
Custom Host Credentials: Select these credentials to use an alternate set of named credentials. If this option is chosen, select the named credential from the Named Credential drop-down menu.
-
-
Named Credential: Specify the named credential to be used when executing the script. This selection is only applicable if Credential Type is set to Custom Host Credentials.
-
Credential Parameters: Select one or more configured credentials to be passes as parameters for this script. To select the credentials to be passed to the script, move those credentials from the Available Values column to the Selected Values column.
-
-
Click Save.
4.4.2.1.2 Configuring Mount or Unmount Scripts Using EMCLI Commands
To configure a mount or unmount script, run the following emcli command using the command-line interface:
emcli create_siteguard_script
-system_name="system_name"
-operation="operation_name"
-script_type="type_of_script"
[-host_name="name_of_the_host"]
-path="path_of_the_script"
[-component="path_of_the_entity_in_software_library"]
[-runtime_script="flag_to_specify_if_prechecks_should_check_availability_of_this_script"]
[-run_on="flag_specifying_hosts_that_will_run_the_script"]
[-all_hosts="flag_to_run_the_script_on_all_the_hosts_on_the_system"]
[-role="role_associated_with_the_system"]
[-credential_type="type_of_credential"]
[-credential_name="name_of_the_credential"]
[-target_storage_credential_name="target_storage_credential"]
[-source_storage_credential_name="source_storage_credential"]
[-credential_owner="credential_owner"]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system for which the script is being configured. |
-operation |
Specify the function of the operation. Example: Switchover or Failover. |
-script_type |
The type of script. Depending on the function you want to perform, enter one of the following options:
|
-host_name |
Specify the name of the host where the script will be run.
To specify a list of hosts, separate host names with semi-colons, or provide the Note: Ensure that all hosts are part of the system specified in |
-path |
Enter the path to the script.
If you are configuring the bundled For example:
If you are configuring a user-defined script that you have added to the Enterprise Manager software library, provide only the name of the script and any additional arguments that the script requires. For example:
If you are configuring a user-defined script that you will deploy on all the configured hosts, provide the full path to the script location and any additional arguments that the script requires. Note: The script must reside at the same path location on each host. For example:
|
-component |
Specify the path to the entity in the software library. If the component is specified, the -path option should contain only the script name and its parameters. |
-runtime |
Specify if the script is a runtime script. If the script is a runtime script, Prechecks will not verify the existence of script. This option can be used when the script is dynamically mounted or generated as part of execution of operation plan. By default, all scripts staged from the software library are designated as runtime scripts. For scripts that are not staged from the software library, the default value is false. |
-run-on |
Specify whether the script needs to be executed on only one of the available hosts (enter any) or on all hosts (enter all). |
-all_hosts |
Specify this optional flag to enable the script to run on all the hosts in the system. This parameter overrides the -host_name parameter. |
-role |
This option is not applicable for scripts of type Mount and UnMount. |
-credential type |
Specify HostNormal credentials or HostPrivileged credentials for users with root privileges. If values for credential_type are not specified, then the values for credential_name must be specified. |
-credential_name |
Specify an alternate named credential to use when executing this script. If the values for credential_name are not specified, then the values for credential_type must be specified. |
-target_storage_credential_name |
This option is not applicable for scripts of type Mount and UnMount. |
-source_storage_credential_name |
This option is not applicable for scripts of type Mount and UnMount. |
-credential_owner |
This option is not applicable for scripts of type Mount and UnMount. |
4.4.3 Configuring Storage Scripts
Storage scripts are used for Storage Switchover and Storage Failover operations. There are two types of storage scripts:
-
Bundled
Oracle Site Guard provides a bundled script for handling file-system mount and unmount operations. The script,
zfs_storage_role_reversal.sh, is part of the Enterprise Manager Software Library. Oracle Site Guard automatically deploys bundled scripts on all hosts on which the scripts are defined to run. -
User-defined
You can define your own custom script for the file system mount and unmount operations.
You can add your own scripts to the Enterprise Manager software library. If you do this, Oracle Site Guard will deploy your scripts to all configured hosts at runtime. This is similar to how Oracle Site Guard automatically deploys bundled scripts like
zfs_storage_role_reversal.sh. However, if your scripts are not part of the software library, you must deploy them on all hosts where they need to run.
4.4.3.1 zfs_storage_role_reversal.sh
This section provides the syntax and usage for the zfs_storage_role_reversal.sh script. This script comes bundled with Oracle Site Guard and can be used to perform storage role-reversal operations as part of a switchover or failover operation plan.
For switchover and failover operations, configure the bundled zfs_storage_role_reversal.sh script as shown in Example 4-2 and the following table.
| Option | Description | Mandatory? |
|---|---|---|
--target_appliance or -t |
Specify the host name of the target ZFS appliance.
For example:
|
Yes |
--target_user or -w |
Specify the username on the target ZFS appliance with privileges to execute the script. If not specified, the username of the user executing the script will be used.
For example: |
No |
--source_appliance or -h |
Specify the host name of the source ZFS appliance.
For example:
|
Yes |
--source_user or -u |
Specify the user name on the source ZFS appliance with privileges to execute the script. If not specified, the user name of the user executing the script will be used.
For example: |
No |
--project_name or -j |
Specify the name of the replicated ZFS project.
For example: |
Yes |
--target_pool_name or -p |
Specify the name of the storage pool on the target ZFS appliance.
For example: |
Yes |
--source_pool_name or -q |
Specify the name of the storage pool on the source ZFS appliance.
For example: |
Yes |
--operation_type or -o |
The operation for which this script is being configured.
For example: |
Yes |
--is_sync_needed or -c |
Specify whether the replication package should be updated or synchronized before starting the role reversal. Applicable values are Y or N.
If not provided, the default value is |
No |
--continue_on_sync_failure or -f |
Specify whether the role reversal should continue if the update or synchronization fails. Applicable values are Y or N.
This option only applies if the parameter |
No |
--sync_timeout or -e |
Specify the timeout value (in seconds) before declaring that the update or synchronization has failed. This option only applies if -is_sync_needed is enabled.
For example: |
No |
--keep_log_file or -l |
Specify whether the script should send output to a log file. Applicable values are Y or N.
If not specified, the default is N (no log output will be sent to log file). |
No |
--zfs_lag_in_seconds or -z |
Specify the ZFS replication lag threshold value (in seconds). If the replication lag exceeds this value, do not reverse storage roles.Example: 300 (equivalent to five minutes) |
No |
--is_source_reachable or -x |
Specify whether Site Guard should check whether the source appliance is reachable. This option only applies to the failover case and should be used to prevent the script from trying to check source appliance reachability. Applicable values are Y or N.
If not specified, the default value is |
No |
--source_user_equivalence or -m |
Specify the SSH user name to use when establishing an SSH connection to the source appliance. If this is not specified, the script attempts an SSH connection without specifying an alternate user name.
For example:
|
No |
--target_user_equivalence or -n |
Specify the SSH username to use when establishing an SSH connection to the target appliance. If this is not specified, the script attempts an SSH connection without specifying an alternate username.
For example:
|
No |
Configure Storage scripts using one of the following options:
4.4.3.2 Configuring Storage Scripts Using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console
-
Log in to Enterprise Manager as an
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORuser. -
From the Targets menu, click Systems.
The Systems page is displayed.
-
Select the system name (Generic System) on which the script must be configured.
The Generic System page for that site is displayed.
-
Click Generic System > Site Guard > Configure.
The Site Guard Configuration page is displayed.
-
Click the Storage Scripts tab.
-
Click Add.
The Add Storage Scripts page is displayed.
-
Enter the following details:
-
Software Library Path: Enter the path to the software library entity that contains the script. Alternately, browse for the entity in the software library by clicking the search icon. This only applies if the script has already been added to the Enterprise Manager software library.
-
Script Path: Specify the bundled
zfs_storage_role_reversal.shscript with the appropriate options (see Section 4.4.3.1, "zfs_storage_role_reversal.sh"), or provide a path to your own user-defined script. To browse for a user-defined script you can click the search icon and browse the file system. You can also browse file systems on the remote host after specifying login credentials.For example:
sh zfs_storage_role_reversal.sh -t zfssite1.mycompany.com -h zfssite2.mycompany.com -j ZFS-DR-Project -p zfssite1-pool-0 -q zfssite2-pool-0 -c N -f Y -z 300 -l Y switchover
-
Target Hosts: Select one or more target hosts, or select All to configure the script to run on all hosts.
-
Script Type: Select one of the following options depending on the function that Oracle Site Guard needs to perform:
-
Storage Switchover
-
Storage Failover
Selecting Storage Switchover or Storage Failover for the Script Type changes the available options in the dialog. Two additional options called Target Storage Credential and Source Storage Credential appear.
-
-
Run On: Select All Hosts to run the script on all selected hosts. To run the script on any one of the selected target hosts, select Any Host.
-
Operation Type: The operation during which this script will run. Choose from the options - Switchover or Failover.
-
Runtime Script: Select whether this is a Runtime script that will only be available during operation execution. Normally, scripts that are part of the Software Library should be designated as Runtime scripts. However, any user script may be designated a Runtime script.
Note:
During a Precheck or Health Check, Oracle Site Guard checks the existence of runtime scripts that have been added to the Software Library. However, if the scripts are not part of the Software Library, Oracle Site Guard does not check for their existence before an operation plan is executed. -
Credential Type: Select one of the following credential types to use for executing the script.
-
Normal Host Credentials to use the Normal (non-root) privileges configured for that script host.
-
Privileged Host Credentials to use the Privileged (root) privileges configured for that script host.
-
Custom Host Credentials to use an alternate set of named credentials. If this option is chosen, select the named credential to use from the Named Credential drop-down menu.
-
-
Named Credential: Select the named credential to use when executing the script. This selection is only applicable if Credential Type is set to Custom Host Credentials.
-
Target Storage Credential: Select the named credential to be used for accessing the target storage appliance.
-
Source Storage Credential: Select the named credential to be used for accessing the source storage appliance.
-
Credential Parameters: Select one or more configured credentials to pass as parameters to this script. To select the credentials to pass to the script, move those credentials from the Available Values column to the Selected Values column.
-
-
Click Save.
4.4.3.3 Configuring Storage Scripts Using Enterprise Manager Command-Line Interface
To configure a storage script, run the following emcli command using the command-line interface:
emcli create_siteguard_script -system_name="name_of_the_system" -operation="name_of_the_operation" -script_type="type_of_the_script" [-host_name="name_of_the_host_where_the_script_will_be_run"] -path="path_of_the_script" [-component="path_of_the_entity_in_software_library"] [-runtime_script="flag_to_specify_if_prechecks_should_check_availability_of_this_script"] [-run_on="flag_specifying_which_hosts_will_run_the_script"] [-all_hosts="flag_to_run_the_script_on_all_the_hosts_in_the_system"] [-role="role_associated_with_the_system"] [-credential_type="type_of_the_credential"] [-credential_name="name_of_the_credential"] [-target_storage_credential_name="target_storage_credential"] [-source_storage_credential_name="source_storage_credential"] [-credential_owner="credential_owner"]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system for which the script is being configured. |
-operation |
Specify the function of the operation. Example: Switchover, Failover, Start, or Stop. |
-script_type |
Specify the type of script depending on the operation you want to perform.
For example: |
-host_name |
Specify the name of the host where the script will be run.
This option can be specified more than once to configure multiple hosts. Ensure that each host is part of the system specified in the parameter |
-path |
Enter the path to the script.
If you are configuring the bundled For example:
If you are configuring a user-defined script that you have added to the Enterprise Manager software library, provide only the name of the script and any additional arguments that the script requires. For example:
If you are configuring a user-defined script that you will deploy on all the configured hosts, provide the full path to the script location and any additional arguments that the script requires. Note: The script must reside at the same path location on each host. For example:
|
-component |
Specify the path to the entity in software library. If component is specified, the -path option should contain only the script name and its parameters. |
-runtime_script |
Specify if script is a runtime script. If the script is designated a runtime script, Prechecks will not verify the existence of script. This option can be used when the script is dynamically mounted or generated as part of execution of operation plan. By default, all scripts staged from software library are designated as runtime scripts. The default value is false for scripts that are not staged from software library. |
-run_on |
Specify whether the script needs to be executed on only one of the available hosts (enter any) or on all hosts (enter all).
This parameter is optional and default value is |
-all_hosts |
Specify this optional flag to enable the script to run on all the hosts in the system. This parameter overrides the host_name. |
-role |
This option is not applicable for scripts of type Storage Switchover and Storage Failover. |
–credential_type |
Specify HostNormal credentials or HostPrivileged credentials for users with root privileges. If the values for the parameter credential_type are not specified, then the values for credential_name must be specified. |
-credential_name |
Specify an alternate named credential to use when executing this script. If the values for the parameter credential_name are not specified, then the values for the parameter credential_type must be specified. |
-target_storage_credential_name |
Specify the named credential to be used for accessing the target storage appliance. This option is only applicable for scripts of type Storage Switchover and Storage Failover. If the values for the parameter target_storage_credential_name are specified, then the values for source_storage_credential_name and credential_owner must be specified. |
-source_storage_credential_name |
Specify the named credential to be used for accessing the source storage appliance. This option is only applicable for scripts of type Storage Switchover and Storage Failover. If the values for the parameter target_storage_credential_name are specified, then target_storage_credential_name and credential_owner must be specified. |
-credential_owner |
Specify the owner of the named credential for target_storage_credential and source_storage_credential. |
4.4.4 Configuring Credentials as Parameters for Scripts
Oracle Site Guard provides EM CLI commands for adding, deleting, and getting credentials as parameters to scripts. Before you configure a script to receive credentials as parameters, ensure that you have created these credentials as described in Section 3.2.4, "Creating Credentials." Also, ensure that the script for which you will configure credential parameters for, is already configured as described Section 4.4, "Configuring Scripts."
The following actions can be performed for configuring credentials as script parameters:
4.4.4.1 Adding Credential Parameters to a Script
To add credentials parameters to a configured script, run the following EM CLI command using the command-line interface. You must execute this command once for each set of credentials that need to be configured as parameters to a script:
emcli add_siteguard_script_credential_params
-script_id="id_associated_with_the_script"
-credential_name="name_of_the_credential"
[-credential_owner="credential_owner"]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-script_id |
Specify the script ID. |
-credential_name |
Specify the name of the credential. |
-credential_owner |
Specify the credential owner details. You need not specify the values of this parameter if the owner of the credential is same as that of the logged-in user. |
4.4.4.2 Deleting Credential Parameters from a Script
To delete one or more credentials parameters that are already configured for a script, run the following EM CLI command using the command-line interface:
emcli delete_siteguard_script_credential_params
-script_id="Id associated with the script"
[-credential_name="name of the credential"]
[-credential_owner="credential owner"]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-script_id |
Specify the ID associated with the script. |
-credential_name |
Specify the name of the credential. If this argument is not specified, all credentials associated with the script will be deleted.
This parameter is optional. |
-credential_owner |
Specify the owner of the credential. This parameter need not be specified if the owner of the credential is the same as the logged-in user. |
4.4.4.3 Getting Credential Parameters for a Script
To get a list of one or more credentials parameters configured for a script, run the following EM CLI command using the command-line interface:
emcli get_siteguard_script_credential_params
-script_id="Id_associated_with_the_script" [-credential_name="name_of_the_credential"] [-credential_owner="credential_owner"]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-script_id |
Specify the ID associated with the script. |
-credential_name |
Specify the name of the credential. If this argument is not specified, all credentials associated with the script will be deleted.
This parameter is optional. |
-credential_owner |
Specify the owner of the credential. This parameter need not be specified if the owner of the credential is the same as the logged-in user. |
4.4.5 Cloning a Script Using Existing Scripts
You can create and configure new scripts by cloning (copying) an existing script. This applies to all types of scripts.
To clone a script using the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console, follow these steps:
-
Log in to Enterprise Manager as an
EM_SG_ADMINISTRATORuser. -
From the Targets menu, click Systems.
The Systems page is displayed.
-
Select the system name (Generic System) on which the script must be configured. The Generic System page for that site is displayed.
-
Click Generic System > Site Guard > Configure.
The Site Guard Configuration page is displayed.
-
Click the Pre/Post Scripts tab or the Storage Scripts tab.
The Pre/Post Scripts page or the Storage Scripts page is displayed.
-
Select a configured script from the Scripts table and click Add Like.
-
Modify any pre-configured values that you want to change.
-
Click Save.
4.5 Configuring Auxiliary Hosts
You can configure one or more hosts managed by Enterprise Manager, as an auxiliary host to the site. An auxiliary host needs to be managed by Enterprise Manager. It can be part of one or more sites. These hosts can be used to run Pre Scripts, Post Scripts, or Storage Scripts on a site.
The following actions can be performed:
4.5.1 Adding an Auxiliary Host Using EMCLI Commands
To add an auxiliary host on a site, run the following EMCLI command in the command-line interface:
emcli add_siteguard_aux_hosts
-system_name="system_name"
-host_name="host_name"
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system on which you are performing the operation. |
-host_name |
The name of the host where the script will be executed.
Note: Ensure that the hostname is part of the system specified in |
4.5.2 Deleting an Auxiliary Host Using EMCLI Commands
To delete a auxiliary host on a site, run the following EMCLI command in the command-line interface:
emcli delete_siteguard_aux_host
-system_name="system_name"
[-host_name="name_of_the_host"]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system on which you are performing the operation. |
-host_name |
The name of the host where the script will be run.
Note: Ensure that the hostname is part of the system specified in |
4.5.3 Listing Auxiliary Targets Using EMCLI Commands
To view a list of all auxiliary targets for a system, run the following command:
emcli get_siteguard_aux_hosts
-system_name="system_name"
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system on which you are performing the operation. |
4.6 Configuring Database Lag Checks
This section describes how to configure values of Apply Lag and Transport Lag for one or more Data Guard enabled databases.
It contains the following topics:
-
Updating Threshold Value for Database Lag Using EMCLI Commands
-
Deleting Threshold Value for Database Lag Using EMCLI Commands
4.6.1 Configuring Database Lag Checks Using EMCLI Commands
You can configure values of Apply Lag and Transport Lag for one or more Data Guard enabled databases by running the following commands:
emcli configure_siteguard_lag
-system_name="system_name"
[-target_name="database_target_name"]
-property_name="lag_type"
-value="max_limit"
Note:
[ ] indicates that the parameter is optional.| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system on which you want to configure the threshold limit. |
-target_name |
Specify the database target name for which the threshold limit is configured. If this parameter is not specified, then the threshold value is applied to all databases of the system. |
-property_name |
Specify the property name. Valid values are ApplyLag and TransportLag. |
-value |
Specify the threshold value to be configured (in seconds). |
4.6.2 Updating Threshold Value for Database Lag Using EMCLI Commands
To update the values of Apply Lag and Transport Lag threshold for one or more Data Guard enabled database, run the following commands:
emcli update_siteguard_lag
-system_name="system_name"
[-target_name="database_target_name"]
-property_name="lag_type"
-value="max_limit"
Note:
[ ] indicates that the parameter is optional.| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system for which you want to configure the threshold limit. |
-target_name |
Specify the database target name for which the threshold limit is configured. If this parameter is not specified, then the threshold value is applied to all databases of the system. |
-property_name |
Specify the property name. Valid values are ApplyLag and TransportLag. |
-value |
Specify the threshold value to be updated (in seconds). |
4.6.3 Deleting Threshold Value for Database Lag Using EMCLI Commands
To delete the values of Apply Lag and Transport Lag threshold configured for one or more Data Guard enabled databases, run the following EMCLI commands:
emcli delete_siteguard_lag
-system_name="system_name"
[-target_name="database_target_name"]
-property_name="lag_type"
Note:
[ ] indicates that the parameter is optional.| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system for which you want to configure the threshold limit. |
-target_name |
Specify the database target name for which the threshold limit is configured. If this parameter is not specified, then the threshold value is applied to all databases of the system. |
-property_name |
Specify the property name. Valid values are ApplyLag and TransportLag. |
4.6.4 Listing Database Lag Thresholds Using EMCLI Commands
To view values of the configured database Apply Lag and Transport Lag threshold limits of a system, run the following command:
emcli get_siteguard_lag
-system_name="system name"
[-target_name="database_target_name"]
-property_name="lag_type"
Note:
[ ] indicates that the parameter is optional.| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-system_name |
Specify the system for which you want to retrieve the threshold limit. |
-target_name |
Specify the database target name for which the threshold limit is to be retrieved. If this parameter is not specified, then the threshold values of all databases of the system are listed. |
-property_name |
Specify the property name. Valid values are ApplyLag and TransportLag. |