A Architecture of the Guaranteed Event System
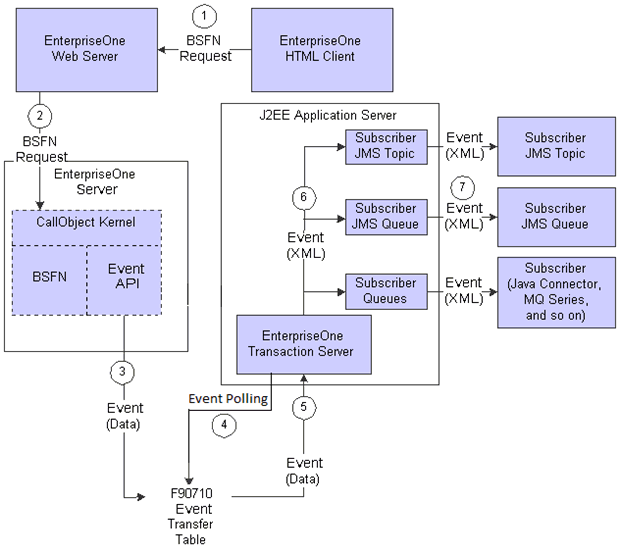
This appendix presents an architectural diagram of the Guaranteed Event System, which is one of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Transaction Server Components. The diagram depicts the general sequence that occurs when an event is published. These steps correspond to the numbered sequence of events in the diagram:
-
An HTML client user executes a business function (BSFN) request.
This request is sent to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne HTML Web Server.
-
The HTML Web Server forwards this request to a CallObject kernel on the Enterprise Server.
-
The CallObject kernel executes the BSFN, which calls the Event API to send the event data to the F90710 Event Transfer table.
If the event is a Z event, the data is sent to F90710 in a final XML format.
-
A database polling application available with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Transaction Server polls any available records in F90710.
-
The transaction server retrieves the event data from F90710 and (for Real-Time and XAPI events) converts the data to an XML document in the appropriate format.
-
The transaction server routes the event to the subscriber queue(s) for each subscriber that has established an active subscription for that event.
-
When a subscriber connects to the Transaction Server, the subscriber is sent all the events that exist in its subscription queue at that time.