| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Advanced Installation and Configuration Guide 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.1) Part Number E24089-09 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Advanced Installation and Configuration Guide 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.1) Part Number E24089-09 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Firewalls protect a company's Information Technology (IT) infrastructure by providing the ability to restrict network traffic by examining each network packet and determining the appropriate course of action.
Firewall configuration typically involves restricting the ports that are available to one side of the firewall, for example the Internet. It can also be set up to restrict the type of traffic that can pass through a particular port such as HTTP. If a client attempts to connect to a restricted port (a port not covered by a security "rule") or uses a protocol that is incorrect, then the client will be disconnected immediately by the firewall. Firewalls can also be used within a company Intranet to restrict user access to specific servers.
You can deploy the components of Oracle Enterprise Manager on different hosts throughout your enterprise. These hosts can be separated by firewalls. This chapter describes how firewalls can be configured to allow communication between the Enterprise Manager components.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Firewall configuration should be the last phase of Enterprise Manager deployment. Before you configure your firewalls, make sure you are able to log in to the Cloud Control console and that your Management Agents are up and monitoring targets.
If you are deploying Enterprise Manager in an environment where firewalls are already installed, open the default Enterprise Manager communication ports for all traffic until you have completed the installation and configuration processes and are certain that you are able to log in to Cloud Control and that your Management Agents are up and monitoring targets.
The default communication ports for Enterprise Manager are assigned during the installation. If you modify the default ports, be sure to use the new port assignments when you configure the firewalls.
If you are enabling Enterprise Manager Framework Security for the Management Service, the final step in that configuration process is to restrict uploads from the Management Agents to secure channels only. Before completing that step, configure your firewalls to allow both HTTP and HTTPS traffic between the Management Agent and Management Repository and test to be sure that you can log in to Enterprise Manager and that data is being uploaded to the Management Repository.
After you have confirmed that the Oracle Management Service and Management Agents can communicate with both protocols enabled, complete the transition to secure mode and change your firewall configuration as necessary. If you incrementally configure your firewalls, it will be easier to troubleshoot any configuration problems.
Oracle Management Service uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request to check the status target host machines. If the ICMP Echo Request is blocked by the firewall, a host machine will be appear to be down.
To determine the status of any machine in the environment, ICMP Echo Requests must be enabled on the firewall. If the ICMP Echo Request is enabled, the ping command can be issued by Oracle Management Service to check the status of the machine.
By default, port 7 will be used for the ICMP Echo Request.
As described in the previous sections of this chapter, it is important to understand and identify the ports used by each of the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10gcomponents before you configure your firewalls.
The last panel in the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Grid Control installer, which is displayed just before the actual installation is started, list all of the ports assigned during the installation.
Post-installation, you can view these values in the staticports.ini file at the following location on the OMS host:
MIDDLEWARE_HOME/.gcinstall_temp/staticports.ini
You can get the Middleware Home value by viewing the Oracle Home target for the Oracle Management Service in Cloud Control.
Table 12-1 notes the default ports and/or port ranges assigned to various Enterprise Manager components that should be accessible through a firewall. These components include WebLogic Server components created as part of the WebLogic domain the Enterprise Manager installation belongs to, as well as optional components such as JVM Diagnostics and Application Dependency and Performance.
Table 12-1 Default Ports and Port Ranges for Enterprise Manager Components
| Port | Default Values |
|---|---|
|
Enterprise Manager Upload HTTP Port |
4889 - 4898 |
|
Enterprise Manager Upload HTTPS (SSL) Port |
1159, 4899 - 4908 |
|
Management Agent Port |
3872 |
|
Management Repository Database Port |
1521 |
|
Cloud Control Console HTTP Port |
7788 - 7798 |
|
Cloud Control Console HTTPS (SSL) Port |
7799 -7809 |
|
EM Domain WebLogic Admin Server HTTP Port |
7001 |
|
EM Domain WebLogic Admin Server HTTPS (SSL) Port |
7101 - 7200 |
|
Cloud Control Managed Server HTTP Port |
7201 - 7300 |
|
Cloud Control Managed Server HTTPS (SSL) Port |
7301 - 7400 |
|
WebLogic Node Manager HTTPS (SSL) Port |
7401 - 7500 |
|
JVM Diagnostics Managed Server |
3800 |
|
JVM Diagnostics Managed Server (SSL) |
3801 |
|
Application Dependency and Performance RMI Registry Port |
51099 |
|
Application Dependency and Performance Java Provider Port |
5503 |
|
Application Dependency and Performance Remote Service Controller Port |
55000 |
Your main task in enabling Enterprise Manager to work in a firewall-protected environment is to take advantage of proxy servers whenever possible, to make sure only the necessary ports are open for secure communications, and to make sure that only data necessary for running your business is allowed to pass through the firewall.
Figure 12–1 provides a topology of an Enterprise Manager grid environment that is using a firewall, and also illustrates the default ports that can be used.
Figure 12-1 Firewall Port Requirements (Default)
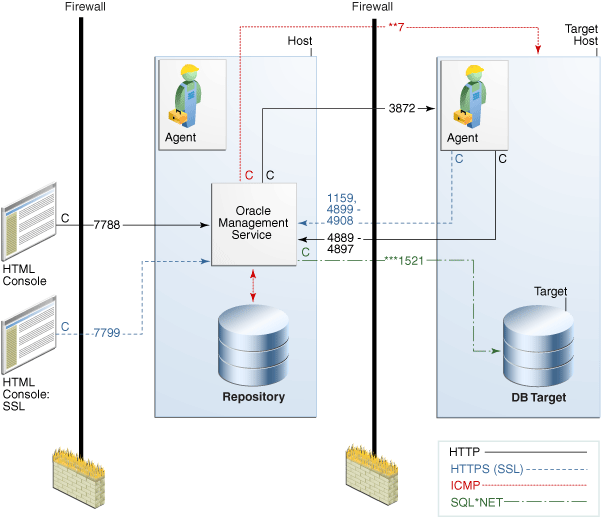
The conventions used in the preceding illustration are as follows:
Table 12-2 Conventions Used In Illustration
| Convention | Description |
|---|---|
|
C |
Is the entity that is making the call. |
|
* |
Enterprise Manager will default to the first available port within an Enterprise Manager set range. |
|
** |
Enterprise Manager will default to the first available port. |
|
*** |
Are the Database listener ports. |
Notes:
The direction of the arrows specify the direction of ports.
Port 1159, 4898-4989 specify that 1159 is the default. If this port is not available, the Oracle Management Service will search in the range that is specified.
To clone between two target hosts separated by a firewall, the agents will need to communicate to each other on the agent ports. The initiating Management Agent will make the call.
The following sections describe the ports and types of data required by Enterprise Manager in a secure, firewall-protected environment:
Firewalls Between Your Browser and the Cloud Control Console
Configuring the Management Agent on a Host Protected by a Firewall
Configuring the Management Service on a Host Protected by a Firewall
Firewalls Between the Management Service and the Management Repository
Firewalls Between Grid Control and a Managed Database Target
Configuring Firewalls to Allow ICMP and UDP Traffic for Beacons
Connections from your browser to the Cloud Control console are performed over the default port used for your Oracle HTTP Server.
For example, the default, non-secure port for the Oracle HTTP Server is usually port 7788. If you are accessing the Cloud Control console using the following URL and port, then you must configure the firewall to allow the Cloud Control console to receive HTTP traffic over port 7788:
http://omshost.example.com:7788/em
On the other hand, if you have enabled security for your Oracle HTTP Server, you are likely using the default secure port for the server, which is usually port 7799. If you are accessing the Cloud Control console using the following URL and port, then you must configure the firewall to allow the Cloud Control console to receive HTTPS traffic over port 7799:
https://omshost.example.com:7799/em
If your Management Agent is installed on a host that is protected by a firewall and the Management Service is on the other side of the firewall, you must perform the following tasks:
Configure the Management Agent to use a proxy server for its uploads to the Management Service.
Configure the firewall to allow incoming HTTP traffic from the Management Service on the Management Agent port. Regardless of whether or not Enterprise Manager Framework Security has been enabled, the default port is 3872. Incoming traffic can be received only if the port corresponding to the Management Agent is open in the firewall.
Figure 12-2 illustrates the connections the Management Agent must make when it is protected by a firewall.
Figure 12-2 Configuration Tasks When the Management Agent Is Behind a Firewall
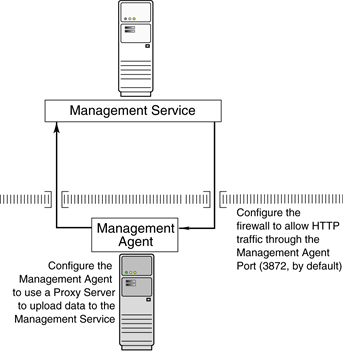
You can configure the Management Agent to use a proxy server for its communications with a Management Service outside the firewall, or to manage a target outside the firewall.
From the Setup menu, select Agents.
Click the Agent you want to configure in the Name column in the Management Agents table. The target home page for the Management Agent opens.
Select Properties from the Agent menu.
Select Advanced Properties from the pull down menu.
Supply the correct values for the proxyHost and proxyPort properties.
Click Apply to save your changes, which will be saved to the AGENT_HOME/sysman/config/emd.properties file.
Note:
The proxy password will be obfuscated when you restart the Management Agent.While the Management Agents in your environment must upload data from your managed hosts to the Management Service, the Management Service must also communicate with the Management Agents. As a result, if the Management Agent is protected by a firewall, the Management Service must be able to contact the Management Agent through the firewall on the Management Agent port.
By default, the Enterprise Manager installation procedure assigns port 3872 to the Management Agent. However, if that port is occupied, the installation may assign an alternate port number.
After you determine the port number assigned to the Management Agent, you must then configure the firewall to allow incoming HTTP or HTTPS traffic (depending upon whether or not you have enabled Enterprise Manager Framework Security) on that port.
See Also:
Your firewall documentation for more information about opening specific ports for HTTP or HTTPS traffic.If your Management Service is installed on a host that is protected by a firewall and the Management Agents that provide management data are on the other side of the firewall, you must perform the following tasks:
Configure the Management Service to use a proxy server for its communications to the Management Agents.
Configure the firewall to allow incoming HTTP traffic from the Management Agents on the Management Repository upload port.
If you have enabled Enterprise Manager Framework Security, the upload URL uses port 1159 by default. If this port is not available, Enterprise Manager will default to first available port in the range 4899-4908. If you have not enabled Enterprise Manager Framework Security, the upload port is the first available port in the range 4889 - 4897.
Figure 12-3 illustrates the connections the Management Agent must make when it is protected by a firewall.
Figure 12-3 Configuration Tasks When the Management Service Is Behind a Firewall
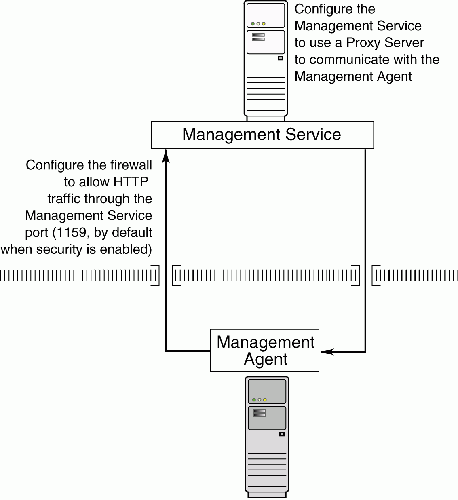
This section describes how to configure the Management Service to use a proxy server for its communications with Management Agents outside the firewall.
To configure the Management Service to use a proxy server, do the following:
From the Setup menu, select Proxy Settings.
Under “Agent Connection Setting”, click Manual Proxy Configuration.
Supply the necessary HTTP or HTTPS property values for your configuration.
Click Apply to save your changes to the OMS_HOME/sysman/config/emd.properties file for the OMS instance.
After you have supplied your configuration, supply a Management Agent URL (or use the URL supplied by default) to test it.
While the Management Agents in your environment must contact the Management Agents on your managed hosts, the Management Service must also be able to receive upload data from the Management Agents. If the Management Service is behind a firewall, you must configure the firewall to allow the Management Agents to upload data on the upload port.
By default, the Enterprise Manager installation procedure assigns port 4889 as the Repository upload port. However, if that port is occupied, the installation will assign an alternate port number.
In addition, when you enable Enterprise Manager Framework Security, the upload port is automatically changed to the secure 1159 HTTPS port.
Administrators can also change the upload port after the installation.
After you determine the port number assigned to the Management Service upload port, you must then configure the firewall to allow incoming HTTP or HTTPS traffic (depending upon whether or not you have enabled Enterprise Manager Framework Security) on that port.
See Also:
Your firewall documentation for more information about opening specific ports for HTTP or HTTPS trafficUnless online access to the Internet is strictly forbidden in your environment, Oracle Management Service should be enabled to access My Oracle Support. This access is necessary to enable updates and patches to be downloaded, for example.
At minimum, the following URLs should be made available through the firewall:
ccr.oracle.com
login.oracle.com
support.oracle.com
updates.oracle.com
When you configure the Management Service or a Management Agent to use a proxy server, it is important to understand the purpose of the dontProxyFor property, which identifies specific URL domains for which the proxy will not be used.
For example, suppose the following were true:
You have installed the Management Service and several Management Agents on hosts that are inside the company firewall. These hosts are in the internal .example.com and .example.us.com domains.
You have installed several additional Management Agents on hosts that are outside the firewall. These hosts are installed in the .example.uk domain.
You have configured Enterprise Manager to automatically check for critical software patches on My Oracle Support.
In this scenario, you want the Management Service to connect directly to the Management Agents inside the firewall without using the proxy server. On the other hand, you want the Management Service to use the proxy server to contact the Management Agents outside the firewall, as well as the My Oracle Support site, which resides at the following URL:
http://support.oracle.com
The following properties will prevent the Management Service from using the proxy server for connections to the Management Agents inside the firewall. Connections to My Oracle Support and to Management Agents outside the firewall will be routed through the proxy server:
proxyHost=proxy42.example.com proxyHost=80 dontProxyFor=.example.com, .example.us.com
Secure connections between the Management Service and the Management Repository are performed using features of Oracle Advanced Security. As a result, if the Management Service and the Management Repository are separated by a firewall, you must configure the firewall to allow Oracle Net firewall proxy access.
When you are using the Cloud Control console to manage a database, you must log in to the database from the Cloud Control console in order to perform certain monitoring and administration tasks. If you are logging in to a database on the other side of a firewall, you will need to configure the firewall to allow Oracle Net firewall proxy access.
Specifically, to perform any administrative activities on the managed database, you must be sure that the firewall is configured to allow the Oracle Management Service to communicate with the database through the Oracle Listener port.
You can obtain the Listener port by reviewing the Listener home page in the Cloud Control console.
Enterprise Manager supports the use of multiple Management Services that communicate with a common Management Repository. For example, using more than one Management Service can be helpful for load balancing as you expand your central management capabilities across a growing e-business enterprise.
When you deploy multiple Management Services in an environment protected by firewalls, be sure to consider the following:
Each Management Agent is configured to upload data to one Management Service. As a result, if there is a firewall between the Management Agent and its Management Service, you must configure the firewall to allow the Management Agent to upload data to the Management Service using the upload URL.
In addition, each Management Service must be able to contact any Management Agent in your enterprise so it can check for the availability of the Management Agent. As a result, you must be sure that your firewall is configured so that each Management Service you deploy can communicate over HTTP or HTTPS with any Management Agent in your enterprise.
Otherwise, a Management Service without access to a particular Management Agent may report incorrect information about whether or not the Management Agent is up and running.
See Also:
"About Availability" in the Enterprise Manager online help for information about how Enterprise Manager determines host and Management Agent availabilityOracle Beacons provide application performance availability and performance monitoring. They are part of the Application Service Level Management features of Enterprise Manager.
See Also:
"About Application Service Level Management" in the Enterprise Manager Online HelpEnterprise Manager uses the industry-standard Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to transfer data between Beacon and the network components you are monitoring. There may be situations where your Web application components and the Beacons you use to monitor those components are separated by a firewall. In those cases, you must configure your firewall to allow ICMP, UDP and HTTP traffic.