| Oracle® Health Sciences Clinical Development Analytics Administrator's Guide Release 2.1 for Plus Configuration E28551-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Health Sciences Clinical Development Analytics Administrator's Guide Release 2.1 for Plus Configuration E28551-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter contains the following topics:
To load data from the source systems to the data warehouse, CDA uses Extract Transform and Load (ETL) programs that
Identify and read desired data from different data source systems,
Clean and format data uniformly, and
Write it to the target data warehouse.
In CDA, Oracle Clinical and Oracle's Siebel Clinical are the source systems for which Oracle provides predefined ETL.
Figure 3-1 displays the ETL process delivered with CDA.
Note:
This figure does not cover Multi-source Integration, which is an optional CDA capabililty. For CDA architecture including this option, see Chapter 4, "Multi-Source Integration,".CDA uses Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub (Oracle LSH) to maintain star-schema tables that enable user reporting. Set up as a recurring job, the Oracle LSH Extraction, Transformation, and Load process (ETL) is designed to periodically capture targeted metrics (dimension and fact data) from multiple clinical trial databases, transform and organize them for efficient query, and populate the Oracle LSH star-schema tables.
While the CDA data model supports data extraction from multiple sources, CDA only includes source-dependent extract (SDE) mappings for the Oracle Clinical and Siebel Clinical databases. However, you can also define SDE mappings from additional external sources that write to the appropriate staging tables. Note that you are responsible for resolving any duplicate records that may be created as a consequence. For more information about how to add a new data source to CDA, refer to Adding a New Source System in LSH.
Oracle LSH uses pass-through views to access transactional data from source databases. The SDE programs map the transactional data to source specific staging tables, in which the data must conform to a standardized format, effectively merging the data from multiple, disparate database sources. This is the architectural feature that accommodates external database sourcing.
A pooling program reads the data from all the source specific staging tables, and loads it into the common staging table.
Oracle LSH thence transforms the staged data (in the common staging table) using source-independent loads (SILs) to internal Star-schema tables, where such data are organized for efficient query by the Oracle BI Server.
There is one SDE mapping for each target table, which extracts data from the source system and loads it to the respective source specific staging tables. SDEs have the following features:
Incremental submission mode: CDA supplied ETL uses timestamps and journal tables in the source transactional system to optimize periodic loads.
Bulk and normal load: Bulk load uses block transfers to expedite loading of large data volume. It is intended for use during initial data warehouse population. Bulk load is faster, if data volume is sufficiently large. However, if load is interrupted (for example, disk space is exhausted, power failure), load cannot be restarted in the middle; you must restart the load.
Normal load writes one record at a time. It is intended to be used for updates to the data warehouse, once population has been completed. Normal load is faster, if data volume is sufficiently small. You can also restart load if the load is interrupted.
You must set the appropriate target load type for an ETL program in Oracle LSH to indicate bulk and normal load. In CDA, by default, bulk load is enabled for all SDEs.
See Also:
Setting Up the Target Load Type for information about setting the appropriate table processing type.
There is one SIL mapping for each target table. The SIL extracts the normalized data from the common staging table and inserts it into the data warehouse star-schema target table. SILs have the following attributes:
Concerning changes to dimension values over time, CDA overwrites old values with new ones. This strategy is termed as Slowly Changing Dimension approach 1.
CDA's data model includes aggregate tables and a number of indexes, designed to minimize query time.
By default, bulk load is disabled for all SILs.
The results of each ETL execution is logged. The logs hold information about errors encountered, during execution.
Informatica provides the following four error tables:
PMERR_DATA
PMERR_MSG
PMERR_SESS
PMERR_TRANS
During ETL execution, records which fail to be inserted in the target table (for example, some records violate a constraint) are placed in the Informatica PowerCenter error tables. You can review which records did not make it into the data warehouse, and decide on appropriate action with respect to them.
Adding Data Source Information
As you read data from different database instances, you need to specify the source of the data. CDA provides the W_RXI_DATASOURCE_S table (in RXI schema) that stores all information about all data sources from which data is extracted for CDA. The following are some of the columns in this table:
ROW_WID - A unique ID for each record in the table.
DATASOURCE_NUM_ID - The ID for the database. Must be coordinated with the value given to the database when ETL is run.
DATASOURCE_NAME - A meaningful name of the database.
DATASOURCE_TYPE - Application system that manages the database.
DESC_TEXT - Optional text describing the purpose of the database.
INTEGRATION_ID - Set this to the same values as DATASOURCE_NUM_ID
See Also:
Oracle Health Sciences Clinical Development Analytics Electronic Technical Reference Manual, for more information about the W_RXI_DATASOURCE_S table.
Adding a New Source System in LSH, for more information about how to add a new data source to CDA.
Handling Deletions in Siebel Clinical
CDA provides an optional feature to manage hard deletion of records in Siebel Clinical. You create triggers in the source system to handle deletion of records. To do this:
Navigate to the temporary staging location where the CDA installer copies the installation files.
Connect to the Siebel Clinical data source and run the ocda_sc_del_trigger.sql script delivered with CDA. This script creates the RXI_DELETE_LOG_S table and triggers on tables provided as input. The following are the tables in Siebel Clinical for which CDA supports creating triggers:
S_CL_PTCL_LS
S_PROD_INT
S_CL_SUBJ_LS
S_CONTACT
S_CL_PGM_LS
S_PTCL_SITE_LS
S_EVT_ACT
Provide a list of comma separated values of table names for which the triggers needs to be created as the script's input. For example, S_CL_PTCL_LS,S_PROD_INT,S_CL_SUBJ_LS. The tables names that you provide can only be a subset of the tables listed above.
Note that when the user deletes a record in the table, the primary key of the deleted record is inserted in the RXI_DELETE_LOG_S table on the Siebel source system.
Update the remote location of the OCDA_RXI_DELETE_LS load set in OCDA_DELETE_LOG_WA to Siebel Clinical source database connection and install this work area.
Navigate to the OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA.
Click OCDA_DELETE_LOG_WA work area.
Click OCDA_RXI_DELETE_LS loadset.
Click Check Out.
Click Apply.
In the Load Set Attributes section, click Update.
Click the Search icon.
Select OCDA_SC_OLTP_RL/<Connection_Name>.
Click Apply.
Reinstall the work area containing the load set and passthrough views.
For more information, refer to Oracle Health Sciences Clinical Development Analytics Installation Guide (Post Installation Tasks)
Modify the value of the DELETE_FLOW submission parameter for the following dimension programs based on the triggers created in step 2:
OCDA_INFA_Study_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
OCDA_INFA_Study_Site_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
OCDA_INFA_Study_Region_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
OCDA_INFA_Program_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
OCDA_INFA_Product_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
OCDA_INFA_Study_Subject_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
OCDA_INFA_Party_Per_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
OCDA_INFA_SS_Con_Dim_SDE_SC_PRG
Perform the following steps:
Navigate OCDA_domain > OCDA_CODE_APP_AREA > OCDA_SDE_SC_WORK_AREA.
Click the Name hyperlink of the program.
Click Submit.
Enter the following information in Submission Details:
Submission Type: Backchain
Force Execution: Yes
In Submission Parameters, enter the value of DELETE_FLOW as Y. The default value is N, which indicates that CDA does not handle deletion in Siebel Clinical.
Click Submit.
Execute the ETLs as listed in the Executing the ETL Programs section.
The Siebel Clinical related SDE mappings reads the above instance of the RXI_DELETE_LOG_S table.
Note:
Records that are deleted in the source system are soft deleted in the data warehouse.See Also:
Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub User's Guide, (Tracking Job Execution), for more information about viewing job execution logs.
The steps below will consider Oracle Clinical work areas as an example to demonstrate adding new OLTP source system to be read for the ware house load.
The process involves:
Creating a remote location for the new source OLTP pass-through views.
Creating a clone and configuring the new replica of the OC source Pass through the view's work area.
Creating a clone and configuring the new replica of the OC SDE work area and programs.
Modifying the pool program to include the new source specific stage tables.
This section describes how to create a LSH remote location which connects to the new instance of the OC OLTP source system.
Perform the following steps to configure the remote location OCDA_OC_OLTP_RL_Inst2:
Click the Remote Location subtab under the Administration tab. The Maintain Remote Locations screen opens.
Click Add Remote Location. The Create Remote Location screen appears.
Enter values in the following fields:
Remote Location Name - OCDA_OC_OLTP_RL_Inst2.
Description - Description of the remote location.
DBLINK Prefix - The name of the database link. If another DBLINK Prefix with the same name exists in the database, the system adds an additional string to make it unique. The DBLINK_NAME is usually the global name or the TNS name of the remote database.
Connect String - The name of the string that Oracle LSH must use in the USING clause of the create database link SQL statement. Connect string has following format:
((DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=hostname)(PORT=dbportnumber))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=dbsid))))
Adapter - Select Oracle Tables and Views from the drop-down list.
Click Apply.
To configure the connection for location OCDA_OC_OLTP_RL_Inst2:
Select the remote location just created.
Click CREATE CONNECTION and provide the following OPA connection details:
Name — Enter a name for the connection. For example, RXA_DES.
User Name — Enter the database username. For example, RXA_DES.
Password — Enter the database password for above user.
Click Apply.
Repeat steps 1 through 3 for the other two database connections RXC, OPA.
Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub System Administrator's Guide (Chapter 6, Registering Locations and Connections), for more information on registering locations and connections in Oracle LSH.
This sections describes how to replicate a source work area and set the connection of load set.
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA and select the OCDA_OC_DATA_WA.
Click CLONE.
On the Clone Destination page, select OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA within OCDA_domain.
Provide the desired clone label.
Click Review and select Finish.
A replica of New OC Sources work area is created with the name OCDA_OC_DATA_WA_1.
To rename it, click OCDA_OC_DATA_WA_1.
Click Update and modify the name to OCDA_OC_DATA_WA_Instance_2.
Click Apply.
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA > OCDA_OC_DATA_WA_Instance_2.
Check individual Loadset Instances:
OCDA_OC_OPA_LS
OCDA_OC_RXA_DES_LS
OCDA_OC_RXC_LS
Update their respective Load Set Attributes with remote location/connections which was created in Creating Remote Location for New Source OLTP Pass-through Views.
Install the OCDA_OC_DATA_WA_Instance_2 work area in full mode.
This section describes how to create a clone of OC SDE work area and configure it to read from the new OC pass-through work created in Creating Clone and Configuring New Replica of OC source Pass Through View's Work Area.
Create new application area and clone the SDE OC work area.
Click OCDA_domain and select Add Application Area.
Create a new application area with name OCDA_CODE_APP_AREA_NEW.
Click Apply.
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_CODE_APP_AREA and select OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA.
Click CLONE.
On the Clone Destination page, select OCDA_CODE_APP_AREA_NEW within OCDA_domain.
Provide the desired clone label.
Click Review and select Finish.
A replica of the new OC SDE work area named OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA is created.
To rename it, click OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA.
Click Update and modify the name to OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA_Instance_2.
Click Apply.
Modify the table instances.
Navigate to OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA_Instance_2.
Click on the Table instance W_HS_OC_APPLICATION_USER_DS.
Click Update and change the fields :
Name - For example, W_HS_OC_APPLICATION_USER_DS_1.
Oracle Name
SAS Name
Note:
Ensure that the Name, Oracle Name and SAS Name above should not be beyond 30 chars. Exceeding this limit will cause errors in any program that reads from this table instance.Modify the table descriptors' mapping and set the parameter for each SDE program.
This step describes how to unmap and remap the source table descriptors to the new OC Source instance work area that was created in Creating Clone and Configuring New Replica of OC source Pass Through View's Work Area.
Click on OCDA_INFA_Application_User_D_SDE_OC_PRG in OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA_Instance_2.
Click Check out.
Select Copy definition to the local Application Area and checkout.
Note:
This will check out the SDE program and create a local copy of it thereby not affecting the definition of the program, which was cloned for the original OCDA_doman > OCDA_CODE_APP_AREA. When further CDA patches are applied, programs within this work area will remain unaffected.Select Table Descriptors. Each source table descriptor can be identified by Is Target = No in the table that shows all table descriptors.
Note:
Ignore W_CONTROL_S table as it is not an Oracle Clinical source table.Click the following mapping icon:
Click Update, then Unmap and Apply.
Repeat step d for all the source table descriptors.
To remap all the source table descriptors for a SDE program, select Automatic Mapping by Nam" from the Actions drop down.
To get to OC source pass through view's work area that was created in Creating Clone and Configuring New Replica of OC source Pass Through View's Work Area, select:
Domain - OCDA_domain.
Application area - OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA
Workarea - OCDA_OC_DATA_WA_Instance_2
Select the source table for current program that is in consideration.
Click Map. This will map all the table descriptors.
Click the Parameter tab for the program that is in consideration.
Change the default for the parameter DATASOURCE_NUM_ID from 1 to 3. This number should be unique the program within this work area and should not be repeated.
Repeat steps a through m for all the Programs in the OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA_Instance_2 work area.
Once the entire program's mapping and parameters are changed install the work area in full mode. Create a new execution setup and submit it in back chain for all the programs.
This section describes how to modify the pool program to include table instances that were created in Creating Clone and Configuring New Replica of the OC SDE Work Area and Programs. By performing the following steps, newly created OC SDE target table instances will propagate data to the target dimension and fact warehouse tables.
Navigate to OCDA_doman > OCDA_CODE_APP_AREA > OCDA_POOL_WORK_AREA.
Click OCDA_PLS_Application_User_D_SDE_Pool_PRG.
Click Check out.
Check out the existing definition and click Apply.
To add the new table descriptor for this program, select Create Table Descriptors from Table Instances from the Actions drop down.
To get to the OC source SDE work area that was created in Creating Clone and Configuring New Replica of the OC SDE Work Area and Programs, select the following:
Domain - OCDA_domain
Application area - OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA_New
Workarea = OCDA_SDE_OC_WORK_AREA_Instance_2
Select the Table Instance W_HS_OC_APPLICATION_USER_DS_1 that was created in Creating Clone and Configuring New Replica of the OC SDE Work Area and Programs.
Click Create table descriptor.
Repeat steps 2 to 9 for all the programs in the OCDA_POOL_WORK_AREA work area. This will read all OC SDE Target table instance data corresponding to their SDE's.
After the entire program's table descriptors are added into their respective pool programs, install the work area in full mode. Create a new execution setup and submit them in back chain for each of programs in OCDA_POOL_WORK_AREA.
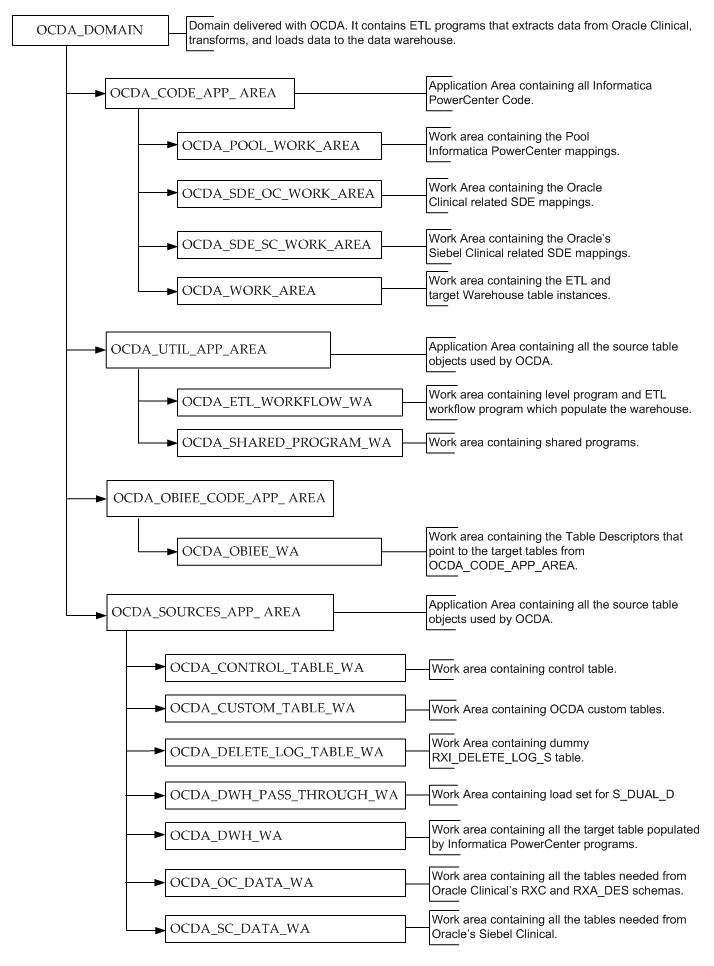
Figure 5-2 displays the CDA domain hierarchy in Oracle LSH:
Figure 3-2 CDA Domain Hierarchy in Oracle LSH
This section describes the ETL mapping in DAC. Figure 3-4 displays the hierarchy:
Following is the ETL mapping hierarchy:
CONTAINER (CDA_Warehouse) - A single container that holds all objects used for OHSCDA. For deduplication, however, there is a container for every deduplicated dimension that holds all the objects involved in deduplication.
EXECUTION PLAN - A data transformation plan defined on subject areas that needs to be transformed at certain frequencies of time. An execution plan is defined based on business requirements for when the data warehouse needs to be loaded. Single Execution Plan to Load Complete Warehouse.
SUBJECT AREAS - A logical grouping of tables related to a particular subject or application context. It also includes the tasks that are associated with the tables, as well as the tasks required to load the tables. Subject areas are assigned to execution plans, which can be scheduled for full or incremental loads.
TASK GROUPS - This is a group of tasks that should be run in a given order.
TASKS - A unit of work for loading one or more tables. A task comprises the following: source and target tables, phase, execution type, truncate properties, and commands for full or incremental loads. Each task is a single Informatica workflow.
ETL Programs are responsible for bringing the warehouse target tables up to date with respect to the current state of the source application database tables. You run ETL programs as either a Full load or an Incremental Load.
You perform a Full load when you want to completely refresh the target tables. This occurs when you first load the warehouse, and at any subsequent time when you need to do a complete refresh. Full loads drop the indexes on the warehouse target tables, truncate the tables, load all the appropriate records from the source into the target tables, and rebuild the indexes on the target tables.
Once a full load has been done, you run periodic Incremental loads to update the warehouse target tables with changes that have occurred in the source tables since the last prior load.
CDA has an optional capability, called Multi-Source Integration, which enables you to perform deduplication of data coming from multiple source databases. This capability is described in Section Multi-Source Integration below. If you use it, Deduplication requires the execution of additional ETL; additionally, the method for triggering the execution of the ETL differs if you use Deduplication.
The processes for executing CDA's ETL is described below in four sections, as outlined here:
Important:
Before you reinstall, ensure that:Informatica DP Server is up and running
LSH Job Queue is running
If you are running Deduplication ETL, you must also ensure that the LSH Message Queue is running.
Refer to Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub System Administrator's Guide for information on these components.
This section gives steps for full load of the warehouse target tables. You will need to do a full load after the initial install of the CDA software. This is referred to as an Initial Load. You may subsequently need to do additional full loads; these are referred to as Reloads. A Reload would be necessary, for example, if you initially load from a test database, and then shift to a production database.
If this is the first time you are executing the ETL programs after the initial install, or you need to reload the complete warehouse, follow the steps given below.
Certain steps are required only if doing a reload, rather than an initial load. They are called out accordingly.
This section gives information on setting up and executing the LSH program to perform a full load to load, in the case where you are not running the Deduplication ETL.
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA > OCDA_DWH_PASS_THROUGH_WA
Note:
Ensure that you have installed the domain, Application Area, and Work Area in Oracle LSH before you can perform the subsequent steps.For more information, refer to Oracle Health Sciences Clinical Development Analytics Installation Guide (Post Installation Tasks).
If you are executing the ETL programs for the first time after installing CDA, submit the OCDA_PLS_S_DUAL_D_PRG program before submitting any fact in backchain.
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_CODE_APP_AREA > OCDA_WORK_AREA.
Note:
Ensure that you have installed the domain, Application Area, and Work Area in Oracle LSH before you can perform the subsequent steps.For more information, refer to Oracle Health Sciences Clinical Development Analytics Installation Guide (Post Installation Tasks).
If you are executing the ETL programs for the first time after installing CDA, submit the following programs in the given order before submitting any fact in backchain:
OCDA_PLS_DUAL_PRG
OCDA_INFA_DayDimension_SIL_PRG
OCDA_INFA_MonthDimension_SIL_PRG
Important:
Ensure that you submit the above programs every time you modify them.Perform this step only if you are reloading the complete warehouse. In this step, you clear all records from the W_CONTROL_S table.
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA > OCDA_CONTROL_TABLE_WA.
Click the OCDA_CONTROL_TABLE_POPULATE_PRG hyperlink.
Click Submit.
Enter the following values for submission parameters:
Config_days: Accept the default. This parameter is ignored when Delete_mode is selected.
Delete_mode: ALL
Input_values: Leave this parameter blank.
In Submission Type, select Immediate.
In Force Execution, select Yes.
Click Submit.
Navigate to my home and monitor the job. This will clear all the entries from the control table
Submit the program to populate the control table in backchain.
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_SOURCES_APP_AREA > OCDA_CONTROL_TABLE_WA.
Click the OCDA_CONTROL_TABLE_POPULATE_PRG hyperlink.
Click Submit.
Enter the following values for submission parameters:
Config_days: Offset relative to the beginning of the current day, used to determine the latest record timestamp that will be loaded. See the following note for considerations in setting Config_days.
Delete_mode: None
Input_values: Leave this parameter blank.
Considerations for Config_days parameter
The Control Table (W_CONTROL_S) stores the time span that determines which source records for base dimensions and facts are extracted from the database during each ETL execution. That is, source records for base facts are extracted if their creation or modification timestamp is between the start and end timestamps specified in the Control Table record for a given ETL execution.
These endpoints are defined before the execution of the ETL mapping begins. The start timestamp is the end timestamp of the previous execution of the same ETL mapping. The end timestamp is calculated as follows:
a. Start with the current time at the warehouse.
b. Truncate that time, yielding the midnight that started the current day
c. Subtract the value of the CONFIG_DAYS parameter. CONFIG_DAYS is expressed in days, or fractions of days, and defaults to a value of 1.
The truncation is performed in case the source is in a later timezone than the warehouse. This ensures that no record will fail to load because it falls into a gap between the end of one load's timespan and the start of the next.
CONFIG_DAYS can be used to ensure that there are no temporarily "orphaned" fact records. An orphaned fact record will be created in the warehouse if a dimension, and a fact that depends on it, are created in the source database during the period after a parent dimension has been loaded but before the fact load starts. This is avoided by setting CONFIG_DAYS to a value greater than zero.
It is possible, for example, that after the data for the study-site dimension have been loaded, but before the received CRF fact has been loaded, that a new study site would be created in the source database, and some received CRFs recorded. With config_days at zero, the received CRFs would be loaded, but their parent study-site would not be.
Lacking a proper parent for these received CRF records , CDA would set their foreign key to the Unknown study-site. Reports would reflect that allocation; users would not be able to tell where the orphaned CRFs came from.
Orphaned records remain orphaned only until the next ETL execution; at that time the absent parent records are extracted, and the foreign keys are adjusted. But the CONFIG_DAYS parameter is provided to enable you to avoid having any records be temporarily orphaned.
By setting it to one, you instruct CDA to not load any base fact records from a source, if they were created or modified less than a day before loading from that table commences. As long as your entire load takes less than a day, you will have no orphaned fact records. But the other side of the coin is that your warehouse will reflect the state of the database as of a day before the ETL ran.
If reporting that approaches real-time is valued more than avoiding temporary orphans, you will want to set CONFIG_DAYS to a value close to zero. You also should adjust CONFIG_DAYS to reflect the actual frequency of creation of new dimension records, and fact records dependent on them, in your source database. The expected frequency may be less than once/day, in which case you would be safe to set CONFIG _DAYS to less than 1.
In Submission Type, select Backchain.
In Force Execution, select Yes.
Click Submit.
Adjust Table Descriptors depending on source applications used
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_UTIL_APP_AREA > OCDA_ETL_WORKFLOW_WA.
If Oracle Clinical is your only data source, remove the following Table Descriptors from OCDA_PLS_LEVEL1_FACT_PRG:
W_ACTIVITY_F
W_RXI_RGN_ENRLMNT_PLN_F
If Siebel Clinical is your only data source, remove the following Table Descriptors from OCDA_PLS_LEVEL1_FACT_PRG:
W_RXI_DISCREPANCY_F
W_RXI_DISCRPNCY_STATUS_F
W_RXI_RECEIVED_CRF_F
Install the program OCDA_PLS_LEVEL1_FACT_PRG.
If Siebel Clinical is your only data source, remove the following Table Descriptors from OCDA_PLS_LEVEL1_AGG_FACT_PRG:
W_RXI_DISCREPANCY_A
W_RXI_DISCRPNCY_STATUS_A
W_RXI_RECEIVED_CRF_A
Install the program OCDA_PLS_LEVEL1_AGG_FACT_PRG.
Submit the job to execute the Full Load:
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_UTIL_APP_AREA > OCDA_ETL_WORKFLOW_WA.
Click the OCDA_PLS_ETL_WORKFLOW_PRG hyperlink.
Click Submit.
Enter the following values for submission parameters:
Config_days: Must be the same value as you specified for the OCDA_CONTROL_TABLE_POPULATE_PRG program in Step 6 of this section.
MATCH_MERGE_FLOW: N
FULL_LOAD: Y
In Submission Type, select Immediate.
In Force Execution, select Yes.
Click Submit.
Note:
Execution of the ETL (specifically theOCDA_ETL_RUN_S_POP_PRG program) populates W_ETL_RUN_S.LOAD_DT with the timestamp for the execution of the ETL. This ETL execution timestamp is used in the calculation of CDA measures concerning the amount of time that currently open discrepancies have been open.
While the timestamp is captured in CURRENT_ETL_LOAD_DT, it is only available for calculation of discrepancy intervals through the OBIEE Dynamic Repository Variable CURRENT_DAY. CURRENT_DAY is refreshed from LOAD_DT at a fixed interval, by default 5 minutes, starting each time the Oracle BI Service is started. Between the time that the ETL is run, and the time that CURRENT_DAY is refreshed, calculations of intervals that currently open discrepancies have been open will be inaccurate.
There are two remedies: (i) restart the Oracle BI Server after every execution of the ETL. This will cause CURRENT_DAY to be refreshed to the correct value. (ii) If this is inconvenient, you can modify the intervals between refreshes of the value of CURRENT_DAY. For more information on how to modify the refresh interval for CURRENT_DAY, refer to Chapter 1, "Maintaining the Repository and Warehouse,"
This section gives information on executing the ETL programs for full load when the ETL includes both the direct path ETL and also the Deduplication ETL.
This section assumes that:
You have two or more source application databases. This can be one OC and one SC database, multiple OC databases, multiple OC databases and an SC database, or (unlikely) multiple SC databases along with zero or more OC databases.
You are using OHMPI for deduplication of dimension data from the source databases.
You have installed OHMPI and loaded the pre-defined Projects for identifying matches on dimensions.
Execute steps 1 to 6 from Full Load Without Deduplication. This loads confirmed dimensions.
Refer to Chapter 4, "Multi-Source Integration"and the OHMPI documentation, for details of how to set up and use OHMPI for deduplication of CDA dimension data.
Execute the initial load of each dimension into the Master Index.
For each source database, perform the following steps:
Determine the execution plan for the source applications from which you are deduplicating data, according to the following table:
CDA - Oracle Clinical Initial De Dup: Oracle Clinical database or databases
CDA - Siebel Clinical Initial De Dup: Oracle Siebel database or databases
CDA - Complete Initial De Dup: One Oracle Clinical and one Siebel Clinical database
In DAC, define the source database with the selected Execution Plan. If you have multiple instances of a source application database, add a copy of the appropriate execution plan for the subsequent instances.
Run the selected Execution Plan. This generates a flat file for each dimension extracted from the database.
Clean up each flat file. If you fix errors by modifying the source database, use the Initial DeDup execution plans to re-extract the data to flat files.
For each dimension, combine the flat files that have been generated for that dimension into a single flat file.
For each dimension, run the dimension's project to identify matches. Review the results, adjust the project's rules and re-execute the project until they generate the optimum set of non-matches, potential matches, and matches for your data. When satisfied run the project in Bulk Load mode so that it places its results in the dimension's Master Index.
For each dimension, perform data stewardship.
This completes the initial load of the dimensions into their Master Indexes.
Confirm that the LSH Job Execution Message Queue is running.
Use DAC to trigger the execution of Deduplication and Direct Path ETL
Since you are using Deduplication, you must submit the program via through DAC console. This is necessary to properly coordinate the execution of the ETL on deduplication path before executing the ETL on the direct path. Perform the following steps to start the combined ETL through the DAC console:
Select the CDA_Employee_De_Dup container.
Navigate to the Design Task. Select PLP_Start_LSH_MasterProgram task and navigate to the Task Level Parameters tab.
Set parameters to the following values:
PIN_DOMAIN: OCDA_domain
PIN_APP_AREA: OCDA_UTIL_APP_AREA
PIN_WORKAREA: OCDA_ETL_WORKFLOW_WA
PIN_PROGRAM: OCDA_PLS_ETL_WORKFLOW_PRG
PIN_EXESETUP: OCDA_ES
Enable The triggered option for the OCDA_ES execution setup.
PIN_FL: Y
PIN_USERID: CDRMGR@ORACLE.COM
This is LSH application user who has access to OCDA_domain and has privileges to execute the ETL.
Ensure that you have a LSH User Database Account for the user.
Navigate to the Execute view and select one of the sources specific execution plans. Selection of the execution plan is based on the source system that you own.
CDA - Oracle Clinical Initial De Dup: Oracle Clinical database or databases
CDA - Siebel Clinical Initial De Dup: Oracle Siebel database or databases
CDA - Complete Initial De Dup: One Oracle Clinical and one Siebel Clinical database
Set the parameter values on the Parameter tab.
Build the execution plan.
Click Run.
This section lists steps for incremental load of warehouse tables.
The first subsection describes incremental loads if you are using direct path loads only (no deduplication).
The second subsection describes how to perform incremental loads if you are using deduplication in addition to direct-path loading.
Tip:
You can schedule the jobs to execute at regular intervals. For more information on scheduling jobs, refer to Scheduling an ETL Program.To perform incremental loads without deduplication, you need to submit an LSH Job. Perform the following steps to do so:
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_UTIL_APP_AREA > OCDA_ETL_WORKFLOW_WA.
Click the OCDA_PLS_ETL_WORKFLOW_PRG hyperlink.
Click Submit.
Enter the following values for submission parameters:
Config_days: Must be the same value as you specified for the OCDA_CONTROL_TABLE_POPULATE_PRG program.
MATCH_MERGE_FLOW: N
FULL_LOAD: N
Caution:
You must set FULL_LOAD parameter to N else full load will be executed.In Submission Type, select Immediate.
In Force Execution, select Yes.
Click Submit.
To perform incremental loads including deduplication, you need tosubmit the Job through the DAC console. This is necessary to properly coordinate the execution of the ETL on deduplication path before executing the ETL on the direct path. Perform the following steps to start ETL through the DAC console:
Confirm that the LSH Job Execution Message Queue is running.
In DAC, select the CDA_Employee_De_Dup container.
Navigate to the Design Task. Select PLP_Start_LSH_MasterProgram task and navigate to the Task Level Parameters tab.
Set parameters to the following values:
PIN_DOMAIN: OCDA_domain
PIN_APP_AREA: OCDA_UTIL_APP_AREA
PIN_WORKAREA: OCDA_ETL_WORKFLOW_WA
PIN_PROGRAM: OCDA_PLS_ETL_WORKFLOW_PRG
PIN_EXESETUP: OCDA_ES
Enable The triggered option for the OCDA_ES execution setup.
PIN_FL: N
This is important. The setting of 'Y' will trigger a full reload.
PIN_USERID: CDRMGR@ORACLE.COM
This is LSH application user who has access to OCDA_domain and has privileges to execute the ETL.
Ensure that you have a LSH User Database Account for the user.
Navigate to the Execute view and select one of the sources specific execution plans. Selection of the execution plan is based on the source system that you own.
CDA - Oracle Clinical Initial De Dup: Oracle Clinical database or databases
CDA - Siebel Clinical Initial De Dup: Oracle Siebel database or databases
CDA - Complete Initial De Dup: One Oracle Clinical and one Siebel Clinical database
Set the parameter values on the Parameter tab.
Build the execution plan.
Click Run.
The following rules apply when you customize an ETL program:
You can customize ETL programs in different ways. You can create a new domain, new Application Area within same domain, or a new Work Area within the same Application Area. Creating a new domain, and storing customized definitions in the new domain will ensure that the definitions are not overwritten on the next CDA upgrade.
Oracle recommends that you set up a single domain for all customization to CDA. This will ensure that all the customized object definitions are available in the same top-level container.
After you create your own Work Area, clone the Oracle-supplied Work Area on to your own Work Area. This creates copies of object instances inside your Work Area, but they point to the object definitions inside the Oracle-supplied Application Area.
Caution:
To correctly track the timing of CDA ETL execution, Oracle recommends that no Program in the CDA Domain, other than the SIL provided with CDA, read from any CDA staging table. The staging tables, at any given time, hold only transient records that were loaded during the most recent ETL execution. Ideally, you may not read from them. If it is necessary to read from an CDA staging tables, Oracle recommends that you define the Program in a Domain other than the CDA Domain containing the staging table, and execute it in that separate Domain.Though CDA includes ETL programs for extracting data from Oracle Clinical and Siebel Clinical to CDA data warehouse, you may want to create your own ETL to extract data from other data sources.
Note:
The value of DATASOURCE_NUM_ID is set to 1 for Oracle Clinical and 2 for Siebel Clinical. If you want to add your own data sources, set this value to a number greater than 100.See Also:
Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub Application Developer's Guide (Defining Programs)
Informatica PowerCenter Online Help
To add one or more tables or columns along with the associated ETL programs to populate data into these table, perform the following tasks:
Create the new source and target table metadata inside your Work Area.
If the tables exist outside Oracle LSH in some remote schema, flat file, or SAS file, you can upload the table structure into Oracle LSH using an Oracle LSH Load Set.
Create a Program in Oracle LSH and specify that the Program is an Informatica-type Program.
Add these tables as sources or targets.
Install the new Oracle LSH Program to ensure that the new tables are created in the Work Area schema.
Check out your new Oracle LSH program.
Important:
Do not use the Copy definition to the local Application Area and check out option when checking out the program.In the Program's screen, click Launch IDE.
This launches Informatica PowerCenter client installed on your machine.
Work in Informatica PowerCentre and create the ETL components (transformation or workflow) used by this Oracle LSH Program.
Go back to Oracle LSH and upload the ETL file from Informatica PowerCenter to Oracle LSH.
Install and run the Program in Oracle LSH.
Important:
Before you reinstall, ensure that the Informatica DP Server is up and running.Tip:
If the target table you added relies on new source tables, and if you want the source tables to be automatically populated when you trigger the ETL program for the final target table, enable backchaining for the Oracle LSH Program that populates the source tables.If there are no new source tables in your customization, Oracle LSH will automatically trigger the population of the source tables when the ETL program to populate the final target table is executed. Note that the backchain submissions are not cloned to the Work Area, and you have to manually create them.
For more information on backchaining, refer to Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub Application Developer's Guide (Execution and Data Handling).
You may also want to modify an existing ETL to meet your reporting requirements.
See Also:
Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub Application Developer's Guide (Defining Programs)
Informatica PowerCenter Online Help
To modify an ETL without any changes to the associated tables or columns, perform the following tasks:
Install your Work Area and run the ETL to ensure that you can see data populated in the target data warehouse tables.
Identify the Oracle LSH program that contains the metadata for the ETL that needs to be modified.
Check out the Oracle LSH program that contains the metadata for that ETL.
Important:
Use the Copy definition to the local Application Area and check out option to check out the program. This ensures that you do not modify the definitions inside the domain shipped with CDA.In the Program's screen, click Launch IDE.
This launches Informatica PowerCenter client installed on your machine.
Modify the ETLs (transformation and/or workflow) used by the Oracle LSH Program.
Test and upload the ETL from Informatica PowerCenter to Oracle LSH.
Install the program in Oracle LSH, and run it to verify the changes.
Note:
The ETL programs that extract data for the warehouse fact tables assume that the dimensions to which each fact is related are up-to-date at the time the fact ETL programs are executed. This assumption is the basis for certain fact calculations that would provide erroneous results if the assumption were not true. For example, in the received CRFs fact, the value of the pCRF entry complete measure depends on whether or not the study requires second pass entry. But that piece of information -- second pass entry required -- is obtained from an attribute of the Study dimension. So, if the second-pass requirement for a study changes, and the change is not applied to the Study dimension, the Received CRF fact attributes will contain incorrect values.As shipped, CDA ETL workflows ensure this interlock by executing the ETL for related dimensions immediately before running the ETL for a fact. This is standard warehouse management practice, but especially important given the interdependence of the dimensions and the fact. The need to execute dimension ETL immediately before corresponding fact ETL, and the danger of not doing it, is emphasized here because it is possible (though discouraged) to modify these shipped workflows.
To modify one or more tables or columns without any changes to the associated ETL programs:
Install your Work Area and run the ETL to ensure that you can see data populated in the target data warehouse tables.
Check out the Oracle LSH program that contains the metadata for that ETL.
IMPORTANT:
Use the Copy definition to the local Application Area and check out option when checking out the program. This ensures that you do not modify the definitions inside the domain shipped with CDA.Change the table properties.
To change the underlying columns and variables, check out the variables that the columns are pointing to. Ensure that you use the Copy definition to the local Application Area and check out option when checking out the variable.
Note:
If the changes to the tables or columns are not compatible with the table that is installed in the data warehouse schema, you will get a warning while making the change. For example, if you are reducing the length of a number column from 15 to 10, the change is not compatible with the data existing in the table. Such changes will not let you perform an Upgrade install on the table. You will have to drop and create the table using Partial or Full install.Install the changed table or column, and run the ETL program that populates it.
Scheduling can be categories as
Scheduling without Deduplication
When you submit a Program for execution in Oracle LSH, you can schedule it execute at regular intervals. In the appropriate Work Area, navigate to the installed executable instance you want to submit and click Submit.
For more information on how to submit an Execution Setup, refer to Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub Application Developer's Guide (Submitting Jobs for Execution).
To schedule a Program, perform the following tasks:
Navigate to OCDA_domain > OCDA_UTIL_APP_AREA > OCDA_ETL_WORKFLOW_WA
Click OCDA_PLS_ETL_WORKFLOW_PRG.
Click Submit.
Enter the following values for submission parameters:
Config_days - Must be the same value as you specified for the OCDA_CONTROL_TABLE_POPULATE_PRG program.
MATCH_MERGE_FLOW - N
FULL_LOAD - N
Submission Type - Select Immediate.
Force Execution - Select Yes.
In the Submission Details section, select Submission Type as Scheduled.The Schedule Submission section is displayed.
Enter the required details and click Submit.
DAC Execution plans as discussed in incremental load can be scheduled for execution. For more information, refer to the Oracle® Business Intelligence Data Warehouse Administration Console User's Guide section on Scheduling an Execution Plan.
When you submit a Program for execution, perform the following tasks to specify the table processing type:
In the appropriate Work Area, navigate to the installed executable instance you want to submit.
In the Program's screen, click Launch IDE.
This launches Informatica PowerCenter client installed on your machine.
In the Workflow Manager, modify the Target load type setting to Bulk or Normal.
Reinstall the program in Oracle LSH.
Navigate to the installed executable instance you want to submit, and click Submit.
The Submit Execution Setup screen is displayed.
For more information on how to submit an Execution Setup, refer to Oracle Life Sciences Data Hub Application Developer's Guide (Submitting Jobs for Execution).
In the Submission Parameters section, select the Parameter Value for Bulk Load based on what you have set up in Step 3. Select Yes if the table processing type is bulk, and No if it is normal.
Enter the required details and click Submit.