 PeopleSoft Cube Builder Overview
PeopleSoft Cube Builder OverviewThis chapter provides an overview of PeopleSoft Cube Builder and discusses:
PeopleSoft Cube Builder business processes.
Other sources of information.
Essbase Cube Builder implementation.
 PeopleSoft Cube Builder Overview
PeopleSoft Cube Builder OverviewPeopleSoft Cube Builder is an extract-transform and load (ETL) application that enables you to use PeopleSoft Query and PeopleSoft Tree Manager to build Essbase applications and online analytical processing (OLAP) databases. It comprises an easy to use graphic user interface to create metadata of cubes based in PeopleSoft structures and to give a look and feel similar to the Essbase Outline Editor. It also uses an enhanced cube builder program that provides fast performance to load data and metadata, as well as interconnections with the Oracle Performance Manager - Smart View.
Note. To view outputs from PeopleSoft Pure Internet Architecture, you must have Smart View for Office installed on the client machine. Please refer to the Oracle Smart View for Office Installation Guide for details.
 Essbase Cube Builder Business Processes
Essbase Cube Builder Business ProcessesThe following process flow illustrates the Cube Builder business processes:
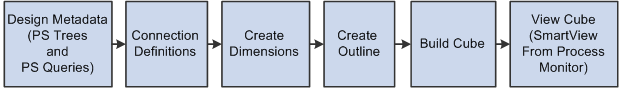
Essbase Cube Builder business process flow
Note. Oracle Essbase, SmartView, and other Oracle Hyperion tools are not delivered as part of our application; therefore, the PeopleSoft Cube Builder PeopleBook does not include documentation about how to use Oracle Hyperion applications. It does, however, include a reference to the appropriate documentation.
 Other Sources of Information
Other Sources of InformationThis section provides information to consider before you begin to use PeopleSoft Cube Builder.
Take advantage of all PeopleSoft sources of information, including the installation guides, release notes, PeopleBooks, red papers, the Updates and Fixes area of My Oracle Support, and curriculum courses of Oracle PeopleSoft.
See PeopleSoft Cube Builder Preface.
See PeopleTools 8.52: Getting Started with PeopleTools.
 Essbase Cube Builder Implementation
Essbase Cube Builder ImplementationEssbase Cube Builder implementation can be divided into the following phases:
Designing cube metadata.
Defining connection definitions.
Creating dimensions.
Creating an outline.
Building cubes.
Designing Cube Metadata
The initial phase for creating cubes is to define their metadata, that is, the data that describes the cube structure. You can define metadata with either PeopleSoft trees or queries. To design cube metadata, perform the following steps:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
Create new trees or use existing trees. |
|
|
Create new queries or use existing queries. |
See Creating New Queries. |
Defining Connection Definitions
The second phase of creating Essbase cubes is to create connectivity information. To set up the Essbase server connection information, perform the following step:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
Define Essbase Cube Builder connection definitions. |
Dimensions are equivalent to fields in a relational database. In data analysis terms, dimensions can be thought of as criteria that are used to pinpoint a particular piece of data, for example, time, account, and salesperson. Dimensions are subdivided into categories called members; for example, the time dimension contains the members 2007, 2008, 2009. You can add members to dimensions manually; members are populated by the results of a PeopleSoft Query or populated from a PeopleSoft Tree structure.
To create dimensions, perform the following steps:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
Set up cube dimension builder. |
|
|
Create Essbase dimensions. |
To create an outline, you group dimensions together to define the cube structure, and then you define the data queries that will be used to populate the cube.
To create an outline, perform the following steps:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
Define cube outlines. |
|
|
Add cube dimensions to a cube outline. |
|
|
Add cube data queries to a cube outline. |
The last phase of Essbase Cube Builder implementation is sending all of the defined information—cube structure and data—to the Essbase server using the Create Cube component, which runs the Process Scheduler.
To build Essbase cubes, perform the following step:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
Build Essbase cubes. |