78 Set Up Customer Bank Information
This chapter contains these topics:
78.1 Setting Up Customer Bank Information
From Accounts Receivable (G03), enter 29
From Accounts Receivable Setup (G0341), choose a bank account option under the System Controls heading
To transfer funds electronically, you must set up address book bank account information for your customers and suppliers external bank accounts. This information is necessary for processes such as Accounts Receivable automatic receipts (lockbox), drafts and automatic debits as well as Accounts Payable EDI and EFT payment processes.
You set up customer bank account information by accessing either Bank Codes from Customer Master Information, or by setting up Bank Account Cross References. The program (P0030) is the same regardless of which method is used to set up the information. This program will allow you to do the following:
-
Define and use more than one bank account per customer/ supplier.
-
Provide a Pre-Note status for each bank account, rather than one per customer/supplier.
-
Provide a mechanism to 'retire' one bank account using an expiration date while keeping it in the file as an audit trail.
78.1.1 Bank Type Code
The bank type code associated with a bank account is used to:
-
Distinguish external bank accounts from internal bank accounts.
-
Define the type of external bank account, for example a customer or a supplier bank account.
78.1.2 Bank Type Code User Defined Table
Suppliers and customers must have valid supplier bank type (V) and customer bank type (D) accounts in order to process drafts, EFT payments and other receipt and payment functions. You may only have one bank account per bank type however; your customers and suppliers may use multiple bank accounts for different processes, locations or specific to a currency denomination.
To accommodate multiple bank accounts per bank type you can set up additional bank type codes to be used as alternative customer/supplier bank accounts. The Bank Type Code field is two characters, so an example of an alternative customer bank type code could be D1. Bank type codes are set up and defined in User Defined Codes (UDC) table 00/BT. The special handling code for the bank type is used to determine if the bank type code will be associated with A/R processes or A/P processes.
From UDC table 00/BT, inquire on your existing values for bank type codes. To add a new value:
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Bank Type Code
-
Description
-
-
Access the Detail (F4)
-
Enter the appropriate value in the Special Handling Code field
-
For A/R bank types, enter '1'
-
For A/P bank types, enter '2'
-
For example, you may have a customer that uses two bank accounts, each for a different location. Bank type D is set up in the UDC table but you need to add an alternative bank code to accommodate the second bank account. As shown below, bank type D1 has been set up for the second supplier bank account.
Figure 78-1 General User Defined Codes (Bank Type) screen
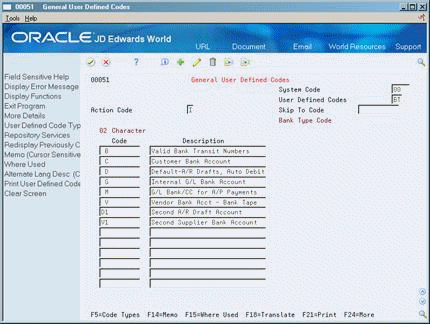
Description of ''Figure 78-1 General User Defined Codes (Bank Type) screen''
78.1.3 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Master Information (P01054) | You may assign a default bank type to your customer. |
| Standard Invoice Entry (P03105) | You may assign a bank type to individual transactions at the time of invoice entry. |
78.1.4 Bank Account by Currency
You may identify a bank type with a specific currency code. The bank type code and the currency code make a unique combination allowing you to set up multiple customer or supplier bank accounts that are specific to currency transactions.
For example, your customer may want drafts made in Euro currency to be sent to a bank located in a Germany whereas drafts made in Japanese yen (JYP) are to be sent to a bank located in Tokyo. In this instance, you would set up two customer bank accounts, bank type code D, with the currency code EUR assigned to the German bank and the currency code JYP assigned to the Tokyo bank. When drafts are collected for the customer, the draft transaction currency will determine which customer bank account to use.
Note:
The Currency Code field is displayed only if currency processing is activated.78.1.5 Effective Date/Expiration Date
There may be instances where your supplier opens a new bank account and closes an existing account. You may retire a current bank account and designate an effective date for new accounts. Enter the appropriate date to start using a bank account in the Effective Date field for the bank account. To retire an account but keep the account information in the bank file for audit purposes, set the Expiration Date for the bank account that will be retired.
78.1.6 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Expiration Reason Code | When entering an Expiration Date, you must enter a valid reason code for the expiration. Expiration Reason Code values are set up and maintained in User Defined Table (UDC) 00/XC.
If you do not want to designate specific reasons for retiring an account, you must set up blank as a valid value. |
78.2 Adding Customer Bank Account Information
From Supplier Master Information (P01053), choose the Bank Codes function (F8)
Figure 78-2 Bank Accounts by Address screen
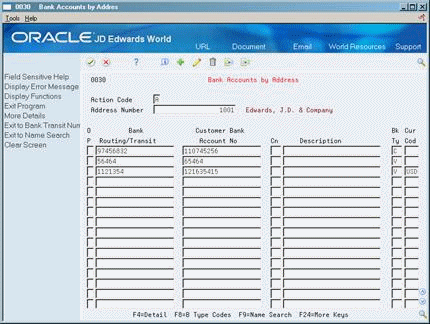
Description of ''Figure 78-2 Bank Accounts by Address screen''
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Bank Routing/Transit Number
-
Bank Account Number
-
Bank Type Code
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Control Digit
-
Currency Code - this field will only be displayed if currency processing is activated.
-
-
Press F4 to access the detail area.
Figure 78-3 Bank Accounts by Address (Detail) screen
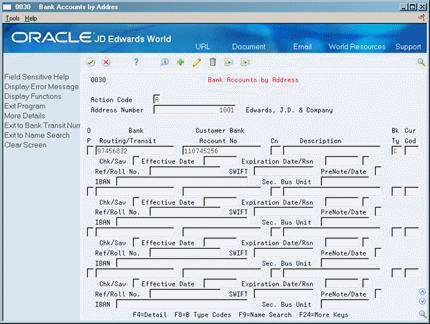
Description of ''Figure 78-3 Bank Accounts by Address (Detail) screen''
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Checking/Savings account
-
Effective Date
-
Expiration Date/Expiration Reason Code
-
Reference/Roll Number
-
SWIFT Code
-
Pre-Note Code
-
IBAN
-
Secondary Business Unit
-
78.2.1 What You Should Know About
There are options for additional information relating to each bank account record:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Audit Information (Opt 1) | Provides audit information in regard to updating a bank account record. |
| Additional Information (Opt 2) | This option allows you to enter Beneficiary and Corresponding bank account information for each bank account. |
78.3 Setting Up Bank Account Cross-References for A/R
You must set up bank account cross-references for your customers who use electronic remittances.
Setting up bank account cross-references consists of:
-
Adding A/R cross-references
-
Verifying A/R cross-references
Bank account cross-references link customer addresses in the Address Book Master table (F0101) to their bank account information in the Bank Transit Number Master table (F0030).
78.3.1 Adding A/R Cross-References
To establish a relationship between your customer and their bank account, add a bank account cross-reference. This lets you process their receipts quickly with limited information, such as the bank transit number and bank account number.
On Bank Account Cross-Reference
Figure 78-4 Bank Account Cross-Reference screen
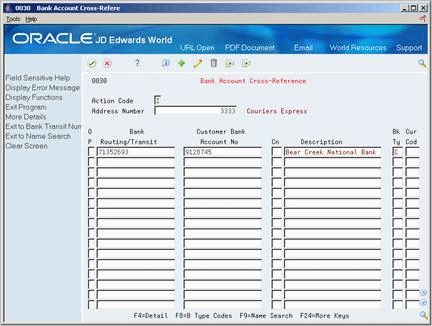
Description of ''Figure 78-4 Bank Account Cross-Reference screen''
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Address Number
-
Routing/Transit
-
Account Number
-
Control Digit (optional)
-
Description (optional)
-
Type
-
-
Press Enter.
78.3.3 Verifying Cross-References for A/R
After you set up bank account cross-references, run two exception reports to verify the information before you produce your first batch of automatic receipts.
Verifying cross-references consists of:
-
Reviewing the Bank Account Exception Report
-
Reviewing the Address Book Exception Report
These reports compare information in the Address Book Master (F0101) and the Bank Transit Number Master (F0030) tables.
78.3.3.1 Reviewing the Bank Account Exception Report
The Bank Account Exception report edits all the addresses for each bank account cross-reference. This report lists any record that does not exist in the Address Book Master table, and bypasses bank account records that have a blank address number.
This report does not update any information. You must either enter missing address records or remove them from Bank Account Cross Reference.
Figure 78-5 Bank Account/Address Book Exception Report
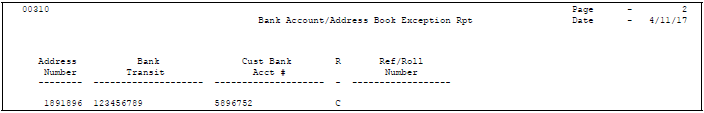
Description of ''Figure 78-5 Bank Account/Address Book Exception Report''
78.3.3.2 Reviewing the Address Book Exception Report
The Address Book Exceptions Report lists any customers in the Address Book Master table that do not have a corresponding bank account record on Bank Account Cross Reference. The system only edits customers with a method of payment that requires a bank account record. For example, A/R bank tape processing requires bank account records.
This report does not update any information. You must either enter missing bank account records or change the payment instrument code for the customer in the customer master record.
Figure 78-6 Address Book/Bank Account Exception - Suppliers report

Description of ''Figure 78-6 Address Book/Bank Account Exception - Suppliers report''
78.4 Setting Up Bank Account Addresses
To assign address book information to a customer's bank account, set up a bank account address. This lets you update a customer's bank transit code, as well as locate other customer address numbers with an associated bank transit type of B (valid bank transit number).
To set up bank account addresses
On Bank Account Addresses
Figure 78-7 Bank Account Addresses screen
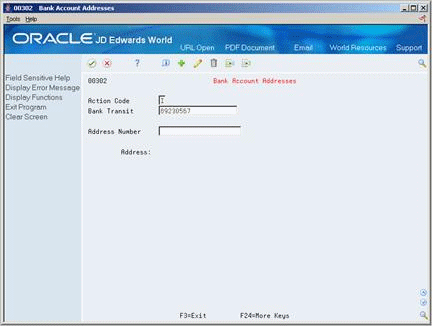
Description of ''Figure 78-7 Bank Account Addresses screen''
78.5 Setting Up Bank Account Information for A/R
To create an electronic funds transfer (EFT) for the automatic debiting of a customer's account, you must set up bank account information for your internal bank account.
This information is stored in the Bank Transit Number Master table (F0030).
78.5.1 Before You Begin
-
Set up the G/L account information for each bank account
To set up A/R bank account information
Figure 78-8 Bank Account Information screen
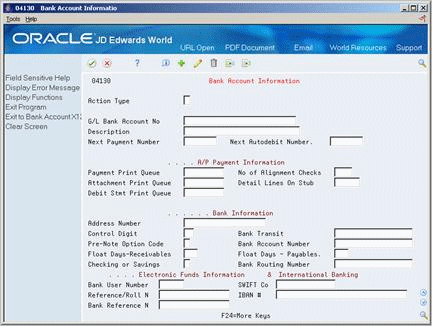
Description of ''Figure 78-8 Bank Account Information screen''
-
Complete the following required fields:
-
G/L Bank Account Number
-
Description
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Address Number
-
Control Digit
-
Bank Transit
-
Pre-Note Option Code
-
Bank Account Number
-
Float Days - Receivables
-
Checking or Savings Account
-
SWIFT Code
-
Bank User Number
-
Reference/Roll Number
-
Bank Reference Name
-
78.5.2 Processing Options
See Section 112.3, "Bank Account Information (P04130)" for more information.