27 Overview to Manufacturing and Distribution Environments
This chapter contains these topics:
27.1 Objectives
-
To use the Manufacturing and Distribution Planning (MDP) system to manage a variety of manufacturing and distribution environments
27.2 About Manufacturing and Distribution Environments
Today's customer-driven manufacturing strategies require flexible manufacturing and distribution systems.
The following graphic shows manufacturing and distribution environments that vary along a continuum from discrete, low-volume production of customized designs to process, high-volume production of commodities.
Figure 27-1 Continuum of Manufacturing and Distribution Environments
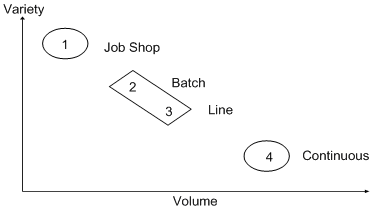
Description of "Figure 27-1 Continuum of Manufacturing and Distribution Environments"
Depending on the products manufactured, companies tend to create manufacturing and distribution environments along the diagonal of the graph. Competitive advantages occur when a company can move upward and to the right (that is, manufacture more volume along with more variety).
Sometimes a firm can gain a competitive advantage by creating a mixed-mode manufacturing environment. In mixed mode, some high-volume products and some high-variety products are made within the same company, but in different manufacturing and distribution environments.
The Manufacturing and Distribution Planning system's shared database provides mixed-mode capability. Manufacturing and Distribution Planning can simultaneously manage discrete items for a job shop, rate based items for a flow shop, and continuous items for a process industry.
Working with manufacturing and distribution environments includes the following tasks:
-
Working with batch manufacturing
-
Working with rate based manufacturing
-
Working with process manufacturing
27.2.1 Discrete Manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing uses bills of material and routings. The bill of material contains individual parts or components, such as a nut, bolt, wire, or a plastic or metal part of a fixed or variable quantity. Products are further divided into subassemblies that are used in various larger assemblies.
Typical examples of products of discrete manufacturing are:
-
Cars
-
Furniture
-
Electronics
-
Airplanes
Discrete manufacturing is usually further characterized by the strategy used, such as:
-
Make-to-stock, using either a highly repetitive or process order based system
-
Any of the "to-orders," such as make-to-order, assemble-to-order, or engineer-to-order
-
The "one-off" or job shop environment
27.2.2 Batch Manufacturing
With batch manufacturing, you produce products from formulas or recipes in a standard run or lot size that is determined by vessel size or standard run length.
27.2.3 Rate-Based Manufacturing
Use rate-based manufacturing for highly repetitive production for which you do not need to account for each work order's labor and inventory in detail.
27.2.4 Process Manufacturing
Process manufacturing uses recipes or formulas and resources or ingredients. The manufacturing process either consumes or produces these resources. Many processes create co-products and by-products. In a process or discrete formula, the quantity of a component can vary according to its grade or potency.
Unique features of process manufacturing are:
-
Pacing co-products
-
Planned co-products (by-products are unplanned)
-
Additional processing options in MPS/MRP
27.2.5 Distribution
Distribution systems work together with manufacturing systems to ensure that the right item is in the right place at the right time to meet customer demand. Supply and demand components must balance to ensure that this can occur. For example, the Inventory Management system does the following:
-
Stores item information for the manufacturing systems
-
Stores sales and purchasing costs and quantities available by location
-
Tracks holds for locations from which you should not sell
-
Updates the inventory account balances in the general ledger with any change in inventory valuation, count variances, or movement