23 Plan Bills in the MPS/DRP System
This chapter contains these topics:
23.1 Purpose
The purpose for planning bills is to generate forecasts for saleable end items. Planning bills are commonly used in a manufacturing environment where the saleable end items have a large number of features and/or options. The forecasts for these saleable end items are based on percentages of the features and options offered that you expect to sell.
Planning bills consist of groups of pseudo items that reflect how an item is sold. They are entered into the system in a bill of material format, and represent the variety of possible options and features that might be included as a saleable end item.
Planning bills are typically used to "explode" a forecast for the total number of products down to the level of the specific combination of options and features included in each saleable end item.
23.2 Demand Structure
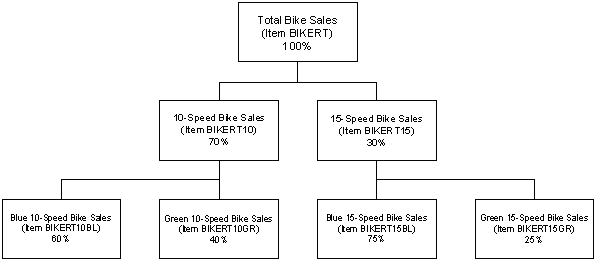
In the following diagram, the demand for item BIKERT (top level) represents the total demand for all bicycles.
The demand for items BIKERT10 and BIKERT15 (middle level) represents the demand for 10-speed and 15-speed bicycles, which in this case is 70% of the total demand of BIKERT for the 10-speeds (BIKERT10) and 30% of the total demand of BIKERT for the 15-speeds (BIKERT15).
The demand for items BIKERT10GR, BIKERT10BL, BIKERT15GR, and BIKERT15BL (bottom level) represents the demand for green 10-speed bicycles, blue 10-speed bicycles, green 15-speed bicycles, and blue 15-speed bicycles, respectively. Their demand is expressed as a percentage of the demand for items BIKERT10 and BIKERT15.
23.2.1 Component Item Master/Item Branch Plant Information
Each level of the item hierarchy above the end item (in this example items BIKERT, BIKERT10, and BIKERT15) should be coded as phantom items in the Item Master and Branch/Plant (stocking type zero).
Each level of the item hierarchy above the end item should also be coded as a Planning Code 4 in the Plant Manufacturing Data (P41027 - F10 from the Branch/Plant).
Each item on the end item level (items BIKERT10GR, BIKERT10BL, BIKERT15GR, BIKERT15BL) should be coded as Planning Code 5 in the Plant Manufacturing Data.
23.2.2 Bill of Material Record
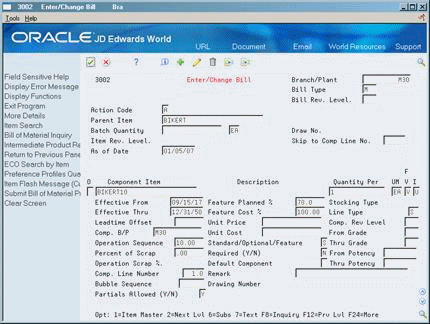
Each level of the item hierarchy above the end item will have a record in the F3002. The field Feature Planned Percentage in the detail area of the BOM is where the user specifies what percentage of the sales of the parent item that this group of features represents. In this example, item BIKERT10 represents 70% of item BIKERT, and item BIKERT15 represents 30%. For each parent item BIKERT, two component items are created for BIKERT10 and BIKERT15 on Enter/Change Bill.
Figure 23-2 Enter/Change Bill (BIKERT10) screen
Description of "Figure 23-2 Enter/Change Bill (BIKERT10) screen"
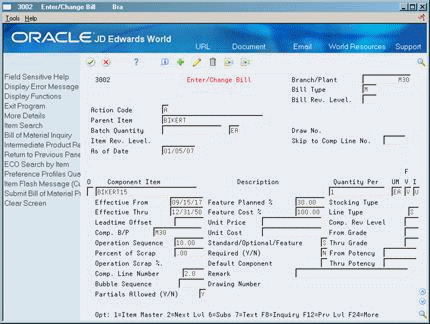
Figure 23-3 Enter/Change Bill (BIKERT15) screen
Description of "Figure 23-3 Enter/Change Bill (BIKERT15) screen"
In a similar manner, items BIKERT15 and BIKERT10 are then divided by color into items BIKERT15BL, BIKERT15GR, BIKERT10BL, and BIKERT10GR.
To sum up our example, if total bicycle sales (parent item BIKERT) last year was 1000:
-
The forecast for 10-speed bikes would be 700 (1000 x .70)
-
The forecast for 15-speed bikes would be 300 (1000 x .30)
-
Demand for green 10-speed bikes would be 280 (700 x .40)
-
Demand for blue 10-speed bikes would be 420 (700 x .60)
-
Demand for green 15-speed bikes would be 75 (300 x .25)
-
Demand for blue 15-speed bikes would be 225 (300 x .75)
23.3 Gross Regeneration
After you add the component items with their planned percentages, you run the Gross Regeneration program (P3482) to regenerate a forecast based on the existing forecast for the parent item and the numbers for each component item.
Before you run the Gross Regeneration, be sure that:
-
Planning bill logic is turned on (a 2 in processing option 5)
-
Processing option 15 references the forecast type created for Planning Bills. The system will write quantities for this forecast type for all of the lower levels of the hierarchy (including the saleable end item) based on the feature planned percentage in the BOM.
-
Processing option 14 references the forecast type in the F3460 for the parent item at the top of the hierarchy. This is the forecast for which all the calculations for the lower levels quantities are based on.
Processing option 14 should also reference the forecast type that you designate as the forecast to create when using planning bills (same one as entered in processing option 15). The system will first calculate the forecast for the lower levels based on the parent levels forecast and write those quantities to the F3460 (for forecast type referenced in processing option 15). You designate the forecast type created by the planning bills (processing option 15) as the second forecast type to be read as input so the system will read the forecast for the second level, which it will then apply to the saleable end items.
After you successfully run the Gross Regeneration, you should have the following:
-
Records in the F3460 for all levels (except the very top level) of the hierarchy for the forecast type designated in processing option 15 of the P3482. These forecasts will be based on the Feature Planned Percentage Of values in the parent item's BOM.
-
A Time Series (P3413) and messages in the F3411 for all of the saleable end items (in this case items BIKERT10BL, BIKERT10GR, BIKERT15BL, and BIKERT15GR) in the quantities that match the RT forecast.