B Lead Time Calculations
This appendix contains this topic:
B.1 Understanding Lead Time Calculations
Determining lead time is an essential part of any manufacturing or scheduling process. For any product that you purchase or manufacture, you encounter a time lag between when you order or start it and when you receive or finish it. To account for the lag, you must estimate the extra time and allow for it in your planning.
Several JD Edwards World Manufacturing systems use lead times. In Product Data Management, you enter routing and work center information, and run the Leadtime Rollup program to calculate lead times. The Shop Floor Control system uses the lead time information to calculate the start date of a work order based on the order's due date. For more information, see also Appendix A - Lead Times in the Shop Floor Control - Process Guide or Appendix B - Lead Times in the Shop Floor Control - Discrete Guide.
This appendix describes how the Leadtime Rollup program calculates lead times. The following information on the Enter/Change Routing form is used by the Leadtime Rollup program.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Time basis code | Identify the rate used for machine or labor hours entered for any routing step. This is how run hours are expressed for an item (for example, 25 hours per 1000 pieces or 15 hours per 10000 pieces). You must define these codes on UDC 30/TB. |
| Run hours | Run hours consists of:
|
| Move hours | The hours a work order is in transit from the completion of one operation to the beginning of the next. |
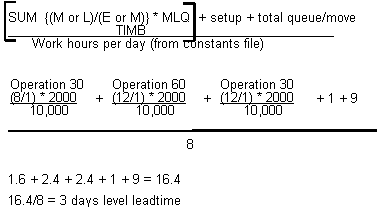
The Leadtime Rollup program calculates the following:
The amount of time a work order is in queue at an operation and the amount of time to move the work order between operations. Total queue/move hours are the sum of the move hours and the queue hours.
Figure B-1 Total queue/move hours calculation
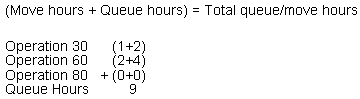
Description of "Figure B-1 Total queue/move hours calculation"
The hours required to set up machinery to run a specific item, regardless of quantity.
Figure B-2 Standard setup hours calculation

Description of "Figure B-2 Standard setup hours calculation"
The system calculates this value if the Fixed Lead time Flag is set to F and the Manufacturing Leadtime Quantity is greater that zero. Otherwise, the system uses the value you entered manually to calculate start dates of work orders.
The following values are defined:
-
The level lead time has been calculated previously:
-
· Queue hours = 9
-
· Setup hours = 1
-
-
M or L – Either the machine or labor hours based on the Prime Load Code
-
SUM – Sum of all operations
-
TIMB – Time Basis Code
-
MLQ – Manufacturing Lead time Quantity
-
E – Number of employees in work center
-
M – Number of machines in work center
The system calculates this value when the Lead time Flag is set to V. It uses the time basis code from the routing to calculate lead time per unit and the time basis code from the Item Master as a common factor to multiply all the lead times per units.
The following values are defined:
-
M or L Either the machine or labor hours based on the Prime Load Code
-
SUM Sum of all operations
-
TIMB Time Basis Code
-
E Number of employees in work center
-
M Number of machines in work center
Figure B-4 Per Unit Lead Time calculation
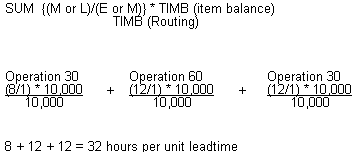
Description of "Figure B-4 Per Unit Lead Time calculation"
The cumulative lead time is the sum of the level lead time and the longest cumulative lead time of any of the item's next lower level components.
Figure B-5 Cumulative Lead Time calculation
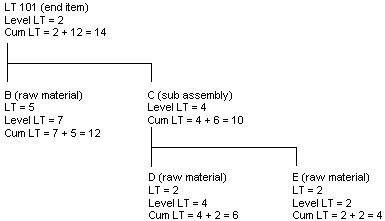
Description of "Figure B-5 Cumulative Lead Time calculation"
Manufacturing Lead Time is the sum of the level lead time and the longest manufacturing lead time of any of the item's lower level components.
Figure B-6 Manufacturing Lead Time calculation
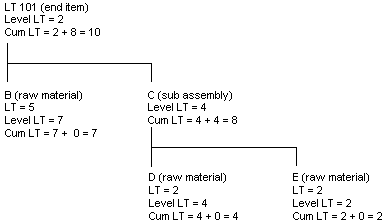
Description of "Figure B-6 Manufacturing Lead Time calculation"
Lead Times for Purchased Parts
For purchased parts you must set the level lead time. The cumulative lead time is equal to the level lead time. The following values are zero:
-
Manufacturing lead time
-
Lead time per unit
-
Total queue/move hours
-
Setup hours