50 Set Up Group Constants
This chapter contains these topics:
-
Section 50.6, "Setting Up Union Local and Job Cross-References,"
-
Section 50.7, "Reviewing the Union and Job Cross-Reference Report,"
50.1 Setting Up Group Constants
You set up group constants to simplify the process of associating the same information with a group of employees. This information includes:
Setting up group constants consists of the following tasks:
-
Setting Up Pay Rate Tables
-
Reviewing the Pay Rate Tables Report
-
Setting Up Group DBAs
-
Reviewing the Group Plans Report
-
Setting Up Union Local and Job Cross-References
-
Reviewing the Union and Job Cross-Reference Report
-
Setting Up Job Classification Constants
50.2 Setting Up Pay Rate Tables
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Pay Rate Tables
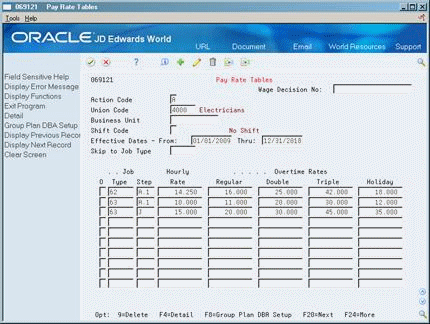
You set up pay rate tables to associate pay rates with a specific group of employees. You set up hourly rates by job type and job step. Any amounts that you enter in the pay rate tables can override rates set up in the employee master record. As you enter time for various job types and job steps, the system finds the appropriate hourly rate.
The system uses pay rate tables in conjunction with the time entry programs. You must set a processing option on the appropriate time entry program so that the system uses the pay rate tables.
Setting up pay rate tables allows you to:
-
Make rates specific to a job, business unit, or shift
-
Establish up to five different rates per job type and step
-
Establish workers compensation codes for each job type and step
-
Establish a flat burden factor for each job type and step
-
Establish a recharge billing rate
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Union Code
-
Effective Date From
-
Effective Date Thru
-
Job Type
-
Hourly Rate
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Wage Decision Number
-
Business Unit
-
Shift Code
-
Job Step
-
Regular Overtime Rate
-
Double Overtime Rate
-
Triple Overtime Rate
-
Holiday Overtime Rate
-
-
Press F4 to access the detail area.
Figure 50-2 Pay Rate Tables screen (Detail area)
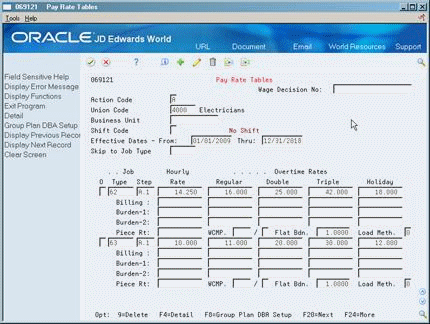
Description of ''Figure 50-2 Pay Rate Tables screen (Detail area)''
-
Complete one or more of the following fields:
-
Billing Rate
-
Piecework Rate
-
Workers Compensation Insurance Code (WCMP)
-
Workers Compensation Subclass Code (not labeled)
-
Flat Burden
-
Labor Load Method Code
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Union Code | A user defined code (07/UN) that represents the union or plan in which the employee or group of employees work or participate. |
| Type | A user defined code (07/G) that defines the jobs within your organization. You can associate pay and benefit information with a job type and apply that information to the employees who are linked to that job type. |
| Rate - Hourly | The employee's hourly rate, which is retrieved during time entry. If you enter a rate in this field on any other form, that rate can override the value in the Employee Master table.
In the Employee Master table, this is the employee's base hourly rate. In the Union Rates table, this is the straight time rate. Note: If you change the number of the data display decimal digits for this field, you must also change fields Rate - Base Hourly (BHRT) and Rate - Hourly (SHRT) so that they have exactly the same number of data display decimal digits. |
| Wage Decision No: | This code is used to reference the government Wage Decision that the contract pay rates fall under. |
| Shift Code | A user defined code (07/SH) that identifies daily work shifts. In payroll systems, you can use a shift code to add a percent or amount to the hourly rate on a timecard.
For payroll and time entry: If an employee always works a shift for which a shift rate differential is applicable, enter that shift code on the employee's master record. When you enter the shift on the employee's master record, you do not need to enter the code on the timecard when you enter time. If an employee occasionally works a different shift, you enter the shift code on each applicable timecard to override the default. |
| Billing: | A rate used for the billing of labor services. This rate is often referred to as the billing or recharge rate. The extended amount based on this rate will be charged to the primary distribution account on the timecard with an offset being made to an account derived from the Accounting Rules table. This rate will not affect the employee's payroll. To allow billing rates in time entry, you must set the employee's record type as either 2 or 3 on the Basic Employee Entry form.
A rate entered on any of the following forms overrides the rate in the Employee Primary Job table:
|
| Piece Rt: | The rate paid for the type of component (piece) produced. If you enter a rate in this field, this rate overrides the rate in the Employee Master table. |
| WCMP | A user defined code (00/W) that represents a workers compensation insurance (WCI) code. This code should correspond to the classifications on your periodic workers compensation insurance reports. |
| Flat Bdn | A multiplier to load direct labor costs with burden. For example, a factor of 1.32 loads every dollar of labor cost with 32 cents worth of burden. |
| Labor Load Method | A code indicating that flat burden is to be calculated. Valid codes are:
0 – Flat burden percentage will always be 1.000 and, therefore, the flat burden amount will equal zero. Basically, this means that there is no distribution. 1 – Flat burden percentage will always be greater than 1.000. Choose this option when distributing the percentage. There are various places within the Payroll system where flat burden rules and percentages can be defined, such as:
|
50.2.1 What You Should Know About
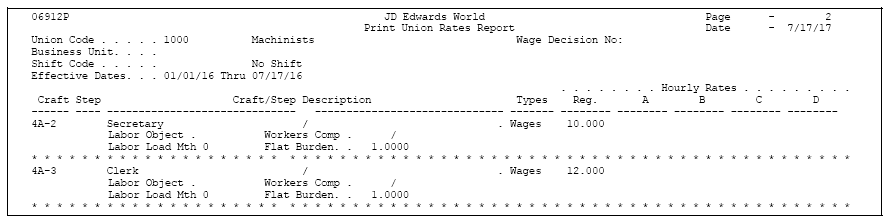
50.3 Reviewing the Pay Rate Tables Report
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Pay Rate Tables
The Pay Rate Tables report lists detailed information for the pay rate tables that you have defined. The standard report lists rate information for all group or union codes.
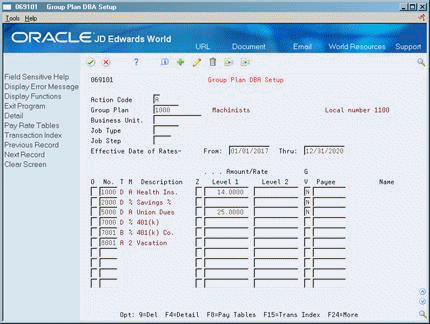
50.4 Setting Up Group DBAs
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Group Plan DBA Setup
You set up group DBAs to specify that deductions, benefits, or accruals apply to groups of employees. You identify each group plan by a user defined code. The user defined code is referred to interchangeably as the group plan code or union code. In addition to the group plan code, you can further define group plans with additional qualifying criteria, such as:
-
Business unit - The plan applies only for work performed in a particular business unit or job location.
-
Job type - The plan applies only to employees working in a certain job type.
-
Job step - The plan applies only to employees in a certain job step within a job type.
-
Date range - The plan applies if the pay period dates fall within the date range you specify. For example, you could use this criterion to establish plans with built-in rate increases that you base on effective dates.
To set up group deductions, benefits, and accruals
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Group Plan
-
Effective Date of Rate From
-
Effective Date of Rate Thru
-
DBA Code
-
Generate A/P Voucher
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Zero Amount Override Flag (Z)
-
Amount or Rate
-
Payee
-
-
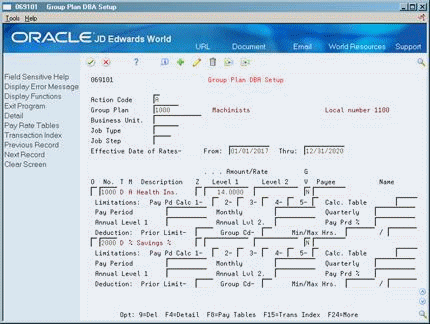
Complete the following fields as appropriate:
-
Business Unit
-
Job Type
-
Job Step
-
Pay Period to Calculate
-
Calculation Table
-
Pay Period Limit
-
Monthly Limit
-
Quarterly Limit
-
Annual Limit
-
Pay Period Percent Limit
-
Prior Limit
-
Group Limit Code
-
Minimum/Maximum Hours
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Z | A Yes/No field indicating whether the system treats the Amount/Rate field as a zero amount override. You use this field primarily when an employee is part of a group plan yet does not receive a particular benefit in that plan. |
| Prior Limit- | A code that identifies another DBA whose limit must be met first before this DBA calculates. For example; deduction 1400 has an annual limit of $2,000.00. After this limit is met, deduction 1500 begins calculation and withholding.
The DBA number of the predecessor must be lower than the successor's number. |
| Group Cd- | A user defined code 07/GR that groups together DBAs that share common limitations. Use this field to group together wage assignments for the split of available wages. |
| Min/Max Hrs | The minimum number of hours worked or pieces produced in order for a DBA to be calculated. If the number of hours worked or pieces produced is less than this amount, the system assumes zero hours when it calculates the DBA. The system uses this field only if the source of calculation or arrearage method is H or I. |
50.5 Reviewing the Group Plans Report
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Plan Benefits
Review the Group Plans report to verify that the information you entered to set up group plan DBAs is correct.
Figure 50-6 Group Plan Instructions report
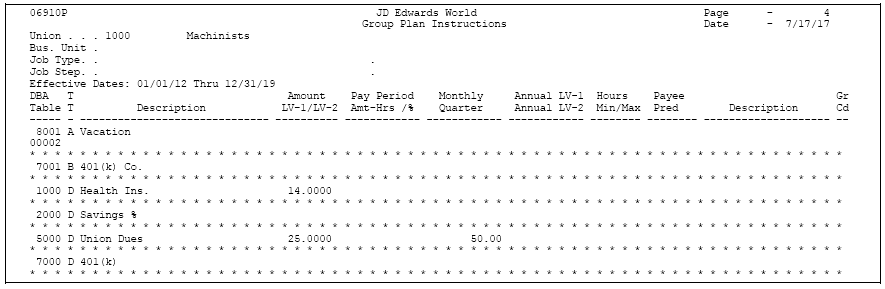
Description of ''Figure 50-6 Group Plan Instructions report''
50.6 Setting Up Union Local and Job Cross-References
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Union/Local Job Cross-Reference
You set up union local and job cross-references to cross-reference parent unions with local unions. You use these tables when a parent union has members working for a local union and those members must be paid the local union's wage rate and receive the corresponding benefits. By cross-referencing one union's (local or parent) job to another union, you ensure that the system uses the correct rates and benefits to calculate payroll.
The cross-reference tables are specific to business units and jobs, and provide for the retrieval of hourly rates and group DBAs. If you define these tables, you do not have to change an employee's union information during time entry. The system substitutes the employee's union and retrieves the related local union.
You can also set up cross-references between local units of the union.
50.6.1 Before You Begin
-
Define both the parent and local union in the system
-
Define the pay rates and group DBAs for the local union that has the job
To set up union local and job cross-references
On Union Local/Job Cross-Reference
Figure 50-7 Union Local/Job Cross-Reference screen
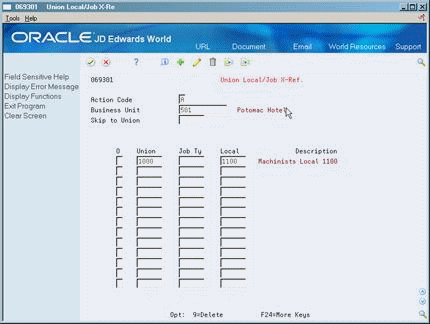
Description of ''Figure 50-7 Union Local/Job Cross-Reference screen''
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Business Unit
-
Union Code
-
Local Union Code
-
-
Complete the following optional field:
-
Job Type
-
50.7 Reviewing the Union and Job Cross-Reference Report
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Union/Local Job Cross-Reference
The Union/Job Cross-Reference report lists cross-reference information for the tables that you have defined.
Figure 50-8 Union/Job Cross-Reference report

Description of ''Figure 50-8 Union/Job Cross-Reference report''
50.8 Setting Up Job Classification Constants
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Job Classification Constants
You set up job classification constants to maintain various classifications of jobs, related to job type, job step, union, and business unit. For U.S. payroll, you can identify combinations of job type and job steps that you want to print on the Certified Payroll Register to meet taxing authority regulations.
You can also specify alternate job types and steps to print on the Certified Payroll Register to meet U.S. taxing authority regulations. Alternate type and step codes replace the codes for job type and job step that exist in either the Employee Master table (F060116) or the Payroll Transaction History table (F0618).
To set up job classification constants
On Job Classification Constants
Figure 50-9 Job Classification Constants screen
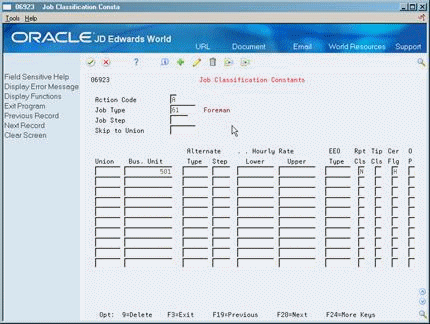
Description of ''Figure 50-9 Job Classification Constants screen''
Complete one or more of the following fields:
-
Job Type
-
Job Step
-
Union
-
Business Unit
-
Alternate Type
-
Alternate Step
-
Certified Flag (U.S. only)
-
Certified Flag
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Certified Edit Flag | A code which specifies the type of information to be printed on the Certified Payroll Register for the Job Type and Job Step. The codes are:
N – Do not print any information related to this Job Type/Job Step on the Certified Payroll Register. Y – Print all information related to this Job Type/Job Step on the Certified Payroll Register. H – Print Hours Only for this Job Type/Job Step on the Certified Payroll Register. |